Swimming pool when a child coughs
“Coughing” is an ambiguous concept. This symptom may be a sign of an acute disease of the respiratory organs (bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia), a symptom of an allergic disease, bronchial asthma, pathology of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and brain, or a residual phenomenon after a cold. For many of these conditions, you should not swim.
To find out the cause of the cough and accordingly decide on visiting the pool, parents must take their sick child to the pediatrician or local physician. It is worth noting that the doctor’s opinion may differ radically from the mother’s, since mothers often underestimate or, on the contrary, overestimate the seriousness of the situation.
Important! Most likely, the pediatrician will allow the child to go to the pool with a cough only if the little patient is practically healthy. In this case, coughing is regarded as a residual phenomenon of the disease. A cough may also be a variant of the norm, for example, short-term after a night's sleep.
If a child has obvious signs of an acute infectious disease (ARVI, influenza, etc.), it will be possible to attend the swimming section only after recovery. Here, parents should definitely listen to the advice of their pediatrician. You cannot risk the health of your children and expose other pool visitors to infection.
Can a child go to the pool with a cough and runny nose?
Almost every mother is faced with the question of whether a baby is allowed to swim in the pool while coughing. This problem can occur in children and adults. For example, what to do if tomorrow is training before a competition, and the signs of illness do not leave you alone. It turns out that a cough pool in a child has a beneficial effect on the respiratory system and promotes a speedy recovery. However, in certain cases you should refrain from visiting it.
The benefits of visiting the pool when you have a cough
If you have a cough, swimming in the pool can be beneficial (of course, if your doctor has not prohibited exercise).
These are the advantages:
- Inhaling moist air facilitates the passage of mucus. A person after swimming may begin to cough more, but more productively. Accordingly, the airways will clear faster.
- Swimming is a kind of breathing exercise, which is indicated for diseases of the respiratory tract, manifested by coughing.
- Exercises in water involve physical activity, and the more a person moves, the better the blood supply to the lungs and the more intense the phlegm leaves the bronchi.
Violation of the barrier function of the nasal mucosa
A decrease in the barrier function of the nasal mucosa is the second most common cause of the development of a runny nose after the pool. Bleach is an aggressive medium and has an adverse effect on the mucous membrane. The outer membrane of the nose secretes exudate, which prevents the penetration of bacteria into the sinuses and promotes the elimination of pathological agents.
With prolonged exposure to bleach, the mucous membrane is gradually destroyed. Chlorinated water gets deeper and deeper, resulting in inflammation of not only the nasal passages, but also the sinuses. To prevent a runny nose after swimming, nose clips should be used, especially for people who dive frequently.
Chronic sinus diseases
Persons with chronic diseases of the sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis) also often complain of a runny nose after swimming. This is due to the fact that the entry of water into the nasal passages, in which the barrier function of the mucous membrane has already been reduced, contributes to the exacerbation of chronic pathology. Moreover, a runny nose is not associated specifically with visiting the pool and can occur after swimming in a pond or sea.
If chronic sinusitis worsens, you should consult a doctor to prescribe antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Swimming in the pool develops and tones the musculoskeletal system, has a positive effect on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and increases the body's resistance to the action of pathogenic microflora. It’s puzzling when you get a stuffy nose after water activities.
In this case, impaired drainage of the paranasal sinuses is provoked by an allergic reaction and dysfunction of the mucociliary apparatus. To prevent undesirable consequences or prevent the progression of pathology, information on how to treat a runny nose after swimming in an adult will be useful.
Contraindications for children and adults
Exercising in the pool with a dry or wet cough in the acute stage is contraindicated for both children and adults, regardless of how the patient feels. In addition, the doctor may temporarily (until complete recovery) prohibit young swimmers from visiting the section under the following conditions:
- elevated body temperature;
- snot, sore throat and other manifestations of acute respiratory disease;
- inflammation of the ear, paranasal sinuses and pharyngeal tonsil.
The contraindications listed above also apply to adults. In addition, it is not advisable for them to go to the pool until recovery in case of a number of other pathological conditions:
- exacerbation of chronic lung diseases;
- tuberculosis.
If a person coughs and suffers from an allergy to the chemicals that pool workers use to disinfect the water, the existing disease may be aggravated by an allergic attack with severe swelling of the respiratory tract. Therefore, individual hypersensitivity of the body to these substances can also be considered a contraindication for visiting the pool while coughing.
Symptom of chlorine intolerance
An allergy to chlorine does not appear immediately, so people can continue to use the pool without knowing about their illness. The first signs of an allergy may appear after 4–7 weeks of regular exposure to bleach on the body.
How does an allergy to bleach manifest?
- increased lacrimation, eyes turn red, swelling appears;
- intolerance to bright light, pain and pain in the eyes;
- itching and rashes on the skin;
- the dermis begins to peel off greatly and changes color;
- hair condition worsens.
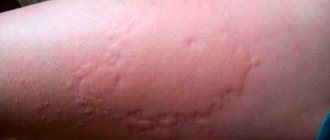
Most often, upon contact with chlorinated water, various forms of dermatitis develop. In the simple form, blisters and severe itching immediately appear on the skin. Symptoms are observed exclusively in those places that have been in contact with an aggressive substance. Contact allergic dermatitis appears 10–14 days after exposure to the allergen on the dermis. Redness and itching spread throughout the body. Repeated exposure to chlorine may cause eczema.

An allergy to chlorine does not lead to a significant deterioration in health; most often it manifests itself mildly and passes quickly. The first areas to suffer from rashes and itching are areas of increased sensitivity - the face, groin area and armpits. As the disease progresses, signs of intolerance to bleach become more pronounced, and problems with the respiratory system may occur - severe rhinitis, difficulty breathing through the nose, sneezing. Such symptoms are often observed in people with bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis.
An allergy to chlorine in the pool sometimes occurs in a severe form - in addition to the main symptoms, severe swelling of the limbs and face appears, and the person suffers from attacks of suffocation. The most severe complication is Quincke's edema, which is accompanied by rapid swelling of the larynx, the person begins to choke. Anaphylactic shock is also dangerous, in which blood pressure drops sharply, vomiting begins, and heart rhythm is disturbed - this can lead to loss of consciousness and coma. Such symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Complications after visiting the pool
A cough is a sign that the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is inflamed. Going to the pool can aggravate pathological changes due to the influence of the following factors on the patient:
- Chlorine-containing chemicals that disinfect water well and no less irritate the skin and mucous membranes. With pharyngitis and laryngitis, such bathing may result in an attack of debilitating cough.
- Temperature changes, which are especially noticeable in winter. After a swimming pool or a warm shower, a steamed person goes outside and quickly freezes. Such hypothermia can cause a reflex spasm of the inflamed bronchi and increased coughing.
- High risk of infection with new viruses and bacteria in the locker room or public transport on the way to the pool.
The result of visiting the pool while coughing can result in various complications:
- The spread of infection deep into the body with the development of bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Obstruction (spasm and swelling) of the respiratory tract, intensification of an existing cough.
- Feverish state.
- A new infectious disease. After an illness, and even more so at its height, a person’s immunity is depleted, so it is very easy to “pick up” something new.
- Sudden loss of strength, dizziness. In case of acute respiratory diseases and cough, any physical activity for a weakened body is a serious test.
