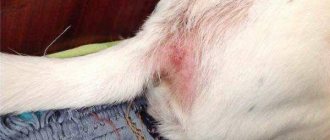
Our little brothers, just like people, suffer from many diseases of various etiologies. One of the most common ailments is pododermatitis - an inflammatory process that develops mainly on the pet’s limbs, in places of contact with the ground (interdigital spaces, paw pads).
In addition, there is a genetic predisposition to this disease that is characteristic of a particular breed. For example, Shar Peis often suffer from pododermatitis.
, bulldogs, Pekingese, German shepherds, dachshunds, Labradors.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of all forms of this pathology is a weakened immune system. With low immunity, pathogenic microflora, constantly present in some quantity on the skin, begins to strengthen and actively reproduce. In this case, it is very important to identify the disease that has undermined the dog’s body’s defenses. Only after this can you fight, but not with pododermatitis itself, since it is only a consequence, but with the main ailment.
Possible causes of the development of pododermatitis are the following:
In addition, painful sensations in the paws
and lameness may appear in the following situations:
- Cracks and injuries on the paw pads;
- skin irritation resulting from prolonged contact with rough road surfaces (asphalt, etc.);
- sharp foreign objects that got under the skin during a walk.
conclusions
You cannot treat a dog with medications without a veterinarian's prescription.
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs should be treated only after identifying the true cause of the disease. In this case, treatment will bring relief to the animal. But the use of all kinds of ointments and lotions without a doctor’s prescription will only aggravate the course of the disease.
Pododermatitis is a disease that is quite common in dogs. Our pets constantly lick their paws and their paws become red. Pododermatitis does not manifest itself as an independent disease, but as a general symptom of malaise in the animal’s body. For timely and effective treatment of pododermatitis, you should immediately contact specialists to make an accurate diagnosis and further monitor the dog.
Pododermatitis is an inflammation of the paw pads in animals. Bacterial pododermatitis is a consequence of deep microbial infection of the dog’s fingers. In relation to various etiological causes, pododermatitis is a secondary pathology. There are other names for the disease, such as interdigital pyoderma. Pododermatitis is a fairly common disease and phenomenon in animals.
The first symptoms can be seen as the dog begins to lick its paws, while the skin is red and moist.
Symptoms
Regardless of the etiology, the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
Characteristic symptoms
Depending on the nature of origin, each type of pododermatitis has its own specific symptoms.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must urgently consult a doctor, who, while collecting anamnesis, will ask the dog owner to answer the following questions:
An accurate diagnosis is made based on the examinations performed and the owner’s answers received during the survey. Examination of the dog's condition includes a biopsy, cytological studies, allergy tests, urine and blood tests, and antibiotic susceptibility tests.
Cytological diagnosis is aimed at identifying or refuting purulent reactions. A smear is examined and the severity of the disease is determined. Some pets have extensive skin damage, while others have limited skin damage. It is very important to differentiate the disease from fungal infections.
Pododermatitis in animals is divided into two types.
Aseptic pododermatitis
. Develops as a result of injury to the limbs. The disease is associated with damage to the skin. To avoid such situations, you need to keep an eye on your tailed friend and not let him go to obviously dangerous places where there are a lot of fragments, debris, and sharp objects. Aseptic pododermatitis causes lameness. The dog has an inflamed pad on its paw, it feels pain when walking, and begins to limp. Some animals experience an increase in body temperature.
Before starting treatment for this disease, it is necessary to carefully but thoroughly clean the paw pads of dirt using Novocain. If you suspect aseptic pododermatitis, you should consult a specialist.
Purulent pododermatitis
is divided into two types: superficial and deep. This type of disease is diagnosed when tissue structures are damaged. In such cases, the dog begins to limp. The purulent type of the disease is more dangerous, since purulent pathogens penetrate the skin. As the disease develops, the pet’s temperature rises, it begins to limp, and when pressure is applied to the paw, the dog feels severe pain and groans.
Pododermatitis in dogs: how to avoid the disease and help your four-legged friend
Our little brothers, just like people, suffer from many diseases of various etiologies.
One of the most common ailments is pododermatitis - an inflammatory process that develops mainly on the pet’s limbs, in places of contact with the ground (interdigital spaces, paw pads). In addition, there is a genetic predisposition to this disease that is characteristic of a particular breed. For example, Shar Peis often suffer from pododermatitis.
, bulldogs, Pekingese, German shepherds, dachshunds, Labradors.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of all forms of this pathology is a weakened immune system.
With low immunity, pathogenic microflora, constantly present in some quantity on the skin, begins to strengthen and actively reproduce.
In this case, it is very important to identify the disease that has undermined the dog’s body’s defenses. Only after this can you fight, but not with pododermatitis itself, since it is only a consequence, but with the main ailment.
Possible causes of the development of pododermatitis are the following:
In addition, painful sensations in the paws
and lameness may appear in the following situations:
- Cracks and injuries on the paw pads;
- skin irritation resulting from prolonged contact with rough road surfaces (asphalt, etc.);
- sharp foreign objects that got under the skin during a walk.
Symptoms
Regardless of the etiology, the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
Characteristic symptoms
Depending on the nature of origin, each type of pododermatitis has its own specific symptoms.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must urgently consult a doctor, who, while collecting anamnesis, will ask the dog owner to answer the following questions:
An accurate diagnosis is made based on the examinations performed and the owner’s answers received during the survey. Examination of the dog's condition includes a biopsy, cytological studies, allergy tests, urine and blood tests, and antibiotic susceptibility tests.
