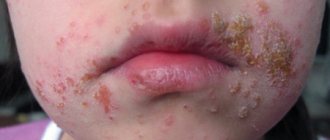
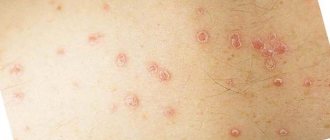
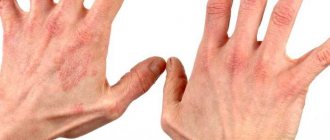
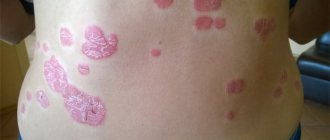
In children with psoriasis, plaques appear that are prone to flaking and itching. Patients complain of rash, redness, and sores. In 75% of cases, the first symptoms of a chronic disease are observed in children under 5 years of age. The pathology is differentiated from candidiasis and diaper dermatitis. Treatment is selected taking into account the stage and clinical picture.
Types of childhood psoriasis and their description
The main cause of psoriatic rash in children is considered to be genetic predisposition. If the parents have the disease, the probability of its manifestation in the child exceeds 60%. In addition to genetics, scientists identify a number of factors that can become triggers:
- liver dysfunction;
- hormonal changes;
- infectious diseases;
- allergy;
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- synthetic clothing;
- helminths.
Triggers can give rise to the development of psoriasis, but the main condition for its development is a weakened immune system.
Chronic dermatosis of a non-infectious form, or psoriasis in a child, is a pathology without gender and age restrictions. Symptoms are associated with changes in the skin and nail plates. When seeing classic signs in a child, they are most often mistaken for some form of dermatitis.
The initial diagnosis, accompanied by a specific treatment regimen, is not confirmed after some time, when the disease begins to progress and take on more obvious forms. From psoriasis, a child suffers not so much from pain as from somatic and psychological discomfort. After all, the pathology manifests itself not at all aesthetically.
The table shows the main forms of pathology with a description.
| Type of disease | Localization | Peculiarities |
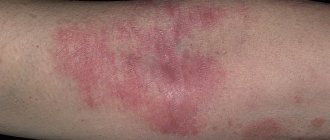
| Plaque psoriasis | Lower lumbar region, knees, elbows | The most common type, diagnosed in 80% of cases |
| Nail psoriasis (psoriatic onychodystrophy) | Nail plates of fingers and toes | The nails change color, the plate acquires a gray, white or yellow tint. Nail brittleness increases. Sometimes they disappear completely. |
| Pustular psoriasis (exudative) | Skin folds, armpits, groin area, genitals and buttocks | Bright red, smooth, shiny spots appear. Sweating worsens the course of the disease. Diagnosed in overweight children. |
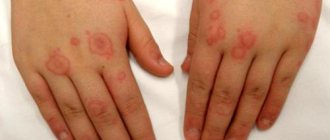
| Guttate psoriasis | Different areas of skin | Small red spots, similar to drops, cover the skin. It occurs suddenly and often as a result of stress or after suffering another type of illness. |
| Generalized pustular psoriasis | Different places | Affects large areas of skin. Characterized by complications in the form of heart failure, diseases of internal organs. |
| Diaper psoriasis | Skin on the buttocks and thighs | It is very similar to diaper dermatitis, so it is difficult to diagnose. |
| Psoriasis of the flexor surfaces | Knee and elbow joints, armpits and groin | There is little or no peeling. |
| Erythrodermic | Different areas of skin | A very dangerous look. Can lead to massive skin peeling and, without treatment, death. |
| Arthropathic | Joints | It is rarely diagnosed in children. Accompanied by changes in the nail plates, muscle pain, swelling and deformation of small joints. |
Diagnosis of the disease
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by rashes, itching, and fever. The rash appears first on the elbows and knees, then in the armpits and groin areas, then begins to cover increasingly larger areas of the skin, merging into huge contours.
Signs
Despite the fact that there are a diverse number of forms of psoriasis, it is still possible to identify 3 common signs:
- if you scratch red spots, white scales will begin to separate, and the spot will look like a drop of paraffin or stearin;
- when all scales are removed, the surface of the stain will become smooth, shiny and bright red;
- If you scrape off a psoriasis plaque completely, droplets of blood will appear on the surface.
