It is known that mother's milk is considered the ideal nutrition for a baby. Its composition directly depends on the diet of a nursing woman. Therefore, it is especially important to exclude allergenic foods from the menu when breastfeeding. The body of a newborn baby is highly sensitive and can react sharply to an ingredient familiar to the mother.
What is a hypoallergenic diet?
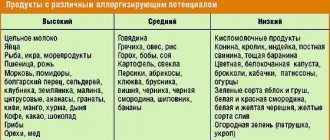
With a nonspecific hypoallergenic diet, foods that are most likely to cause allergies are excluded from the diet. All products, depending on the degree of allergenicity, are divided into 3 groups.
Highly allergenic include :
- seafood;
- whole milk, cheese, fermented baked milk, ayran, cottage cheese;
- bird eggs;
- porridges: wheat, millet, semolina and oatmeal;
- smoked foods, pickles, marinades;
- canned food;
- sausages;
- beef and pork;
- sauces, mayonnaise, ketchup;
- berries, vegetables and fruits with red, yellow, orange colors;
- citrus and exotic fruits;
- honey, chocolate, any nuts, dates;
- carbonated drinks, coffee, strong tea, cocoa.
Products with a moderate degree of allergenicity :
- offal;
- bell peppers, peas, beans, potatoes;
- watermelon, cranberries, black currants, bananas;
- corn, rice or buckwheat bread, biscuits;
- fruit compotes, herbal infusions.
Low allergenic products:
- Corn, buckwheat, rice;
- rabbit, chicken and turkey fillet;
- cucumbers, zucchini, all types of cabbage, squash;
- green vegetables (lettuce, dill, parsley, spinach);
- butter and vegetable oil (sunflower, olive);
- pears, green apples, gooseberries, white cherries and white currants;
- fruit decoction without sugar (from apples, pears, prunes), rosehip decoction;
- still mineral water, weakly brewed black or green tea.
A hypoallergenic diet consists only of low-allergenic foods. You will have to forget about any fried foods: meat and fish should be steamed.
But allergies can develop even to foods with low allergenicity. Allergy is an individual reaction of the body; it cannot be predicted.
For a child from 1 to 3 months: replenishing the menu
The diet of a nursing mother of a newborn aged 1 to 3 months becomes freer, her table is replenished with:
- lean beetroot soup (some experts allow adding a little tomato juice);
- a small amount of nuts, except pistachios and peanuts (according to some recommendations, it is better to include the consumption of nuts for the period from 3 months);
- raw fruits (preferably homemade), you need to include them gradually, adding one product at a time;
- homemade jam (in small quantities).
During this period, it is strictly not recommended to break the diet, including whole cow's milk, full-fat sour cream, meat broths, baked goods, cocoa beans, coffee, strong tea, and raisins in the menu. Other foods may also be excluded from a woman’s diet on the recommendation of a pediatrician.

A pediatrician can help give advice on the optimal diet for mom. He will check the baby’s condition, calculate compliance with weight standards, and conduct neurological tests. It happens that mom needs to exclude some foods, although they are formally allowed
Does a nursing mother need a hypoallergenic diet?
Currently, not all scientists share the view that a nursing mother needs to strictly adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, believing that the newborn should “train” the immune system.
Therefore, there are 2 diet options for nursing mothers - classic and alternative.
The classic version of the diet involves compiling a daily diet of hypoallergenic foods, which is a rather difficult task. After all, the authors of such recommendations indicate not only a list (not so extensive) of hypoallergenic products, but also a desire to ensure the completeness and diversity of the diet, which is necessary for the development of the baby: the child receives all useful nutrients from mother’s milk.
Depriving a child of many useful substances (microelements, proteins, vitamins) can cause developmental delays. The mother’s body will also suffer if it does not receive nutrients in a complete set with food: reserve resources will begin to be used. For example, calcium from teeth and bones will be actively used; nutritional deficiencies can reduce lactation.
And the lists of these hypoallergenic products on different Internet sites (one of the main sources of such information) differ. For example, some authors recommend excluding even fermented milk products, while others advocate the need to consume them.