Cytological diagnosis is aimed at identifying or refuting purulent reactions. A smear is examined and the severity of the disease is determined. Some pets have extensive skin damage, while others have limited skin damage. It is very important to differentiate the disease from fungal infections.
Pododermatitis in animals is divided into two types.
Aseptic pododermatitis
. Develops as a result of injury to the limbs. The disease is associated with damage to the skin.
To avoid such situations, you need to keep an eye on your tailed friend and not let him go to obviously dangerous places where there are a lot of fragments, debris, and sharp objects. Aseptic pododermatitis causes lameness.
The dog has an inflamed pad on its paw, it feels pain when walking, and begins to limp. Some animals experience an increase in body temperature.
Before starting treatment for this disease, it is necessary to carefully but thoroughly clean the paw pads of dirt using Novocain. If you suspect aseptic pododermatitis, you should consult a specialist.
Purulent pododermatitis
is divided into two types: superficial and deep. This type of disease is diagnosed when tissue structures are damaged. In such cases, the dog begins to limp.
The purulent type of the disease is more dangerous, since purulent pathogens penetrate the skin.
As the disease develops, the pet’s temperature rises, it begins to limp, and when pressure is applied to the paw, the dog feels severe pain and groans.
Treatment
Single lesions are treated with antiseptic drugs
. These may be the following medications:
- Streptocide ointment;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Tetracycline.
For mild interdigital pododermatitis, antibiotics are not prescribed. Paws should be washed regularly with warm water and soap.
Multiple lesions require a different approach. First of all, the doctor treats the underlying disease with antibiotic therapy.
In this case, medications are given to the pet until all symptoms disappear and for another two weeks after that. The skin between the fingers must be cleaned several times a day.
By curing the underlying disease, you will relieve your pet of pododermatitis.
Treatment of pododermptitis requires quite a lot of time. It is worth considering that there is always a possibility of relapses.
Typically, the progression of the disease is observed in winter due to the fact that the dog’s paws are wet for a long time, this creates ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
In order to identify the pathogenic microflora that caused the disease, a scraping from the affected area and a smear for bacterial culture are taken from the dog. A scraping can confirm or deny the presence of a subcutaneous demodex mite.
A smear often reveals the yeast fungus Malassezia, which significantly complicates the treatment of pododermatitis.
To alleviate the pet’s condition, relieve itching and eliminate pain, the dog is given herbal compresses that have an antiseptic effect.
Prevention
Pododermatitis is a rather insidious disease
, which has a long treatment period and is dangerous due to its relapses. Therefore, every pet owner should take certain measures aimed at reducing the likelihood of developing the disease. The owner must ensure that the following actions are taken:
Some breeds require especially careful care for their limbs - Yorkshire terriers, poodles, Pekingese. These pets need to have their nails trimmed and the hair between their toes trimmed regularly. When walking, it is better to wear waterproof shoes for your dog, which will provide protection from salt, snow, water and reagents. Or rub the animal's paws with special wax.
Pay more attention to your tailed pet, monitor its condition, respond to any changes in a timely manner, and then your pet will be healthy, vigorous and cheerful for many years.
Attention, TODAY only!
Pododermatitis is a disease that is quite common in dogs. Our pets constantly lick their paws and their paws become red.
Pododermatitis does not manifest itself as an independent disease, but as a general symptom of malaise in the animal’s body.
For timely and effective treatment of pododermatitis, you should immediately contact specialists to make an accurate diagnosis and further monitor the dog.
Pododermatitis is an inflammation of the paw pads in animals. Bacterial pododermatitis is a consequence of deep microbial infection of the dog’s fingers. In relation to various etiological causes, pododermatitis is a secondary pathology. There are other names for the disease, such as interdigital pyoderma. Pododermatitis is a fairly common disease and phenomenon in animals.
The first symptoms can be seen as the dog begins to lick its paws, while the skin is red and moist.
Symptoms of pododermatitis
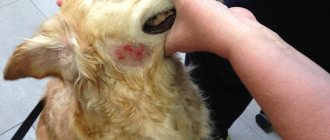
- Wounds on the pads of a dog's toes.
- Blood-filled blisters on the paws.
- Swelling of the dog's paws.
- Lameness when walking.
- Purulent processes.
Any type of pathogenic fungus causes fungal pododermatitis. Lupus erythematosus or vasculitis can cause pododermatitis based on autoimmune etiology.
Tumors can also be factors. Most often these are melanoma and papilloma.
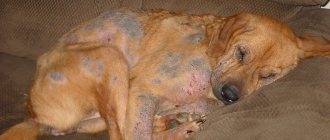
If pododermatitis has allergic factors, the skin on the dog’s paws turns red and swells. Due to the itching that has arisen, the dog begins to constantly scratch, rub and lick its paws. At the same time, the fur begins to fall out, the skin is constantly wet due to the abundant amount of saliva on it.
Causes of the disease
The causes of pododermatitis manifest themselves as single or multiple lesions.
For single lesions, the main causes are the following:
- Injuries to the animal's fingers
- stone blows, high temperature. - Foreign bodies in dog tissues
- thorns, glass. - Oncological processes
– tumor, plasmacytomas.