Causes
With this disease, a dysfunction of the upper skin layer, the epidermis, has been detected. Skin cells mature in 4-5 days, normally 30 days.
In addition, the patient’s body exhibits disturbances in several organ systems: nervous, immune, and metabolism.
What causes psoriasis in a child? The reasons are:
- heredity - from one of the parents;
- environment – stressful situations, contact with tight clothing, seasonal changes;
- infections - after an illness.
Can a baby have a disease?
Psoriasis, as a rule, is classified as an “adult” disease that occurs primarily due to severe stressful situations, however, in 4% of cases, pediatricians encounter manifestations of the disease in newborns and infants. Psoriasis rarely develops in children, but is more severe than in adults.
The main reasons contributing to the development of psoriasis in infants are:
- hereditary factor (genetic predisposition leads to the development of psoriasis in children in 30-65% of cases);
- past infections;
- decreased immunity;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- allergic reactions;
- taking medications;
- injury to the skin.
Treatment method
There are several approaches to treating psoriasis in children:
- drug effects;
- physiotherapy;
- nutrition correction;
- use of traditional medicine.
Stopping the progress of the disease is possible only with an integrated approach.
The use of medications is aimed at relieving the acute manifestations of psoriasis. For this purpose, non-hormonal ointments for external use and supporting antihistamines, sedatives and vitamin-mineral complexes are used. In advanced forms of pathology, hormonal ointments may be prescribed.
Important! Prescription of medications should only be done by a specialist. Self-medication can aggravate the situation and cause complications.
Physiotherapy
Significant results in the treatment of psoriasis in children include ultraviolet irradiation and baths.
Classic signs of psoriasis in children
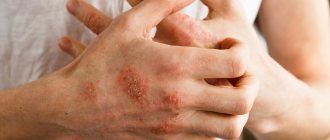
Parents whose children have been diagnosed with this disease do not believe in it in most cases. After all, pathologists have a fairly serious history. It takes a chronic form and is practically incurable. Skin cells begin to divide more intensely - and this results in the appearance of rashes, flaky itchy or weeping plaques and ulcers located above the skin level.
And although the signs are very obvious and characteristic, only a dermatologist can make an accurate diagnosis. Some forms of the disease resemble diaper dermatitis and even candidiasis in their manifestations. Their treatment regimens are different.
Statistics
Of the 100 children who were initially diagnosed with dermatosis or dermatitis, 15 cases had a form of psoriasis. In approximately 75%, the first manifestations of the disease begin in children under 5 years of age. This pathology is merciless even to infants.
What are the types
The following forms (types) of psoriasis most often develop in infants:
- diaper;
- plaque (plaque-like);
- pustular;
- teardrop-shaped;
- erythrodermic.
Manifestations of diaper psoriasis spread to the buttocks and thighs, especially in the area of skin contact with the diaper. Characteristic signs are irritation and a rash, which subsequently becomes covered with scales and contains liquid inside. In this case, the boundary between affected and healthy skin is clearly defined.
The plaque-like form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of papules and vesicles on the baby’s body. Moreover, the rash initially appears on the buttocks, later spreading to the face, hands and skin folds.
Over time, the affected areas become thicker, begin to rise above the general level of healthy skin and peel off.
Pustular psoriasis in infants is characterized by the formation of red spots on the skin, which gradually transform into blisters with liquid contents. Another sign of this rare form of the disease is enlarged lymph nodes.
The teardrop form most often occurs after a streptococcal infection and appears 2 weeks after recovery. Small round papules with a diameter of up to 1 cm form on the baby’s skin on the arms, legs and torso. The spots may merge with each other, and their surface may peel off.
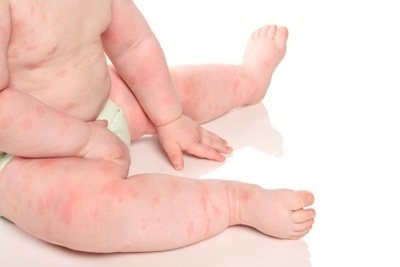
Erythrodermic psoriasis is the most severe form of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of multiple red spots; the baby is bothered by itching and pain in the joints. Possible increase in body temperature.