The classic hypoallergenic diet requires complete exclusion from the diet:
- strong rich broths (meat, fish, mushroom);
- caviar and seafood;
- nuts, honey;
- chocolate, cocoa, coffee, kvass;
- exotic fruits;
- canned food; products containing preservatives and dyes;
- sausages and ham;
- semolina;
- mushrooms in any form;
- hot seasonings, garlic and onions, radishes and radishes;
- fruits, berries, orange and red vegetables;
- confectionery products;
- alcoholic beverages, including beer.
It is recommended to reduce the amount of wheat bread, pasta, sugar by 25%, and salt by 30%.
Recommended for use:
- Fermented milk products without restrictions;
- unsalted and mild cheeses;
- vegetarian soups (from cereals and vegetables);
- lean meat (beef, veal, pork; turkey and chicken fillet);
- bread made from rye flour or 2nd grade wheat flour;
- fruits, vegetables, berries of white or green color;
- vegetable and ghee;
- tea, fruit infusions or berry fruit drinks (without sugar).
This diet should be followed throughout the entire period of breastfeeding, provided that the child has no allergic manifestations (rash, dyspepsia).
Proponents of an alternative version of the hypoallergenic diet argue their point of view by the fact that the baby’s immune system, encountering “provocateurs” of allergies obtained from mother’s milk, learns to resist and protect against them.
According to these scientists, mothers should adhere to minimal restrictions: maintain their usual diet, but control both portion sizes and the frequency of consumption of certain foods.
It is known that 85% of children with food allergies have hypersensitivity to cow's milk protein, and 62% of children have hypersensitivity to chicken eggs. But since both of these foods contain important nutrients, they should not be completely excluded from the mother's diet. You need to try to minimize the risk of allergies using heat treatment: boil eggs for 10 minutes, ferment milk or cook porridge with it.
With an alternative hypoallergic diet, it is recommended to exclude:
- raw whole cow's milk;
- fast food;
- carbonated drinks.
Eat no more than 2-3 times a week:
- eggs and fish;
- sausages and boiled sausage;
- vegetables, berries, fruits of red and orange color;
- beans, peas, cabbage;
- grape;
- rye bread (no more than 150 g);
- confectionery and baked goods.
Selecting a diet for a nursing mother is a rather complex process in each case, and this problem should only be solved in contact with a pediatrician or allergist.
The baby grows, the diet expands: from 3 to 6 months
After the newborn has lived through its first three months, has matured and become stronger, the diet is softened for the nursing mother. The diet is becoming more varied, but the entire previous list of prohibited foods is still relevant.
Mom is allowed to include fresh juices or fruit drinks (they should be squeezed before drinking):
- pumpkin;
- apple;
- carrot;
- beetroot
The diet during this period allows you to eat pearl barley and wheat porridge, and allows the consumption of fresh onions. Whole cow's milk is still not recommended. Although, according to some reports, tea with milk is a good remedy for lactation. And if the child does not have an allergy to cow protein or lactose intolerance, this remedy is quite applicable.

Freshly squeezed homemade juices are an excellent remedy for a nursing mother, adding a lot of vitamins to the diet. They should be prepared immediately before use, avoiding the addition of chemical preservatives (even citric acid) to the product.
Such an unpleasant and dangerous disease as food allergy affects even the smallest – infants; in addition, their body’s reaction is usually more acute than that of adults.
There is a common misconception among new mothers that as long as the baby is breastfed, he is not afraid of allergies, but in fact this is not the case. Health-threatening allergens can even be components of breast milk. A number of factors may be involved in the development of such a problem in a baby (poor nutrition during pregnancy, difficulties with the mother’s health while carrying a child, smoking and other bad habits, parents having allergies and even medications they take).
Often, an allergic reaction of the body develops to proteins contained in food; a reaction to fats or carbohydrates is extremely rare. The mechanism of the process is as follows: when an allergen enters the digestive tract, the active production of E-class immunoglobulins begins, which, upon repeated contact with a dangerous product, trigger a number of reactions.
An interesting fact is that often an allergic reaction occurs within a few minutes after consuming a particular product, but in some situations it can be delayed by an hour or even a day.