Causes of multiple lesions:
First of all, cytological studies are carried out, which help identify purulent processes. In the smear, with pododermatitis, cocci or rods are present. During diagnosis, the degree of skin damage is determined. Skin inflammation can be either limited or widespread.
There are a number of diseases that should be distinguished by symptoms from pododermatitis. These are diseases such as demodicosis or actinomycosis, mycobbacteriosis or fungal infections.
Pododermatitis can be purulent and aseptic.
Aseptic pododermatitis
observed as a result of a bruised paw, compression or long walks on hard and uneven roads.
The main signs of aseptic pododermatitis are lameness when walking and pain in the animal when the paw and affected areas are squeezed. The dog's temperature may also increase.
For treatment, the dog should clean its paw pads, and novocaine should be used if necessary.
Purulent pododermatitis
can be deep and superficial. With deep purulent pododermatitis, the tissues of the skin base are affected. Such symptoms occur when pyogenic microbes enter the base of the skin. At the same time, the dog begins to limp, the body temperature rises, and when pressure is applied to the paw, the animal feels a sharp, severe pain.
Prevention of pododermatitis
In order to prevent and reduce the risk of pododermatitis, you should adhere to the following recommendations for caring for your dog:
- Trim your pet's claws in a timely manner and monitor their length.
- Trim the fur between your toes.
- Keep the dog's enclosure, booth or kennel clean.
- Clean the area where the dog sleeps and keep her dishes clean.
- Monitor your dog's diet and maintain a balanced diet.
- After walks and if necessary, wash your pet’s paws.
Monitor your pet and be attentive to all changes in your pet’s body. Have your pet examined regularly at a veterinary clinic and specialists. If pododermatitis occurs due to an allergen, eliminate the allergen from the dog’s diet or environment. Timely identification of the symptoms of the disease allows it to be cured faster.
The expression “movement is life” is especially true for our pets. Only those dogs that take long walks every day maintain their health and well-being for a long time. But there are more than a dozen diseases in which an animal simply physically cannot frolic happily in the fresh air. One of them is pododermatitis in dogs.
This is the name for inflammation of the paw pads. What are the reasons for such an unpleasant phenomenon? There can be a lot of them: infections, allergies, hormonal disorders, autoimmune diseases, poor ecology (salt on city streets), oncology. Before visiting the veterinarian, it is advisable to know the answers to the following questions:
- Where does the dog live (city or countryside)?
- Do clinical signs appear constantly, or is the phenomenon seasonal?
- Are the lesions only observed on the paws, or can they be seen on other parts of the body?
- Have you tried home treatment?
- Has your dog's diet changed?
- Have you traveled anywhere recently?
- Does the dog have any other health problems?
The veterinarian’s choice depends on your exact answers: what to treat, what treatment regimen to use, how long it will take.
What causes the disease?
Let's consider the main factors that cause the occurrence of this disease. So, here is a short list of them:
Source: https://crois.ru/glaukoma/pododermatit-u-sobak-kak-izbezhat-bolezni-i-pomoch-chetveronogomu-drugu/
Treatment
Single lesions are treated with antiseptic drugs
. These may be the following medications:
- Streptocide ointment;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Tetracycline.
For mild interdigital pododermatitis, antibiotics are not prescribed. Paws should be washed regularly with warm water and soap.
Multiple lesions require a different approach. First of all, the doctor treats the underlying disease with antibiotic therapy. In this case, medications are given to the pet until all symptoms disappear and for another two weeks after that. The skin between the fingers must be cleaned several times a day. By curing the underlying disease, you will relieve your pet of pododermatitis.
Treatment of pododermptitis requires quite a lot of time. It is worth considering that there is always a possibility of relapses.
Typically, the progression of the disease is observed in winter due to the fact that the dog’s paws are wet for a long time, this creates ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
In order to identify the pathogenic microflora that caused the disease, a scraping from the affected area and a smear for bacterial culture are taken from the dog. A scraping can confirm or deny the presence of a subcutaneous demodex mite. A smear often reveals the yeast fungus Malassezia, which significantly complicates the treatment of pododermatitis. To alleviate the pet’s condition, relieve itching and eliminate pain, the dog is given herbal compresses that have an antiseptic effect.
How to treat pododermatitis on a dog’s paws between the toes
The soles of dogs' paws are often affected by a common disease called pododermatitis. It is of a secondary nature and occurs as a result of inflammatory or autoimmune disorders in the animal’s body.
general information
The owner of a cheerful, cheerful and active pet suddenly notices that the dog has stopped loving to walk. During walks he limps heavily, and at home he constantly licks his paws. An external examination shows that the pads and interdigital spaces are inflamed, reddened, and the hair around them is moist. If this is the case, there is every reason to assume that the dog has pododermatitis.
Bulldogs, German shepherds, Pekingese, Shar Peis, Chow Chows, Labradors, Mastiffs, Boxers, and Bull Terriers are especially susceptible to the disease. Pododermatitis is especially difficult in overweight dogs.
Treatment options
There is no general scheme for treating pododermatitis in dogs. In each case, an individual approach is important.
Treatment tactics depend on the diagnostic results. The goal is to combat the causative agent of the underlying disease.
Based on the examination results, the following treatment may be prescribed:
- treatment of affected areas with antiseptic agents;
- antibacterial therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- antifungal therapy;
- antihistamines;
- dietary nutrition;
- lifelong maintenance therapy.