The plaque-like form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of papules and vesicles on the baby’s body. Moreover, the rash initially appears on the buttocks, later spreading to the face, hands and skin folds.
Causes of childhood psoriasis
Scientists have been studying psoriasis for more than a hundred years. The examinations and observations of patients made it possible to establish that pathology develops as a result of the influence of several provoking factors on the body at once.
The determining factors in the development of psoriasis in infants are:
- Heredity. Psoriasis can appear in infants due to illness of parents and blood relatives. Genetic predisposition leads to the development of pathology in 30–65%.
- Skin injury.
- The effects of drugs.
- Infections.
- Decreased immunity.
Psoriasis in infants often appears against a background of reduced immunity. The disease can be caused by past streptococcal and staphylococcal infections (tonsillitis, pharyngitis), influenza, and chicken pox.
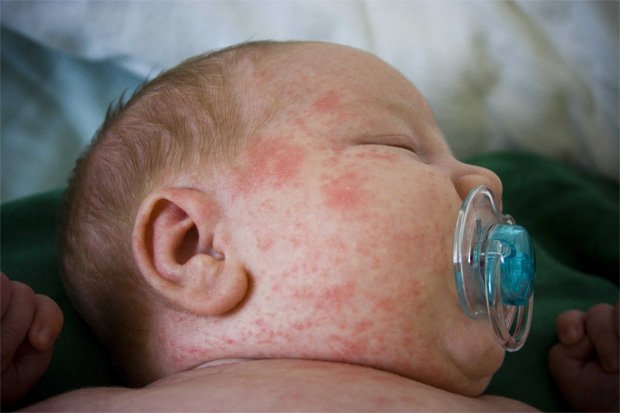
The active stage of the psoriatic process often occurs during the rehabilitation period after infectious diseases. Usually in this case, the initial signs of psoriasis are visible 2-3 weeks after recovery.
Psychotraumatic situations have less influence on the development of psoriasis in infants. Although sometimes the impetus for the appearance of psoriatic rashes is given by severe fear (stress factor).
The causes of psoriasis in children, including infants, continue to be studied. It is impossible to completely protect your child from this disease, but you can reduce the risk of developing a severe and protracted course of the disease. To do this, if alarming changes appear on the baby’s skin or behavior, you should contact a dermatologist, or tell your local pediatrician about your problem.
Modern doctors make many discoveries, millions of studies are conducted every day. However, the exact reasons for the development of the disease in children are not yet known to science. There are several theories about the occurrence of the disease, including autoimmune.
The risk definitely increases, and significantly, if one of the biological parents suffers from the disease. The chances of hereditary transition are one in four. If both parents have the disease, the risk of genetic connections increases to 60-70%.
Psoriasis worsens during critical periods in children's age cycle - nursery, kindergarten, school, and during peak psycho-emotional stress and stressful situations - public speaking, exams, important tests.
Cleansing the body for psoriasis
Tibetan teachings have been teaching about psoriasis (from the Greek “psora” meaning scabs or skin lesions) since ancient times. This skin disease was associated with “dirty blood” in the patient’s body, and therefore they tried to treat the hematopoietic organs and carry out a comprehensive cleansing of the body with psoriasis from toxins and harmful substances in order to cleanse the liver, intestines and lymph. Scientists still have not found clear causes for this disease; they tend to associate the formation of dry, flaky halos on human skin with genetic inheritance and experienced emotional upheavals and permanent stress.
How to cleanse the body of harmful substances?