If an infant is intolerant to a particular type of food, symptoms of three categories may develop: a reaction from the digestive tract, from the skin, and a respiratory type reaction. The main elements of the symptomatic complex include:
- A rash, redness of various localizations, and manifestations of diathesis (peeling and redness of the cheeks, itching) may appear on the baby’s skin. In addition, diaper rash, despite proper and careful care of the baby’s skin, does not go away. Problems may also occur on the scalp (flaking, formation of scales);
- Due to the entry of an allergen into the body, swelling of the mucous membrane that lines the respiratory tract may occur. This can cause a runny nose or bronchospasm, which makes it difficult to get air into the lungs;
- reactions from the digestive system are stool disorders (constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea), bloating, unusually frequent and profuse regurgitation.
The most dangerous manifestation of food intolerance in infants is considered to be Quincke's edema (an attack accompanied by difficulty breathing in the larynx). Initially, some hoarseness appears in crying, a barking type cough occurs, followed by noisy breathing, which resembles the development of an attack of bronchial asthma.
Not only the baby’s diet, but also the nutrition of the nursing mother requires careful attention. All new products for the baby’s body should be introduced gradually, observing the absence of a negative reaction. Doctors recommend trying to breastfeed your baby for as long as possible - this is one of the main principles of preventing such a problem.
A child can develop a food allergy even to a product to which such a reaction has not previously been observed - all this is due to the fact that banal overfeeding can provoke an allergy. In medicine, there are cases where infants developed intolerance to breast milk.
There is a list of foods that are most likely to cause an allergic reaction in children:
- one of the most common allergens is cow's milk (this is what is used in baby formula and cereals);
- eggs (not only in their pure form, but also as a component of other dishes and baked goods);
- honey and some fruits (all citrus fruits, apples, peaches, especially those that are orange or red in color);
- It is not recommended to give nuts, fish roe, all types of mushrooms and chocolate products to a child under two years of age;
- soy;
- cocoa and coffee;
- various crustaceans and fatty fish.
Summary for parents
In the interests of a newborn baby, a nursing mother should pay attention to her diet, paying attention to the baby’s well-being and its changes depending on the foods the mother eats.
This connection can be easily tracked using a food diary, recording absolutely all foods eaten and the appearance or exacerbation of allergic manifestations (rashes, itchy skin, bowel movements).
Such a diary will also make it possible to identify a possible other cause of the allergy (detergents, house dust or mold in the apartment, pet hair, etc.), if there is no connection between the allergy and the food.
Which diet option a nursing mother should choose (classic or alternative) is up to her to decide together with her pediatrician, depending on the baby’s condition.
In most cases, allergies go away as children get older.
The program “Doctor Komarovsky’s School” will tell you about safe nutrition, including hypoallergenic food:
babyfoodtips.ru
Nutrition for a nursing mother with allergies in a child
To prescribe a special nutritional principle, there must be strict indications, therefore an anti-allergenic diet for nursing mothers is prescribed for:
- severe allergic reactions in the baby - atopic dermatitis;
- the first 4 weeks of breastfeeding – when it is not yet possible to diagnose a true allergy;
- Diseases of the digestive system can provoke pseudo-allergy - individual intolerance;
- even if one parent of the baby has an allergy, in this case they speak of a hereditary allergy. In this case, the nursing mother must follow a diet for 4 to 6 weeks. In the absence of allergic manifestations, all restrictions are gradually lifted.
By adhering to a hypoallergenic menu, nursing mothers can continue breastfeeding without fear; this will limit the supply of allergens to the baby, thereby minimizing the negative consequences. These conditions will not allow allergies to develop into severe forms. By strictly monitoring the baby's reaction, the mother will be able to calculate which product the baby reacts to.
At-risk groups
A breastfed baby, as a rule, is at risk only if the mother has eaten a product that is “aggressive” for him, for example, citrus fruits, strawberries, chocolate, smoked meats. Normally, antibodies contained in mother's milk support the newborn's imperfect immunity.
The risk of an undesirable reaction depends on how strong the immunity of the child’s parents is and whether they suffer from allergic diseases. Practice shows that the presence of allergies in both parents is 50% likely to be passed on to their child in one form or another.
Children who are not provided with proper hygienic care are also at risk.
Allergies in a child: menu for a nursing mother
Initially, the anti-allergenic diet may seem quite strict to the nursing mother, but in the future it can be expanded, adhering to only non-strict restrictions. When planning a diet, you must first consult with a specialist - a pediatrician or allergist. Only a specialist can differentiate a real allergy from any other skin reaction (prickly heat, etc.).