The choice of treatment method depends on what type of pododermatitis (type of inflammation) you are experiencing.
Aseptic pododermatitis
It manifests itself as a persistent inflammatory process and pain syndrome. There is no purulent tissue damage. The main treatment is thorough treatment with antiseptic drugs. It is carried out by the owner himself.
Purulent pododermatitis
A disease complicated by purulent tissue infection. This species has pronounced symptoms: the dog groans in pain and the body temperature rises. Antimicrobial therapy is indicated for the treatment of purulent pododermatitis. And in severe cases, surgery may be required. The doctor opens the abscesses and rinses the cavities with an antiseptic and antibiotics.
Prevention measures
The best prevention is careful adherence to the rules of keeping the animal - paw hygiene, organization of a healthy lifestyle, regular visits to the veterinarian.
To comply with these rules you must:
- promptly shorten overgrown claws;
- trim the hair growing between the toes and around the pillows;
- regularly deworm and destroy skin parasites;
- keep the dog clean;
- wash paws after walks.
Be attentive to your pet. The sooner you notice symptoms and take action, the sooner recovery will occur.
Source: https://VeterinarGid.ru/dogs/bolezni/pododermatit-u-sobak.html
Prevention
Pododermatitis is a rather insidious disease
, which has a long treatment period and is dangerous due to its relapses. Therefore, every pet owner should take certain measures aimed at reducing the likelihood of developing the disease. The owner must ensure that the following actions are taken:
Some breeds require especially careful care for their limbs - Yorkshire terriers, poodles, Pekingese. These pets need to have their nails trimmed and the hair between their toes trimmed regularly. When walking, it is better to wear waterproof shoes for your dog, which will provide protection from salt, snow, water and reagents. Or rub the animal's paws with special wax.
Pay more attention to your tailed pet, monitor its condition, respond to any changes in a timely manner, and then your pet will be healthy, vigorous and cheerful for many years.
Attention, TODAY only!
Good afternoon Dog, Cane Corso, 8 years old, Moscow. I noticed several inflammations in different places on different paws. Mainly in the area of the fingers and pads. I noticed because the dog began to periodically lick the pads of its front paws. The pads themselves are in good condition and not cracked. At first I thought he was injured, but the last two sores were on the upper (outer) side of the front paw and on the back, almost at the joint. The inflammation itself looks like a dense lump, ranging in size from a penny to two rubles, from which ichor leaks. Some inflammations that were present from the very beginning, as I noticed (about a week ago), were cured with Vishnevsky ointment. But the latter do not give in - they get wet and do not heal. Previously (about a year or two ago) this happened, and not only on the paws, even on the tail. The experience of going to doctors was not the most successful - I was in 3 clinics, Eremin said that it was “inflammation of the hair follicles” and told me to apply levomekol (which, by the way, did not help), other doctors did not say anything specific at all. By chance I remembered about Vishnevsky’s ointment, and it cured all her ailments. But there have never been such abundant rashes in different places as this time! Questions: a) what could it be? From what? General weakening of the immune system? Is it worth giving something to boost immunity? What do you advise? b) What other options could there be besides Vishnevsky ointment? Now I sprinkle Baneocin so that it is at least not an ointment, and the sore dries out. When I go for walks, I cover it with a plaster and a bandage so that the wound doesn’t get dirty. Although in the current weather it still gets wet from time to time. What else can you do about this? Let’s say I’m treating an external wound, but this “ruble” is inside? Am I pushing the infection inside? Does he need to take antibiotics? c) Who can I go to who can deal with this? Considering that the “great” leather workers from the White Fang have appointments a month in advance? Thank you in advance!
UPD August 27: I will write general recommendations here, because many animals have this, but not every doctor can accurately diagnose it. We visited a doctor - surgeon Chadin in Belant. A very attentive and friendly doctor, explains a lot to the owner. He said it was PODODERMATITIS. It is often found in Molossians - Cane Corso, Mastiffs, Bordeaux and other large dogs. Most likely, autoimmune, with the addition of infection. It often happens that exacerbations occur in spring and autumn, in damp weather. Treatment: the main thing is to keep the paws dry. Therefore, in rainy weather, wear something waterproof on sore paws. He made us a bandage (very thick) from a bandage, and on top - two rubber gloves, with the fingers turned inward. It’s also good to use household gloves - they are thicker. You can also wear a sock on top so that the rubber does not rub off on the asphalt. This is a “rubber boot” for a dog :) This is only for a walk, so that the paw inside is dry. Leave only the bandage at home. Treat with chlorhexidine. Wash your paws after a walk, it would be good with tar soap - it dries out (during exacerbations, and not throughout life). It is good to use baths with weak potassium permanganate - 5 minutes for each paw. The main thing: he made us “blockades” under the big shots. So, if the inflammation is severe, you still have to go to the doctor for these injections - the lump itself is injected with an insulin syringe, there is an antibiotic and something hormonal. I was very glad that I didn’t have to cut anything. He said that when a lump like this opens up, you don’t need any ointment, just treat it with chlorhexidine. If the lump has not yet opened, the ointment is hormonal with an antibiotic. I don’t know if it’s possible to write the name here - if you need it, write in a personal message. He also prescribed me to take an antibiotic and a hormonal drug. So, for appointments, go to the doctor. We have such a massive attack because this is already a relapse, and there are several sores on all paws.