Chiropractor John Pegano gives a detailed model of cleansing the body to cure psoriasis. He suggests taking care of the condition of the intestines, from which, due to a leaky intestine, toxic substances leak into the blood and lymph, spreading throughout the body. When the liver, kidneys and lymph stop performing the cleaning function, psoriasis appears as a way to rid the body of internal impurities. Dr. Pegano, in his most popular work on psoriasis, states: “The diet, if I may call it that, is more of a diet, which includes 6 to 8 glasses of bottled or mineral water and, of course, medicinal herbal tea. It is advisable to drink water or tea between meals.” So, 3 pillars on which the Pegano diet “stands”:
- cleansing the intestinal tract;
- diet;
- herbal drinks;
Guided by Pegano’s recommendations, you can display a whole table of food products that are important to consume correctly for psoriasis in order to get rid of this disease.
| Can | It is forbidden | ||
| Water | 8 tbsp. in a day | Fruits, berries | Citrus fruits, strawberries or wild strawberries |
| Lecithin granules | 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day, for a week in a row | Grain products | All bakery products made with white flour |
| Fresh fruit, frozen | Date, nectarine, apple, cherry, lime, fig, kiwi, raisin, prune and peach | Fried, smoked, marinated fish | Fatty fish, shellfish, anchovies, crustaceans, caviar, salmon, oysters |
| Fresh vegetables | Beets, onions, asparagus, garlic, beans, pumpkin, celery (stem), olives, cabbage, spinach | Poultry meat | Duck, dishes with skin, fat, spices, roasts, goose meat |
| Stewed or steamed fish | Better daily, salmon, cod, flounder, tuna, sardine, trout, sturgeon, sushi | Dairy | High fat dairy products |
| Cereals | Barley, crispbread, oats, buckwheat, brown rice, durum pasta, corn, rye, sprout seeds | Yeast | Yeast products |
| Lean poultry | Turkey, dietary game, chicken | Coffee | With caffeine, more than 3 cups per day |
| Meat products | Lamb (up to 2 times a week) | Vinegar | Marinades |
| Dairy | Fat-free milk, goat milk, cottage cheese, buttermilk, yogurt, kefir, cheese | Alcohol | Alcohol |
| Egg white | Cook soft-boiled or as an omelet all week long | Sweet porridge | With butter, with sugar |
| Vegetable oil | Olive, sesame, rapeseed, cotton, soy, almond, 1 tsp each. in a day | Coconut | Chips and coconut milk |
Both world medical science and Dr. Pegano say that the diet for psoriasis is built individually, as well as taking into account the patient’s chronic diseases, allergies and other factors.
Key points in cleansing the body for psoriasis
The course of cleansing the body for psoriasis should consist of:
- changing your usual diet;
- colon cleansing;
- toning the body through short-term fasting;
- washing the gastrointestinal tract;
- maintaining calm and good mood.
For five weeks you should perform a colon cleansing cycle (using enemas and laxatives), fast for 3 days (with the doctor’s permission), drink a lot of water, flushing the digestive tract, use silicon enterosorbents, like white coal, monitor the condition of the liver, bring her work back to normal. You should forget about alcoholic drinks. Carry out such cleanings once a year, and psoriasis will either disappear or alleviate its external manifestations.
Just like the causes of the disease, it has not yet been possible to determine one diet plan for psoriasis for everyone, because food is the main factor influencing the condition of the disease. It has long been noted that by adjusting the diet, you can achieve minimal manifestations of psoriasis, which almost does not interfere with a normal life.
The importance of cleansing the lymphatic system in psoriasis
First of all, doctors recommend starting with lymph when cleansing the body during psoriasis, because lymph is an intercellular substance that connects the cells of all tissues of the body. So, some facts about lymph and its role in life processes:
- Metabolism occurs through lymphatic channels, beneficial microelements are absorbed and waste products are removed;
- thanks to lymph, tissues are renewed, lymph is capable of removing up to 1 billion dead cells every day, playing the role of a “sewer” in the human body;
- lymphotoxicosis is poisoning of the body when 83% of substances harmful to humans accumulate in the intercellular lymph. This is one of the causes of psoriasis;
- “yellow vessels” contribute to the body’s immune resistance to bacteria and viruses, neutralizing their effect.
When taking the first step towards curing psoriasis, it is important to remember about comprehensive therapy for the whole body. Tibetan medicine advises taking a whole course consisting of acupressure and cupping massage , vacuum therapy, and herbal medicine. Also, according to Tibetan methods, psoriasis is considered a multi-causal disease associated with lesions of the regulatory systems in the body Bad Kan, Mkhris-pa and Rlung (respectively: lymph, liver, nerves). In more detail it looks like this:
- from the liver: a malfunction in the body occurs due to the consumption of large amounts of salt, hot spices, fat, and alcoholic beverages. The situation can be corrected through a diet that excludes these nutritional components, as well as through normalizing the functioning of the bile ducts;
- from the nervous system: psycho-emotional disorder, stress, neuroses. A way to rehabilitate the unsatisfactory condition of the nerves: phytotherapeutic procedures, cleansing the blood of toxins that excite the nervous system, harmonizing impulses through acupuncture, restoring the immune membrane of the body.