A hypoallergenic diet implies the exclusion of all known allergens, and can be recommended only if indicated. Allergenic foods for a nursing mother include: milk and its derivatives, mushrooms, fish, black/red caviar, honey, chocolate and cocoa, brightly colored vegetables and fruits, preservatives, marinades and pickles.
Products containing dyes, flavors, strong spices and spices are excluded. It is necessary to limit fatty meat broths, chicken, eggs, and berries. Controversies often arise around a fruit such as quince, which is considered an exotic fruit and therefore is prohibited for mothers whose babies suffer from allergies.
Nutrition during pregnancy
If a woman ate allergic foods during pregnancy, she can cause the disease to appear in the child after birth. An allergenic background occurs when consuming exotic fruits, chocolate, nuts, honey, and tonic drinks.
Intemperance in eating, lack of diet and culture of food consumption will to some extent affect the future health of the child. A bad habit such as smoking increases the chance of a predisposition to allergies.
List of hypoallergenic products for nursing mothers
For a nursing mother with allergies, the diet consists of hypoallergenic foods. Analysis of the table of hypoallergenic nutrition for a nursing mother made it possible to highlight:
- sour milk;
- different types of oils: vegetable and butter;
- cereals: buckwheat, corn, oatmeal, rice, pearl barley, etc.;
- vegetables and fruits of green or white color: cabbage, broccoli, potatoes (pre-soak), squash, greens;
- soups with cereals with the addition of a small amount of potatoes in vegetable broth;
- lean meat, such as veal, turkey fillet, chicken breast, but only boiled or steamed. Some types of fish are introduced with caution - pike perch, cod;
- rye or wheat bread of the second grade, it is best if it is dried;
- Drinks: still mineral water, dried fruit compotes, weak tea.
Sample hypoallergenic menu
It is worth remembering that allergies are purely individual and can develop to any product, even from the low-allergenic group. But to make it easier for parents to identify the “culprit,” it will be necessary to keep a food diary, which notes everything that the mother ate and the baby’s reaction. This visual information is easier to analyze.
In the first days of keeping a diary, the diet should be especially strict, and one might say monotonous. Eating the same foods for 2–3 days, and if the baby’s reaction is normal, a new product is introduced on the 4th day, and further reactions need to be monitored. Thus, it is possible to finally find out all the products that provoke food allergies in infants.
For every woman, sharp dietary restrictions are very difficult, both psychologically, as worries about the baby add fuel to the fire, and physically, because due to restrictions, the amount of vitamins and minerals is reduced. Therefore, women are often prescribed complexes of vitamins and minerals.
detstrana.ru
A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers is needed not so much by the mother as by the baby, whose digestive system is just beginning to form. To avoid dermatitis, diathesis and other skin rashes, it is necessary to minimize the risk of allergens entering the child’s body. It should be noted that the problem of allergies in a newborn is not directly related to the fact that there is a nursing mother, but rather to how well the mother’s body accepts food and digests it. That is, if the mother has poor digestion, even harmless oatmeal can cause an undesirable reaction in the child in the form of allergic rashes or colic. Thus, all antihistamines used in the treatment of allergies in a child only neutralize the symptom, and the solution to the problem lies in normalizing the digestive process in the mother.
A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers involves switching to a specialized diet at the first symptoms and suspicions of an allergy in the baby. The menu includes the following hypoallergenic products:
- Vegetables are white and green, carrots, beets, and tomatoes are excluded.
- Fruits are green, all fruits and berries of pink, bright red color and citrus fruits are excluded.
- Gluten-free porridges - rice, corn chaff or flour, buckwheat. Avoid oatmeal, which contains avenin, which has properties similar to gluten.
- Gluten-free pasta is made from durum wheat.
- Gluten-free sweet products - biscuits, crackers, marmalade.
- Poultry meat is excluded. What remains is beef and white river fish.
- It is better to make all fermented milk products at home (yogurt, kefir or yogurt fermented using special dry mixtures).
The basic rules within which a hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers is drawn up are as follows:
- The entire diet should consist only of hypoallergenic products, even if neither the mother nor the baby has any manifestations of allergies. These products include bread with bran (preferably rye and dried), gluten-free grain porridges - rice, buckwheat, white and green vegetables, which must be soaked for at least half an hour before eating or cooking.
