What is a milk allergy?
A common reason for visiting pediatricians lately is a child’s milk allergy. Most often, allergies are caused by cow's milk, less often by goat's or sheep's milk. Children do not have allergies to mother's milk, which means that if a fully breastfed child shows signs of an allergy, we can confidently say that the nursing mother is eating allergenic foods.
Why does milk allergy occur?
Milk contains several types of protein molecules, and any of them can cause sensitization in the baby’s body, followed by the formation of antibodies and the development of type 1 allergies. It is interesting that in milk from different animals, even proteins of the same type will have their own amino acid composition, and this is good, since the so-called cross-allergy to milk from different animals is not observed. That is, a child with an allergy to cow's milk can tolerate goat's or sheep's milk well.
In cow's milk, the main allergenic protein is casein. This protein has rather large molecules that are difficult to break down under the influence of enzymes produced by the baby’s intestines. So many casein molecules in a semi-split form can be absorbed into the blood, where they are recognized by immune cells as foreign, from which they need to be protected.
Sometimes milk allergies are caused by various chemicals, such as antibiotics, that get into the milk of pets receiving any treatment. If manifestations of allergies are observed when feeding the baby not only with whole cow's milk, but also with adapted milk formulas, there is no doubt that it was the milk protein that caused the allergy.
Allergy to cow's milk
Allergy to cow's protein is one of the most common allergies in infants; on average, allergy to cow's milk occurs in 5% of children. A distinction must be made between cow protein allergy and cow protein intolerance. A milk allergy occurs because the immune system views cow protein as foreign and turns on the body's defenses, and the cause of cow protein intolerance is a problem with digesting milk.
In most cases, a milk allergy does not pose a threat to life and health, but can cause a lot of inconvenience for both the baby and the parents. In about half of the cases, a milk allergy occurs in the first year of a baby’s life, and most often goes away by the age of 3-5, but sometimes the allergy can remain for life.
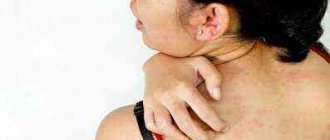
The manifestations of milk allergy are very diverse, ranging from rashes on the face to digestive disorders, but most often the allergy symptoms appear in a complex. 50% of babies experience skin rashes: urticaria, peeling, atopic dermatitis, facial swelling. In the other 50% of cases, intestinal disorders occur: regurgitation, intestinal colic, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Children may also experience rhinitis, cough, and difficulty breathing. The first signs of an allergy appear a few weeks after the introduction of cow's milk or an adapted milk formula to the baby's menu. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between lactase deficiency and allergies, but there are cases of a combination of these diseases.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a thorough examination by a pediatrician is necessary.
The diagnosis should be made on the basis of a complete medical history: an assessment of the child's allergy symptoms, the presence of allergies in the parents, the presence of concomitant diseases, poor weight gain.
After collecting an anamnesis, the doctor prescribes allergy tests to detect immunoglobulin E to cow protein in the blood.
One of the diagnostic stages is the exclusion of cow protein from the child’s diet. A provocative test is sometimes required to make an accurate diagnosis. It should only be carried out under the close supervision of medical personnel.
The development of an allergic reaction to cow's milk protein must be differentiated from lactose intolerance, a disease in which a deficiency of a special lactase enzyme is detected or its production is reduced.
Lactase is involved in the breakdown of milk sugar into glucose and galactose; in the absence of this, digestive disorders appear, the child does not gain weight well, and in severe cases is delayed in development.
This disease is successfully treated with drugs designed specifically to break down lactose, for example the drug Lactazar.
Comparison of cow's milk and human milk
The energy value of human and cow's milk is the same - about 100 kilocalories per 100 grams, but there are differences in composition. Human milk is composed of 60 percent whey proteins, mostly lactalbumin, and 40 percent casein. Cow's milk has more proteins, providing 20 percent of energy, compared to human milk proteins, which provide only about 7 percent of energy. For this reason, it is not recommended to give cow's milk unchanged to children under 1 year of age. Lactalbumin from human milk forms a soft curd in the baby’s stomach, which is easily digestible, while casein from cow’s milk forms a rough, viscous mixture that is quite difficult to digest.
