Causes
The disease is associated with a genetic factor, but also occurs in people with uncomplicated heredity.
Its provocateurs can be:
- vitamin deficiency;
- weakened immune system;
- mechanical damage to the skin;
- intoxication;
- poor nutrition and, as a consequence, gastrointestinal pathology;
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- stress.
Scientists offer 2 views on the nature of plaque psoriasis:
- Functional disorders in cellular structures, leading to uncontrolled mitosis (indirect cell division).
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
Both theories do not reveal the essence of the pathological changes occurring in the body of patients. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established.
Features of lipid metabolism in patients
Until recently, or rather until the 90s of the twentieth century, it was the violation of water-fat metabolism that no one took into account as a factor in the development of psoriasis. We talked about metabolic disorders throughout the body.
At the level of cellular research, it was confirmed that the composition of psoriatic plaques includes essential fatty acids, which, by the way, are also involved in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
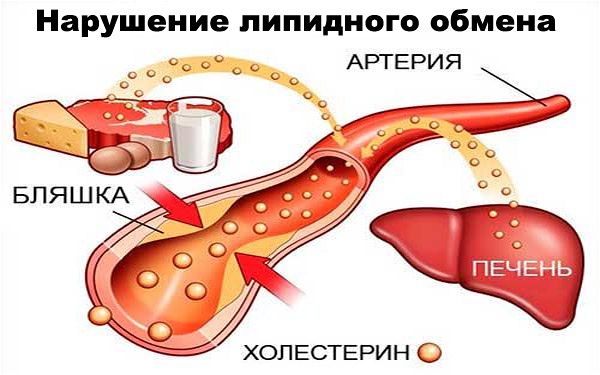
You don’t have to be a genius not to make a connection between atherosclerosis, psoriasis, and impaired water-fat metabolism.
Most patients with psoriasis have problems with the cardiovascular system.
Kinds
There are the following types of plaque psoriasis:
- oyster, with a concave spot center;
- rupoid with cone-shaped or saucer-shaped lesions;
- ring-shaped, which is characterized by partial resolution of the center of the plaque;
- gyrata - a variety characterized by a peripheral spiral distribution of plaques;
- geographical, the location of the papules resembles a map;
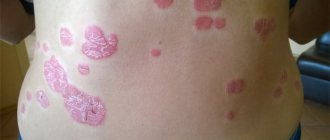
- ivory with large plaques, on top of which dense, thickened scales are formed.
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic disease. Stages (progressive, stationary, regression) replace each other. After an exacerbation, remission occurs.
Stages of plaque psoriasis
There are three key stages of psoriasis:
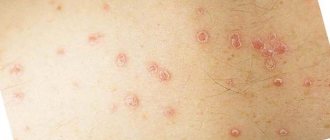
- Initial or progressive. In certain areas of the skin, you may notice the appearance of reddish rashes. Depending on their size, they are called papules or plaques. They are small in size and located separately from each other. Subsequently, they begin to increase in size. Sometimes there is itching or burning. You can look at images of psoriasis on the Internet; photos of plaques will demonstrate the symptoms better than a description.
- Stationary. New rashes do not appear at this stage; old ones may increase in size. Some of them combine with neighboring ones, forming larger formations. Excessive peeling can be seen on top of the rash. The peeling scales have a silvery tint and are densely located.
- Latest or regressing. Gradually the spots fade and disappear completely. The peeling also goes away smoothly. After the rash disappears, there may remain a pigmented area or a slightly lighter area compared to the surrounding skin.
All three stages are repeated in the sequence described above. However, if you start treatment early, you can stop the disease in the first stage or significantly reduce all three stages. For clarity, you can see photos of common plaque psoriasis at different stages.
Since psoriasis is a chronic disease, its course is cyclical: outbreaks of rashes alternate with periods of remission. The duration of the latter depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body, his lifestyle and the quality of treatment.
Forms
The severity of the disease depends on a number of factors, including:
- high uric acid levels;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased ESR levels;
- degree of pathogenesis;
- affected area.
