.
Sooner or later, every person has to go to the dentist in order to have a tooth filled. In most cases, this procedure takes place without any problems, but there are exceptions. After the filling is installed, the gums may become swollen and red, pain and simply discomfort may occur in the area of the tooth. Sometimes this is temporary and ends after 2-3 days. But in some situations, an allergy to the filling material may manifest itself.
At this stage of time, such a problem exists only in isolated cases, and in order to prevent its development, you should regularly visit the dentist for a preventive examination, then the need for installing fillings will be significantly reduced.
Allergies on the lips after dental treatment are rare
Types of reactions to filling material
An allergic reaction is the body’s sensitivity to various substances (allergens), which causes negative reactions.
In this condition, the body produces antibodies that reduce or increase susceptibility to the allergen. But, despite the body’s fight against allergens and the use of only high-quality materials in dentistry, an allergic reaction can still occur.
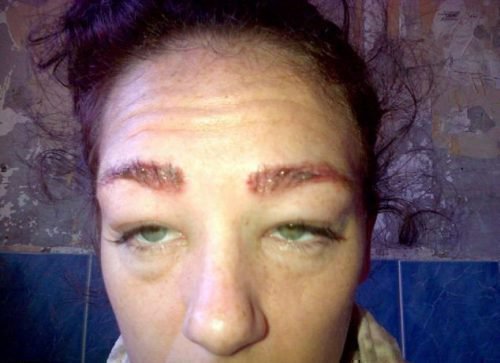
Swelling of the face after filling
Today, the following types of allergic reactions to materials used in the dental field are distinguished:
- toxic;
- carcinogenic;
- teratogenic;
- direct allergies;
- mutation.
Allergy to permanent filling
A permanent filling, if done well by a dentist, will last for many years and even decades. A wide variety of materials are used for fillings - from phosphate cement, usually used in the provision of free dental care, to the most modern light-curing composites of complex composition. And not a single filling material, cheap or expensive, unfortunately, excludes allergies. Despite the fact that entire corporations are trying to develop a completely hypoallergenic composition for fillings, the ideal does not yet exist. The individual reaction of the body is unpredictable.
Symptoms of allergies to components used in dentistry
If you are allergic to filling material, you may experience the following symptoms:
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- painful sensations in the area of the filled tooth, contributing to an increase in temperature;
- destruction of tissue near the tooth that has been filled.
Swelling of the gums and burning near the filling
There are less pronounced allergy reactions to a filling:
- sensation of metallic taste;
- there is a burning sensation in the cheeks, tongue and mucous membranes;
- there may be a bitter, sour and salty taste in the mouth;
- excessive salivation;
- sore throat;
- a rash may occur in the area of the cheeks, eyelids, nose and lips;
- there is a feeling as if the bronchi are compressed;
- asthmatic attacks occur;
- stomatitis develops.
Allergy to the palate - development of stomatitis
What to do if you suspect an allergy?
Do not self-medicate, do not use traditional medicine methods that are useless in this case. Constant exposure to an allergen can cause serious complications.
If pain and swelling persist, consult a dentist and rule out the possibility of an inflammatory process associated with dental intervention. If the dentist, after examining the oral cavity, confirms that the treatment was carried out correctly and the symptoms are not related to the manipulations performed, it is necessary to visit an allergist-immunologist to take a test to sample the filling material used for treatment and to select an alternative material.
How can you identify allergies before filling?
It is difficult to find out about an existing allergy to dental material, since this topic is poorly studied. The only way out is skin testing. To do this, take the material that will be used to install the filling, tie it with a thread to the wrist and leave it for a day. The appearance of itching or redness indicates the presence of an allergic reaction. It is important to understand that this experiment does not provide a 100% guarantee of veracity.
Regarding the manifestations of allergies, they can appear immediately or after a certain time.
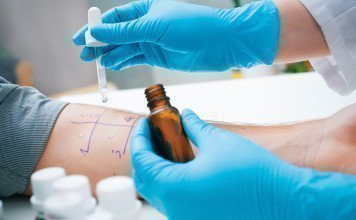
Allergy test for dental materials
But if there are any signs of it, you need to contact dentistry (to remove the structure) and an allergist (to identify the cause of this reaction).