Diet for cow's milk allergy
The characteristic symptoms of a milk protein allergy can be eliminated through diet by eliminating milk protein from the child's diet.
Allergy to cow's milk is one of the most common, especially in children. If you have such an allergy, you will need to exclude from the diet all products that contain milk or are prepared on its basis. Often, people who are allergic to cow's milk tolerate goat's milk normally, which allows them to slightly expand their diet.
Prohibited for use:
– any soups prepared using milk;
– cheese (including homemade), sausages containing milk, fish, poultry, egg dishes and egg substitutes, sometimes beef;
– mashed potatoes prepared with milk;
- Pasta with cheese;
– bakery products prepared with the addition of milk: donuts, cookies, cakes, pancakes, pancakes, waffles, pies, crackers;
– porridge with milk, as well as cereals with a high protein content;
– butter, cream, sour cream, cottage cheese (some patients tolerate cottage cheese in moderate quantities);
– mayonnaise and margarine containing milk;
– yoghurts and curd cheeses;
– condensed milk with or without sugar, powdered milk, cocoa with milk;
– milkshakes, alcoholic drinks with added cream;
- milk chocolate;
– products cooked in butter;
– products prepared in breading (in breadcrumbs);
– for children – artificial formulas prepared on the basis of milk; Some children cannot tolerate kefir and cottage cheese; others can be given these products, but in moderation.
It should be remembered that milk contains: butter, margarine, cottage cheese, cheese, sour cream, dry and condensed milk, ice cream and many ready-made confectionery products. Milk also includes names: whey, lactose, casein, casein hydrolysate, which can be read in the composition of products. Before buying a product, be sure to ask the seller how it was prepared and what is included in it, or read the label carefully. If the label does not indicate the composition of the product, then it is better not to take it.
Allowed for use:
– broths and decoctions seasoned with foods included in the diet;
– products with a high protein content – meat of all types, fish, poultry, ham, kidneys, liver, sausages and canned meats that do not contain milk and its components;
– eggs, nuts and legumes;
– any vegetables and fruits;
– bakery products: French, Italian and Viennese rolls and other types of wheat bread that do not contain milk and its components (most types of bread contain milk), rye bread;
– cereal dishes: cereals and casseroles from cereals and pasta that do not contain butter, milk and its components;
– drinks: water, weak tea, carbonated drinks, any fruit and vegetable juices without milk or cream.
Yuri Konstantinov, “Allergy. Traditional methods of treatment."
Products prohibited for protein intolerance:
- milk and dairy products;
- bread;
- butter;
- mayonnaise;
- beef, veal;
- chicken egg white;
- mushrooms;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- smoked and sea fish, crustaceans;
- nuts;
- citrus;
- tomatoes, pickled cucumbers, cabbage and others.
Protein intolerance occurs mainly in infants. It usually disappears in the second year of life. However, it happens that it remains for longer, even for life.
Remember that you can live normally food allergies The most important thing is to follow an appropriate diet that excludes foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
How to increase the protein content in cow's milk
- increasing the volume of feed;
- variety of diet;
- proper quality of feed;
- energy intensity of the diet;
- a reasonable balance of vitamins, salts, fiber and protein.
The volume of feed should be increased from the beginning of the lactation period in order to eliminate the lack of energy in the animal. At this time, the cow, which is highly productive, spends over 300 g of protein from the accumulated resources of the body. Adequate energy restores the cow's body weight, which helps stabilize milk protein levels within normal limits. The increased volume of feed will increase the protein content in cows' milk by 0.3% of the norm.
A varied diet ensures the most effective synthesis of milk components by maintaining a reasonable balance between feed containing coarse and juicy fibers and concentrates. Concentrates are responsible for delivering pectin, starch and sugar to the cow’s body. The share of these easily digestible carbohydrates ranges from 20 to 45% of the total dry matter mass.
The quality of concentrates and a balanced diet increases the fat content and protein level in milk. At the same time, excess feeding reduces the fat content of milk by 0.1% or more of the norm, and increases the normative level of protein by 0.2–0.3%.