- Rule of the area. All products, including vegetables and fruits, must grow in the area where the mother and child live. Exoticism, although attractive, is not safe. Citrus fruits and bananas brought from afar should be excluded from the menu.
- It is advisable to combine protein foods with the consumption of biokefirs and bioyogurts made independently. It is better to purchase starter cultures in pharmacies in dry form.
- All dishes must be cooked boiled or baked. An alternative is steaming food.
Allergic reactions in young children are caused mainly by products containing specific amines - histamine and tyramine.
What should be excluded from the diet so as not to provoke an allergic reaction in a child?
- Histamine is found in sauerkraut, ham, all canned seafood, tomatoes and pork liver.
- Tyramine is found in elite types of cheeses: Camembert, Cheddar, Roquefort, and Brie. Tyramine can also be found in processed cheeses. Brewer's yeast and pickled sea fish - herring, mackerel, horse mackerel - contain large amounts of tyramine.
The main list of “prohibited” foods when following a hypoallergenic diet:
- Sea fish, seafood, caviar.
- Hard cheeses, especially sharp ones.
- Whole milk, “store-bought” kefir, yoghurts with additives.
- Eggs and dishes containing eggs.
- Wheat, millet, oatmeal, semolina.
- Without exception, all smoked products, including sausages, sausages, fish and cheese.
- Without exception, all pickled and canned foods, including juices.
- Condiments – ketchup, mayonnaise.
- Vegetables of bright colors, especially red, as well as sorrel and eggplant.
- Fruits are bright in color. A locally grown, pale green apple is preferable to an exotic, attractive fruit.
- Drinks containing preservatives and colorings, carbonated waters.
- Chocolate, products containing cocoa, honey.
A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers is very important in the first two to three months after the birth of the baby, it is during this period that the enzymatic function of the baby’s gastrointestinal system is formed. If within three months the child’s condition does not cause concern, other previously prohibited foods can gradually be included in the mother’s menu. Each new dish should be served for two weeks, and it is necessary to monitor the reaction of the baby’s skin to the new product supplied to him through breast milk.
ilive.com.ua
Hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers - what foods you can eat and what you should avoid
Any food product of the mother can become an allergen (a substance that causes an allergic reaction). Sometimes the baby’s reaction is so severe that life-threatening conditions can develop - laryngospasm, anaphylactic shock.
Currently, fortunately, all possible food “infant” allergens have been studied and special nutritional recommendations have been developed for nursing mothers. These recommendations are based on avoiding hazardous foods and eating approved foods.

What to avoid:
- seafood, fish roe, many types of fish;
- whole cow's milk, cottage cheese, natural yogurt, fermented baked milk, ayran, kefir
- fatty meats
- Exotic fruits,
- vegetables and fruits colored orange (pumpkin, carrots, beets, eggplants, bell peppers),
- Exotic fruits,
- wheat and millet porridge, rolled oats, semolina.
- honey,
- stew, canned fish, pickled vegetables and salads,
- fatty broths,
- eggs, mushrooms, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, alcohol,
- chocolate, coffee, cocoa,
- pickles, smoked meats, pickles, marinades, sausage cheese, salted-smoked fish, sausages, sausages,
- hot seasonings, sauces and ketchups, mayonnaise.
When compiling a diet, we should not forget that the child must receive all nutrients, vitamins and microelements from mother’s milk. Therefore, the diet for nursing mothers should be varied and rich in nutrients, based on those foods that can be eaten without danger.
What can you eat?
- The following products are considered safe from an allergenic point of view: rye bread, vegetables soaked in water, cereals. It is better to eat local fruits (green apples, pears, white currants, gooseberries, white cherries).
- Biokefir and bioyogurt are sources of protein for a nursing mother.
- You can eat cheese of non-spicy varieties.
- Buckwheat, rice and corn are also considered low-allergenic.
- For meat dishes, you can eat rabbit, chicken or turkey fillet.
- As for vegetables, all varieties of cabbage (white cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts), broccoli, spinach, cucumbers, zucchini, squash, turnips, dill, parsley, green salad are allowed for consumption.