Violation of the barrier function of the nasal mucosa
A decrease in the barrier function of the nasal mucosa is the second most common cause of the development of a runny nose after the pool. Bleach is an aggressive medium and has an adverse effect on the mucous membrane. The outer membrane of the nose secretes exudate, which prevents the penetration of bacteria into the sinuses and promotes the elimination of pathological agents.
With prolonged exposure to bleach, the mucous membrane is gradually destroyed. Chlorinated water gets deeper and deeper, resulting in inflammation of not only the nasal passages, but also the sinuses. To prevent a runny nose after swimming, nose clips should be used, especially for people who dive frequently.
Chronic sinus diseases
Persons with chronic diseases of the sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis) also often complain of a runny nose after swimming. This is due to the fact that the entry of water into the nasal passages, in which the barrier function of the mucous membrane has already been reduced, contributes to the exacerbation of chronic pathology. Moreover, a runny nose is not associated specifically with visiting the pool and can occur after swimming in a pond or sea.
If chronic sinusitis worsens, you should consult a doctor to prescribe antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Hello! I have been going to the pool in the morning 3 times a week for the past year and a half. Over the past month I have encountered a problem: nasal congestion after swimming, which gets worse towards the end of the day.
Reactions to the article
Did you like our site? Join or subscribe (you will receive notifications about new topics by email) to our channel in MirTesen!
Do I need certificates and where can I get them?
A health certificate may only be required if you are planning your first trip to the pool. It can be obtained from your local doctor at the clinic at your place of residence.
If a child or adult is already visiting the pool, medical documents are not needed (except for breaks lasting more than 2 months due to illness or personal circumstances for children). A visit to the doctor if you have a cough is first and foremost necessary for yourself - to find out the cause of this symptom and make sure that there are no obstacles to swimming.
Thus, despite all the benefits of water sports, cough and swimming are not always compatible. There are many contraindications, you can’t do it without a doctor. If he doesn’t give the go-ahead to visit the pool, you shouldn’t risk your health. The desire to swim can result in increased coughing, worsening health, or even a new illness.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction
An allergy to bleach is manifested by symptoms, and if you detect them, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Skin reaction:
- dryness;
- peeling;
- redness;
- itching
In the mildest cases, there may simply be a feeling of tightness of the skin, especially in the groin and armpit area, since the skin is most sensitive there.
Eye reaction:
- redness of the whites of the eyes;
- burning and pain in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- eyelash loss;
- swelling;
- blurred vision.
Respiratory response:
- the appearance of a runny nose, nasal congestion;
- itching in the nose and throat;
- labored breathing;
- dry mouth;
- sneezing;
- temporary lack of sense of smell.
When an allergy to chlorine appears in a swimming pool, all of the listed symptoms can appear either immediately or several hours after contact with water. It happens that immediately after water exercise, unpleasant manifestations make themselves felt only in a mild, unnoticeable form, and after a few hours they intensify significantly. For example, after leaving the pool, a slight runny nose may appear, and after 2-3 hours, swelling of the nasal mucosa and complete congestion with loss of smell may appear.
If an adult cannot understand whether he is really allergic to chlorine, then he can check this in a simple way. It is enough just to swim in a river or sea. If the same symptoms that he had after visiting the pool did not arise after swimming in a natural body of water, then the problem is in chlorinated water.
Allergy to chlorine in the pool in children manifests itself in the same way as in adults, however, the child’s body is even more susceptible to irritation from chlorinated water. Children often develop allergic rashes all over their bodies after visiting swimming pools. If in adults an allergy to chlorine can manifest itself only as itching and redness of the skin, then in children symptoms such as severe peeling and even eczema can occur. In addition to the slight discomfort in the throat that appears in an adult after contact with bleach, a child often develops a strong dry cough and a significant rise in temperature. Children's eyes also react more strongly, usually with severe itching and increased tearing.
Since swimming lessons with infants have now become very popular, all young parents strive to start performing water procedures with their child as early as possible. In some places, children are accepted for classes even from three weeks of age. Water procedures for infants are indeed very useful and greatly contribute to their health and development, but we should not forget that young children are the category that is most sensitive to irritants and allergies. The younger the child, the higher the likelihood that he or she will exhibit symptoms of an allergy to bleach.
There are cases when a baby began to choke in the pool or began to have convulsions. If this happens, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Therefore, if parents want to accustom their baby to water activities from infancy, then in order to avoid allergies, it is better to choose a pool in which the water is not chlorinated.
For older children, it is preferable to start water activities in the summer or early autumn, since their immunity is strongest at this time of year, and the risk of allergies is significantly lower.
Since the manifestations of an allergy to chlorine in a child are much stronger, it is important to recognize the symptoms in time and do everything to eliminate the unpleasant consequences.
Is it okay to go to the pool if you have a cough?
First you need to understand the cause of the cough. Coughing is a reflex of the body necessary to protect it. It clears the airways from foreign accumulations and mucus. Cough is also the main symptom of the following diseases:
- Angina.
- Respiratory infection.
- Asthma, bronchial asthma.
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis.
Regardless of what kind of cough or whether there is snot, it is worth going to the doctor and checking the health of both children and adults. If a person is completely healthy, then there will be no contraindications. Because only a doctor determines whether a cough is a symptom of a disease or is a natural reaction of the body as a residual cough. For example, sometimes coughing occurs after sleep or when too cold air enters the lungs.
Any disease, even ARVI, is a contraindication to going to the pool, because it is a threat both to the patient and to the people around him whom he can infect. During illness, each person's immunity decreases, so physical activity can worsen the general condition of the body and lead to complications. Also, after swimming, people do not always have time to dry their hair sufficiently, which can also complicate the situation, especially in the cold season.
Pros of visiting the pool:
- humid air facilitates the process of mucus discharge, so after bathing a person’s cough may intensify, this means that the airways will clear faster;
- Swimming is gymnastics for many body systems, including the respiratory system. Therefore, swimming is prescribed to strengthen the immune system in general and the lungs in particular;
- blood supply to the lungs improves during sports;
- some doctors note the effect of chlorine water. There is an opinion that it quickly clears the upper respiratory tract during diving, when air actively leaves the body through the nose.
Exposure to chlorine is especially noteworthy because some visitors develop allergic rhinitis. It manifests itself in the form of a runny nose and constant sore throat, and is a consequence of an allergic reaction to chlorine. This usually occurs in people with weakened immune systems and a predisposition to allergies. Then, due to contact with chlorinated water on the skin and respiratory tract, a reaction begins.
If you notice such effects, you should consult a doctor, because allergic rhinitis can lead to bronchial asthma. The doctor also prescribes antihistamines, strictly in adjusted dosages and compatible with training. In other cases, it is suggested to purchase nose clips. The doctor may also suggest changing the pool, because in sports complexes they monitor the concentration of chlorine in the water to prevent such reactions in visitors.
Runny nose after the pool: what to look for and what to do?
· You will need to read: 5 minutes
The usual routine of life can be untimely disrupted by a runny nose. A person will try to immediately connect the presence of a disease with its possible causative agent.
During such an analysis, it may turn out that the person was overtired doing physical exercises in the gym, visiting an outdoor pool in cold weather, etc.
