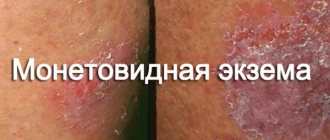
Many skin diseases are similar to each other, which is why they are often confused. But, with a little understanding of the causes and symptoms, you can separate one disease from another. This also applies to psoriasis and eczema, which have both similar symptoms and pronounced differences. Knowing them, you will definitely not confuse one with the other. Let’s say right away that psoriasis and eczema are not the same thing. But for a better understanding, let’s look at these diseases in more detail.
Features of psoriasis
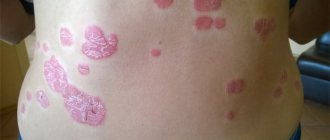
What kind of disease is this? Psoriasis is a skin pathology that manifests itself in the form of rashes of pink plaques with dense silvery scales. This disease is characterized by a chronic form. Psoriasis is a severe type of dermatosis, during the period of exacerbation of which almost all internal organs and systems are affected.
If you do not treat this defect, over time its symptoms will worsen and take on a more extensive form. For people suffering from psoriasis, even the onset of disability is possible, and in advanced cases, even death.
This pathology can occur in different ways. Depending on the type, psoriasis can affect different areas of the body. Appearing papules can also have different sizes and shapes. In some cases, in addition to the skin, the disease affects nails and even joints. It is because of its versatility that doctors decided to classify pathology.
There are two types of psoriasis:
- the usual form and psoriatic erythroderma, devoid of pustules;
- a large group of species that imply the presence of pustules.
What's worse
Psoriasis is a more severe pathology due to the fact that it is incurable. Competent therapy will achieve remission, but sooner or later the disease will make itself felt. You can get rid of eczema with timely treatment. On the other hand, it can become chronic.
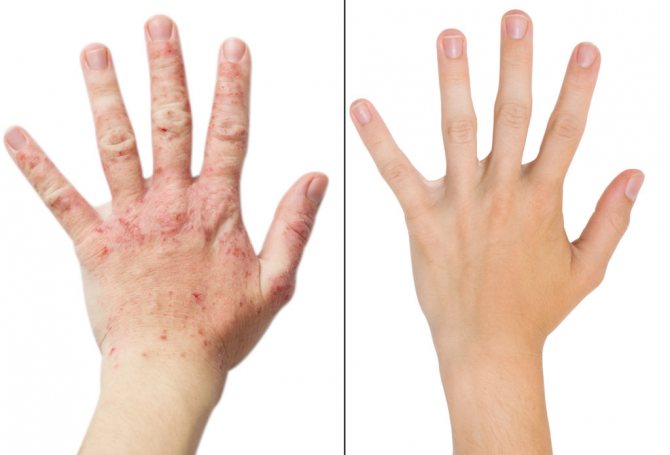
If we evaluate the symptoms, then eczema manifests itself more pronouncedly, accompanied by severe itching, which, of course, creates discomfort in everyday life. It affects delicate areas of the skin that are constantly susceptible to some kind of influence, which can irritate the formations even more.
In the initial stage of psoriasis, the patient is practically not bothered by the symptoms, but in case of exacerbation, the condition will be no better than with eczema.
Causes of psoriasis
What causes this disease? Further treatment tactics depend on the answer to this question. The causes of psoriasis are:
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- genetic predisposition;
- disturbances in the activity of the endocrine system;
- pathological changes in metabolic processes.
The following factors can lead to such problems:
- various injuries;
- decreased protective properties of the immune system as a result of disease;
- unbalanced diet;
- stress, depression, emotional stress;
- sudden climate change.
Although this list is not exhaustive, because psoriasis is such an insidious disease that can appear even due to a common runny nose. At least this applies to people who have already had pathological rashes.
Description of psoriasis
In order to know the difference between psoriasis and eczema, you need to familiarize yourself with both diseases. They have both common features and differences. Psoriasis is a skin pathology characterized by the appearance of a rash in the form of pink plaques. The rashes are always covered with dense gray scales. There are two types of psoriasis: regular and pustular. The disease is caused by a number of reasons:
- disruption of the immune system;
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders;
- disruptions in the endocrine system.