Experience shows that only those dogs that take long walks every day remain healthy and in excellent health. The only trouble is that there are diseases in nature that prevent the owner and his pet from spending time in the fresh air.
In this article we will tell you what pododermatitis in dogs is, the dangers of this disease and how it is treated.
What is it about
Prodermatitis is what veterinarians call inflammation of the paw pads in dogs. Most often it develops against the background of:
- infections;
- hormonal balance disorders;
- allergic reactions;
- autoimmune diseases;
- exposure to chemicals;
- oncological diseases.
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment. He will ask you to tell him the following:
- clinical signs (constantly present or only in a certain season);
- habitat (city, village);
- the presence of lesions on the paws or other parts of the body;
- previously taken treatment measures;
- diet;
- recent travels with a pet;
- the presence of other chronic diseases.
All this will allow the veterinarian to form an anamnesis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Distinctive features of pododermatitis
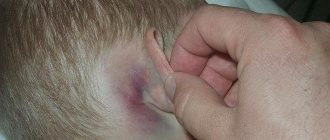
Pododermatitis on a dog's paw.
Pododermatitis is detected on the paws or pads of dogs.
The main provoking factors include fungal and bacterial infections, allergies. The first symptoms that caring owners pay attention to are:
- Constant, extremely thorough licking of paws. The limbs look wet and the skin is red and moist.
- The appearance of wounds around the pads, between the fingers.
- Bloody blisters on the extremities.
- Swelling of the affected limb.
- Pain occurs when walking.
The dog begins to limp, it is hard for her to stand on her damaged paw. - The addition of a bacterial infection manifests itself in the form of pustules and abscesses.
Treatment
If the lesions on the extremities are few in number, they can be treated and the wounds can be expected to heal. In this case, you don’t need to use medications; it will be enough to treat the damaged areas with chlorhexidine or any bactericidal drug.
In winter, you can purchase special shoes for your dog.
- When dermatitis has affected a large part of the skin, they begin to fight the main disease, while prescribing antibiotic therapy is a justified step.
The course of treatment is long, until the symptoms completely disappear, and then another 14 days to consolidate the results. - Pododermatitis often occurs due to contact with allergenic substances. For example, during ice storms, a special anti-icing consistency is used to sprinkle icy roads. Specifically, it will negatively affect dog skin. To protect your pet from problems in the winter, you can buy him special walking boots.
- In advanced cases or in situations where wounds appear due to incorrect paw placement, surgery may be prescribed.
- To relieve itching, use anti-allergenic agents and herbal lotions.
- A balanced diet and the use of immunomodulators will help restore immunity and overcome the disease.
Causes
According to experts, the following infections most often provoke pododermatitis in dogs:
- Proteus;
- staphylococcus;
- streptococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- cryptococcosis;
- blastomycosis.
In addition, many pathogenic fungal infections cause pododermatitis.
The autoimmune form occurs against the background of:
- vasculitis;
- erythema;
- lupus erythematosus;
- epidermal necrolysis.
A rather rare type of pathology is plasmacytic pododermatitis, however, it most often affects cats.
Hormonal reasons are as follows:
- Cushing's disease (hypercortisolism);
- hypothyroidism
Dysfunctional liver disorders also lead to pododermatitis.
Of the oncological diseases, the pathology in question is caused by:
- exocrine adenocarcinoma;
- melanoma;
- inverted papilloma.
External negative factors are mainly limited to contact with chemicals used in winter to destroy ice. In addition, jogging on asphalt is also harmful to dog paws.
Signs
Symptoms differ depending on the etymology. The infectious form is accompanied by:
- redness;
- swelling;
- inflammation;
- papules;
- ulcerations;
- ulcers.
In advanced forms, baldness of the legs is noted.
Allergic pododermatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling;
- redness (without local increase in temperature);
- severe itching.
The autoimmune form is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers on the entire surface of the paws.
Hormonal pododermatitis manifests itself in the same way as infectious ones.
What do you prefer to feed your pets?
Diseases What is pododermatitis in dogs and how to cure it
A disease of a secondary type, pododermatitis in dogs, is a consequence of deep bacterial contamination of the skin on the paws with the development of pyoderma or purulent inflammation. Almost always, allergies, demodicosis, hypothyroidism or autoimmune pathologies are diagnosed simultaneously with pododermatitis.
Without treatment, the disease may develop complications, the consequences of which can never be restored.
Another name for pododermatitis is interdigital pyoderma; easily excitable dogs with “fine mental organization”, dachshunds, sharpeis, bulldogs, Great Danes, and boxers are prone to it. Pododermatitis is often diagnosed in Labrador retrievers as a result of compulsive licking between the toes of the front paws.
The inflammatory process affects places on the paws that are in more contact with the ground (snow, asphalt) - the pads. Redder spots appear on them and between the fingers, which gradually grow in width, covering areas of healthy skin.
In dogs living in the city, cases of pododermatitis increase in winter due to contact with snow sprinkled with reagents.
A weakened immune system provokes the development of opportunistic microflora that is constantly present on the skin (Malassezia), but for most of the dog’s life it is in “sleeping mode.”
If the skin is affected only in a few places, the disease proceeds well and even treatment at home is possible.