Once the root cause is identified, the question arises: should he continue the activities that led him to the infectious disease? This depends on the list of factors determined by the attending physician. For example, it is necessary to determine the effect of physical activity on the current state of the body, the degree of development of pathogenic microflora.
Active water procedures during a cold should be treated with caution.
Swimming in the home pool
Quite often, young mothers are interested in whether it is possible to bathe a child in a home pool or bath during an infection in the nasopharynx. A qualified pediatrician will advise you to monitor your baby's body temperature. If the temperature is normal, you can safely continue water procedures.
Please note: if you decide to take a bath or go to the pool with a runny nose, monitor your temperature. The water temperature should be 4-5 degrees higher than usual. The time frame for staying in pools should be reduced to 10 minutes.
Using a home pool or bath to treat a runny nose can be very effective. For example, during one bath you and your child will be able to relax, strengthen the immune system, and promote speedy treatment. In what cases will a child and an adult benefit from a bathtub or home pool:
- The water temperature will be high enough to warm the body thoroughly. This will help relieve swelling and strengthen the body's protective functions;
- add sea salt, useful minerals, useful medicinal plants (their decoctions) to the water. After taking a bath, drink tea with medicinal herbs. You will immediately feel a surge of strength and notice an improvement in your general condition;
- make sure that you or your baby do not have a runny nose, chills, weakness, cough, or high fever;
- when the humidity of the room is increased, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- for complications after flu or cold.
The most important thing to remember is the patient's desire to engage in such therapy. Under no circumstances should you force your child to go into the water without the appropriate desire.
There is only one contraindication that concerns adjacent rooms, such as a swimming pool and steam room. Going to the sauna if you have an infectious disease is strictly prohibited.
This is especially true for the following group of patients:
- with inflammation of the adenoids;
- anatomically narrow nasal passage;
- deviated nasal septum.
Be careful to bring the water temperature up to 4 degrees above normal. Follow this simple rule so that your runny nose after visiting the pool does not get worse and become chronic. Hot fumes can have a negative effect on the body.
Possible swelling of the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx, increased runny nose, provoking increased mucus secretion, etc. Basically, similar symptoms occur with a runny nose caused by a bacterial infection.
The steam will have an effect on pathogenic microflora, which will begin to multiply and possibly provoke complications in the form of acute rhinitis/sinusitis.
What to pay attention to when visiting the pool?
Most often, the body reacts to the disease by deteriorating its physical condition 2-3 days after infection. These few days, without suspecting anything, you can go to any public places, feeling some discomfort (itching, burning in the nasopharynx). If you go to the pool and begin to notice the following factors, contact your doctor immediately:
- you lose your breath;
- distances that are familiar to you become more difficult to overcome, you constantly “take a breath”;
- characteristic whistle during exhalation;
- copious mucous discharge from the nasal passages;
- a feeling of heaviness in the chest (this occurs due to the filling of the bronchi with a special secretion secreted during illness);
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- loss of coordination;
- pressure in the frontal part of the brain;
- swelling, congestion of the nasal passages.
If you notice any of the symptoms, stop using the public pool immediately and make an appointment for a comprehensive examination with your healthcare provider.
Remember: physical activity performed during illness can aggravate the general condition of the body, affect the time frame of the disease, complications, etc.
You should not exhaust yourself with training and run the risk of deteriorating the general condition of the body.
What to do if you have a runny nose after swimming?
If you develop a runny nose due to prolonged contact with cool water, try to avoid the root cause of the illness.
Experts advise avoiding visiting public swimming pools and saunas when the level of natural immune defense is weakened, if you have a runny nose, elevated body temperature, etc.
The level of physical activity on the body should be limited, reduced to a minimum (but not eliminated). Most often, a runny nose after swimming appears for the following reasons:
- mucous discharge from the nose may be due to a high concentration of chlorine in the pool;
- physical activity gave an additional “impetus” to pathogenic microflora for development. The infection began to develop and affected the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx.
Advice: if the disease is viral in nature, you yourself become contagious. Doctors advise not to go to the pool or any other public places to avoid infecting other visitors.
Carefully monitor the condition of your own body. Remember: hot water (or rather, evaporation) can also cause harm in the form of additional irritation and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx. Consult your doctor to rule out any negative effects on your current condition.
One of the recommendations may be therapy in sea water (there are special pools that use sea water). Such treatment will be effective, efficient, and will help you overcome the disease in the shortest possible time. Sea water will dry out the sinuses, clear the nasopharynx of pathogenic infections, improve the body's condition and the level of immune protection.
Source
Source: https://03-med.info/lor/nasmork-posle-basseyna-na-chto-obratit-vnimanie-i-chto-delat.html
Possible consequences
Visiting the pool if you have an illness that causes a cough is generally prohibited. Causes:
- Chemicals that purify water from bacteria irritate the mucous membranes. For example, if you swim in water saturated with antiseptics with laryngitis, a severe coughing attack may occur.
- After classes, a person with a wet head goes out into the fresh air; even a slight cold wind creates a temperature difference. Spasms begin and the cough gets worse.
- In the cold season, when traveling on public transport, the development of the disease can be accelerated.
As a result of physical overload, the following types of complications can occur:
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- spasms and swelling of the respiratory tract;
- febrile attacks;
- the immune system is depleted, therefore, in addition to the existing disease and the development of its complications, you can catch something additional;
- loss of strength, fever, weakness, nausea and other effects.
During the first training, a certificate from a doctor is required confirming the absence of diseases that prevent training, especially when visiting any sections. In other cases, a certificate is not required, so you need to know about your health status.
Visiting the pool is a wellness procedure. Thanks to it, you can significantly improve your well-being. Thanks to swimming, a person becomes more resistant to various diseases and gets sick much less often.
You are allowed to visit the pool if you have a cough, unless it is caused by any illness. In other cases, it is better to refuse training to avoid complications. When a person’s body is weakened, physical activity, on the contrary, can be harmful, so it would be more logical to return to exercise after the disease has subsided.
What to do and how to treat it?
Antihistamines, which can only be prescribed by a doctor, will help relieve allergic reactions. Medicines should not be taken for a long time; they are used only if there are clear signs of chlorine intolerance.
Basic medications for the treatment of allergies:
- modern antihistamines that act quickly and have a minimal number of side reactions - Zodak, Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadine, Claritin;
- nasal drops based on beta-agonists - Vibrocil, Tizin;
- eye drops to eliminate inflammation and pain - Claritin, Allergodil;
- ointments that help cope with dermatological signs of allergies - Cloderm, Laticort.

Severe allergies require treatment with corticosteroids - taking them on your own is dangerous, since they have many contraindications and adverse reactions. The complex of therapeutic measures should necessarily include those aimed at strengthening the immune system - regularly doing hardening procedures, creating a balanced diet, taking vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
With the help of some folk remedies it is possible to get rid of allergy symptoms to bleach. Garlic tincture strengthens the immune system, eliminates negative signs of the disease - crush 270 g of peeled garlic, pour in 500 ml of high-quality vodka, put in a dark room for 28 days. Before use, 5 ml of the medicine should be diluted in 120 ml of water and taken with food three times a day. Duration of treatment is 15-20 days.
You can wash your eyes after swimming with an infusion of dill or red clover - these products are used to treat allergic conjunctivitis. Brew 220 ml of boiling water and 5 g of crushed raw materials, leave in a closed container for a quarter of an hour. Soak cotton pads in the solution, hold the compress for 20 minutes, do the procedure 3-5 times a day.
