22.07.2017
Allergy to cottage cheese is a type of cross-disease. Occurs in those people who have a predisposition to allergic manifestations to dairy products.
In the presence of dysfunction of the immune system, the human body begins to perceive the necessary protein as a foreign agent. This becomes a powerful response to the human body’s defenses, which begin to produce hormones.
The presence of allergic reactions in infants to cottage cheese has become common; genetic heredity and predisposition are possible. This is observed with allergic manifestations in both parents.
The cause of an allergy in a baby will be a consequence of oxygen starvation when he was in the womb or during an abnormal birth process. Another factor that provokes the occurrence of allergies is the transmission of infectious diseases in infancy, based on a violation of the microflora in the digestive tract.
With a reduced level of specific antibodies, allergens begin to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
During the growth and formation of the child’s organ systems, its functions improve and the presence of any allergies disappears. The digestive organs and the liver, which filters toxins, begin to fulfill their duties. This means that an allergy to cottage cheese in a mature person is a rare manifestation.
When and how to introduce it into the diet
Any pediatrician will confirm that cottage cheese is a very important product in an infant’s diet.
A growing body, as you know, requires a large amount of nutrients.
You can get them from various sources, but it is cottage cheese that contains animal proteins, calcium and phosphorus, which are so necessary to strengthen the baby’s bones and muscles.
Preparing the right diet will be the key to the successful development of a child.
Children's doctors recommend giving a baby cottage cheese little by little at 7-8 months of life, but do not overdo it - portions should be small but regular.
In rare cases (for example, with rickets, underweight), it is allowed to feed this dairy product from 4 months.
For a child to successfully digest cottage cheese, parents should carefully consider the following recommendations:
- the baby has reached six months of age;
- the child is able to sit independently;
- the baby watches with interest the adults eating and strives to take food from their plate;
- the baby's weight doubled after birth;
- The baby is in normal health and has not received any medications during the previous week.
Dairy products for allergies: what is life like without milk?
Food allergies, and in particular cow's milk protein intolerance, are a very common disease.
In children suffering from atopic dermatitis, approximately 80% of cases are diagnosed with an allergy to this product. Moreover, the number of such children is growing every year.
Signs and true causes of dairy allergy: milk, kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt
Many people confuse an allergy to dairy products with lactase deficiency, which consists of a deficiency of the lactase enzyme, which is responsible for the breakdown of lactose in the gastrointestinal tract. Meanwhile, the latter disease is less common.
A milk allergy is a reaction of the immune system to cow's milk protein. Its manifestations can be very different, since allergens enter the blood and can affect any organ. When the immune system is weakened (for example, during illness), these symptoms are more pronounced.
Let's name the reactions that occur most often:
- From the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, loose stools, undigested food in the stool, constipation, in infants - frequent and profuse regurgitation and weight loss.
- Skin manifestations: urticaria, atopic dermatitis with lesions under the knees and in the bends of the elbows, in children there is eczema and milk scab (the appearance of crusts on the scalp that are combed off with a comb).
- From the respiratory system: runny nose and sneezing, difficulty breathing, cough, in advanced cases - bronchial asthma.
Children are usually susceptible to this type of allergy. In this case, the disease may go away by the age of three. But there are also adults who also cannot tolerate cow’s milk protein. Their allergy symptoms to this product usually manifest themselves in the gastrointestinal tract.
The reasons for such a complex relationship between milk protein and the immune system may vary. In most cases, this is heredity, less often – immune changes . in children, this is the immaturity of the digestive system and the result of the mother’s excessive consumption of dairy products during pregnancy.
How dairy products affect allergy sufferers
Proteins that cause allergies can be found in any milk, but are most often found in cow's milk.
When allergen proteins enter the body (especially children’s), the human immune system, perceiving them as a threat, begins to fight. This is manifested not only in the behavior of the baby, who is very capricious. His digestion is also disturbed, gases, colic, and rash appear. And if an adult can cope with this condition, then the child definitely needs help by contacting a specialist.