List of typical reasons:
- Injuries. There are many factors that can lead to damage - stone impact, high or low temperatures, etc.
- Foreign bodies. The seeds of some types of herbs penetrate the surface layers of the skin, causing an inflammatory process. Thorns and wood chips are also dangerous.
- Tumors. In dogs after 5-6 years of age, pododermatitis develops due to the development of tumor-like processes, in particular squamous cell carcinoma, plasmacytoma, etc.
Extensive and severe lesions with bacterial pododermatitis in dogs can develop against the background of other diseases:
- Hookworms, ticks, fleas, lice eaters.
- Dermatophytosis or fungus.
- Food allergy, the body's reaction to one or more components in the diet.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system. More often, symptoms of pododermatitis accompany low levels of thyroid hormones, Cushing's syndrome, or excess production of adrenal hormones.
- Malfunctions of the immune system.
Pododermatitis often develops when a dog accidentally comes into contact with strong chemicals. Individual skin reactions to detergents for animals or hygiene products for humans are possible.
This is why veterinarians do not recommend using soap or human shampoos to wash pets.
How to treat
If the lesions are isolated, then it is usually not difficult to cope with them with the help of antiseptic drugs.
- Chlorhexidine;
- Streptocide ointment;
- Tetracycline.
Antibiotics are not prescribed if there is mild interdigital pododermatitis. Paws should be washed regularly with warm water and soap.
Multiple lesions require a different approach. First of all, it is necessary to begin treatment of the underlying disease. Here antibacterial therapy is advisable. Moreover, the drugs are taken until all symptoms disappear and for another 14 days after that. It is mandatory to clean the skin between the fingers several times a day.
It will take a lot of time to cure a dog. It is worth understanding that sometimes there is a risk of relapse. As a rule, the progression of the disease occurs more often in winter due to the fact that the paws remain wet for a long time, which creates an ideal environment for microbes.
At home, veterinarians advise applying compresses of antiseptic herbal mixtures to sore paws - this helps relieve itching and pain.
Prevention
- your pet’s claws must be trimmed regularly (long ones can injure surrounding soft tissues when walking);
- remove hair growing directly between the toes with scissors;
- carry out systematic sanitary treatment in the enclosure or booth;
- all dishes from which the pet eats and drinks must be washed daily;
- After a walk, paws should be rinsed with warm water and wiped dry.
Four-legged pets are eternal children who love fresh air and active games. Space and movement are necessary for all breeds, from small to large, as this ensures the physical and psychological health of the animal. One of the significant obstacles to the correct rhythm of life can be pododermatitis in dogs.
Most often, the skin disease manifests itself in cold conditions with high humidity. This is the end of autumn, winter and beginning of spring, which is characterized by snow and slush, which directly affects the dog's paws. Under the influence of dampness, pododermatitis occurs, covering the areas of the pads and the places between the fingers.
The main danger of the disease is that it is a secondary infection and often indicates the presence of a more serious illness. Thus, inflammatory and necrotic processes in the tissues of the paws can develop against the background of:
In addition, the causes of the development of dermatitis can be mechanical damage caused by excessive walking on paved areas, as well as foreign bodies. Cracks and injuries to the pads, combined with dampness and unsanitary conditions in the environment, are ideal conditions for the development of a fungal form of the disease, as well as damage by staphylococcus, streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other infectious pathogens. They are the ones that cause bactericidal pododermatitis in dogs, which is diagnosed in most cases.
It is also interesting that sometimes the dogs themselves are the culprits of skin diseases. Active animals with a high level of nervous system excitability sometimes have the bad habit of constantly licking their paws. Thus, they provoke irritation and, consequently, dermatitis.
After the diagnostic results determine the cause and methods of combating the disease, in most cases, treatment of pododermatitis at home is allowed. However, this disease can torment a pet for a long time, since recovery requires eliminating the original source of the disease. For example, inflammation caused by allergies will disappear safely if you follow the diet prescribed by your doctor and also avoid contact with irritants.
The treatment complex includes external treatment of the affected tissues with bactericidal and antiseptic drugs based on sulfonamide and tetracycline.
For mild forms of the disease, the use of chlorhexidine is effective. Fans of natural medicine can supplement their therapy with herbal compresses that have an anti-inflammatory effect. However, this approach requires the approval of a specialist.
Pododermatitis is often detected in dogs. The disease occurs against the background of other pathologies and has predisposing factors. Pododermatitis requires complex treatment; if you suspect this disease, you need to show your pet to a veterinarian! Research is carried out to confirm the diagnosis. The doctor collects anamnesis and performs differential diagnostics.
Pododermatitis on the paws of dogs: symptoms and treatment | at home
Pododermatitis in dogs is a fairly common occurrence. It is better to entrust its treatment to a specialist, since inflammation in dogs’ paws indicates the development of some disease or disruption of various processes in the body.
That is, pododermatitis is a secondary manifestation of some pathology. Its treatment can be done at home, however, a veterinarian's consultation is required first.
The doctor must determine the true cause of pododermatitis in the dog in order to prescribe adequate therapy.
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 Treatment
- 5 Prevention
Causes
Pododermatitis is an inflammation of the outer tissue of the limbs. It can be infectious (the penetration of a bacterial infection) or aseptic (mechanical damage) in nature. The pathology causes significant discomfort to the dog and can cause lameness. In advanced forms, inflammation spreads to other tissues.