Allergic manifestations in children
A child's immune system does not always work effectively, so their body reacts more sharply to chlorinated pool water, and allergy symptoms appear quickly. The disease is especially acute in preschool children - sometimes the child begins to have convulsions right in the pool, the mucous membranes swell, and shortness of breath occurs.
To prevent the possibility of developing anaphylactic shock and angioedema, you should call a doctor and give the child Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Prednisolone. Many parents prefer to teach their children to swim when they are still babies - for these purposes it is better to choose a pool that does not use chlorine. It is better to start training in the summer, early autumn - at this time the immune system is strong.
If allergy symptoms appear in children, you should contact an immunologist or allergist; you will have to avoid visiting the pool for a while until the treatment is completed. A visit to the doctor should not be postponed if the disease is accompanied by fever, depression, weakness, or bad mood.
Preventive actions
Chlorine intolerance is not a reason to give up swimming; you need to try to minimize the negative impact of the aggressive substance on the body and eliminate the immediate cause of poor health. In many modern pools, less aggressive methods are used for disinfection - ozonation, disinfection using ultraviolet rays - the amount of chlorine in this case is minimal. It is impossible to find a public swimming pool with water without chlorine.
How to reduce allergic reactions:
- be sure to take a shower, thoroughly cleanse your skin before and after training, and do not use cosmetics when visiting the pool;
- protect hair and eyes with a cap and glasses, use a nose clip;
- try not to swallow water;
- buy a closed suit.
After swimming, you need to apply lotion or body milk with a moisturizing effect to clean skin, rinse your nose, gargle with clean water, especially sensitive areas can be lubricated with baby cream. If spots and irritations appear on the skin, take a bath with a decoction of nettle, chamomile, celandine, and calendula.
It is better not to use contact lenses in the pool - special swimming goggles with diopters will help correct your vision and protect your eyes while swimming. Allergies to chlorine when visiting a swimming pool often indicate a weakening of the body's protective functions. It is better to abstain from the pool after severe stress, illness, or a strict diet - all this suppresses the immune system, and there is a high probability of chlorine intolerance.
Source: limelady.ru
How can a visit to the pool end with a cough?
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to go to the pool if they have such an undesirable symptom as a cough. This is no coincidence, because such a procedure is considered healthy. Some are sure that it will do no harm. Cough can occur for various reasons. You can go to the pool if you have such a symptom only after consulting a specialist. Thanks to this, you can be sure that the procedure will be beneficial.

Treatment
If an allergy appears, the doctor prescribes methods to eliminate the symptoms. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. Repeated contact with the irritant will lead to an increase in existing symptoms. Therefore, if you are allergic to the pool, you should avoid visiting such places. To relieve the symptoms of the disease, the following measures are taken:
- If unpleasant symptoms occur after being in chlorinated water, you should immediately take a shower and stand under water for a long time. This will get rid of residual chloride compounds. After this, the skin should be treated with moisturizers.
- If sensitivity is associated with inhalation of chloride compounds, you need to go outside or ventilate the room.
- At home, you brew chamomile or chamomile and make baths with it. This method helps cope with itching and inflammation. Such remedies help children especially well. If there is no effect from the herbs, then moisturizing ointments like Bepanten are prescribed.
- If you are concerned about a runny nose after swimming or allergic rhinitis, then antihistamine eye drops and nasal sprays are prescribed. Only the attending physician should prescribe such medications.
Antihistamines are also prescribed. They are selected taking into account the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the body’s condition. To obtain the desired effect, the correct dosage should be used in accordance with the age of the patient.
Cause of cough
The manifestation of coughing can be due to a variety of reasons. In some cases, you can go to the pool with it. Coughing can be natural or pathological. This symptom is extremely necessary to clear the respiratory tract of all kinds of accumulations.
In order to determine whether it is possible to go to the pool with it, you need to find out the reason for its appearance.
Coughing is a protective reflex of the body. It allows you to clear the airways of mucus or foreign objects. You can get rid of it only by knowing the root cause of the disease. Most often, coughing is associated with the following disorders:
- asthma;
- respiratory infection;
- bronchitis;
- bronchial type asthma;
- pneumonia.

Such root causes of the disease are the most common. However, cough can also occur with:
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- pathologies in the functioning of some internal organs;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- metabolic disorders;
- treatment using certain medications;
- psychogenic changes.
In some cases, paroxysmal cough may appear spontaneously. In this case, it can be said with a high degree of probability that there is a foreign body in the respiratory system that makes breathing difficult. In case of such a violation, it is advisable to immediately call an ambulance.
The coughing attack will last as long as the foreign body is present in the body.
Allergy complications
There are also complications of an allergy to chlorine contained in water, such as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
Quincke's edema is a severe and rapidly progressing swelling of the upper respiratory tract. Swelling occurs within a short time after contact with chlorinated water. It is important to notice its signs in time in order to provide help.
Symptoms of Quincke's edema:
- severe swelling of the neck and face;
- burning and pain in the area of edema;
- hives;
- elevated body temperature.
What to do if a child has Quincke's edema?
Anaphylactic shock is the most severe manifestation of allergies, threatening human health and life.
Symptoms of anaphylactic shock:
- cardiac arrest and lack of breathing;
- pale skin;
- the appearance of cold sweat;
- lack of consciousness.
If you notice such symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Swimming pool when a child coughs
Visiting the pool is a wellness procedure. Thanks to it, you can significantly improve your well-being. It is especially useful for children. Thanks to swimming, the child becomes more resistant to various diseases. Typically, such children get sick much less often than their peers who do not go to the pool.
Many parents ask the question: “Is it possible to take a child who has such an undesirable symptom as coughing to the pool?” Children are often taken to swim with a cough, believing that this will have a positive effect on the body and the disease will be easier.
Experts say that a child with a cough and other pathogenic symptoms cannot be taken to the pool. It is not recommended to give preference to swimming to adults with this symptom. Visiting the pool when sick can aggravate the condition or lead to the emergence of new pathologies. The health procedure will need to be postponed until complete recovery.

It is worth noting that some doctors, on the contrary, believe that visiting the pool if you have a cough will only be beneficial. They explain this by the fact that the water in it contains chlorine. Flushing while diving will help cleanse the respiratory system. However, the positive effect of the pool for diseases that are accompanied by coughing has not been proven.
Doctors do not recommend giving preference to swimming also for the reason that it is physical activity. It can further weaken the baby’s body.
Swimming pools are visited by a huge number of people. Some of them can be carriers of infections and a wide variety of diseases. By bringing a coughing child to swim, parents are putting their body in danger. A sick baby has weak protective functions. There is a high probability that after contact with a sick person, he will become infected. In this case, the child’s condition will worsen significantly. Significant complications will arise.
You can visit the pool if you have a cough only if the symptom is not pathological. A healthy person can cough up to 20 times a day. This sign is normal. Having it, you can safely give preference to swimming.
Diagnostics
At a doctor's appointment, a medical history is usually sufficient to diagnose an allergy to pool water. Reactions to chemicals containing chlorine occur quite often. Differentiation of an allergic reaction from mechanical irritation of the skin is carried out by an allergist using an application test.