By combining these methods (diet, an emotionally positive attitude, cleansing the lymphatic flow and liver with local treatment of psoriasis lesions), you can achieve a significant improvement in the skin and neutralize the disease as much as possible. When cleansing the body with psoriasis, it is important to drink a lot of clean water - plain or mineral, not to abuse alcohol, medications, or use chemicals or cosmetics (deodorants, shower gels, creams, lotions). By gradually eliminating irritating factors from the external environment, removing toxins from body tissues, you can achieve complete recovery from psoriasis.
| Psoriasis of the legs and feet |
How to increase the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease?
Symptoms of psoriasis in infants have their own characteristics. The first to appear are rashes in the buttocks area, then other areas of the skin are affected. The disease is usually divided into several stages:
- Initial stage. Several small pink spots appear on the baby’s body, which do not cause much discomfort; over time, easily removable silver scales form on their surface;
- Progressive. New rashes appear, papules merge into plaques that differ from the color of healthy skin, and scales form on the plaques. There is a characteristic rim around the peelings. Increasing burning and itching causes discomfort to the baby, and body temperature may rise. This stage is quite long - from 2 weeks to several months;
- Stationary. This stage can last indefinitely, the growth of new papules and plaques stops, the number of scales covering the surface of the affected skin increases, and there is no rim around the peeling;
- Regressive. The final stage, which is characterized by active detachment of scales, stopping the inflammatory process. Already existing plaques flatten in the center of the spots and gradually disappear. The child's general condition is improving. At this stage, we can talk about recovery, however, given that the disease is chronic, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures.
The symptoms of psoriasis in an infant differ significantly from the symptoms of this disease in an adult. In children at the initial stage, red rashes appear in the folds of the skin (in the gluteal region, armpit), on the head, face, and genitals. It is also localized in places subject to constant friction by clothing. Rarely, the rash occurs on the palms and soles of the feet.
The rash resembles diaper rash, but it has the main symptom of psoriasis - the horny ball of papules flakes off and peeling appears. Gradually, the delicate skin becomes covered with a layer of crusty scales. Single small papules merge into conglomerates. Their size gradually increases, covering large areas of the epidermis.
In most cases, the rash is itchy, causing great discomfort to the child. He scratches the papules, risking infection. You can see what childhood psoriasis looks like in the photo.
Stages of psoriasis in a child: progressive, stationary and regressive.
- Progressive - the appearance of a small rash of red or bright pink color. It itches, flakes, increases in size and spreads across the skin. Soon the rash becomes covered with cracks and begins to bleed a little. Unlike adults, children have virtually no phenomenon of stearin stain or terminal film. In the severe form of the progressive stage, the child’s body temperature rises, the surface of the epidermis thickens, the lymph nodes become enlarged, swelling of the skin and severe redness are observed.
- Stationary – the formation of new rashes and their growth stop, the intensity of peeling decreases.
- Regressive - the rash begins to gradually resolve. After its disappearance, depigmented rims appear on the skin.
When signs of the disease completely disappear, remission occurs. Its duration depends on the characteristics of caring for the child, in particular on the diet. Relapse of the disease in children is often a consequence of infectious diseases.
Psoriasis in children has a special clinical picture of development. In the youngest, the disease begins in the skin folds, where pinkish spots appear, which is often perceived as a manifestation of diaper rash.
In children of the first years of life, the development of the disease begins with the formation of small papules in different parts of the body. Over time, the spots and papules in the center swell, peel off, become covered with scales, and their boundaries expand.