The disease occurs in areas of the limbs that come into contact with the ground. Basically, localization is noted on the paws in the space between the toes and on the pads. Also, the inflammatory process can spread to the nail bed, which in the future leads to loss of the claw.
Pododermatitis itself is not an independent disease. It develops against the background of certain pathologies that lead to a decrease in the body’s protective functions - weaken the immune system. Provoking factors may be:
- immunological disorders (thrombocytopenia, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- fungal skin infection (mycosis);
- the presence of parasites (helminths, ticks, fleas, etc.);
- contact with an allergen;
- endocrine disorders and metabolic diseases (hypo- and hyperthyroidism, hypercortisolism, diabetes mellitus);
- oncological pathologies (negatively affecting the entire body, regardless of the location of the primary focus, blocking the functioning of the immune system).
In addition to internal pathologies, pododermatitis can develop against the background of mechanical damage to the skin:
- with injury to the paw pad;
- with prolonged contact of the paws with a rough surface (for example, asphalt), which causes irritation and cracks in the pads;
- when the paw is injured by a sharp or prickly object.
There is also a genetic predisposition to pododermatitis. This pathology is most often observed in dogs of the following breeds:
- Labrador;
- Doberman;
- Dalmatian;
- Shar Pei;
- dachshund.
Characteristics of the disease, clinical picture
Pododermatitis (not to be confused with dermatitis) affects the quality of life. The disease leads to inflammation of the paws; the pads and nearby skin are involved in the pathological process. Bacterial pododermatitis is common and occurs when microbes enter the body. The second name for pododermatitis is pyoderma. How to recognize the disease?
It is worth paying attention to how your pet behaves. With pododermatitis, he begins to intensively clean his paws.
- You need to look at the pads; as the disease develops, they are red and wet.
- The disease manifests itself as sores on the pads.
- Vesicles filled with blood form on the paws.
- A characteristic symptom is swelling of the paws.
- With pododermatitis, the animal limps.
The disease can manifest itself as purulent processes; it develops under the influence of certain factors.
Causes and predisposing factors
If your dog has signs of fungal or bacterial diseases, pododermatitis is possible. Allergic pododermatitis is common, it requires special treatment, and it is important to eliminate the source of the allergy. Pets are also affected by fungal pododermatitis.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a cytological diagnosis. Doctors identify or deny purulent reactions. A smear is examined. The severity of the disease is determined. Some dogs have limited skin lesions, while others have extensive skin lesions. Differential diagnosis allows you to distinguish pathology from others, such as demodicosis. It is equally important to differentiate pathology from fungal infections. Pododermatitis in dogs is divided into 2 types.
Aseptic occurs due to the fact that the pet injures its paws. The disease is associated with skin damage. To avoid aseptic pyodermatitis, you need to monitor your quadruped. Do not let him go to places where there is garbage, fragments, or sharp objects. Aseptic disease leads to lameness. The animal is limping because it feels pain when walking. Some dogs develop a fever. Before treating pododermatitis in dogs, you need to clean the pads. If the breeder suspects this disease in a pet, it is worth contacting a veterinarian. Novocain can be used to cleanse paws.
Purulent pododermatitis is divided into deep and superficial. If a dog is diagnosed with this disease, it means that the tissue structures are damaged. In this case, the pet limps. Purulent pododermatitis is more dangerous, since purulent pathogens penetrate under the skin. As the disease progresses, the dog limps and the temperature rises.
How is therapy carried out?
The veterinarian determines the cause and extent of the disease. Antiseptics and antibacterial agents are prescribed for treatment. To avoid the development of an infectious process, you need to maintain hygiene. The paws should be cleaned of dirt, dust, and foreign particles. The pads need to be washed. It is necessary to treat the pathology that is the root cause. Antibacterial medications are taken until the illness subsides.
Complex therapy includes antibiotics. Treatment of pododermatitis in dogs at home should be long-term. The pathology can worsen and often recurs in the spring. If pyodermatitis progresses to severe stages, surgery is prescribed. Surgery is necessary if the disease poses a threat to health. The areas of inflammation are opened, and purulent foci are removed. To improve the condition of the skin, you need to use herbal lotions; they help overcome itching.
If the pathology is associated with food allergies, it must be included in special foods; they must contain hypoallergenic products. Before purchasing, you should consult your doctor! If you use the food for 2.5 months, the body will adapt to the therapeutic diet and forget about the allergen. Feeds are used in addition to the main therapy; they improve skin condition, promote hair growth, and reduce swelling and itching. Proper therapy can help your pet get rid of lameness.
Treatment of allergic pododermatitis is not complete without diet. If the breeder refuses to use feed, it is necessary to include hypoallergenic products in the diet. The dog should be protected from contact with cosmetics, household chemicals, pollen, and fur of other animals. Treatment must be comprehensive. The doctor may prescribe combination therapy using antihistamines and antibacterial agents. Medicines are recommended to prevent mycosis. Treatment is individual, in each case the doctor selects the optimal tactics.
The autoimmune form of the disease can be confused with an allergic one. Autoimmune pododermatitis affects the quality of life and is severe. In some dogs, the disease lasts 10 years and can lead to myositis. Not only young, but also older pets are prone to pathology. Pyodermatitis manifests itself as lameness and pain in the pads.