It has a very significant effect on the quality of milk and the quality of grain mass. It is known that corn flakes increase the proportion of protein in milk, and oat flakes reduce its level by 0.2% of the norm. High-quality grain mass obtained by steaming, pressing, granulating or crushing helps to increase the proportion of protein in milk.
To maintain the quality of milk in terms of protein, it is necessary to ensure a reasonable protein balance (digestible and crude protein). Attention should also be paid to the depth of protein breakdown in the rumen, which depends on the composition of the feed. Increasing the proportion of crude protein in them increases productivity, but does not have any effect on the protein level in milk. At the same time, its deficiency leads to a sharp decrease in protein levels.
It is known for certain that when the proportion of crude protein in feed is reduced from 17 to 9%, with each reduced percentage the protein level in milk decreases by 0.02% of the norm.
The proportion of digestible protein in the diet should not be less than 65% of raw protein. When it decreases, the productivity and protein content in the milk of cows is significantly reduced. However, an excess of fed proteins negatively affects the synthesis in the rumen. And reducing the amount of acetic acid produced reduces the fat level in milk. Prolonged oversaturation with protein entails the risk of poisoning, the development of rumen atony and possible problems with the placenta.
The introduction of protected proteins into feed in a proportion of 35–38% of the total protein mass, as well as amino acids, significantly increases the protein content in cows’ milk. Such proteins bypass the rumen and disintegrate in the abomasum. At the same time, the flowing blood and duodenum are saturated with amino acids, which has a positive effect on protein synthesis in the mammary gland.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
The quality of milk directly depends on the presence of roughage and succulent feed in the diet. They contain a considerable amount of fiber, which stimulates the functioning of the salivary glands and the contraction of the rumen. The ratio of such feeds should not be less than 50–40% of dry matter. If the proportion of fiber in such feeds exceeds 25%, this can lead to a decrease in the protein content in milk.
The quality of milk directly depends on the size of the feed particles, which should not be less than 1 cm. Smaller fractions increase the protein level by 0.2–0.3% of the norm, but significantly reduce the fat content of the milk.
1. To increase milk yield:
- by 243 kg (4.3%) per dry cow;
- by 385 kg (6.8%) for lactating.
2. To increase fat content:
- by 9.8 kg (4.5%) per dry cow;
- by 14.1 kg (6.4%) for lactating women.
3. To increase protein:
- by 8.4 kg (4.8%) per dry cow;
- by 13.5 kg (7.7%) for lactating women.
The quality of milk directly depends on comfortable conditions and proper maintenance of cows. Thus, in summer, a decrease in the fat content in milk is associated with high humidity in the barn and an increase in atmospheric temperature. We should not forget that a comfortable temperature in a barn is 5... 15 ° C, and humidity is no more than 75%.
Systematic walks have a significant impact on the cow's condition. Winter exercise and summer free grazing of cows determine the stable quality characteristics of milk.
The fat content of milk per milking can be increased by milking the first streams into a separate container. The fat content of such milk is no more than 1%. Subsequently, the proportion of fat increases, reaching its peak (10% or more) by the end of milking. Therefore, the cow should be milked completely, while massaging her udder. We should not forget that the milk of young cows is fattier than the milk of old ones.
From all of the above, it follows that the protein content in cows’ milk directly depends on the genetic potential, condition and performance of the animal, stage of lactation, number of calvings, time of year, quality of feed and feeding intensity.
Properties of milk
The quality of milk is determined by its physical and chemical properties.
- In appearance, color. The liquid should be homogeneous and opaque. Whole milk has a white, pale cream color. The low-fat drink has a blue tint.
- Fresh milk has a sweetish taste. The higher the fat content of the drink, the more tender it is.
- The healthy drink has a specific milky taste.
- The naturalness of the product is determined based on density indicators using a hydrometer. If the density index is less than 1.027, it means the product is diluted with water or obtained from a sick animal.
- The freshness of milk is determined by its acidity. The fresh product has an acidity of 16-18 degrees on the Turner scale. The longer a product is stored, the greater its acidity becomes - this is affected by the action of milk microorganisms.
Is milk healthy? Disputes about the benefits and harms of milk still lean towards the usefulness of the product. The main beneficial properties of milk are due to the content of a large and varied amount of valuable nutritional components that a person needs throughout his life.