The most likely forms of psoriasis in infants:
- Diaper room. Develops in children under one year of age. The main symptoms are observed in the gluteal region. Erythematous lesions with a rash appear; over time, they become covered with scales soaked in exudate. The boundary between inflamed areas and healthy skin is clearly visible. Psoriasis in newborns in the area where diapers are worn is usually initially mistaken for irritation from contact with urine and feces - diaper dermatitis.
- Teardrop-shaped. Characteristic symptoms are the formation of plaques, papules of a round shape and a diameter of no more than one centimeter. Over time, the surface of the elements may also begin to peel off, and individual spots merge with each other. The teardrop type of psoriasis in children has a close connection between a previous streptococcal infection and the appearance of rashes. In this case, spots on the body appear approximately two weeks after the infection. Drug toxicoderma can also cause a teardrop-shaped disease in a child.
- Plaque. The first skin symptoms appear in the face, buttocks, hands and large natural folds. In children, instead of the psoriatic plaques characteristic of an adult sick person, erythematous spots appear on the body, in some cases - papules and vesicles. Pathological elements rise above the skin and increase in size. Over time, islands of desquamated epithelium form in the middle.
- Pustular. Manifested by the appearance of foci of swelling and inflammation. Small blisters filled with exudate form on reddish-colored areas of the skin. Nearby lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged.
In addition to the most common forms, the disease in an infant can also occur in a different scenario. The erythrodermic form of the pathology is difficult to tolerate, manifested by inflammation of a larger surface of the body, peeling of areas of the dermis, and severe pain.
Psoriasis in children can occur with damage to individual joints, nails, and scalp; with complications, the pathology affects internal organs. Psoriatic elements can spread to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and external genitalia.
Skin symptoms of any subtype of psoriasis are accompanied by a deterioration in well-being. The psoriatic process leads to dryness of the body, a feeling of skin tightness, and itching. Such discomfort leads to the fact that the sick baby begins to scratch the skin, and its injury causes the formation of new lesions and increases the risk of infection.
Body irritation increases the baby’s nervousness, impairs his sleep and appetite. The severity of all symptoms of any form of the disease is determined by the stage of development, there are four of them:
- Initial. It is characterized by the appearance of only a few spots on the body; their formation does not lead to significant discomfort.
- Progressive. Already emerging lesions increase in size, new elements grow, and their connection (fusion) occurs. General symptoms, such as itching, are acute.
- Stationary. The process freezes - the size of the plaques remains at the same level, there are no new elements. Peeling of the surface of the spots increases.
- Regressive. Reverse development begins with the flattening of existing plaques in the central part. Gradually all the scales peel off, the inflamed lesions disappear, and in their place there will be spots of light or, conversely, dark color for some time.
Determining the form of psoriasis and its stage is required to choose the optimal course of treatment, the goal of which is not only to eliminate symptoms, but also to prevent possible complications.
— stationary — 2;
A pathology such as psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that can completely destroy a child’s immunity. Therefore, it is important to do everything possible to strengthen the protective functions of the child’s body. You can increase the amount of natural vitamins. It is important to ventilate the room well, especially before going to bed.
The form of psoriasis is usually chronic. With properly selected and comprehensive treatment and compliance with all the doctor’s requirements, stable remission can occur. Psoriasis will go away. Almost 90% of success is the correct choice of medications. And desire and perseverance will overcome any disease.
In the initial stages, it is very difficult to diagnose psoriasis visually. Rashes are often attributed to an allergic reaction or heat rash. Lack of treatment contributes to the further development of the disease with its possible complications.
What does psoriasis look like in children, and what are its symptoms?
Diaper psoriasis
First manifestations:
- the appearance of rashes in the gluteal area.
This type of disease is observed in children under one year of age. Difficult to diagnose due to the similarity of symptoms with other dermatological problems.
Characterized by:
- the appearance of purple spots on the skin, their severe peeling and subsequent keratinization;
- increased local body temperature;
- severe itching;
- deterioration of the child’s condition, drowsiness and fatigue.
A gray coating forms on the surface of the plaques. The rash has no specific localization, so any part of the body can be affected.
Guttate psoriasis
Characterized by:
- the appearance of single rashes that look like small dots or drops;
- pale pink rash;
- dryness of pathogenic elements and their itching.
In the absence of therapy, this type can develop into a severe form that is difficult to treat.