Important! Before visiting the doctor, a breastfeeding woman should exclude not only milk, but also all dairy products from her diet. This simple rule applies to both children who already eat on their own and adults.
When purchasing this or that packaged product, which, in theory, has nothing to do with milk, you need to pay attention to the composition. Sometimes the manufacturer indicates that the product may contain traces of lactose.
Diet for milk protein allergy
Of course, a person who discovers symptoms of this condition should exclude the product from the diet.
If it turns out that one of the relatives of a breastfeeding woman suffered from milk protein intolerance, it is better for her to exclude milk during lactation - even if she herself does not have this type of allergy.
Important! A formula-fed baby may also develop an allergy to milk, since most formulas are based on casein (an allergenic protein). In this case, it is advisable to replace the baby’s formula with a hypoallergenic one.
Replacing cow's milk with any other milk in an “adult” diet will not eliminate the symptoms, since allergenic proteins are contained in almost all types.
Nutritionists recommend keeping a food diary, in which you should indicate what you ate and drank throughout the day, as well as your reaction to certain foods.
When keeping a diary, it makes sense to follow a special hypoallergenic diet, which is based on:
- Vegetable, fish and less often chicken broths.
- Meat and offal.
- Eggs.
- Nuts.
- Legumes.
- Porridge with water without butter.
- Pasta without adding butter.
- Water.
- Weak tea.
- Vegetables and vegetable juices.
- Fruits and fruit juices.
Based on these products, a sample menu is compiled. For an adult, the daily diet can consist of 4 meals: .
- Breakfast: boiled egg, porridge with water without butter, tea.
- Lunch: boiled beet salad with raisins, nuts and vegetable oil; soup with chicken (vegetable) broth without sour cream and mayonnaise; Steamed fish.
- Afternoon snack: berry jelly and baked goods without milk (or with coconut milk).
- Dinner: cauliflower in egg, fried in vegetable oil; chicken cutlet; tea.
Adjust the menu depending on personal preferences and tastes.
How can you replace dairy and fermented milk products in your diet with health benefits?
Cow's milk can be replaced without health risks only with milk of plant origin:
Based on them, you can prepare different dishes yourself. For example, you can make cottage cheese, cheese or kefir from soy milk.
How to cure allergies to milk, kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt and other dairy products?
Before we talk about treating allergies, you need to avoid foods that can cause them.
You also need to keep in mind that traces of milk protein may be contained in chocolate, flour, margarine, and brown sugar.
Your doctor will tell you how to replace milk and milk-based products. For example, sometimes you can use plain water, juice or liquids containing vegetable protein instead of milk to prepare a certain dish.
Of course, you should not self-medicate, because only a doctor can create the right diet and select medications that will “reconcile” your immune system and dairy products.
or login using:
THANK YOU FOR REGISTERING!
An activation letter should be sent to the specified e-mail within a minute. Just follow the link provided and enjoy unlimited communication, convenient services and a pleasant atmosphere.
RULES FOR WORKING WITH THE SITE
I give my consent to the processing and use by the web portal UAUA.info (hereinafter referred to as the “Web Portal”) of my personal data, namely: first name, last name, specified dates of birth, country and city of residence, email address, IP address, cookies, information about registration on websites – social Internet networks (hereinafter referred to as “Personal Data”). I also give my consent to the processing and use by the Web portal of my Personal data taken from the websites I specified - social Internet networks (if indicated). The Personal Data provided by me can be used by the Web Portal solely for the purpose of my registration and identification on the Web Portal, as well as for the purpose of my use of the Web Portal’s services. I confirm that from the moment of my registration on the Web portal, I was notified of the purpose of collecting my Personal data and the inclusion of my Personal data in the personal database of users of the Web portal, with the rights provided for in Art. 8 of the Law of Ukraine “On the Protection of Personal Data”, read. I confirm that if it is necessary to receive this notification in written (documentary) form, I will send a corresponding letter to the address indicating my postal address.
A letter has been sent to the specified e-mail. To change your password, simply follow the link provided.
Is this possible?