The mild form is characterized by small papules, occupying up to 3% of the skin surface. After a slight increase in spots, pathogenesis stops. The psoriatic plaque in the center becomes lighter and then completely disappears.
With moderate severity, the skin is affected by 3-10%. Primary elements grow and form groups that merge with neighboring ones. Large plaques covered with scales form. The spots may be pale pink or deep red. Microtraumas, scratching, and poor nutrition lead to the spread of psoriatic elements. The disease often worsens in winter.
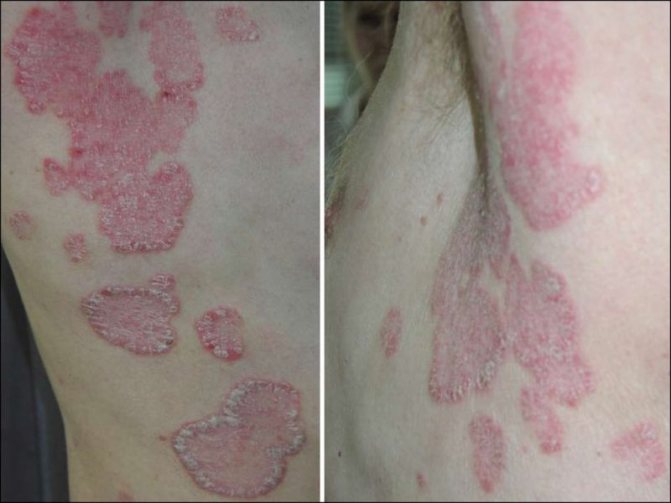
If psoriatic plaques cover more than 10% of the skin, then a severe or widespread form of the disease is diagnosed. Causes may be related to allergies to medications, severe infections, or severe stress. The spots have different shapes.
Obesity, pathologies of the endocrine and immune systems lead to oozing, yellowish-gray scales that stick together to form crusts. In such cases, we are talking about an exudative form, which most often affects children, elderly patients and workers in the cold.
Symptoms
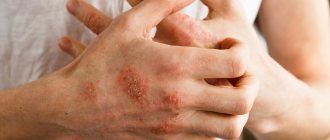
The first symptom in the medical history is the appearance of pink or red rashes on the skin. Inflammation is accompanied by itching and peeling in the affected area. Typically, psoriasis affects the scalp and the skin over large joints.
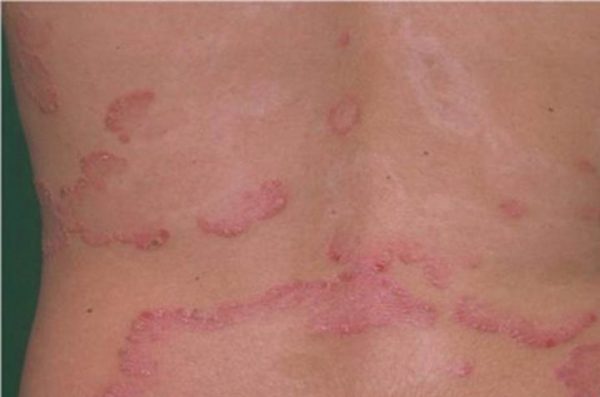
According to the degree of prevalence of the lesion, there are:
- limited psoriasis, which occupies up to 10% of the total body area;
- widespread psoriasis, covering more than 10% of the skin;
- universal psoriasis - it affects the entire or almost entire surface of the skin.
The disease is characterized by such symptoms as the psoriatic triad. The phenomenon is a set of consistent signs in the medical history that can be used to diagnose plaque psoriasis. The symptom manifests itself as follows:
- When the plaque is scraped, the scales are separated by “chips.”
- After the scales separate, a thin film forms on the skin.
- With further scraping of the papule, bleeding occurs.
Dividing the disease into stages helps determine the treatment method. In its development, widespread psoriasis sequentially goes through the following stages:
- progressive;
- stationary;
- regressing.
Plaque parapsoriasis or Broca's disease
Severe form, which can be provoked by:
- viral and bacterial infections;
- immune disorders;
- vascular changes;
- allergic conditions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands.