Psoriasis can be caused by a change in climate zone, injury, or nervous stress. The disease appears against the background of poor nutrition and a decrease in the body's protective functions.
Diagnostic features
How is psoriasis different from eczema? This disease has several features that allow it to be differentiated.
- If the papule that appears on the skin is slightly scraped, it will begin to peel off greatly. This means that the dermis is covered with stearin stains.
- When the scales are removed, a smooth pink surface appears - this exposes the upper shiny layer of the skin, which is also called the terminal film.
- If you damage this pink surface, miniature blood spots will appear on it.
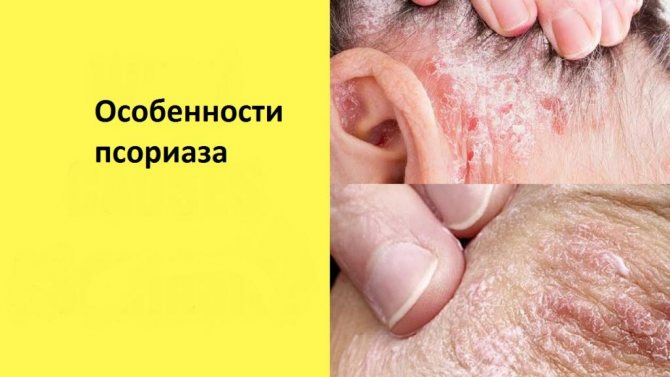
With aggressive influence, injury and attempts to get rid of rashes mechanically, new papules appear. So you should not engage in such “treatment”.
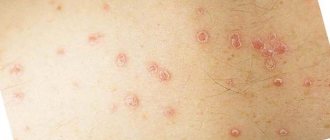
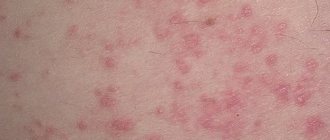
Causes of eczema
This is a skin pathology, which is characterized by the formation of inflammatory rashes on the integument. There are acute and chronic forms of eczema. The disease itself is prone to regular relapses. Patients always complain of severe burning and itching in the affected areas.
There are several types of eczema, which differ in the location of the foci of inflammation, the nature of the symptoms and the reasons for their appearance. Most often, doctors associate the occurrence of this disease with the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine disorders;
- insufficient functioning of the immune system;
- nervous tension;
- infectious and allergic pathologies.

Most often, damage and inflammation that appears on the skin are the immune system's response to various irritants.
What causes eczema and what are the distinctive symptoms?
This dermatological pathology represents a whole complex of characteristic symptoms. In addition to skin rashes and a pronounced inflammatory process, the greatest discomfort for patients is caused by unbearable itching and burning. Eczema can occur in both acute and chronic forms. There are many varieties of this disease, since they differ in the nature of the symptoms, the location of the rash, and the provoking causal factors. That is why eczema is often classified as a disease of a polymorphic nature.
No doctor can say with absolute certainty why dermatosis occurred in a particular clinical case. However, the origin of the pathology is mainly explained by:
- decrease in the body's immune forces;
- stress and nervous overstrain for a long time;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous or endocrine systems;
- the course of infectious processes;
- allergic reaction.
In any case, the origin of the pathology is associated with weakened immunity and its inability to fully resist internal and external stimuli.