- You can use olive, sunflower and butter for cooking.
- It is useful to cook compote from dried apples and pears; you can add prunes to it.
- You are also allowed to drink weak green or black tea and still mineral water.
- It is best to cook dishes in a double boiler or bake in the oven.
By combining these products with each other, you can use your imagination and get rid of the daily monotony.

Sample menu for three days
The first day:
- Breakfast - rice porridge, tea, cookies
- Lunch - vegetable soup, mashed potatoes, steamed cutlets, tea
- Dinner - cheesecakes, tea, cheese
Second day:
- Breakfast - oatmeal, porridge, kefir
- Lunch - rice soup with low-fat beef broth, buckwheat porridge with boiled veal, compote
- Dinner - cottage cheese, jelly, sushi
Day three:
- Breakfast - cottage cheese, tea, cookies
- Lunch - vegetarian soup, baked fish and potatoes, tea
- Dinner - stewed zucchini, greens, compote
Why is it important to follow a hypoallergenic diet in the first month of a baby’s life?
The first month of a baby’s life is a very important period when the baby’s body adapts to life in new conditions. The immune system of a newborn is not yet sufficiently developed, so an allergic reaction can stretch out over time, developing gradually and imperceptibly, but such an allergy in the future leads to more severe complications, up to the development of bronchial asthma.
Some foods consumed by women may cause colic in babies in the first month of life. Therefore, there is also a special diet for nursing mothers with colic. It is almost the same as hypoallergenic, only with greater restrictions on products that cause increased gas formation.
But even when following a diet, reactions sometimes develop even to low-allergenic foods. These foods should also be excluded from the diet.
Errors in the diet should not be allowed, as this can lead to the development of allergic diseases in the child. Proper nutrition for the mother will help avoid health problems for the baby.
ralinda.ru
Allergies always occur unexpectedly, they are unpredictable and insidious. Allergies in a newborn baby can arise from a weakened immune system, congenital diseases of the child, or hyperreactivity of the body to substances from the external environment. Since the baby is fed on the mother's breast milk, these substances can enter the baby's body through the milk. A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers will help avoid such problems.
An allergen can be any substance in a mother's food product, and provoke illness in the child, manifesting itself in the form of skin rashes or stomach upset. Sometimes a baby's allergic reaction can be so severe that he may develop life-threatening conditions - laryngitis, respiratory spasm.
A hypoallergenic diet is designed to protect the baby’s fragile body from the entry into his body of most of the most aggressive allergens with mother’s milk.
There is a single principle of a hypoallergenic diet for a nursing mother, as well as a hypoallergenic diet for children, which includes a certain set of nutritional rules and a certain limited list of acceptable foods for every day.
The menu for a nursing mother should consist of products that are allergenic: rye bread, cereals, vegetables soaked in water. The rule for fruits and vegetables is that it is better to consume those species that grow in the area where the nursing mother and child live. Exotic fruits and vegetables brought from afar are not acceptable. Citrus fruits should be excluded from the diet completely.
It’s good if the protein deficiency in a nursing mother’s body is replenished with products such as biokefir and bioyogurt.
Cheese can be eaten, but non-spicy varieties. It is best to prepare dishes by steaming or baking in the oven.
When limiting foods, you should still avoid the monotony of your diet in every possible way and change food combinations daily.
It is especially important to follow a hypoallergenic diet in the first months of a child’s life, especially in the first month of life. The fact is that the insidiousness of allergies can appear much later. The baby’s immune system is not sufficiently developed to fight the allergens entering his body, and therefore manifestations of allergies may appear at a later date.
A nursing mother, thinking that the absence of rashes on the child’s skin indicates the absence of allergies, begins to eat all foods without restrictions, which subsequently causes severe reactions in the baby’s body.
To avoid this, a hypoallergenic diet should be followed by all breastfeeding women without exception.
Hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers
Below are three groups of foods according to their degree of allergenicity - you need to use this list to create your own allergen-free diet.
1) Highly allergenic products
(they should be excluded from the diet of a nursing mother!).
— Seafood, many types of fish, fish caviar in any form.
— Spicy cheese, whole milk, cow's milk, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, natural yogurt, ayran, kefir.
- Bird's egg.
— Wheat porridge, millet porridge, rolled oats, oats, semolina.