Broca's disease affects mainly men over the age of 25, most often over 60. In the photo, plaque parapsoriasis appears as yellowish-pink or yellowish-brown spots of various shapes, often strip-like with irregular outlines. They don't itch. The patient's general condition remains satisfactory. Small elements can merge into large ones.
Plaques, as a rule, do not resolve in their central part. There is almost no peeling. The skin usually does not atrophy. In summer, the spots partially disappear, but as the weather gets colder they appear again. The rash is symmetrical, appears on the legs and torso, less often on the arms.
Remission may be incomplete, and the disease rarely resolves completely. More often it lasts for months or years.
Types of plaque parapsoriasis
There are 2 types of Broca's disease:
- Large plaque parapsoriasis with flat spotty rashes with clear boundaries and different shapes. The diameter of the elements is on average 5-10 cm, sometimes reaching 30 cm. The scales are small, pityriasis-like. The spots are localized on areas of the body that often come into contact with clothing or rub against each other. Possible damage to the skin of the mammary glands.
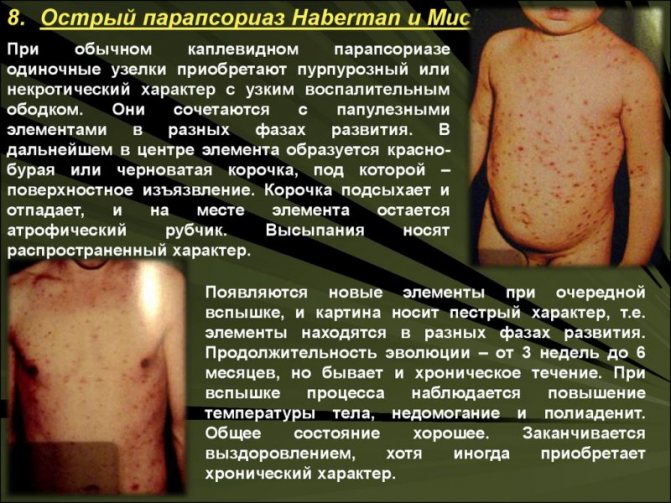
The large plaque form of parapsoriasis can last for decades. In 10-30% of cases, it transforms into mycosis.
Over time, to a triad of signs, including:
- mottled pigmentation;
- wrinkled skin;
- telangiectasia (non-inflammatory dilatation of blood vessels) is accompanied by itching and swelling of the affected dermis. Malignant skin lymphoma cannot be excluded.
- Small plaque parapsoriasis manifests itself in the form of smooth, slightly rough stripes up to 5 cm in diameter, with pointed ends. They can remain unchanged for quite a long time: months or years.
This form does not degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
be careful
People suffering from psoriasis often make one big mistake:
The patient is trying to eliminate the external signs of the disease, but eliminating the external manifestations of psoriasis does not solve the problem from the inside.
Roughly speaking, even if it is possible to remove the signs of psoriasis from the outside and put the skin in order, inside the body the disease continues to devour the autoimmune system, which provokes severe diseases, many of which are fatal. Particularly scary is the fact that psoriasis can provoke cancerous tumors.
The only remedy that is currently available for self-use by patients with psoriasis is the special product “PsoriControl”, which is available at a discounted price. Read the details in the official source.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that manifests itself in skin lesions, and this lesion is not transmitted from person to person, that is, it is not infectious. Today, doctors have classified several types of psoriasis, but they are all characterized by the presence of inflammation on the skin, which is covered with white scales, sometimes with a silvery tint. Psoriasis appears in people at any age, it can even occur in a baby, but it can just as easily make itself felt for the first time in a 60-year-old person.
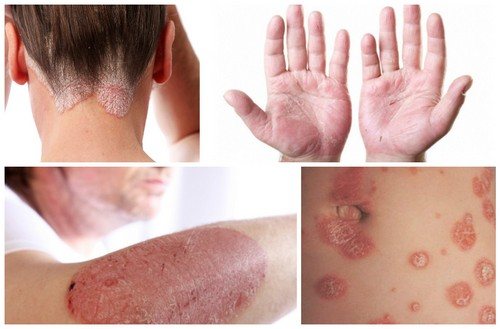
Psoriasis is a serious disease, and today medicine cannot cure it completely. This has a negative impact on a person’s psycho-emotional state, which in turn increases the manifestations of psoriasis, since it is one of the manifestations of stress.