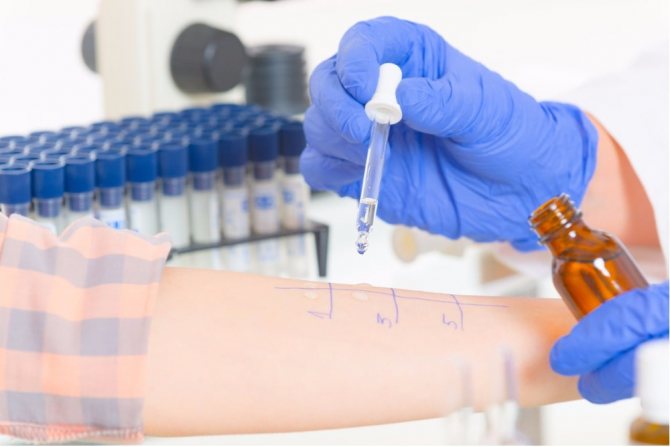
A patch test is the application of certain compounds to the skin in order to determine its ability to cause skin rashes in the form of dermatitis and eczema. Used for allergies to chemicals. Patch skin tests are done during remission, at least 30 days after an exacerbation (see “Skin tests for diagnosing allergies”). A special patch treated with antigens is attached to the back or inner forearm for 48 hours. Before removal, the testing boundaries are marked with a marker. After removing the patch, the results are assessed twice: after 30 minutes and after 3-4 days. The appearance of erythema, papules and blisters on the skin indicates an allergy to the tested component.
For children under five years of age, testing for allergen intolerance is carried out by examining venous blood to identify specific immunoglobulins. The procedure is absolutely safe; there is no direct contact of the child with the allergenic component.
What to do if you have an allergy in the pool
First steps if there are signs of an allergy to chlorine in the pool:
- rinse the skin with warm running water;
- carefully blot the skin with a towel, lubricate with restorative cream;
- leave the room with toxic fumes that irritate the eyes and nasopharynx.
For minor allergic reactions, the symptoms go away on their own. Severe damage to the eyes and respiratory tract requires drug treatment, which is prescribed by a doctor.
Drug therapy
Medicines to improve general well-being:
- Antihistamines are the main type of therapy. Adults are usually prescribed Claritin, Tavegil, Akrivastin. Zyrtec and Erius are more suitable for children.
- Eye and nasal drops - Azelastine, Levocobastine, Adrianol have antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Sorbents - remove allergens, excess histamine and serotonin from the body. The most effective are Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel.
- Hormonal drugs in tablets and injections are used in severe cases as prescribed by a doctor.

To treat contact allergic dermatitis, ointments with anti-inflammatory and healing effects are used:
For allergies in children, ointments and creams are used: Fenistil-gel, Bepanten, Skin-cap.
Weeping papules and large blisters are treated by applying bandages with Burov's liquid and applying hormonal ointments. Depending on the severity of symptoms on the skin, ointments with a short-term effect are prescribed - Prednisolone, Afloderm, Lorinden S, or potent ones - Akriderm, Advantan, Cutivate.
Complete regression of contact allergic dermatitis occurs after 1-3 weeks.
Therapy for toxicoderma includes the use of sorbents and drugs to restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and kidneys.
It is worth noting that visiting the pool is prohibited until all signs of allergic syndrome have completely disappeared.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine recipes are used to alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Allergic rhinitis is treated using a decoction of horsetail herb. 2 tsp raw materials, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, filter. Place 2-3 drops of infusion into each nostril. 3 times a day.
To eliminate irritation on the skin, make lotions with a solution of baking soda in a 3:1 ratio and infusion of chamomile. To relieve itching, baths and tampons moistened with a decoction of string herbs are used.
Complications after visiting the pool
Swimming with a wet or dry cough can cause various complications. For this reason, coughing will be much more difficult to cope with. After swimming, a rapid increase in body temperature may occur. It is also possible to develop:
Going to the pool while coughing can worsen inflammation of the larynx. Experts identify the following first signs of complications:
- the occurrence of a severe headache;

- significant increase in body temperature;
- congestion of the nasal passages.
If such signs appear, you should immediately seek the help of specialists. This is necessary so that the emerging disease does not spread throughout the body. After visiting the pool, the cough may get worse. This will cause insomnia. In addition, dehydration may occur, which is accompanied by vomiting and loose stools.
A patient with a cough may faint after going to the pool. This may be due to a sudden coughing attack. Thus, if you have such an undesirable symptom as a cough, you must avoid any physical activity, including visiting the pool. Otherwise, complications cannot be avoided.
From the video you will learn that you can go to the pool if you have a cough:
Recommendations
To reduce the risk of allergies to pool water, you must follow the following visiting rules:
- Before the pool, take a warm shower, thoroughly rinse off cosmetics and hygiene products from the body and face;
- use protective equipment for swimming: special nose clips, ear plugs, pool goggles, a cap;
- avoid swallowing water during exercise;
- after training, take a warm shower, cleansing your skin of water with chemical reagents;
- lubricate the skin with moisturizing cream or cosmetic body milk;
- remove contact lenses before class;
- eat food 1-2 hours after the pool.
If you follow the recommendations, contact with chlorinated water will cause less harm.
Strengthening the immune system, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following the rules for visiting the pool reduce the risk of allergic reactions. This approach allows you to avoid unpleasant situations and benefit from physical training in water.
source
Contraindications for children and adults
Coughing is a natural function of the body that clears mucus from the airways. Normally, a healthy person coughs up to twenty times a day. If coughing does not occur regularly and your overall health is good, there is no reason to put off going to the pool.
A weak cough is also not always a sign of a cold. In the absence of other symptoms, it often does not cause noticeable discomfort and passes quickly. But still, much more often, a cough indicates a cold or accompanies the onset of a respiratory disease.
To understand whether an adult can go to exercise when coughing, you should consider what benefits physical exercise can provide:
- the load on the muscles improves blood circulation, the lungs receive blood flow;
- swimming movements promote deeper breathing, which is useful for respiratory infections;
- moist air softens the cough and improves sputum discharge.
If the illness has not reached a serious stage, swimming has a positive effect on the lungs and helps cleanse the airways.
But training in the pool also has negative sides:
- irritating effects on mucous membranes of chlorine and other disinfectant impurities in water;
- the body is exposed to sudden changes in temperature, hypothermia often leads to worsening symptoms;
- a weakened body has low immune defense, and visiting the locker room and public shower increases the risk of infection with ARVI and influenza viruses.
Swimming and hypothermia from being in water can lead to increased coughing, as well as infection getting deeper into the bronchi and lungs. Complications can be quite serious - bronchitis and pneumonia. Most experts recommend postponing a health procedure if you have a cough.
Visiting the pool with a cough can lead to complications
A trained body accepts the load better, in this case there is a greater chance that visiting the pool will give a positive result.
Coughing in children should be treated more carefully, because a child’s body has fewer protective resources compared to an adult. It is easy to miss the onset of a respiratory illness, which can lead to serious complications.
The most dangerous cough is accompanied by any additional symptoms:
- redness of the throat, pain;
- runny nose, nasal congestion;
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness, fever;
- cough lasts longer than one or two days.
Only a pediatrician can determine whether a child’s body has recovered enough to visit the pool.