Rejection of dairy products by a child’s body is a fairly common phenomenon.
And although most often it manifests itself in poor absorption of milk itself, an allergy to cottage cheese in an infant can also occur.
This delicacy is incredibly useful for the baby, but the immune system can act at its own discretion.
It should be remembered that each body reacts individually to food: one child will digest cottage cheese well, while another will develop skin rashes and vomiting.
The appearance of allergies when eating cottage cheese
Allergies to cottage cheese have become very common lately.
The most dangerous products are considered to be milk and its derivatives (kefir, yogurt, cheeses, etc.). Cottage cheese is included in this list, while being the main product used in various diets. Despite the fact that dairy products, as a rule, are more present in the daily diet of children, saturating their bodies with the necessary microelements, this type of allergy can also be found in adult patients.
Reasons for the development of the disease
An allergic aversion to cottage cheese can occur when there are disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, when the protein of the product is perceived by the body as foreign.
Another reason for the development of allergies to milk proteins is hormonal disorders.
Genetic predisposition to various types of allergies is of great importance. If there are allergy sufferers in the family, the likelihood that this disease will subsequently be inherited is quite high.
Cross-reactions should not be underestimated, when one allergen enhances the effect of another and can cause a negative reaction.
In an infant, a reaction to cottage cheese may be due to intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), as well as due to insufficient production of antibodies. This leads to high sensitivity of the stomach walls to allergens and their rapid absorption into the blood.
In addition, rejection may be a consequence of previous viral infections, resulting in an imbalance in the intestinal microflora. As a rule, as the baby grows, the functionality of his internal organs (liver, stomach) develops.
Symptoms
An allergy to cottage cheese, like all food reactions, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- hyperemia of the outer skin;
- the occurrence of stomach cramps;
- difficulty breathing;
- dry mouth;
- slight swelling around the lips;
- swelling of the skin;
- sudden attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- the appearance of pinpoint rashes on the body;
- digestive system disorders (colic, loose stools, bloating);
- discharge of mucus from the nose;
- lacrimation;
- painful cough.
The severity of allergic symptoms may depend on the individual characteristics of the body. It can develop rapidly, a few minutes after the product enters the body. The second path of development can have a long course with gradually increasing symptoms.
In the case when intolerance appears to cottage cheese, it is necessary to distinguish its symptoms from lactose intolerance. In the first case, the body rejects milk proteins of all types.
In other words, all products that contain milk are excluded from the diet. These include margarine and butter, sour cream and cream, kefir and yoghurt.
With timely measures taken and avoidance of all allergens, all symptoms disappear within 3–4 days.
Clinical picture of the disease in childhood
Most often, an allergic reaction to cottage cheese can occur in a child in infancy. Due to the fact that cow's milk contains many allergenic proteins, it is not recommended to wean the child from the mother's breast until the baby is one year old.
Introduction to dairy and fermented milk products should be at the beginning of the second year of life. Mother's milk is the most beneficial for a child's physical and emotional development. It contains all the necessary microelements and substances for active growth and development. Gradually, curds, kefir and other milk-containing products are added to the food.
Complementary foods must be introduced very carefully. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the reaction, since new products are foreign to the baby. An allergy to cottage cheese in an infant is manifested by a rash, redness, heavy breathing and restless behavior, which indicates that it is necessary to stop the intake of the product into the body.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic identification of the cause of cottage cheese rejection in adult patients and children is quite simple.
Initially, the patient is examined by a doctor, then laboratory tests are performed. A common way to identify an allergen is a skin test: an incision with a small amount of the suspected allergen is made on the patient’s skin using a sterile scarifier.
Based on the results of the reaction, the doctor can make a conclusion about the nature of the disease. The advantages of this method include speed of execution.
Another examination is the elimination method, which consists of gradually eliminating suspicious foods from the diet. In this way, it is possible to identify the allergen that provokes an acute reaction.
It should be borne in mind that quite often the disease is activated as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis in adults, a mandatory consultation with a neurologist and endocrinologist is necessary. This will allow you to correctly differentiate the symptoms of these diseases from the manifestations of true food allergies.