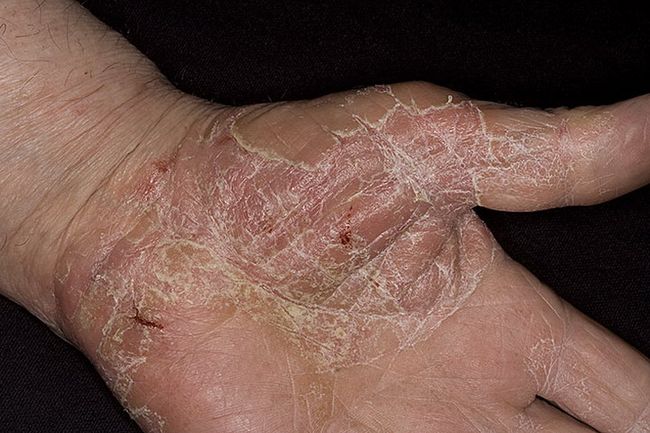
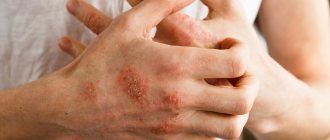
Manifestation of eczema on the palm.
Features of eczema
How is eczema different from psoriasis? There are several stages of this disease, through which most patients with this diagnosis go.
- Erythematous phase. Swelling, redness, and then severe itching occurs on the skin - this is how the disease begins.
- Papulovesicular form. At this stage, groups of bubbles called vesicles appear on the skin.
- Wet phase. Papules rupture, small erosions appear without definite outlines, from which serous exudate oozes. As a result, the skin constantly gets wet, and the itching intensifies.
- Cortical stage. Gradually the exudate dries out, forming serous crusts.
Over time, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic, and the skin becomes dense. The crusts begin to peel off, at the same time new vesicles and papules may appear on the integument.
Common signs of skin diseases
Psoriasis and eczema have some similarities in the clinical course and pathogenesis of the disease.
There is a theory about the key role of exposure to provoking factors that trigger the autoimmune mechanism for the development of diseases. The essence of this mechanism is:
- in the elimination of normal skin epithelial cells in both cases;
- in place of dead epithelial cells, there is an intensive proliferation of connective tissue with the formation of a chronic focus of inflammation;
- inflammation gives a picture of pathology in the form of skin rashes.
The clinical course of both diseases has similar symptoms. The first pathological process in both cases occurs at a young age and after exposure to a provoking factor. Then comes a period of remission, when the manifestations of the disease disappear without a trace.
- The duration of the remission period varies.
- Relapse of the disease can occur under the influence of external factors.
- Triggers, for example, include cosmetics or synthetic detergents that come into direct contact with the skin.
The role of the allergic factor in the occurrence of chronic skin diseases cannot be ruled out. In this case, the triggering mechanism is precisely the immediate type reactions, which cause nonspecific inflammation in the epidermis.
For patients suffering from skin diseases, it is common to identify a specific allergen.
- The sensitizing substance is detected in cosmetics or substances that come into contact with the skin.
- To determine the allergen, skin tests are done with different substances and materials to identify sensitization of the body.
- Such reactions are accompanied by local redness, itching and swelling.
Psoriasis or eczema manifests itself as skin rashes on the body, but psoriasis often affects internal organs and joints with minimal skin manifestations. In this case, skin lesions have a multiple morphological picture: from spots to papules filled with liquid (pustular appearance).
Therefore, if you suspect a skin disease, you should consult a doctor, since only a doctor with experience in dermatology can distinguish eczema from psoriasis.
Similarity of pathologies
Psoriasis and eczema are completely different diseases, but they still have some common features:
- both defects occur in a chronic form;
- cover the skin;
- some localization sites coincide - both psoriasis and eczema often develop on the palms, scalp, feet and face;
- seborrheic eczema is characterized by severe peeling, similar to regular psoriasis;
- diseases appear for the same reasons.
Can eczema turn into psoriasis? These are completely different diseases, which, although they appear for the same reasons, have different symptoms and nature of origin. So eczema and psoriasis are in no way related to each other.
If the doctor doubts the correctness of the suspected disease, the patient is additionally prescribed examinations.
Common features of diseases
For those who are interested in whether psoriasis and eczema are the same thing or not, the specialist will answer in the negative. These are completely different diseases, they have different causes, course, symptoms, therapy, and general effect on the body.
The first manifestations of any skin disease should make you see a dermatologist, because the symptoms of psoriasis may indicate the onset of a disease that has the most complex health consequences. Whatever the form of skin abnormalities, it is necessary to consult with a specialist in the appropriate field.