Treatment of psoriasis is purely individual, but it is necessary to treat psoriasis, since it can lead to a number of complications in the functioning of joints, muscles and internal organs. Today there are several classifications of types of psoriasis that are used in the medical literature. All of them are based on certain features of the manifestation of the disease.
Types of psoriasis and their symptoms
Most often, doctors divide psoriasis into two forms: pustular and non-pustular psoriasis.
Pustular psoriasis
This form of psoriasis is considered very rare and is very difficult for patients to tolerate. With this form of psoriasis, blisters (pustules) appear on the skin, completely filled with clear liquid (exudate). Around these pustules, the skin begins to take on a reddish tint, thickens, and even begins to peel off. An infection can get into the cavity of the pustules and in this case they are filled with pus. Most often, pustular psoriasis appears on a person's arms and legs, although in some particularly severe cases, pustules can cover a variety of parts of the body and even merge, forming large areas of lesions.
Pustular psoriasis, in turn, can be divided into subtypes:
- Generalized pustular psoriasis. In the medical literature, this form of psoriasis may be called Tsumbusch psoriasis, named after the physician who described this form of the disease in 1909. This type of psoriasis always begins suddenly, but one of the conditions for its occurrence is the presence of other forms of psoriasis. In addition to the rash, the patient’s body temperature rises, there is a feeling of weakness in the body, and the number of leukocytes in the blood test increases. This form is extremely dangerous as it can be fatal;
- Generalized acrodermatitis Allopeau. The peculiarity of this form is that it is localized on the feet and hands of a person. Pustules in this form are small and form crusts after opening. It is believed that the development of this form of psoriasis is often preceded by various types of trauma. There is no threat to life with this form of the disease;
- Localized acrodermatitis Allopeau. This form appears only in the genital area;
- Impetigo herpetiformis. A very specific form of psoriasis that appears in women during pregnancy. The main locations of the rash are the groin area and the armpit area. In some cases, pustules may form on the inner thighs;
- Palmoplantar psoriasis. This form has several synonymous names, palmoplantar or Barber psoriasis. This form is characterized by the presence of pustules in the area of the hands and feet. When dry, pustules can form dense brown crusts. Without treatment, this form of psoriasis is quite capable of capturing more and more new territories, spreading throughout the body.
Nonpustular psoriasis
This type of psoriasis causes problems for the vast majority of people diagnosed with this disease.
This type of psoriasis includes:
- Vulgar (plaque-like) psoriasis. This disease occurs in 90-95% of cases. The disease manifests itself in the form of plaques covered with scales. Plaques can coalesce and form large lesions. The reason for the formation of plaques is the excessively rapid division of skin cells (in 5 days instead of the required 25);
- Psoriatic erythroderma (erythrodermic psoriasis). This form is considered generalized. An exacerbation occurs suddenly, although it is often seasonal. It manifests itself not only in a rash of plaques, but is also accompanied by fever, weakness, severe peeling and peeling of the skin over large areas. Often accompanied by hair loss and nail psoriasis.
Separate types of psoriasis that are not included in the general classification
Are there several types of psoriasis? do not fit into the division into pustular and non-pustular psoriasis.
These forms include:
- Seborrhea-like psoriasis. This disease occurs when seborrhea already exists on the hair-covered part of the head. The disease “sinks” to the upper chest and back, as well as to the face and behind-the-ear areas;
- Drug-induced psoriasis. This form manifests itself as a result of uncontrolled use of drugs and is one of the forms of an allergic reaction;
- Inverse psoriasis. A disease that is localized in areas of the skin on surfaces capable of bending. This is the area of the elbow, under the knee, in the groin folds, and also in women on the skin under the breasts.
Classification of psoriasis according to the severity of the disease
Doctors divide psoriasis according to its severity. This parameter refers to the percentage of skin surface area covered by psoriasis.