Treatment
Treatment of an allergic reaction is primarily aimed at suppressing the main symptoms.
It is quite natural that at the first sign of an allergic reaction to cottage cheese and other products, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. Under no circumstances should such a disease be left to chance, hoping that it will go away on its own. This is especially important when allergies are detected in a child.
Various medications and techniques are used to relieve symptoms of the disease. The most widely used are the following:
- antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil, diazolin, claritin, etc.);
- corticosteroids (advantan, acriderm);
- anti-inflammatory (dexamesatone, mometasone, movalis);
- steroid preparations for external use (hydrocortisone, clioquinol);
- bronchodilators (salbutamol, Berotec, etc.);
- immunotherapy (use of vaccine, gamma globulin, immune serum).
Cottage cheese causes food rejection, which is why the course of the disease mainly develops in the digestive tract.
To eliminate such manifestations, enterosorbents (polyphepan, activated carbon, polysorb, entrosgel, etc.) are used. These drugs are able to absorb toxic substances released by the intestinal microflora, protecting it from their effects. Thanks to adsorption, the epithelial layer is preserved and the intestinal barrier permeability control system is restored.
Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli can be used. They are diluted with warm water and taken orally for 10 days. Subject to additional indications (liver dysfunction, renal failure, development of internal viral infection), the course of treatment may be extended.
In addition to drug therapy, it is necessary to protect the patient from contact with the allergenic product. The best way to do this may be to follow a hypoallergenic diet, compiled by a nutritionist taking into account the individual characteristics of a person.
The reintroduction of curd products into the diet is introduced gradually. It is necessary to start with a minimum amount and then increase. You cannot do this on your own, risking a severe allergic relapse. Diet adjustments should be carried out under the supervision of a nutritionist and allergist.
You need to maintain moderation in your diet and lead a healthy lifestyle. Timely treatment of chronic, somatic and acute diseases is of great importance. Sometimes an allergy to cottage cheese can go away on its own, but this is quite rare.
Preventive actions
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. To fulfill this condition, cottage cheese should be consumed very rarely. It is advisable to alternate different types of product, adding foods with different fat content to your diet.
For example: if you are hypersensitive to high-fat cottage cheese (especially in a child), you can try a small amount of curd mass or a little yogurt and kefir.
Changing the consistency of a dairy product can significantly change its digestibility.
In traditional medicine, it is widely believed that any allergy cannot be cured, however, it is quite possible to mitigate its manifestations. The result of this process in adult patients is the neutralization of the main symptoms of the disease.
Holistic (alternative) medicine involves a completely different conceptual direction, primarily aimed at the overall treatment of the body. For the holistic direction, a prerequisite is the general balance of the body. This involves a combination of drug therapy, diet, special gymnastics, and meditation.
What can replace cottage cheese?
Many nutritionists tend to believe that cottage cheese, which is a fairly healthy protein product, cannot be easily replaced with other products. However, it is possible to make some replacements.
Of course, not all useful microelements will be present in the original quantity. According to the amount of calcium (100 grams of cottage cheese contains 125 grams.
calcium), the following products may correspond to it:
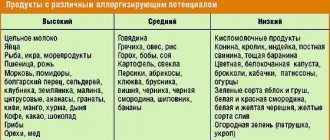
Product Amount of calciumProduct Amount of calcium
| Swiss cheese | 850 | Hazelnut | 226 |
| Hard cheese | 750 | Rice | 230 |
| Sesame oil | 783 | Watercress | 214 |
| Halva | 670 | Plain yogurt | 200 |
| Soft cheese | 260 | Spinach | 145 |
| Broccoli | 250 | Eggs | 55 mg/piece |
If there is an absolute rejection of cottage cheese, it is allowed to use a similar product, but soy-based - tofu. This product is completely opposite in taste, appearance and smell. You will have to get used to its taste, but in terms of its mineral and vitamin complex it is most similar to natural cottage cheese.