Pustular form
Peculiarities:
- skin inflammation, formation of pustules (blisters);
- itching and burning in the affected area;
- pustules are filled with fluid, which, if infected, can be replaced by pus.
Pustules form on the feet and palms. Burning and itching intensify at night when in contact with diapers.
Features of the initial stage:
- the appearance of pale pink plaques;
- rapid increase in the area of rashes;
- formation of fluid in the lesions;
- gradual keratinization of plaques.
The usual place of localization of pathological elements are folds on the child’s body, as well as limbs.
Inverse psoriasis
Characteristic features:
- the appearance of deep pale pink spots with a smooth shiny surface;
- rashes appear in the groin and axillary area.
Is it possible to sunbathe with psoriasis in the sun?
Psoriasis and the sun - are these two things compatible? This question does not appear in the cold season, but with the onset of the summer season, when many go on vacation to hot countries, it becomes relevant. And this is normal, because a skin disease at any time can lead to an exacerbation, which is fraught with the development of negative symptoms.
In approximately 70% of clinical pictures, it is in the summer that the condition of the patients’ skin improves significantly. And sunbathing for psoriasis contributes to this. They have a positive effect on the condition of the epidermis and have a drying effect.
But sometimes ultraviolet radiation is harmful, therefore, in some cases, psoriasis and tanning are incompatible. Therefore, while being in open sunlight or swimming in the sea, you must adhere to certain rules.
So, is it possible to sunbathe with psoriasis - is it beneficial or harmful to the body? Basic recommendations for sunbathing for patients – we will consider further.
- Compatibility of the disease and the sun Impact of ultraviolet radiation on psoriatic plaques
- The benefits of sunbathing for psoriasis
- Tanning rules for patients
- When is the sun harmful?
Compatibility of disease and sun
Sunbathing for psoriasis is a good way to prolong the remission stage. Summer seems to be the most favorable time for treating this disease. Therefore, to achieve a good result, patients are recommended to visit the sea annually.
It has long been proven that a pronounced therapeutic effect is achieved through the combined effects of sea water, sunlight and clean air. The latter is replete with negative ions and other beneficial substances.
The chemical composition of sea water is similar to the composition of human blood plasma, which promotes accelerated regeneration of damaged skin. Sea water provides disinfecting properties and helps get rid of psoriatic manifestations on the skin.
Resorts in Bulgaria, the Krasnodar Territory, Slovenia and Crimea provide good conditions for the treatment of psoriasis. But it is best, if possible, to go to the Dead Sea - a unique place where natural and climatic factors are ideally combined, which allows you to extend the time of remission of the disease.
Recent clinical studies have shown that 90% of patients who were treated in health resorts on the Dead Sea coast forgot about the negative manifestations of the disease for almost a year.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on psoriatic plaques
Psoriatic disease is a chronic pathology that cannot be completely cured. Light treatment is an auxiliary method of therapy that helps stop the progression of the disease and the growth of pathological elements on the skin.
Ultraviolet rays are beneficial, that's a fact. Tanned skin regenerates faster against the background of damage, as a result of which psoriatic plaques lighten, become smaller, and disappear over time. Thanks to sunbathing, the pathological process is inhibited not only on the skin, but also inside the body.
Tanning in psoriasis causes increased production of vitamin D, which helps reduce harmful symptoms. The sun's rays are a guarantee of rapid healing of wounds.
The benefits of sunbathing for psoriasis
Ultraviolet rays for psoriasis have a positive effect on the condition of the human skin. When exposed to rays on the body, the following therapeutic effects are revealed:
- The functioning of the immune system improves, the barrier functions of the body increase.
- Regeneration processes in epidermal tissues are accelerated.
- Symptoms – burning, itching, redness, peeling – are reduced.
- Further progression of the disease is inhibited.
- The severity and size of psoriatic plaques decreases.
Dermatologists allow patients with psoriasis in any form of pathology to be in the sun. However, the stage of the disease matters.
Is it possible to sunbathe?
So, is it possible to sunbathe with psoriasis in the sun? Subject to certain rules and recommendations, the answer is yes. Patients need to protect their sensitive skin from excessive exposure to sunlight and use protective equipment - apply a special protective cream before tanning.
