Anesthesia became one of the main discoveries in medicine of the twentieth century. With its help, painless surgical interventions became possible. But there are cases when the patient is allergic to anesthesia. It is associated with individual intolerance by the patient’s body to a certain pharmacological drug.
The doctor finds out the patient's allergy history
Types of anesthesia
An allergy to anesthesia in dentistry is very sad, because dental problems can unsettle any person. And it’s one thing to treat teeth with pain relief, when you just need to wait a couple of seconds while the dentist inserts the needle. And it’s quite another to suffer from piercing pain the entire time the doctor is operating the drill. But there is always a way out, because there is no such thing as an allergy to absolutely all types of anesthesia. And you can find an alternative option.
The main classification involves dividing anesthesia into general and local. General in dentistry is rarely used (only for complex operations or when the patient has pathological fear), but if this happens, then doctors choose the second between inhalation and non-inhalation. Because to perform inhalation general anesthesia, the patient must wear a mask. And this makes dental procedures difficult.
Non-inhalation general anesthesia is the best option for dentists. They can estimate how long the procedure will take and calculate the required dose of medication to be administered (taking into account the age and size of the patient). So, a doctor can put a person under short-term anesthesia for just a few minutes. The drug is administered by infusion, i.e. into the blood through a vein.
But more often, dentists turn to local anesthesia, which has 5 specific types (as complexity increases):
- application (external anesthesia using ointments or sprays);
- infiltration (blocking specific small nerves in a certain area);
- conductor (introduced into the paraneural space, blocking the source of pain - a large nerve node);
- intraosseous (introduced between the roots of teeth during complex operations and the ineffectiveness of infiltration and conduction anesthesia);
- stem (to block the masticatory nerve in case of problems with opening the mouth due to inflammatory processes accompanied by painful spasms).
Causes of allergic reactions
An allergy to anesthesia implies an individual reaction of the body not to the fact of putting a person into a narcotic sleep or anesthesia of a specific part of the body, but to the substances contained in the administered medicine or air mixture. It can appear immediately after anesthetic procedures, during the action of anesthesia, or even a few hours or days after the end of the operation.
There are several reasons for allergies to anesthesia. The most popular is individual intolerance to the components in the anesthetic. An adult usually knows about such features of his body, so he warns the doctor in advance. Less often, the patient is allergic to common substances and materials: latex of doctor’s gloves, mixtures for fillings.
In a person without allergies, a reaction may occur with an overdose of the drug. This is already a mistake by the doctor who incorrectly calculated the dose of the medicine. In this case, symptoms do not appear immediately, which is extremely dangerous, because sometimes the patient becomes ill in the midst of surgical procedures.
Important! The anesthesiologist must select and prepare the solution for pain relief. Especially if we are talking not about local, but about general anesthesia.
Another probable cause of allergic reactions during dental anesthesia is the poor quality of the medicine. Young, newly opened clinics (or private dental offices) may purchase drugs from dubious suppliers in order to get cheaper prices. But there is a risk that the anesthetic substances may contain toxic substances. Even if they are not life-threatening, an allergic person can still experience severe symptoms.
Options for solving the problem
If the patient’s body reacts negatively to the preservatives included in the injection, the dentist can simplify the composition of the solution, leaving only one active ingredient. At the same time, the specialist must increase the dosage of the drug so that it is enough until the end of the treatment. By the way, epinephrine can be replaced with prilocaine or melivacaine, which are much less likely to be allergens.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with White coating on the tongue in adults: causes and treatment associated with bitterness and dry mouth, what it means and how to get rid of it
If the problem is still an allergy to “cains,” then you can solve the problem using one of the following methods:
- Apply general anesthesia
- Apply histamine blockade. This is a painful method, so it is used only in extreme cases
- Try using other "cains". Often a patient who cannot tolerate, say, lidocaine will tolerate marcaine or septocaine
- Treatment without anesthesia. Allowed only for simple dental operations (such as cleaning tartar) and with the agreement of the doctor and the patient
Important! If during dental treatment the patient develops symptoms of a side effect of the anesthesia, the doctor should stop the session and advise a different type of treatment or wait until the effect of the given anesthetic wears off and then use another. At the same time, the doctor is obliged to enter all the information into the patient’s record in order to avoid such situations in the future.
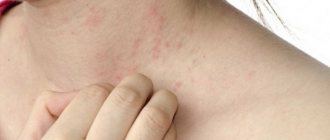
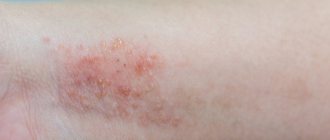
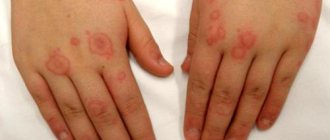
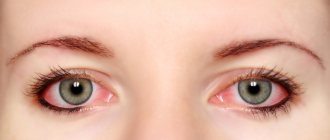
Allergy symptoms during anesthesia
Signs of intolerance to anesthesia imply dysfunction of a variety of organs and systems. The main external symptoms that a doctor can determine include the following:
- redness of the skin on the face (usually cheeks, forehead);
- swelling on the face or at the injection site, swelling of the mucous membranes;
- uneven breathing, shortness of breath;
- increased sweating;
- weakness, loss of consciousness;
- vomit.