As a last resort, you can use kefir with a similar fat content. It will not cause a negative impact, and its beneficial properties are in no way inferior to natural cottage cheese. As a protein source, cottage cheese is an excellent substitute for meat, fish, legumes, and eggs.
Every patient predisposed to a food allergy to dairy products should know that treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified specialist. Only a doctor is able to establish an accurate diagnosis and select individual anti-allergy programs for an adult patient and a child.
It must be remembered that self-medication can lead to severe consequences: anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. The symptoms of these complications develop rapidly, they require emergency medical intervention, otherwise the patient may die.
Source: https://AllergiyaNet.ru/allergeny/produkty/allergiya-na-tvorog.html
What exactly gives the reaction?
A study of the composition of cottage cheese showed the presence in this product of:
- animal protein;
- vitamins;
- calcium;
- phosphorus.
Analyzing the effects of food components on the body, doctors came to the conclusion that an allergic reaction can rarely be caused by micro- and macroelements.
This factor cannot be completely excluded, but protein rejection still occurs more often.
Products of animal and plant origin have an individual chain of amino acids, which the body of any person strives to break down and obtain the necessary components for life.
However, there are cases when the immune system perceives them as a foreign body and danger, and therefore seeks to destroy it.
It is not the natural digestion of protein that occurs, but its neutralization using protective reactions.
When breastfeeding, the baby's body gets used to a certain set of nutritional elements.
The influx of cottage cheese can be regarded as an attack from the outside, which is primarily due to the high concentration of foreign protein in the delicacy.
Photo: Food allergies
How does an allergy to cottage cheese manifest in a baby?
Allergies in each child can have a different character and manifest themselves individually.
A common symptom is a skin rash that can cover both local areas and the entire body.
In addition, infants often have a gag reflex, which is caused by a sharp rejection of unfamiliar food.
In young children, an allergy to cottage cheese has the following symptoms:
- lips and skin around the mouth swell;
- the oral cavity is characterized by high dryness;
- the skin all over the body swells from excess fluid, becomes covered with a rash, and sometimes with pustules;
- frequent vomiting;
- The baby's belly may swell;
- indigestion causes diarrhea.
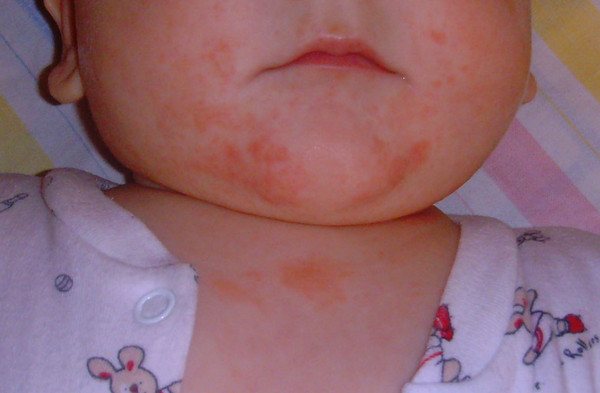
Photo: The appearance of a rash after homemade cottage cheese
Lactase deficiency
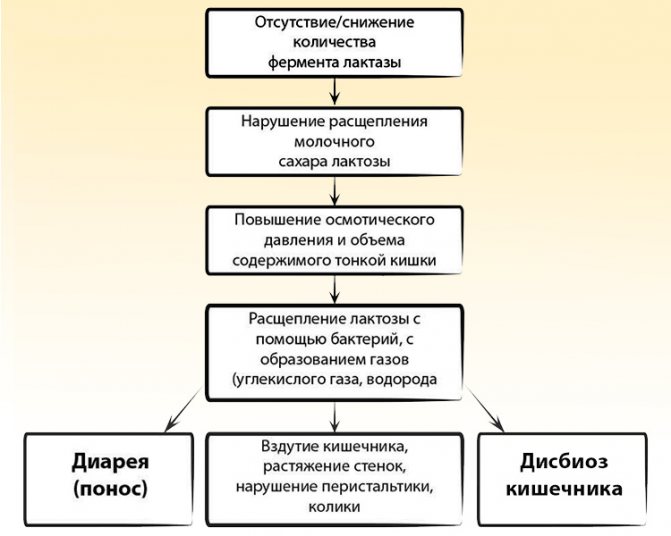
To distinguish allergies from lactase deficiency, you need to have an idea of the manifestations of each pathology. It is worth understanding that in some cases, allergic intolerance can be combined with enzyme deficiency - then the signs of diseases are combined into a common picture.