How does psoriasis differ from eczema?
Contrary to popular belief, there are quite a lot of differences between these diseases, so it is almost impossible to make a mistake with the diagnosis. To determine the pathology, you need to know the symptoms of eczema and psoriasis.
Doctors identify several features of eczema.
- When you scrape off the crust on the papule, a bright red patch of skin appears.
- The rash is constantly wet.
- The development of pathology is accompanied by severe burning and itching in the affected areas.
- Eczema occurs on softer, sensitive areas of the skin - on the bends of the elbows and knees, on the inside, and in the armpits.
- Detachment of scales is most often accompanied by inflammation and exudate.
- The lesions have unclear outlines.
- The onset of the disease is characterized by the appearance of blisters.
- If the pathology affects the hands, it feels as if it is a fungus, but there is no thimble syndrome.
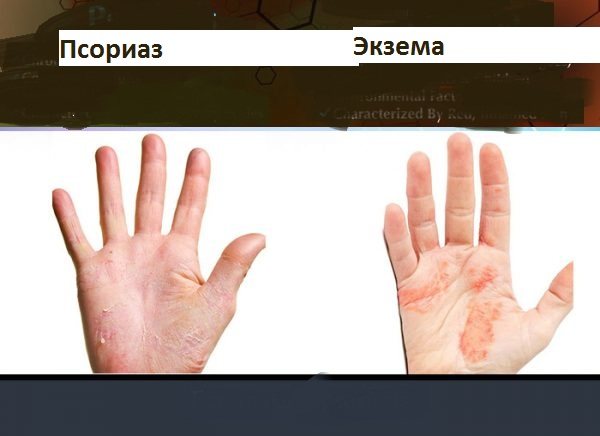
How is psoriasis different from eczema? This disease also has a number of characteristic features that make it possible to accurately determine the diagnosis.
- When the scales are scraped off, pink skin appears, on which small spots of blood appear.
- Psoriasis is usually localized on rougher areas of the skin - directly on the knees and elbows.
- The scales on papules always remain dry.
- Patients rarely complain of burning and itching at the initial stage of the disease.
- The first signs of psoriasis are miniature papules.
- Dead particles of neoplasms slightly rise above the integument.
- The main difference between psoriasis and eczema on the hands is inflammation of the nails with the occurrence of thimble-pit syndrome.
- The outlines of the affected areas almost always remain clear, since they are limited by a pink stripe.
How to distinguish eczema from psoriasis
The main difference between psoriasis and eczema is their external manifestations. With eczema - a vesicular rash in the form of small blisters that break open and lead to the formation of crusts. With psoriasis, a psoriatic rash in the form of many spots with scales, when removed, begins to bleed.
Other differences between eczema and psoriasis:
- Psoriasis is a disease that has only a chronic form. Eczema has acute (lasts 2 months) and chronic forms. Psoriasis cannot be eliminated forever, so it is considered a more severe disease. Eczema can be cured with proper treatment.
- Psoriasis is based on autoimmune processes (inadequate response of the immune system). The exact mechanism of development of eczema is still not clear. At the same time, the provoking factors of the diseases are largely similar.
- Eczema is more common in childhood. Adults encounter it less often. They simply “outgrow” the disease—the symptoms go away as they grow older. Psoriasis occurs in children and adults with the same frequency; the disease does not depend on age, but develops due to the influence of risk factors.
- Eczema affects only the skin, while psoriasis can affect the nails, joints and internal organs.
- With eczema, severe itching and burning are observed. With psoriasis, itching may only sometimes be felt.
- Eczema spots do not have clear boundaries, they are blurred. Psoriasis spots, on the contrary, have contours.
- Psoriasis can appear anywhere. Eczema affects the most delicate areas: skin folds, inner bends of the limbs, and the area between the fingers.
- In eczema, the lesion has severe swelling. With psoriasis it is practically not observed.
- Scales in eczema are present only in the seborrheic form of the disease. It is also possible for blisters filled with pus to appear.