The Myth of Protein Supplements
In modern society, a healthy person does not need protein supplements. The amino acids from the proteins contained in these supplements are no different from the proteins consumed in food. Eating excessive amounts of protein to promote muscle growth is a myth. In order for muscles to grow, you need physical stimulation and a sufficient amount of protein. Any nutritional component (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) consumed in excess of what is necessary will be deposited in the body as fat mass. The extra amino acids simply make the kidneys work harder.
Harm of milk protein
First of all, it consists of an excess of a substance in the human body. We should receive a maximum of 40 g of milk protein per day from food. At the same time, the largest amount of digested protein is somewhat different: 100 - 120 g. If this value is significantly exceeded, you can “earn” real protein poisoning with all the ensuing consequences. Ketone bodies (namely, they, being products of the breakdown of milk protein, act on the body as poison) have a negative effect, first of all, on the main cleansing organ - the liver. However, in the future, signs of disturbances and failures of functions will make themselves felt in other segments of a wide variety of organ systems. How do you know if you have been poisoned? There are certain symptoms: excessive gas formation in the intestines, acetone taste and bad breath.
Another important nuance: whey protein intolerance. People suffering from this disease, after consuming fermented milk products, experience unpleasant sensations such as intestinal colic, flatulence, and indigestion. Experts suggest that milk protein intolerance is associated with that of milk sugar.
When Protein Supplements Are Necessary
Some diseases, infections, injuries, burns and surgeries put the body in a state of “hypermetabolism.” In this condition, nutritional supplements are usually needed because the body does not get enough nutrients from food. Protein supplements will also be necessary for vegetarians participating in competitive sports and weightlifting training, as well as pregnant women in the third trimester. In any case, the need for supplements is purely individual and determined by the needs of a particular organism.
Photo: Mowie Kay
Recipes for a dairy-free diet
A nursing mother deserves the best - including a diet based on fresh, natural products. Do not allow chemical components into the body - nitrates, preservatives, thickeners; carefully read the ingredients on labels, carefully select products on market stalls. Vegetables grown in your own beds or in the fields of reputable farms are the best option for the kitchen while breastfeeding.
And don’t forget to include in your daily menu a substitute for milk – products with calcium.
Vegetable soup
To prepare a light tasty soup, take:
- water - 1.2 l;
- peeled potatoes - 5 pieces;
- carrots - 1 medium-sized root vegetable;
- egg - 1 piece;
- frozen spinach - 200 g;
- butter - 20 g;
- salt to taste.
Let's prepare it like this:
- We cut potatoes and carrots, put them in a pan with water, and put them on fire.
- Melt butter in a preheated frying pan; Add the spinach, simmer until defrosted, then add the spinach to the soup.
- Cook the vegetables until done.
- Beat the egg with a fork, then pour it into the pan with the soup in a thin stream; stir the soup.
- Salt the dish and turn off the heat.
If desired, sprinkle the vegetable soup with finely chopped herbs on top (parsley and dill contain calcium).
A good first course option for a dairy-free diet is vegetable soup with spinach.
Baked chicken fillet
This dish “harmonizes” with a side dish of boiled rice or buckwheat. To cook meat you will need:
- chicken fillet - 0.8 kg;
- onion - 1 head;
- low-fat sour cream - 2 tbsp. l.;
- chopped dill and parsley - 2-3 tbsp. l.;
- salt and pepper to taste.
Sour cream is a dairy product, and although there is not much of it in the dish, eat a small portion for the first time and monitor the baby’s reaction. If negative consequences appear, then bake the meat without sour cream.
Procedure:
- We wash the meat and cut it into pieces; salt on both sides and place on a sheet of foil.
- Grease each piece of chicken with sour cream.
- Finely chop the onion (or you can use thin rings) and place it on pieces of meat; Sprinkle with chopped herbs and pepper on top.
- Wrap the chicken in foil; Preheat the oven to 200°C and place the meat in it. Bake for 30 minutes.
Instead of chicken, you can take turkey - cook the same way, just bake for 50 minutes. A second meat course with a side dish will wonderfully complement a salad with fresh vegetables.