The main thing is not to delay so that the condition does not worsen.
It should be understood that even if you have an allergic reaction to one type of filling material, you can opt for another material (even of lower quality). A professional dentist will find a solution to dental problems in any situation.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Dentistry is usually a dark forest for us. We go to the doctor only when it gets hot. And, closing our eyes, we wait for the unpleasant process to end. Of course there are people who are cautious. Close any hole in the tooth as soon as caries appears. And they do it right. An infection in the mouth causes many diseases. This applies to digestion, the trigeminal nerve, microflora, etc.
It's hard for allergy sufferers. The reaction to the filling can begin within a few hours or within a day. But dentists are different; some don’t want to stand on ceremony at all. And they need to be convinced that you have an allergy and you can’t cover your tooth with anything.
True, there are good clinics and good websites on the Internet, where everything is precisely spelled out. What kind of filling and in what cases is used to cover the tooth?
A tooth with a living nerve and a hole located close to the nerve is placed with a filling made of modern material Fuji 9 or 8. It is therapeutic and can be used as a lining. This kind of material is even shown to children.
If the nerve in the tooth has already been removed, and the hole is large, then there is no better material than charisma. This is a strong material, but it cannot be placed in a living tooth, because may be toxic to the nerve.
There are other hypoallergenic materials for fillings; they are from the glass ionomer series.
A small hole, close to the neck of the tooth under the gum or on the outer surface of the front tooth, is closed with polymers. This filling is strong and durable.
To remove the nerve, arsenic is no longer used for three days. In decent clinics they give an injection and then remove the nerve and clean the canals, put in a temporary filling and when the pain in the tooth calms down, they close it permanently.
Instead of an X-ray machine, a risograph is used. The radiation from this device is less harmful to health and the resulting image is larger.
I would like to give one more piece of advice: if a tooth hurts, do not rush to close it completely, it is better to put a temporary filling and wait for the pain to subside. If you continue to be very sick, do not expect that everything will go away on its own. Sometimes a tooth can be saved if the nerve is removed in time, but people get so carried away that all that remains is to remove the entire tooth. Do not rely on one doctor, ask, consult with different doctors, control the entire process, it is in your interests.
R.S. Allergy tests for anesthetics are carried out in the blood. They collect it from the veins into a test tube, then give out the finished solution. With this method, a person does not accumulate antibodies to allergens.
Simple and accessible Photoshop lessons Photoshop in Russian We make the skin in the photo perfect, turn the picture into a retro photo, metamorphoses with text - scratched, going into the distance, voluminous. The site has a library of cheat sheets for all subjects and a complete list of Russian universities.
Allergy to dental filling - symptoms and treatment - Allergy causes, symptoms, treatment A-Z
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Dental allergies are so rare that this allergic reaction has remained virtually unexplored to this day. Therefore, any swelling and redness after the installation of a dental filling can primarily be considered as an allergic reaction.
Allergic reactions occur differently in different people and occur to different irritants.
An allergy can occur to any composite material included in the filling.
The main symptoms – redness, swelling and pain in the area of the treated tooth – in the first few days are really similar to the symptoms of an inflammatory process in the gums or the body’s reaction to the manipulations performed.
But if within three to four days the pain does not calm down and the swelling does not subside, you need to consult a specialist. In this case, there are all the prerequisites for a possible allergic reaction.
The pain that occurs after treatment can have a different nature. This may be the body’s reaction to the measures taken by the dentist to clean the canals or remove nerves.
A reaction in the form of pain may occur after treatment of the gums or peri-gingival area. These painful sensations are temporary, and in the absence of irritation, the pain goes away over time.
The pain that occurs as a result of an allergy will persist as long as there is direct contact with the allergen.
Hypoallergenic filling materials
There are two types of fillings: temporary and permanent.
Temporary ones are installed so that after a while the doctor can easily remove it. It covers the medicine that is placed in the tooth. It is placed when the doctor is not sure that the tooth will have to be opened again after some time.
Permanent fillings, depending on their composition and structure, last for years or even decades. They are classified according to the materials from which they are made. These materials may be allergens.