In this classification it is customary to distinguish:
- Mild form, up to 3% damage to the skin;
- Moderate form, from 3 to 10% of the skin surface affected;
- A severe form, in which 11 percent or more of the patient’s skin surface is affected.
Types of psoriasis by type of rash
Also, in some cases, it is customary to classify psoriasis according to the shape of the rash itself.
In this case, the following are distinguished:
Have you been trying to get rid of PSORIASIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of psoriasis by taking it every day...
Read more "
- Spot psoriasis in which the size of the rash does not exceed 5 millimeters;
- Guttate psoriasis, in which the rash is shaped like a drop of liquid measuring 7 to 8 millimeters;
- Coin-shaped psoriasis, in which the plaques are especially large and reach 4-5 centimeters in diameter.
Psoriatic arthritis and nail psoriasis
Psoriatic arthritis is a dangerous disease because, if not adequately treated, it can cause disability. With this disease, connective tissue in the joints is damaged, and the important thing is that the patient may not have external manifestations of psoriasis. The small joints in the hands and feet are most often affected, but psoriatic arthritis can affect the knee, shoulder, and even hip joints.
As for nail psoriasis or onychodystrophy, it can occur in different ways:
- A dotted form, in which several “dents” appear on the nail plate and the surface of the nail begins to resemble a thimble, the nail becomes brittle and dull;
- The atrophic form is characterized by a gradual thinning of the nail plate itself, followed by its complete disappearance;
- The hypertrophic form is determined by excessive keratinization of the epithelium under the nail plate itself. At the same time, the shape of the plate changes and takes on the most unpredictable shapes.
Types of psoriasis in children
Psoriasis also occurs in children, although not all forms of psoriasis characteristic of adults can appear in children.
The most common are:
- Plaque psoriasis. Occurs most often. Appears in the form of red plaques covered with scales. For a child, this form of psoriasis presents a lot of inconvenience and discomfort, especially if these plaques appear on the knees and elbows, as well as on the hairy part of the head;
- Guttate psoriasis occurs suddenly and appears as small droplet-shaped spots that usually scatter throughout the body. This form may go away on its own, even without treatment, but there is a chance that the rash will turn into plaques. Therefore, it is best to see a doctor if you have guttate psoriasis;
- Pustular psoriasis, unfortunately, can also appear in children, especially in older age. It appears in the form of bubbles with liquid, often accompanied by swelling of the skin and inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- Of particular danger is generalized pustular psoriasis, which can cause complications in any system of internal organs;
- Erythrodermic psoriasis in children manifests itself in the form of inflammation and peeling of the skin. Such diseases can be provoked by temperature disturbances, both in the direction of high and low temperatures;
- Arthropathic psoriasis occurs with a frequency of one case in ten, which is a fairly high rate. Appears as swelling of the joints of the fingers or toes. Sometimes accompanied by conjunctivitis;
- Psoriasis on the flexor surfaces in children appears quite often. As a rule, it appears in children in the groin and genital area.
Psoriasis on the part of the scalp that is covered with hair causes a lot of trouble for children. If you suspect this type of psoriasis, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. The particular danger in this case is not so much the psoriasis itself, but the emergence of an inferiority complex in the child. It should be understood that the cause of the disease lies in the disruption of processes in the immune system and has nothing to do with infection.
Effective treatment of psoriasis
In the treatment of psoriasis, modern medicine uses a fairly wide arsenal of medications: from ointments and creams to immunostimulants and immunosuppressants.
Biotherapy
Today, one of the most modern methods of treating psoriasis is treatment with biological products. These include Enbrel and Remicade. Both drugs are administered intravenously and the dosage and course of treatment are calculated based on the severity of the lesion, as well as the general condition of the patient. The peculiarity of the use of these drugs is that when using them, you have to completely abandon drugs that regulate the functioning of the immune system.
However, despite the risks, the results of treatment with these drugs are worth it. Enbrel is very effective for psoriatic arthritis. However, it is not recommended to use the drug for multiple sclerosis or heart failure. Remicade is recommended for severe forms of psoriasis when large areas are affected by plaques or pustules.