The patient himself may also feel allergy symptoms in the form of body itching, dizziness, and headache. But sometimes this is due to excessive anxiety, and not to an allergy to anesthesia. Nervous stress can also be manifested by rapid heartbeat, redness of the face and perspiration. And the personal reaction of the patient is important for the doctor, who must figure out whether it is an allergy or stress.
More serious symptoms of allergies are angioedema with distribution to the lining of the larynx and difficulty breathing and anaphylactic shock with the production of too many toxic substances in the body. These are critical conditions that require emergency medical attention.
Sometimes heart disease and problems with the respiratory system worsen after anesthesia. This can also be a consequence of allergies, manifested in the form of a general negative effect on the body. Those. During the procedure, the patient may not experience any symptoms, but after a few days he begins to experience exacerbations.
First aid and treatment
Any clinic (including a dental facility) must have first aid equipment, as well as specially trained medical personnel ready to help. For mild cases (urticaria, itching, rash), antihistamines based on diazolin, fencarol, and diphenhydramine are used. For severe manifestations of allergies (Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock), drugs such as adrenaline, epinephrine, and prednisolone are used. They are injected into a vein or muscle. The victim is hospitalized.
Important! It is imperative to inform your doctor if you feel worse after the administration of the anesthetic. Any suspicious symptom may be a sign of an allergy.
After the symptoms of allergy to anesthesia have subsided, the patient does not return to the dental procedure until the exact reasons for the development of this condition have been established. Even if it was a slight redness. Because allergic reactions manifest themselves with different intensity each time, and it cannot be ruled out that next time it will be anaphylactic shock. Because almost all allergy sufferers are at risk for this critical condition.
Spinal anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia is a method of pain relief during which an anesthetic is injected into the spine, or more precisely, into the epidural space of the spine. It is used during childbirth, caesarean section. After it there are much fewer complications. Gynecologists, performing various operations on the pelvic organs, give preference to pain relief in the spine. This method of anesthesia is widely used in traumatology, during surgical interventions on the legs and pelvis.
An analgesic substance is injected into the spine, and after that the patient, remaining conscious, does not feel anything below the level of the lumbar region.
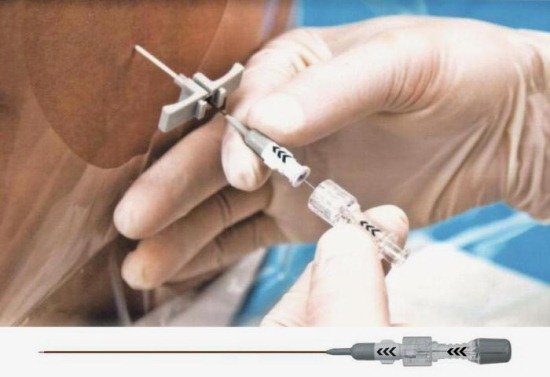
Carrying out epidural anesthesia
Drugs used
In dentistry, the first drugs used for local anesthesia were Lidocaine and Novocaine. They contain the preservative methylparaben, to which people are most often allergic. Today, these two drugs are almost never used. They have been replaced by safer, but no less effective solutions: Ultracaine, Articaine, Mepivacaine, etc. In addition to the active anesthetic substance, they contain adrenaline or epinephrine, which not only prevent the development of anaphylactic shock, but also increase the strength of anesthesia by constricting blood vessels in the area introduction.
The syringes used to inject the anesthetic have also improved. They look like disposable pens with a very thin needle, so the pain from an injection into the gum is minimal.
The safest anesthetics
The most popular pain reliever is lidocaine
Typically, the most popular dental anesthetics do not cause allergies in people. In addition, they are as effective as possible. Among these drugs is lidocaine in combination with a vasoconstrictor. This drug is actively used not only in dental practice, but also in other areas of medicine.
Another fairly harmless anesthetic is mepivacaine. In terms of its effectiveness, the drug is not inferior to lidocaine and almost never causes allergies. It is worth considering that mepivacaine constricts blood vessels.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dry mouth at night: causes and solutions. Why is my mouth dry at night and my tongue sticking to the roof of my mouth?
The drug articaine also has a high level of safety. This is a non-toxic, long-acting anesthetic that is suitable not only for people with allergies, but also for patients who have liver or kidney problems.
Prevention
The dentist will usually ask the patient if they have an allergic reaction to lidocaine or other painkillers. But how do you know if you're allergic to anesthesia if you've never had it before? Unfortunately, people often find out that they have an allergic reaction to anesthesia precisely after emergency situations, when they feel unwell right in the dentist's chair or on the operating table. But this can be avoided if everything is checked first.
Skin tests
The most common allergens are applied to the patient's hand. The doctor monitors the reaction by the skin (redness, itching, local swelling) and sometimes by the patient’s well-being (runny nose, dizziness, weakness).
Enzyme immunoassay blood test
A specific diagnostic method that allows you to identify the presence of protein substances and the level of immunoglobulins to determine the allergen. This is a more accurate analysis than skin tests.