Metal ceramics
The most hypoallergenic materials are metal ceramics, porcelain and gold. Allergic reactions to metal ceramics and porcelain are impossible, and allergies to gold are extremely rare.
Gold cast fillings rarely cause allergic reactions, but are very expensive. The service life of cast gold fillings is about 15 years. Porcelain fillings are made from regular porcelain. This material does not cause allergies.
Porcelain (ceramic) fillings are very durable, and their cost is no different from cast gold fillings. Unlike gold ones, they have one advantage - they do not have a sharp color difference from the natural enamel of the teeth, as happens with gold ones.
Amalgam filling
Amalgam filling
Amalgam fillings have a durable structure and their service life reaches 15 years. But they are the ones that can cause allergic reactions. They include silver, mercury, tin, copper and zinc.
Any of these substances, especially mercury, as well as substances that act as glue for these components, can serve as allergens.
A large amount of copper is added to modern amalgam; such amalgams are called high-copper.
Silver amalgam fillings can cause more than just allergies. When placing gold and silver fillings in two adjacent teeth, a conflict between the two metals may occur through saliva. A symptom of this conflict will be a sharp toothache, this phenomenon is also called galvanic shock.
Subsequently, the pain subsides, but the amalgam will deteriorate over time. Saliva, washing both metals, will create a galvanic couple in which gold is the cathode and silver is the anode. The anode will gradually give up electrons to the cathode, this will cause the anode (amalgam) to dissolve.
This phenomenon has nothing to do with allergies, but has similar symptoms.
Composite and glass ionomer filling
Composite filling
Composite fillings are often used in dental practice. Their main advantage is their low price. Its service life does not exceed 5 years. It consists of fine quartz sand and synthetic resin (plastic).
Allergies to composite fillings occur much more often than to amalgam. Synthetic resin can cause an allergic reaction. Synthetic resin is a completely artificial material in its composition.
Absolutely all synthetic resins are allergenic.
Glass ionomer filling is a modern type of dental cement. Previously, such cements were widely used in dental practice. Modern glass ionomer prevents the recurrence of caries. It can last quite a long time if you do not install it on the chewing surface of the tooth.
All composite fillings, which contain polymers for binding dental cements, as well as dyes that give artificial polymers the color of the enamel, are allergens.
All composite fillings will have high allergenic properties compared to others, regardless of the method of their hardening: chemical or light.
Symptoms of an allergy to a dental filling, treatment
The main symptom of an allergic reaction to filling material is local reactions, such as swelling of the gums, sharp or aching constant pain at the site of tooth treatment, and redness. In addition to local symptoms, symptoms common to an allergic reaction may occur, such as skin rashes, itching, and dry skin.
Treating allergies to filling material at home is not effective. Contacting a medical specialist will help identify the cause of the allergy, if any, through tests, tests, and consultations with specialists.
If an allergy to dental materials is confirmed, the dentist will replace the previously installed filling with a less allergenic one. In addition, to relieve local symptoms, medications will be prescribed to relieve irritation, swelling and pain.
Prescribed comprehensive treatment with medications and compliance with all preventive measures will help avoid a recurrent allergic reaction in the future.
); RESULTS µÑ‚Ñ Ñ Ð½Ð°Ñ Ñ‚Ð¾Ð»ÑŒÐºÐ¾ SOLUTION, CONDITION, CONTROL ¾Ñ тала s ¾Ð¹. RESEARCH,”word_count”:773,”direction”:”ltr”,”total_pages”:1,”rendered_pages”:1}
Source: https://allergia.my1.ru/news/allergija_na_zubnuju_plombu_simptomy_i_lechenie/2017-03-21-455
Complications when diagnosing allergies
At this stage of time, there are several nuances that can complicate the diagnosis of allergies:
- if the filling material is located outside the tooth;
- if the doctor is incompetent (this happens most often).
Rash around mouth after filling
In the modern world there are many traditional methods for treating allergies, but you should not trust them. It’s better to go to the doctor right away, it’s safer and will help solve problems faster.
It should be remembered that the key to quickly and effectively getting rid of an allergic reaction is identifying the cause that caused it.