The drug must be used under the supervision of a doctor. In the event of any infectious disease that occurs during treatment with Remicad, the use of the biological product should be stopped immediately.
Physiotherapy and therapeutic approach
The use of ultraviolet rays in the treatment of psoriasis has been around for decades, but the technique is constantly being improved. Today it is precisely established that UV rays with a wavelength of 360 nanometers are most effective. This treatment is especially effective in combination with modern drugs Sandimmun or Tigazon, which are photosensitizers. Another modern development recommends using UV rays with a wavelength of 315 nanometers. In this case, photosensitizers are not needed, and about 30 procedures are necessary to achieve a positive result.
Treatment with retinoids
This technique appeared not so long ago, about twenty years ago, and during this time it has gone through significant stages of improvement. The active ingredient in this technique is retinol, a fat-soluble vitamin A. The drugs Acitretin and Etretinate are today the newest drugs for retinoid treatment; their rate of excretion from the body is 28 times lower than regular retinol. According to observational results, improvement in treatment with retinols occurs in 84% of cases.
Treatment of psoriasis with folk remedies
When treating a disease such as psoriasis with folk remedies, it is necessary to use not one, but several remedies with different methods of application, while you need to monitor your condition and choose the best for yourself.
To get started, you can try these recipes:
- A decoction of flax seeds. To prepare the decoction, brew one glass of seeds with one glass of boiling water and let it brew overnight in a thermos. You should drink one half of the decoction in the morning on an empty stomach and the other half at night before going to bed. The course of treatment is ten days;
- In the initial stages of psoriasis, a radical treatment method is recommended with birch tar, which can be bought at the pharmacy. The patient smears all the plaques with tar and waits for an hour. After this, the patient must be washed and an infusion of celandine applied to the plaques. There is no need to wash off the infusion, but wait until it dries. The course consists of 15 procedures. For many, after such treatment, psoriasis disappears for years;
- The second option for using birch tar involves mixing it with birch ash in a ratio of one part ash to three parts tar. The whole procedure is the same as in the previous case, however, a decoction of birch buds is recommended as an auxiliary remedy. To prepare such a decoction you will need two tablespoons of birch buds infused in a glass of boiling water in a water bath for half an hour. Take this infusion before meals, 1/3 cup;
- You can also treat psoriasis with celery. To do this, the root of the plant is crushed and the resulting paste is applied to the sore spots for two hours. Repeat the procedure for two months. At the same time, it is recommended to drink two tablespoons of celery juice three times a day before meals;
- Treatment with clover flowers is considered a fairly effective treatment for the disease. To do this, 2-3 tablespoons of clover should be wrapped in gauze and doused with boiling water. Let stand for no more than one minute and apply the steamed flowers to the sore spot. The decoction can be drunk;
- Cabbage brine has long been used to treat various diseases, including psoriasis. The patient is recommended to lubricate all sore spots with brine at night for seven days in a row, which should not be washed off under any circumstances. You can repeat the course of treatment after a month;
- Old medical books also contain a recipe for ointment made from egg yolks for psoriasis. To do this, homemade chicken eggs are hard-boiled. Then the yolk is separated from the white. The resulting yolks are crushed and fried over low heat in a frying pan without oil. As a result, after about 40-45 minutes, a reddish liquid forms, which must be collected. 20 large eggs yield no more than 0.5 tablespoons of oil. This oil should be applied to the affected areas once or twice and the psoriasis will recede;
- The most commonly used method of treating psoriasis at home is to lubricate the affected areas with linseed oil or sea buckthorn oil. Apply to the affected areas two to three times a day for fifteen days;
- For minor rashes, ordinary pink potatoes can help the patient. It is grated and applied to the affected area for two hours. The course of treatment is fifteen days;
- The most popular component for treating psoriasis at home is solid oil. Sometimes it is replaced with Vaseline or pork fat, but the effect of this decreases. The simplest ointment is a mixture of 0.5 kilograms of solid oil, two tablespoons of honey and half a tube of baby cream. Apply this cream to the affected areas once a day, or twice in case of significant damage. To enhance the effect of the medicinal properties of this ointment, it is recommended to add the white of one chicken egg, two teaspoons of chestnut fruit, one teaspoon of sulfur and two teaspoons of rose hip ash. If improvement has begun, but the effect is insufficient, add celandine in the form of crushed herbs in the amount of three tablespoons to the same composition. The course of treatment is at least two months;
- Propolis ointment is made as follows: 15 grams of propolis are placed in 100 grams of butter melted in a water bath. After obtaining a homogeneous mixture, add 3 capsules of vitamin A. The resulting ointment is applied at night and secured with a plaster or bandages for two weeks.