Why does pool allergy occur and how does it manifest?
Visiting the pool is beneficial at any age. In addition to acquiring swimming skills, children have the opportunity to harden the body and harmoniously develop the musculoskeletal system. In adults, regular exercise helps maintain good physical shape and improve immunity. Swimming in the pool is indicated for some forms of chronic diseases.

According to sanitary standards, reagents containing chlorine compounds are used to disinfect water. The question arises: can adults and children be allergic to the pool? The element chlorine itself is not an allergen. It is an irritant substance that may cause skin irritation. Calcium and sodium hypochlorites included in the reagent, in contact with the skin epithelium, sweat, urine, and conjunctiva of the eye, react with certain proteins and cause allergies. The source of intolerance can be toxic fumes released by aggressive compounds.
Compositions containing bleach dissolved in water are odorless. It appears when the pool is contaminated as a result of the reaction of chemical compounds with fragments of the human body. The resulting substances may pose a hazard to human health. These byproducts enter the body, leaving it vulnerable and susceptible to allergens. Even a healthy person can become intolerant to dust, pollen, or develop food allergies.
A special place is occupied by the hereditary factor, a history of allergies. A primary allergic reaction may occur after the first visit to the pool. Sometimes allergic components gradually accumulate in the body. In this case, a secondary allergy occurs.
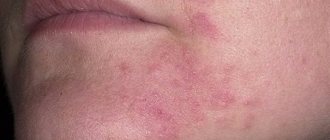
Signs of irritation after visiting the pool:
- redness of the sclera of the eyes, burning sensation, lacrimation;
- discomfort, pain in the nasopharynx;
- skin rashes accompanied by itching.
Frequent use of the pool can lead to contact dermatitis, which is more prone to people with dry skin types. Dryness and redness of the dermis are observed. If left untreated, scabs and cracks develop on the skin. Contact dermatitis progresses slowly, with pronounced manifestations appearing after 1-2 months.
The allergic reaction manifests itself later than mechanical irritation of the cornea and nasopharynx. Several hours or days pass before the first signs appear. Sometimes allergies occur suddenly while swimming.
Respiratory symptoms of pool allergy:
- difficulty breathing;
- itching in the nose, paroxysmal sneezing;
- rhinitis with copious watery or mucous discharge;
- severe swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, which acquires a bluish tint with whitish spots;
- inflammation of the skin around the nose;
- allergic type cough.
Frequent manifestations of an allergic reaction: inflammation of the cornea of the eyes, purulent discharge, lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, loss of eyelashes.
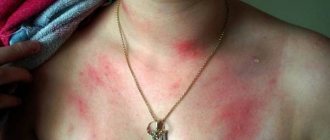
Skin rashes due to allergies manifest themselves in the form of contact allergic dermatitis. The pathology develops 1-2 weeks after contact with chlorinated water and proceeds rapidly. The duration of the disease is 3-7 days. Main signs of the disease:
- itching, redness and swelling of the skin, mainly in the armpits and groin area;
- numerous papules and blisters;
- weeping ulcers in place of spontaneously opening blisters.
In the absence of adequate treatment and the persistence of the allergenic component, the symptoms of dermatitis are accompanied by signs of bacterial infection, and the disease can become chronic. In this case, blisters on the skin are accompanied by peeling and thickening of the dermis, pigmentation disorders and self-damage of the epidermis appear.
Prolonged contact with the allergen by professional swimmers and pool staff can cause the development of a severe syndrome - toxicoderma (toxic-allergic exanthema), which occurs with the following symptoms:
- skin rashes in the form of urticaria;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes and nasopharynx;
- endogenous intoxication;
- development of secondary pathologies of internal organs - vasculitis, nephritis;
- with a complicated course, angioedema and anaphylaxis .
Disturbances in internal organs due to allergies to water with chlorine:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea, vomiting;
- stool disorders;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- decrease in blood pressure.
The pathology is most severe in allergy sufferers and asthmatics. In these cases, a severe attack of bronchial asthma, anaphylactic shock, . Symptoms of suffocation, sharp pain in the epigastrium, a significant drop in blood pressure require urgent medical attention.
Children's immunity is imperfect, so a small child's allergy to the pool manifests itself in a more severe form, and lightning-fast reactions are possible. Allergic syndrome often occurs against a background of elevated temperature and is accompanied by conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and dry cough. The skin rash has the appearance of eczema and is very flaky.
Trainers conducting training in the pool with children's groups are well acquainted with the symptoms of a possible allergic reaction and the rules of first aid for allergies. The task of parents at home is not to miss the first signs of an incipient pathology.
The benefits of visiting the pool when you have a cough
Visiting the pool if you have an illness that causes a cough is generally prohibited. Causes:
- Chemicals that purify water from bacteria irritate the mucous membranes. For example, if you swim in water saturated with antiseptics with laryngitis, a severe coughing attack may occur.
- After classes, a person with a wet head goes out into the fresh air; even a slight cold wind creates a temperature difference. Spasms begin and the cough gets worse.
- In the cold season, when traveling on public transport, the development of the disease can be accelerated.
As a result of physical overload, the following types of complications can occur:
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- spasms and swelling of the respiratory tract;
- febrile attacks;
- the immune system is depleted, therefore, in addition to the existing disease and the development of its complications, you can catch something additional;
- loss of strength, fever, weakness, nausea and other effects.
During the first training, a certificate from a doctor is required confirming the absence of diseases that prevent training, especially when visiting any sections. In other cases, a certificate is not required, so you need to know about your health status.
Visiting the pool is a wellness procedure. Thanks to it, you can significantly improve your well-being. Thanks to swimming, a person becomes more resistant to various diseases and gets sick much less often.
If you have a cough, swimming in the pool can be beneficial (of course, if your doctor has not prohibited exercise).
- Inhaling moist air facilitates the passage of mucus. A person after swimming may begin to cough more, but more productively. Accordingly, the airways will clear faster.
- Swimming is a kind of breathing exercise, which is indicated for diseases of the respiratory tract, manifested by coughing.
- Exercises in water involve physical activity, and the more a person moves, the better the blood supply to the lungs and the more intense the phlegm leaves the bronchi.
A cough is a sign that the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is inflamed. Going to the pool can aggravate pathological changes due to the influence of the following factors on the patient:
- Chlorine-containing chemicals that disinfect water well and no less irritate the skin and mucous membranes. With pharyngitis and laryngitis, such bathing may result in an attack of debilitating cough.
- Temperature changes, which are especially noticeable in winter. After a swimming pool or a warm shower, a steamed person goes outside and quickly freezes. Such hypothermia can cause a reflex spasm of the inflamed bronchi and increased coughing.
- High risk of infection with new viruses and bacteria in the locker room or public transport on the way to the pool.
The result of visiting the pool while coughing can result in various complications:
- The spread of infection deep into the body with the development of bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Obstruction (spasm and swelling) of the respiratory tract, intensification of an existing cough.
- Feverish state.
- A new infectious disease. After an illness, and even more so at its height, a person’s immunity is depleted, so it is very easy to “pick up” something new.
- Sudden loss of strength, dizziness. In case of acute respiratory diseases and cough, any physical activity for a weakened body is a serious test.
Pool and snot: to go or not to go?