An allergy can occur to any composite material included in the filling. The main symptoms – redness, swelling and pain in the area of the treated tooth – in the first few days are really similar to the symptoms of an inflammatory process in the gums or the body’s reaction to the manipulations performed. But if within three to four days the pain does not calm down and the swelling does not subside, you need to consult a specialist. In this case, there are all the prerequisites for a possible allergic reaction.
The pain that occurs after treatment can have a different nature. This may be the body’s reaction to the measures taken by the dentist to clean the canals or remove nerves. A reaction in the form of pain may occur after treatment of the gums or peri-gingival area. These painful sensations are temporary, and in the absence of irritation, the pain goes away over time. The pain that occurs as a result of an allergy will persist as long as there is direct contact with the allergen.
Your IP address is blocked.
Allergology studies a person’s relationship with the outside world and forms of disruption of the immune system’s response when the patient’s body becomes hypersensitive to certain substances. Allergic diseases, such as bronchial asthma. Allergic diseases, such as bronchial asthma, have been known since ancient times, but allergology became an independent medical and scientific discipline only in the middle of the twentieth century. In recent decades, allergic diseases have become a global medical and social problem.
There is a constant increase in incidence. Currently, there is an increase in the number of severe forms of allergic diseases, which leads to temporary disability, decreased quality of life and even disability.
In this regard, early diagnosis of allergic diseases, correct methods of treatment and prevention are of great importance. An allergen is a substance that enters the body and causes a certain type of immune response, resulting in damage to body tissue.
We are surrounded by 5 million xenobiotics, many of them are allergens. The allergist's task is to identify the causative allergen. Allergic diseases are a group of diseases, the development of which is based on damage caused by the immune reaction to exogenous allergens.
The classification of allergic reactions proposed by P. Cell and R. Coombs has become widespread in the world. It is based on the pathogenetic principle. The classification is based on the characteristics of immune mechanisms. Type I - reaginic, anaphylactic. IgE-class antibodies and, less commonly, IgG antibodies participate in the development of the reaction. Clinical manifestations: bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis. Type II - cytotoxic. It is called a cytotoxic type of tissue damage because antibodies formed to cell antigens combine with cells and cause their damage and even lysis through a cytolytic effect.
In the clinic, the cytotoxic type of reaction can be one of the manifestations of drug allergies in the form of leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, etc. The immune mechanism of the reaction is caused by IgG and IgM antibodies.
Type III - damage by immune complexes. Synonyms: immune complex type, Arthus phenomenon. IgG and IgM antibodies are involved in the development of the reaction. Type III allergic reactions are leading in the development of serum sickness, exogenous allergic alveolitis and other diseases.
Type IV is a delayed-type allergic reaction, the development of which involves sensitized lymphocytes. Allergic reactions occur in sensitized people 24-48 hours after contact with the allergen.
The typical clinical manifestation is contact dermatitis. Thus, an allergy is an immune reaction of the body, accompanied by damage to its own tissue. In recent years, an increase in life expectancy, new opportunities that have appeared in ordontology - all this makes us think about the mechanisms of occurrence of certain complications when using materials for dentures.
Metal and plastic dentures can cause not only allergic, but also toxic stomatitis, as well as mechanical irritation. There are certain requirements for materials used for dental prosthetics. Among other things, hardness, aesthetics, etc. These factors can enhance the processes of dissolution and oxidation of the metal. Dentures should not have a harmful effect on the oral mucosa and the body as a whole. Materials that are electrochemically neutral relative to each other should be selected.
For the manufacture of metal prostheses, about 20 metals are used - stainless steels, cobalt chrome, silver-palladium alloys, alloys based on gold and platinum. For metal-ceramics - nickel-based alloys, which include iron, chromium, titanium, manganese, silicon, molybdenum, cobalt, palladium, zinc, silver, gold and other metals. To join dental alloy parts, solders containing silver, copper, manganese, zinc, magnesium, cadmium and other elements are used.
Low-melting alloys used for dies contain lead, tin, bismuth and some other substances. The development of allergies is facilitated by the severity of electrochemical corrosion processes in the oral cavity, which depends on the structure of alloys, heterogeneity of metals, temperature conditions during the manufacture of metal dentures, the chemistry of saliva and other factors.