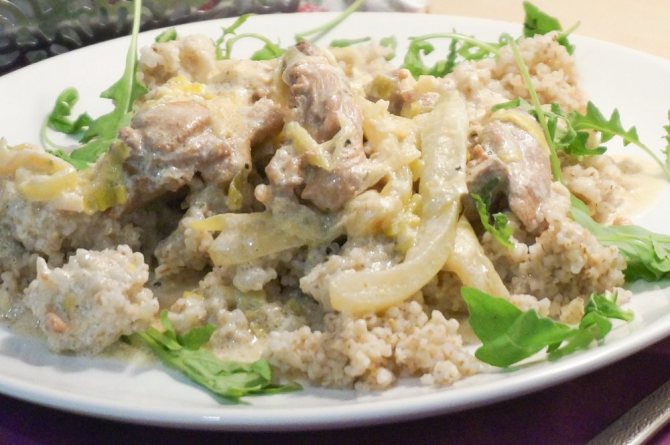

Baked turkey with sour cream is a hearty and healthy dish; Turkey meat is a dietary product and is also hypoallergenic
Vegetable stew
Summer vegetables are tasty, healthy and quick to prepare. For the stew you will need:
- eggplant - 1 piece;
- zucchini - 1 piece;
- potatoes - 2 pieces;
- carrots - 1 piece;
- green bell pepper - 1 piece;
- vegetable oil - 2 tbsp. l.;
- green onions;
- salt to taste.
Cooking method:
- Cut the eggplant and zucchini into cubes, and the pepper into thin slices. We also cut the carrots into small cubes or grate them.
- Simmer the vegetables over low heat without adding oil for 10 minutes.
- Cut the peeled potatoes into strips and add to the rest of the vegetables.
- Drizzle vegetables with vegetable oil and simmer until tender.
- 5-7 minutes before removing from heat, sprinkle the stew with finely chopped onion and salt.
A clove of garlic, crushed into vegetables along with onions, will fill the dish with a magical aroma; It’s a pity, the spicy vegetable spoils the taste of breast milk. However, in small quantities and in stewed form, the effect will be reduced to a minimum, so try it - perhaps the baby will not feel that you have eaten garlic.
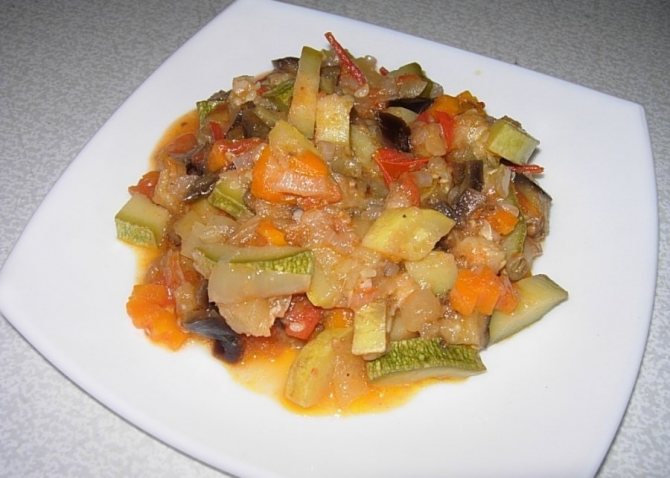

When stewing, vegetables lose some of their vitamins and minerals, but the remaining ones are well absorbed by the body.
Oatmeal with dried fruits
This dish is good to start the day with - it will invigorate you, fill you with vitamins, and improve your mood. Required:
- 1 cup of oat flakes No. 2 - those produced using the technology of preserving bran and germ of the grain; rich in dietary fiber, quick to prepare;
- 2 glasses of water;
- dried apricots;
- prunes.
Procedure:
- Soak dried fruits overnight. In the morning, cut into small pieces.
- Pour water into a saucepan and put it on fire; add oatmeal and dried apricots with prunes.
- Cook over low heat for 10 minutes; stir so that no lumps form.
- Turn off the heat and leave the porridge covered for 15 minutes.