Adults and older children
Symptoms characteristic of lactase deficiency in these categories of patients include:
- loose yellow stools that have a sour odor;
- painful bloating;
- involuntary release of gases from the anus;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- general weakness, sweating, loss of appetite.
Like the signs of an allergic reaction to cottage cheese, the symptoms of lactase deficiency develop quickly - but still not in a matter of minutes, but within several hours. Unlike allergies, low lactase levels do not contribute to the appearance of rashes or itching of the skin, as well as swelling of the mucous membranes and nasal congestion. All these manifestations should alert you, since they are more typical of allergic sensitivity.
Young children and infants
A child suffering from a deficiency of the lactase enzyme becomes restless, capricious, and has a loss of appetite after eating cottage cheese. The following manifestations are observed:
- bloating, colic;
- regurgitation, vomiting;
- release of gases from the anus;
- yellow, sour-smelling, foamy stool.
Unlike adults, young children lose weight very quickly, so prolonged feeding of dairy products, including cottage cheese, is associated with the risk of severe exhaustion, retardation in physical development, and anemia. At the same time, stopping their use leads to a significant improvement in the condition, especially if a deficiency of the lactase enzyme is detected in a timely manner.
Review of children's product manufacturers
The baby food market is quite diverse, and parents have the opportunity to choose the most suitable product.
Children, as you know, are often capricious, not eating all the food offered.
However, there are now so many manufacturers that feeding a child delicious cottage cheese will not be difficult.
Although store shelves are full of baby food, parents usually give preference to well-known companies:
- "Subject";
- "Agusha";
- "Yagotynskoe for children."
Each of these companies supplies curds made using the ultrafiltration method of cow's milk.
The technology is quite complex and is characterized by dehydration of the feedstock and the use of additional components, for example calcium chloride.
Children's curds come both without and with fillers, but they are all environmentally friendly.
The baby may like absolutely any product, and parents do not have to worry about the safety of the child’s health.
However, an allergy to cottage cheese can occur in an infant even with high-quality nutrition.
In rare cases, rejection by the body is associated with the manufacturer, although this option cannot be ruled out either.
Violation of technology, storage and transportation conditions can damage the goods.
But still, allergies more often manifest themselves due to the large amount of protein in cottage cheese, so this problem must be solved, first of all.

Is home cooking the solution?
Many parents do not trust suppliers of fermented milk products to take care of their child’s health and prepare food for the baby themselves.
Although this is painstaking and responsible work, the child receives only natural treats.
There are a lot of time-tested recipes that you can use to make tasty and tender cottage cheese.
The baby will like some of them and not others, but you can always make the product using a new method, pampering your child and promoting the growth and strengthening of his musculoskeletal system.
Read what to do if your child is allergic to the sun. Are you worried about an allergy to formula in your baby? Click to find out.
Kefir cottage cheese
The usefulness of kefir is due to the presence of both protein and lactic acid bacteria, which have a positive effect on digestive processes in the human body.
But it is also possible to make very tasty cottage cheese for children from this product.
You won’t have to perform any particularly difficult actions for this, but it is important to strictly follow the technology:
- fill the pan with the required volume of kefir;
- turn the heat to medium and make sure that the contents do not boil, but only heat up;
- after a few minutes, curd will begin to form on the surface;
- collect the cottage cheese and strain with gauze, removing excess moisture;
- You can give it to your baby right away.
Cottage cheese with calcium chloride
Calcium is one of the most important macronutrients involved in the process of muscle contraction.
In addition, it strengthens bone tissue and activates certain enzymes in the body.