Nickel is a component of stainless steel used for orthopedic treatment. In the oral cavity, nickel corrodes under the influence of saliva, causing allergic reactions. For patients with a history of developing nickel dermatitis from wearing watch bracelets, clothing parts, zippers, fasteners, or jewelry, the use of this material is not indicated.
Chromium is used for dental prosthetics in the form of cobalt chromium and other alloys. It can have a wide range of effects on the human body, including causing allergic reactions. Allergic complications can occur when using manganese and cobalt. In patients with allergic stomatitis caused by stainless steel dentures, antihapten antibodies to manganese are found in the blood.
An insoluble aluminum compound, kaolin aluminum silicate, is used in dentistry as a filling material. Iron is a metal characterized by corrosion resistance. Does not cause allergic complications. Copper is a component of gold and gold alloys, solders, and copper amalgam. Electrochemical processes between metal structures in the oral cavity lead to an increase in copper content in saliva, gastric juice and blood.
Toxic reactions are possible. Zinc oxide is part of dental cement, dental amalgams, solders, and brass. Zinc is more active than iron. In the presence of moisture, these metals form a microgalvanic couple in which zinc is the anode, therefore, when metal dentures corrode in the oral cavity, zinc dissolves first.
The toxicity of zinc compounds when ingested is low. When using metal prostheses, the lead content in saliva is increased. Lead is a corrosive metal and has a toxic effect. Tin is part of low-melting alloys for models used for making crowns.
Tin compounds are toxic and are not used in medicine. Titanium is a component of stainless steel for dentures. The biological role of titanium has not been sufficiently studied.
Silver is part of the alloys silver-palladium, gold standard, etc. Considering the bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect of silver, the silver-palladium alloy is recommended for use in chronic diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract. Gold has high corrosion resistance and is included in gold alloys and solders for dentures.
Platinum metals palladium, platinum, etc. Palladium is part of the silver-palladium alloy for dentures. Platinum group metals, including palladium, are allergens.
Currently, superelastic materials with shape memory have been created. This direction is very promising and determines the future of orthodontics. An example is titanium nickelide Ti, Ni, Mo, Fe. The greatest role in the occurrence of sensitization to metal prostheses is played by the haptens they contain: nickel, chromium, cobalt, and manganese. They become antigens only after combining with proteins of body tissues. As a result, so-called conjugated antigens are formed.
Plastics used in dentistry for orthopedic treatment are high-polymer organic compounds. Acrylic plastic can cause allergic and toxic stomatitis. Let us note a number of nonspecific factors that contribute to the penetration of hapten from the oral cavity into the blood, increasing its dose and thereby increasing the risk of developing an allergic disease. During inflammation, the barrier function of the mucous membrane is disrupted. The permeability of the mucosa is directly dependent on the chemistry of saliva.
It is necessary to differentiate between allergic stomatitis caused by the prosthesis, stomatitis of gastroenterological origin, as well as candidiasis. Stomatitis may be a manifestation of an endocrine system disease: diabetes, pathological menopause, cutaneous lichen planus or systemic Sjögren's syndrome disease. Complaints may be due to a decrease in occlusal height, Costain's syndrome, manifestations of galvanism, and toxic reactions.
Galvanism occurs after the first contact of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity with irritants. Such stimuli are a variety of microcurrent potentials between dissimilar materials. Allergic stomatitis should be distinguished from toxic reactions to metal prostheses.
Toxic stomatitis is characterized by the rapid development of stomatitis, gingivitis, and glossitis after orthopedic treatment. A qualitative and quantitative assessment of the spectrogram of saliva is carried out to identify the toxic dose of heavy metals. Assessing the quality and correctness of the designs of removable dentures in the oral cavity helps to differentiate between mechanical irritation and toxic and allergic stomatitis. To diagnose the nature of complications, it is necessary to collect a dental and allergy history.
An allergic history includes identifying the patient’s hereditary predisposition to allergic diseases. It is necessary to find out whether the patient suffers from allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, eczema, drug and food allergies, etc. It is necessary to examine the patient, including the oral cavity.
Elimination and exposure tests are widely used in orthopedic dentistry. When removing a denture, etc. To confirm the allergic nature of the disease, it is necessary to conduct additional immunological tests and, in particular, for the presence of antibodies to plastic and metals.