Prevention of psoriasis
Prevention of psoriasis is quite simple and at the same time quite strict in terms of its implementation. First of all, you should remember that the patient must constantly take care of his skin, and no one can do this better than himself. The skin should be constantly moisturized. In addition, the skin should not be exposed to extremely high or low temperatures.
The second requirement is maintaining a healthy lifestyle without unnecessary stress, adequate physical activity and strict adherence to a diet. Also, for the prevention of psoriasis, spa treatment is very important, during which the body gains strength to fight the disease.
6 − = five
I accept the user agreement and privacy policy
- Categories
- It is important to know
- Diet
- Other means
- Crema
- Treatment
- Ointments
- Folk remedies
- Reviews
- Symptoms and signs
- Pills
- Photo
- Shampoos
Types and stages
- Recent Entries
- Effective irradiators and lamps for psoriasis at home
- What drugs to use against psoriasis
How to use acid for psoriasis
Headings Select a heading Important to know Types and stages Diet Other remedies Creams Treatment Ointments Folk remedies Reviews Symptoms and signs Tablets Photos Shampoos
Treatment
Treatment methods are selected on an individual basis.
The doctor takes into account:
- prevalence of rashes;
- severity of pathology;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
In case of exacerbation, prolonged progression of the disease, or severe forms, treatment of plaque psoriasis in a hospital setting is indicated, where measures are taken to detoxify the body, local therapeutic effects, drug treatment, and courses of B vitamins.
Hormonal drugs are practically not used, as they have side effects and lead to serious complications. Glucocorticosteroids are used if all other methods have failed. These can be emulsions, lotions, gels, ointments, such as Hydrocortisone, Elokom. In case of exacerbation, hormonal drugs are taken orally.
Treatment with an excimer laser (308 nm) is possible.
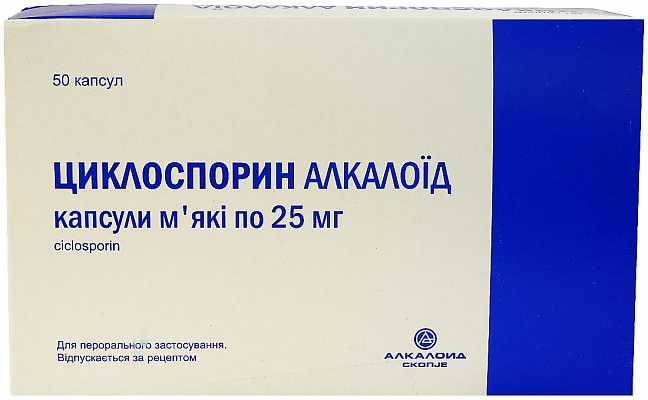
For severe forms of plaque psoriasis, cytostatics are taken:
- Methotrexate;
- Cyclosporine, as well as retinoids (Acitretin).
Modern drugs include Infliximab and Efalizumab, which contain monoclonal antibodies.
For local effects, naftalan paste and lanolin cream are used.
Moderate and localized forms of small plaque psoriasis are treated on an outpatient basis.
Non-hormonal drugs are used for this:
- Tazarotene;
- Calcipotriol;
- Anthralen;
- Dithranol, etc.
Treatment with Locacorten and Belosalik leads to good results.
Ultraviolet light causes an exacerbation in some patients with plaque parapsoriasis, while in others it leads to remission. If the disease debuted after a viral infection, antibacterial or antiviral drugs are used, in particular Azithromycin.
A psychologist helps patients with social adaptation; relaxing techniques and auto-training are effective.