Its deficiency can significantly slow down a child’s development and even lead to some diseases.
To prepare cottage cheese from milk using calcium, you need to follow simple steps:
- pour the required amount of milk into the pan and bring to a boil;
- for 1 liter of milk add 2-3 tablespoons of 10% calcium chloride solution;
- after a few minutes the curd mass will begin to separate;
- Cool the contents of the pan and strain with gauze;
- You can add any fruit puree and feed the baby.
Cooking cottage cheese in a slow cooker
If you have a household appliance such as a multicooker, the process of making cottage cheese can be significantly simplified:
- pour a liter of kefir into a special bowl;
- program a temperature of 80 °C and a time of 45 minutes;
- after turning on, you do not need to change anything in the settings;
- after the time has passed, take out the resulting cottage cheese;
- cool and strain with gauze;
- squeeze well to remove excess liquid;
- You can feed immediately.
Allergy to agusha... Are we the only ones? [PDA] – Littleone 2006-2009
View full version: Allergy to agusha... Are we the only ones?
Lately we've been allergic to agusha (yogurt):001: . I wonder if we are the only ones? Previously, everything was fine, I drank, no problems. Tell us about other dairy products and what kind of reaction you have. Maybe switch to something else? He doesn't drink kefir. Thank you.
Martina+Lana
23-10-2006, 10:29
Listen, there’s something I don’t understand…….I think it’s also an allergy…..Red spots appear, then disappear without a trace after 10 minutes…..then I appear again in another place….What is this? Allergy? It seems like we’ve been drinking this agusha for a long time.....
We have a slightly different reaction (redness, itching), I give fenistil and it seems to go away.
vashnata, and your child cannot, in principle, be allergic to cow’s milk protein? Since this protein accumulates in the body, allergies do not appear immediately...
Ksunushka
23-10-2006, 10:42
We are allergic to cow’s milk protein, BUT we eat fermented milk products without consequences (TTT), although only “Tema” curds.
But there was a typical allergy to Agusha yogurt, it appeared on the 3-4th day and went away 8-10 days after we stopped drinking this yogurt.
To be honest, we later gave up the Agushin curds, and now we only eat Tema (ttt, everything is fine). In general, trust in Agusha has disappeared :((
We are allergic to cow’s milk protein, BUT we eat fermented milk products without consequences (TTT)…
:((Everyone has their own threshold for the accumulation of milk protein after which the body warns with allergic rashes.
We have also been eating Agusha (curds) for about 10 months now, we got used to it gradually, until now there were no manifestations of allergies, but now there are, but for some reason I did not consider Agusha as an allergen... :008:
We also had nothing before: we drank Agusha yoghurt and ate cottage cheese, and then it broke out. For a long time I could not understand the reason. Everyone was excluded, including “Agusha”. Now we eat homemade cottage cheese. I don’t know if it was on “Agusha”, but I don’t risk giving it yet.
We also developed an allergy of strange origin at 23 weeks, because... We didn't give anything new. maybe really on Agusha??
We also had nothing before: we drank Agusha yoghurt and ate cottage cheese, and then it broke out. For a long time I could not understand the reason. Everyone was excluded, including “Agusha”. Now we eat homemade cottage cheese. I don’t know if it was on “Agusha”, but I don’t risk giving it yet. Hmm... We should try to exclude it too... :(
I thought we were alone. Because if you don’t ask, you won’t read it. Everyone gives agusha and everything is fine. In principle, my child has a reaction to sweets, but dairy?! What if from the accumulation of milk protein? But we have been eating milk for a very, very long time. We don’t even have a reaction to regular milk. Although Nastyusha drinks it much less often.
We also had nothing before: we drank Agusha yoghurt and ate cottage cheese, and then it broke out. For a long time I could not understand the reason. Everyone was excluded, including “Agusha”. Now we eat homemade cottage cheese. I don’t know if it was on “Agusha”, but I don’t risk giving it yet.
Tell me, how do you prepare homemade cottage cheese from what kind of milk? Do you add anything to the cottage cheese? :)
And we are like that