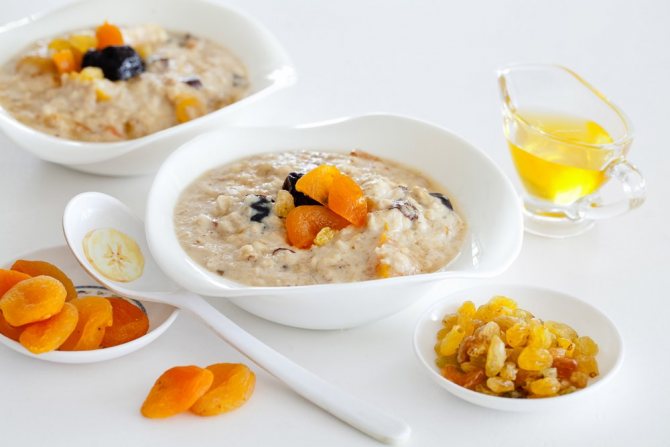

Dried fruits, which are an excellent substitute for sugar, will help improve the bland taste of porridge with water.
Fruit dessert
Suitable for nursing mothers who are not prohibited from fermented milk products. Let's take:
- 1 banana;
- 2 peaches;
- 150 g pineapple;
- 2 tbsp. l. muesli;
- 2 tbsp. l. low-fat yogurt;
- 1 tsp. lemon juice.
Cooking:
- Wash the fruit and cut into cubes.
- Add muesli to the mixture and stir.
- Season the salad with yogurt and lemon juice.
During breastfeeding, it is undesirable to eat exotic fruits; they cause allergies in the baby. Therefore, pineapple can be replaced with a pear or apple.
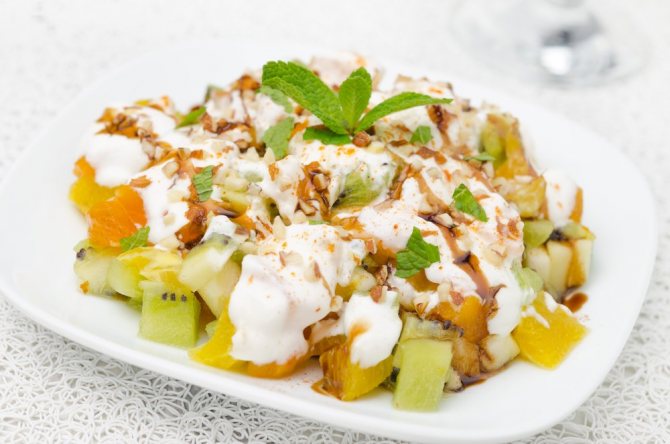

Fresh fruit salad is an excellent dessert for a nursing mother, but you should choose ingredients with an eye on possible allergies in the baby
Varieties of milk protein
Milk consists of two types of the substance we are interested in: casein or calcium caseinate, which occupies the lion's share of the product (up to 87% of a hundred-gram serving of the drink), and 13-18% of whey proteins - globulin and albumin. Each of the listed components has its own characteristics.
Calcium caseinate - unlike other types of animal protein, it is difficult to digest and digest. The human body will need to expend enough energy to carry out these processes. On the one hand, this is a noticeable disadvantage, but there are also positive aspects here: the low rate of breakdown of milk protein contributes to dosed and uniform saturation of the gourmet’s blood with amino acids. The level of the latter is eventually established at the most optimal level, and it is stable for quite a long time - up to six hours. This unique property of casein makes it indispensable for infant nutrition. The disadvantage of this type of milk protein is its insolubility in water.
Calcium caseinate is converted into free protein casein when milk sours. If we speak in the language of chemistry, the enzymes produced by lactic acid bacteria act on lactose - milk sugar, as a result of which the latter becomes lactate, that is, lactic acid. This, in turn, provokes the coagulation of calcium caseinate. So we end up with casein protein plus calcium lactate at our disposal. In this form, milk protein is much better absorbed by the body. Unlike caseinate, casein has good water solubility.
Now let's talk about whey proteins. They, like both forms of milk protein discussed above, have a balanced amino acid composition. However, there is a difference here: according to this parameter, whey proteins are as close as possible to the proteins of the muscle tissue of the human body. In addition, they have the greatest anabolic ability. And whey proteins have left far behind all currently known types of protein in terms of the amount of BCAAs present in them - branched chain amino acids.