Drug therapy
At the initial stage of treatment of vulgar psoriasis, experts recommend the use of external preparations that have a semi-liquid base (creams, ointments). Medicines may or may not be hormonal. Non-hormonal drugs prescribed for vulgar psoriasis include the following ointments:
- Salicylic ointment;
- Zinc ointment;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Naphthalene ointment.
The main advantage of the non-hormonal range of drugs is that they do not lead to addiction, however, their effectiveness is lower than that of the hormonal range of medications. Thus, these remedies are best used when plaque psoriasis or any other type of pathology is at the initial stage.
Of the ointments for lichen planus, the following hormonal-based drugs are most often prescribed:
- Cortisone;
- Elokom;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone ointment.
They are characterized by high efficiency, but can cause some negative reactions from the body.
Folk remedies
At home, you can take calendula and St. John's wort orally in the form of infusions, use ointments containing their extracts, as well as:
- celandine;
- birch bark;
- liquorice root;
- chamomile flowers;
- sequence;
- Kalanchoe;
- eucalyptus.

Before using any folk remedies, the approval of the attending dermatologist is required.
Diet
Treatment is effective if the patient normalizes his daily routine and adjusts his diet. The diet should not contain refractory fats and easily digestible carbohydrates.
You should avoid a number of foods, including:
- smoked meats;
- marinades;
- semi-finished products containing dyes and food additives;
- highly allergenic products;
- spices;
- spicy dishes;
- salt;
- alcohol.
The treatment will be more effective if you take warm baths with calendula, pine needles, and chamomile. It is better not to use washcloths; pat your body dry with a towel. When rubbing, microtraumas may occur, which increases the risk of secondary infection.
It is more difficult to treat plaque parapsoriasis on the head. The bristles on hair brushes should be natural, combs should be made of wood. Drying hair with a hairdryer, using curlers and curling irons is prohibited. Wash your hair, alternating regular and medicated shampoos.

For ordinary psoriasis, swimming in the sea and sunbathing (2 times a day for half an hour) are useful. Specialized sanatoriums offer patients, especially during remission, balneo and mud treatments.
Physiotherapy methods
Part of the complex treatment includes physiotherapy, for example:
- PUVA therapy;
- exposure to ultraviolet light (contraindicated during exacerbation);
- magnetic therapy;
- electrosleep.
Complex treatment, including all of the above methods, gives a lasting effect, eliminates or mitigates symptoms.
With timely treatment of plaque psoriasis, it is possible to achieve long-term stable remission and avoid complications. Specific prevention of scaly lichen has not been developed. It simply doesn't exist. When the disease debuts, the doctor prescribes sedative medications, vitamins, as well as treatment that corrects pathologies that provoke exacerbation of psoriasis.
Diagnostics
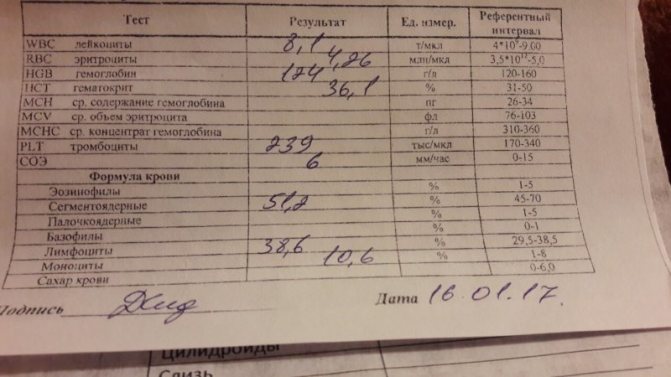
In most cases, in order to diagnose the vulgar type, it is enough for the doctor to conduct an external examination of the patient. There are no special diagnostic procedures other than a standard blood test.
However, at a progressive stage, abnormalities can be found in the blood, due to which specialists pay attention to the presence of a pathological process: systemic autoimmune, inflammatory, or rheumatic (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytosis, etc.), as well as disorders of endocrine function.
In exceptional cases, a skin biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other possible diseases. Also in some cases, dermatoscopy is performed.