A runny nose is a reaction of the nasal mucosa to infections. To prevent the nasal mucosa from drying out, the cells produce a special secretion to moisturize it. When the mucous membrane gets infected, more secretion (mucus) is produced. This is snot.
We thank therapist Ekaterina Gvozdeva for her consultation
Types of runny nose
There are 3 types of runny nose: viral, bacterial and allergic.
Viral. In the first days, clear water flows from the nose. This is how the cells protect the mucous membrane from drying out and prevent bacteria from developing. Because infection develops quickly on dry mucous membranes. Gradually the snot thickens. If at this moment bacterial flora joins, they become yellow or green.
Bacterial. Yellow or green snot comes out of the nose. These are dead neutrophils - the result of the body's fight against infection. Bacteria have appeared on the mucous membrane and the body is actively fighting them.
Allergic. Clear water discharges from the nose. This is a reaction of the mucous membrane to allergens: dust, animal hair on clothes, pollen, poplar fluff. When applied to a swimming pool, children may react to chlorine.
Signs of a runny nose
| Anterior rhinitis | Posterior rhinitis |
| Snot flows out. | No snot is visible visually. |
| The mucus is liquid and comes out naturally. | Mucus flows down the back of the throat and provokes a cough. The child coughs. |
There is such a thing as post-traumatic rhinitis. This is discharge from 1 nostril and a putrid odor. It is formed as a result of the ingress of foreign bodies that interfere with the natural outflow of mucus. Children often stick small objects into their noses - Lego parts, dolls' shoes, etc. They may not notice them, and some are simply afraid to tell their parents.
A foreign body in the nose may not bother a child, but the mucous membrane reacts to it with secretions.
Is it safe for others to take a snotty child to the pool?
In Europe, a child with snot is not taken out of kindergarten, since snot is the body’s natural reaction to infection
Swimming pools exist to help children improve their health. Doctors believe that he encounters infections and his immune system is learning to fight them. For a healthy person with a strong immune system, snot is not contagious. A child with a weakened immune system and prone to illness will catch an infection anywhere - in the locker room, during a temperature change after a shower, or on public transport.
A swimming pool is not the most sterile place. Modern filters disinfect water, but they cannot cope with all infections. The cancellation of medical certificates for the pool also plays an important role. But there is a plus in this - the child’s body faces additional stress and trains.
A swimming pool is not a home bath. Disgusted people don't go to the pool.
The chances of catching an infection in the pool are low due to the humid air and drafts. Children get sick much faster in kindergartens, because the room is poorly ventilated, the radiators are fried, and they are only allowed out for a walk for 40 minutes. The mucous membrane dries out, viruses attack. Snot is less likely to occur after a swimming pool than after visiting the garden. But the body can react to the pool, including snot.
Do I need certificates and where can I get them?
A health certificate may only be required if you are planning your first trip to the pool. It can be obtained from your local doctor at the clinic at your place of residence.
If a child or adult is already visiting the pool, medical documents are not needed (except for breaks lasting more than 2 months due to illness or personal circumstances for children). A visit to the doctor if you have a cough is first and foremost necessary for yourself - to find out the cause of this symptom and make sure that there are no obstacles to swimming.
Important! It is best to clarify all questions regarding the need for a medical certificate in advance with the administration of the sports complex - each institution has its own requirements. In accordance with the sanitary rules in force in the Russian Federation (SanPiN 2.1.2.1188-03), medical documents for a swimming pool are required only when an unfavorable epidemiological situation for specific diseases arises in the city. But a certificate of the results of a test for enterobiasis in children is mandatory.
How to survive an allergy to bleach?
Many people stop training in the pool due to an allergy to chlorine. Everyone can minimize the effects of allergies and continue going to the pool without suffering from the consequences.
If you have personally experienced an allergy to chlorine in a swimming pool, then you are familiar with the following symptoms: discomfort in the eyes (burning, redness), skin manifestations (rashes, flaking from dryness), dysfunction of the respiratory system (cough, sore throat, sneezing) . In order to understand this issue, it is necessary to understand why bleach causes an allergic reaction. Next, you will learn how to continue training in the pool without harm to your health.
Why is chlorine used in swimming pools?
Bleach is a strong toxin, and this is widely known. However, this chemical has been used in all public swimming pools for decades, and the situation is not going to change. Water chlorination does not have an equivalent alternative, since other cleaning methods are many times more expensive.
Chlorine destroys pathogenic flora, which normally should not be in the pool. If the content of microorganisms in the water exceeds the permissible limit, the establishment will be closed in accordance with the requirements of the sanitary and epidemiological service.
Visiting such a pool is dangerous to health; the water becomes a favorable environment for harmful bacteria.
Sanitary and epidemiological services regulate not only the absence of dangerous bacteria in water, but also the level of chlorine content. If there is more bleach than required, visitors may be poisoned.
Often, pool owners use combined cleaning methods in order not to exceed the chlorine level, for example, using ozone or ultraviolet rays. In any case, chlorine will be present to a greater or lesser extent in the water of a public pool.
Only owners of small private pools where there is not a lot of traffic can afford to purify water without chlorine.
Why does chlorinated water cause allergies?
Chlorine itself, as a chemical element, does not cause allergic reactions; the mechanism of action is much more complex.
Elements such as chlorine are called irritants; when they come into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, such substances actively irritate them, so symptoms very similar to an allergic reaction occur.
Chlorine is designed to fight pathogenic flora that enters the water with sweat, particles of human skin and hair. During this interaction, by-products are formed, many of which are much more harmful to the body than chlorine.
By-products enter the body through mucous membranes and pores in the skin, as a result of which a person begins to react more strongly to familiar allergens - household chemicals, plant pollen, animal hair, etc.
After visiting a swimming pool with chlorinated water, a person who is not used to suffering from allergies experiences severe symptoms. The longer the contact with chlorine, the more intense and vivid the symptoms will be (this means not only the duration of one session, but also the frequency of visits).
For some, the reaction manifests itself immediately, while others begin to feel symptoms after some time. In any case, such appearances are unpleasant.
How to avoid being allergic to bleach?
First of all, you should check whether the reactions described above occur specifically for you.
If you can swim in natural bodies of water without experiencing discomfort, but after visiting the pool you observe at least one of the symptoms, this means that your body is susceptible to chlorine.
The easiest way to get rid of allergies is to stop going to the pool, but not everyone is ready to give up their favorite workouts. Athletes are not people who will put up with inconvenience and sacrifice something, they overcome difficulties.
A sure-fire option would be to visit a medical specialist, because if chlorine causes such a reaction in the body, then the person is a latent allergy sufferer.
The allergist will prescribe tests during which the irritant reagent will be identified, and then treatment will be determined until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
It would also be a good idea to choose a pool that uses several cleaning methods; such water will have much less chlorine. By the way, chlorine is present not only in the water itself, but also in the indoor air.
Antihistamines will help, and your doctor will help you choose the right ones. Oral medications are used immediately before training, and if there is irritation of the respiratory mucosa after swimming, nasal drops and sprays are used. Read on for ways to combat specific allergies.
Eye irritation
Eye irritation is the very first reaction to chlorinated water; it occurs in almost all people. Irritation manifests itself in redness in the eyes, they begin to water and itch, and the person constantly wants to rub them. Some people experience eyelashes falling out when exposed to bleach.
How to prevent eye irritation?