Therapy for autoimmune pododermatitis
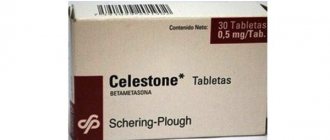
If the animal is overweight and large areas of skin are affected, the prognosis is disappointing. Autoimmune dermatitis must be identified and treated as soon as possible. To treat this type of disease, Dexafort injections are prescribed; they eliminate inflammatory reactions. Dexafort acts instantly, the animal feels relief in the first hours. Dexafort is a hormonal medicine, it is used with the permission of a doctor. The drug helps eliminate inflammatory and allergic reactions, and also relieves swelling.
The effect of Dexafort lasts an hour, the maximum duration is 5 days. One injection is enough for 7 days. The treatment of autoimmune pododermatitis requires complex therapy. Dexafort can be prescribed if emergency assistance is required. The drug is not used for a long time. Dosages and frequency of use vary. To treat autoimmune pododermatitis, hormonal agents are needed. If the symptoms of the pathology have been eliminated, the doctor prescribes hormones.
Treatment is not complete without Prednisolone. The medicine in tablets eliminates inflammation and relieves swelling. It is important to treat fistulas; autoimmune pododermatitis can lead to such ailments! It is necessary to treat the paws in a timely manner, otherwise the disease will cause complications. To eliminate the fistula, the doctor uses hydrogen peroxide, the drug "Levomekol". Medicines are administered intramuscularly, they help remove dead cells.
Pododermatitis in dogs
When taking a dog into your home, you need to be prepared for a lot of hassle, both pleasant and not so pleasant. Like people, animals are susceptible to many diseases, but unlike a person who can clearly describe how they are feeling, a dog will suffer in silence.
Pododermatitis is a fairly common disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the interdigital space and on the pads of a dog’s paws. Severe pain that occurs when moving forces the animal to move less. An attentive and responsible owner will easily identify changes in his dog's behavior and immediately take him to the veterinarian.
Symptoms of pododermatitis in dogs
Depending on the cause that provoked pododermatitis, the symptoms of the disease will vary significantly, but there are also general signs of the disease that are characteristic of all forms of pododermatitis:
- The dog's limbs swell and become swollen.
- The animal begins to limp, and if the disease is particularly severe, the dog may completely lose motor function.
- The pet constantly licks its paws and looks restless.
- In the space between the toes and on the pads of the paws, the skin, as a rule, becomes very red, inflamed, and the animal feels sore. The formation of fistulas, wounds, and abscesses often occurs.
The development of pododermatitis due to fungus or bacterial microflora is accompanied by redness, inflammation and swelling of the areas between the toes and paw pads. Often ulcers and ulcers form on the affected areas. Local body temperature rises.
Allergies that appear after contact with various reagents cause symptoms of pododermatitis such as:
- redness and inflammation of the skin;
- very severe itching on the paws, fingers can hardly be distinguished due to scratching (the skin is so torn);
- baldness of the paws (hair rapidly thins and falls out).
General allergies have similar symptoms to contact allergies, but the affected areas are concentrated not only on the dog’s limbs, but also on other parts of the animal’s body (the muzzle most often suffers).
Pododermatitis, which appears against the background of autoimmune diseases, is more difficult to diagnose than all other forms of the disease. To identify this type of dermatitis, you will need to undergo many tests. The symptoms are similar to allergic pododermatitis, but there are still some differences: the skin of the paw pads becomes very thick and darkens.
The endocrine factor of pododermatitis is manifested by severe redness and inflammation of the skin in the interdigital space.
Pododermatitis of an oncological nature is considered the most dangerous and is characterized by the appearance of various neoplasms, growths and ulcers on the pet’s body.
Find out also about other skin diseases in dogs >>>
Treatment of pododermatitis in dogs
Treatment methods directly depend on the cause of the disease. There are no general treatment tactics; treatment is selected individually for each sick animal.
The following methods are mainly prescribed:
- use of antimicrobial drugs;
- use of antifungal agents;
- antihistamine therapy;
- treating affected skin with antiseptics;
- lifelong use of certain medications;
- special diet;
- surgical intervention.
The veterinarian prescribes treatment depending on the type of pododermatitis identified in the sick dog:
- The aseptic appearance is characterized by persistent inflammation and severe pain. Tissue damage is usually not accompanied by a purulent process. Treatment at home is aimed at daily treatment of wounds with antiseptic agents.
- The purulent form of pododermatitis occurs with the addition of a purulent infection. The symptoms of purulent dermatitis are so vivid (severe pain, high temperature) that there is no doubt about the diagnosis. This form of the disease should be treated only with antimicrobial drugs. In particularly severe cases, surgery is prescribed to remove the affected tissue.
Treatment of pododermatitis is very long, but even after a positive outcome of therapy, relapses of the disease are often observed (especially in winter and autumn).
Preventive measures
You need to keep an eye on your pet. After a walk, the paws should be washed and disinfected, and the hair between the toes should be trimmed.
- You need to watch what your dog eats. Nutrition should be complete and balanced.
- If your four-legged animal is kept in a kennel, you should clean it regularly.
- It is important to pay attention to any changes in behavior and, if necessary, take your pet to the clinic.
- If the cause of the disease is an allergen, it should be eliminated.
The therapy must be correct. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor, but dosages should not be exceeded. If your pet has an allergy, you should inform your veterinarian.