— Smoked products: sausage cheese, salted smoked fish, meat, sausages, sausages, sausages, beef, pork.
— Marinades and canned food: stew, pickled vegetables and salads, canned fish, canned juices, etc.
— Spices, seasonings, salt, hot and spicy foods, pickles, sauces and ketchups, mayonnaise.
— Vegetables of red and bright color: pumpkin, tomatoes, carrots, sorrel, beets, celery, eggplant, bell pepper.
— Fruits and berries are orange, yellow and red, all citrus fruits.
— Carbonated drinks, products with flavors and dyes, chewing gum.
— Honey, marmalade, nuts, dried apricots, figs, dates, chocolate and caramel.
— Cocoa, coffee, strong tea.
— Exotic foods, alcohol.
2) Products of medium activity
This is a list of foods that can be consumed in the diet of a nursing mother, but only if the baby does not have rashes or dyspepsia.
All meat by-products.
— Apricots, red and black currants, bananas, cranberries, watermelons.
— Green bell pepper, all legumes, peas, potatoes.
— Herbal decoctions, compotes from permitted fruits.
— Rice, corn, buckwheat bread or biscuits.
3) Low-allergenic products
A nursing mother’s daily diet should consist of these products in various combinations in order to prevent allergic reactions in the baby’s body.
- Buckwheat, rice, corn.
— Chicken fillet, turkey fillet, rabbit.
— Cauliflower, white cabbage, Brussels sprouts, spinach, broccoli, zucchini, cucumbers, squash, turnips, green salad, dill, parsley.
— Olive and sunflower oil, butter.
— Green apples, pears, white currants, gooseberries, white cherries.
— Prunes, dried apples, pears.
— Rosehip decoction, compote of apples and pears (preferably without sugar).
— Weak green or black tea, still mineral water.
— Corn flakes without sugar.
Even when following a hypoallergenic diet, sometimes there are reactions even to foods on the low-allergenic food list. Allergies are an individual reaction and cannot be predicted.
The diet must be followed daily, without consuming anything from the list of highly allergenic foods, and in case of various rashes in the baby, foods from the middle list must also be excluded.
A hypoallergenic diet should be followed until the child reaches three months. After this age of the baby, the mother’s diet should be gradually expanded, introducing only 1 product every 2 weeks.
When following a hypoallergenic diet, you must, first of all, take into account the interests of the child, eat fresh and varied dishes from the permitted list. You should not eat the same dishes and foods every day.
Alcohol, foods with dyes, flavors, spices, as well as genetically modified foods are strictly excluded from the diet of a nursing mother. A hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers should be followed regularly to avoid allergic reactions in the baby.
Tags: Hypoallergenic diet, nursing mother, allergy, allergen, diet
www.vashaibolit.ru
Hypoallergenic menu for the week
1st day
Breakfast - oatmeal with apples and a piece of butter; Lunch - vegetable soup, baked or boiled beef; Dinner - boiled rice with a steam cutlet, pear and low-fat kefir.
2nd day
Breakfast - natural yogurt, a sandwich with butter and cheese; Lunch - vegetable soup and boiled chicken or turkey fillet; Dinner - mashed potatoes or zucchini and beef goulash. .
3rd day
Breakfast - cottage cheese casserole and banana; Lunch - vegetable broth with beef, toasted wheat bread; Dinner - vegetable stew and steamed cutlet, apple.
4th day
Breakfast - fruit salad with apple, pear and banana with natural yogurt dressing, a sandwich with butter; Lunch - vegetable broth and rice with a steamed cutlet; Dinner - buckwheat porridge and beef goulash.
5th day
Breakfast - cottage cheese with sour cream dressing with the addition of raisins or prunes; Lunch - soup with vegetables, a piece of beef, low-fat kefir and apple; Dinner - oatmeal or corn porridge, vegetable salad with cauliflower and herbs.
6th day
Breakfast - a boiled quail egg, a glass of fermented baked milk and a sandwich with butter; Lunch - vegetable soup, stew with beef and vegetables, banana; Dinner - boiled potatoes and a steamed cutlet.
7th day
Breakfast - rice porridge and pear; Lunch - vegetable broth and boiled meat; Dinner - casserole with meat and vegetables, natural yogurt.