Don't neglect swimming goggles; their use is the most effective way to protect your eyes. When using glasses, the mucous membranes are protected not only from chlorine in the water, but also from chlorine-containing compounds in the air.
Before visiting the pool, girls need to completely remove all makeup, as chlorine compounds can come into contact with cosmetics. The same applies to waterproof decorative cosmetics; if it does not come into contact with water, this does not mean that the products will be equally inert to chlorine.
If you wear contact lenses, they must be removed before swimming. If you have poor vision, you can use prescription swimming goggles.
Skin irritations
This reaction is also quite common, but it does not occur as quickly as the one described above. With regular visits, the skin begins to react to chlorinated water; in people with dry skin, irritation appears earlier.
The range of manifestations is wide, ranging from mild itching and flaking to rashes requiring medical intervention. Most often, a person feels tightness of the skin, it constantly pulls and itches, later microcracks appear, this can be noticed in those places where the skin is most vulnerable, that is, in the groin and armpits.
Bleach is no less harmful to nails and especially to hair; the hair becomes dull, begins to break, and some even begin to fall out.
How can you ensure that contact with bleach is least harmful to your skin and hair?
Before a swimming session, there should be no residues of cosmetics on the body. To make sure of this, you need to take a shower using soap or shower gel and a washcloth. After such treatment of the skin, you can be sure that the products will not come into contact with chlorine.
A swimming cap, silicone or textile, is designed to protect your hair from harmful effects. A fabric cap can be used by those who do not immerse their heads under water, for example, visitors to the water aerobics section.
For those who swim and dive, a silicone cap is suitable; it will not completely prevent water from getting on your head, but your head will not get wet, and the cap will save heat.
After visiting a pool with chlorinated water, you should immediately take a shower and wash your hair using a moisturizing shampoo or conditioner. After a shower, you need to use skin softening products - creams, balms or lotions.
The appearance of respiratory disorders
That is, a reaction to bleach in the respiratory tract is one of the most severe and dangerous manifestations. The mildest reaction is nasal congestion and itching, coughing and sneezing, but it can also lead to difficulty breathing with choking, loss of smell and sense of taste.
Symptoms of a chlorine allergy may not appear immediately; a person may begin to feel a reaction several hours after leaving the pool.
It also happens that while swimming a person feels a slight itching in the nose, and a few hours later he is faced with manifestations in all its glory - complete nasal congestion or a severe runny nose.
If you go to the pool regularly, respiratory disorders will sooner or later make themselves felt, even leading to serious respiratory diseases. Products containing chlorine provoke the development of bronchial asthma.
How to minimize the impact of chlorine on the respiratory tract and reduce the consequences?
Chlorinated water should not enter the body through the nose and mouth; this issue must be constantly monitored. It is recommended to use a nose clip.
If all pool visitors take a shower before the pool, then there will be fewer compounds in the water resulting from the reaction of chlorine-containing compounds with organic compounds.
After visiting the pool, the nasal cavity should be rinsed with special products such as Aqua Maris; saline solution or cool boiled water are also suitable.
You should leave the pool immediately after a swimming session. Just because you're not in the water doesn't mean you've stopped breathing volatile chlorine compounds in the air.
Antihistamines neutralize allergy symptoms; you should choose the latest generation of drugs, but this cannot be done systematically without a doctor’s prescription. Antihistamine tablets are taken immediately before training.
Nasal drops and sprays will eliminate nasal congestion and runny nose; we will not give examples of medications; for the correct selection of pharmacological products, you should consult your doctor.
Life story
In order for the information not to look like a dry theory, we will give a story from the life of a person who began visiting a swimming pool with chlorinated water. The girl has never encountered allergies and its manifestations. For the first few months of visiting the pool, she also did not notice any negative manifestations.
Sometimes after training, the girl noticed a slight redness in her eyes and a temporary decrease in the quality of vision. She did not attach any importance to this, because the redness occurred only when there was direct contact with water, she always used swimming goggles, and if water got into them, she immediately threw it out.
Later, another symptom was added, sneezing; after training, the girl could sneeze for up to 20-30 minutes, but then it stopped until her next visit to the pool.
Then she began to sneeze much more often, and a chronic runny nose appeared, which haunted her for days on end and prevented her from concentrating on work.
However, towards evening all manifestations passed, so this did not cause significant concern either.
It only got worse, the symptoms became stronger and stronger. 4-5 hours after each workout, the girl could not breathe through her nose at all and experienced congestion combined with a severe runny nose.
If the training took place in the evening, then she could not sleep due to the inability to breathe, and would not part with a huge number of handkerchiefs.
The girl adapted to this; before going to bed, she watched a couple of movies while in position, after which she could breathe calmly and fell asleep.
By this point, the feeling of anxiety was growing, the girl changed several swimming pools, one of them was highly chlorinated, and when visiting it, severe dry skin appeared. This problem was solved on my own with the help of a huge number of body moisturizers.
Problems with the respiratory tract could not be solved so simply, so our heroine turned to a therapist at her place of residence. The doctor she saw was not a very experienced specialist, and she recommended that she avoid going to the pool.
The situation is reminiscent of a well-known joke in which a patient asks a doctor about the most effective remedy for sexually transmitted diseases. The doctor replied that you should drink tea, but not before or after, but instead of sexual intercourse.
The girl was not satisfied with this answer; she had no intention of quitting training. Then she received a recommendation to take antihistamine tablets, before or after visiting the pool, the doctor did not say.
Many pool mates took anti-allergy medications, but our heroine decided to deal with the symptoms in a different way.
Through trial and error, she developed a number of rules for herself to minimize the manifestations of allergies.
Practice-tested rules
- It is necessary to ensure that water from the pool does not get into the nose and mouth;
- You should not practice for more than an hour, since the longer the contact with bleach, the stronger the reaction to it;
- There is no need to stay by the pool after training and watch other people swim;
- After training, you should thoroughly wash your body and rinse your nose to get rid of chlorine-containing products;
- If your diet allows you to eat one or two nutritional bars after training, then you need to do it. Our heroine has a protein-carbohydrate window at this time, and if she fills it with a bar, then the manifestations are felt much less. She also tries to eat a full meal no later than a couple of hours after class;
- If your skin feels dry, you should use moisturizing and nourishing products after the final shower;
- If your swimming session occurs in the evening, then it is better to go to bed no later than 2.5-3 hours after training. This way you will be able to fall asleep before symptoms appear. If you sleep on your back, your nose will breathe better.
Conclusion
The girl from the story above did not manage to completely get rid of allergy symptoms, and the same thing happens to everyone else. But if you behave correctly, the manifestations of symptoms can be reduced by 65-85%, primarily this applies to a runny nose. Sneezing after swimming won't go away, but at least you'll be able to sleep peacefully and not feel discomfort.
Main recommendations for those who go to a public swimming pool:
- It would be better to choose a pool with combined methods of water purification;
- Before visiting the pool, you should take a shower with soap and a washcloth, remove any remaining cosmetics from your body and face;
- During training, you should use a swimming cap, safety glasses, and preferably a nose clip;
- After swimming, you should immediately leave the pool area and take a shower; after showering, your skin should be moisturized with nourishing cosmetics;
- Antihistamines may be used occasionally.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a0c331186516515bab4e163/5b0e93295816693a21d840b3