It is on the difference in symptoms that the differential diagnosis of eczema and psoriasis is based. If a patient has a psoriatic triad (the phenomenon of stearin stain, terminal film and “blood dew”), then he most likely has psoriasis, since there are no such symptoms with eczema.
How to treat eczema
Therapy for this pathology is aimed primarily at eliminating the pathogen, symptoms and inflammatory process.
How to treat eczema? During therapy, the patient is prescribed:
- hyposensitizing agents to relieve allergy symptoms;
- To reduce itching, antihistamines are used - Fenistil, Tavegil, Diprazin;
- immune correctors - “Likopid”, “Imudon”, “Ribomunil”;
- antibiotics to relieve bacterial inflammation;
- antifungal agents fight fungal infections;
- B vitamins;
- diuretic medications - Lasix, Trifas, Uregit;
- in severe forms of the disease, corticosteroids are used.
Among other things, to alleviate the condition, patients are allowed to use traditional recipes.
Psoriasis therapy
Treatment of this pathology requires the use of more complex techniques. And all because a wide variety of forms and varieties require individual complex therapy. In addition, if the patient has metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders and joint damage, he requires additional correction.
- To eliminate itching, inflammation and flaking, local preparations with tar and salicylic acid are used. By the way, ointments for psoriasis and eczema can be the same. The following drugs are most often recommended: “Picladol”, “Super Psori Cream”, “Kerasal”, “Hemosol”.
- You can strengthen your immune system with the help of vitamin complexes.
- The patient is necessarily prescribed antihistamines - “Peritol”, “Diazolin”, “Suprastin”.
- Uncontrolled growth of epithelial cells can be stopped with the help of retinoids and cytostatics.
- Non-steroidal drugs help reduce the manifestations of the inflammatory process.
- Steroid medications have antiallergic and immunosuppressive effects and are necessary to stabilize metabolic processes and relieve inflammation.
- If a patient is diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis, he is additionally prescribed chondoprotectors.
- After the acute stage has passed, the patient is recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic measures.
Among other things, both psoriasis and eczema require compliance with a number of rules during treatment:
- power control;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- maintaining a good mood.
These conditions also play an important role in curbing the progress of skin diseases.
Features of the treatment of psoriasis and eczema
Treatment of psoriasis is more complex, which is explained by the autoimmune nature of the disease. Here, ointment for external use is of particular importance, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive (suppress the immune system) drugs. In case of joint damage, chondoprotectors are additionally used.
General principles in the treatment of psoriasis and eczema:
- adherence to an individual diet;
- stress prevention;
- rejection of bad habits;
- psychotherapy and sedatives;
- Physiotherapy methods for general health promotion.
Since eczema causes severe itching, antihistamines may be used. If the disease is bacterial in nature, treatment must include antibiotics for external use.
Alternative medicine
It’s worth saying right away that folk remedies are not able to completely rid you of problems such as eczema and psoriasis. Alternative medicine can only help you eliminate some of the unpleasant symptoms and external manifestations of these diseases. By the way, many of them effectively fight not only eczema and psoriasis, but also other types of dermatitis. Just remember that you cannot stop at traditional medicine alone - therapy must be comprehensive. This is the only way to get rid of eczema and psoriasis.
Folk remedies can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and bring good results, especially in combination with traditional methods.
- Collection of herbs for dermatitis, eczema and psoriasis. It should include nightshade and nettle leaves, soapwort and valerian roots, violet flowers and mint. All ingredients should be taken in equal proportions. Pour the collection with three glasses of hot water and boil under the lid. You need to cook the product over low heat for 5 minutes. The strained broth should be taken hot, half a glass 3-4 times a day.
- There is another, no less effective collection of herbs for skin pathologies. It consists of immortelle, string, rose hips, chicory roots and hawthorn berries. The decoction should be prepared in the same way, and should be taken half a glass 2-3 times a day.
- For eczema and pathologies, you can use compresses with fermented baked milk and orange peels. It is advisable to leave them overnight.