Tanning rules for patients
Treatment of psoriatic disease with sunlight is recommended to begin with a visit to a medical specialist.
If the dermatologist allows you to travel, then you can.
The fact is that there are some contraindications that can lead to serious consequences.
Dermatologists for patients with psoriatic disease voice recommendations that must be strictly followed:
- How long can you stay under the sun? The first sunbath should not exceed 10 minutes in duration. After this, the duration of the sessions can be gradually increased, up to 30 minutes.
- The best time to get a tan on the sea coast is morning. The ideal time to sunbathe is from six to 11 am. In the evening you can from 17:00 to 20:00. The interval is the most dangerous time, because during this period there is maximum sun activity, which can provoke the development of an exacerbation. And sunburn will cause many painful minutes.
- Sunbathing provides a drying effect. And this is good. However, for patients, excessive dry skin is harmful. Therefore, it is recommended to use specialized protection in the form of creams, gels and sprays. Only a doctor should select such a remedy, since it contains substances that can complicate the clinical picture of the disease. In addition, sun protection products may interact with medications for psoriasis.
- It is recommended to sunbathe in the shade; it is advisable to avoid open sunlight.
- After water procedures, gently blot the skin with a towel, then apply any moisturizer. It prevents drying out and therefore injury.
While sunbathing, you can use Skin-cap spray. This product protects the skin and prevents inflammation.
Sea and psoriasis
Swimming in the sea is not only allowed, but also recommended. According to some patients, a 2-3 week rest helps to get rid of the manifestations of a chronic disease for a long time.
Sea water has a therapeutic effect. Thus, bathing disinfects the skin, reduces the number and size of rashes, relieves unpleasant symptoms, and accelerates regeneration processes.
Treatment with the “sea” is especially strongly recommended for guttate psoriasis and psoriatic arthropathy.
When is the sun harmful?
The sun is not only beneficial, but also harmful in some cases for the human body. Therapy using sea water and ultraviolet irradiation is suitable for any form of psoriatic disease, but not in all cases.
It is recommended to avoid sunbathing in severe cases of psoriasis, when generalization of the pathological process is detected. You cannot swim or sunbathe during an exacerbation of the disease - you must wait for a period of remission.
Another absolute medical contraindication is the use of hormonal medications (both externally and internally). The fact is that hormonal drugs, as a side effect, often increase skin sensitivity and cause photosensitivity.
In this case, even a short stay in the sun's rays can result in deep burns. In turn, burns lead to an exacerbation of psoriasis, and more and more new psoriatic plaques appear. So, the desire to improve your health with ultraviolet light will result in a new round of problems.
Dermatologists do not recommend sun treatment for patients who have the summer form of the disease. That is, exacerbation - relapse occurs precisely in the summer months. This type of psoriatic disease is rare - approximately 5% of all cases.
As an alternative to natural ultraviolet light, you can go to a solarium. It has similar properties - strengthens the immune system, promotes rapid healing of ulcers and wounds on the skin, accelerates regeneration in the deep layers of the skin. The best option would be vertical tanning for patients with a session duration of up to 5-7 minutes (the first session is as short as possible).
What does psoriasis look like in children?
In infancy, the disease is similar to thrush, just diaper rash, or at most eczema. The top layer of skin is mottled with areas with borders of rich pink color. Dotted scales are detected.
Older children begin to actively scratch the reddened areas, a specific rash appears, nodules appear, another name is papules, with gray scales. These “attributes” of psoriasis gradually increase and begin to combine with each other. The surface of the papules may become wet and have microcracks. Because of this feature, the pathology is dangerous due to infections.
Prevention
To achieve long-term remission, it is necessary to help the child follow the basic rules:
- avoid skin damage;
- limit the use of aggressive hygiene products and hard washcloths;
- follow the basics of diet;
- wear clothes made from natural fabrics;
- create a favorable emotional atmosphere.
Preventive measures depend more on the parents than on the child.
The treatment of psoriasis in children should not be treated negligently. Ignoring symptoms or self-medicating can aggravate the problem and cause serious complications. Timely seeking medical help will ensure stable remission and relieve the child from unpleasant sensations.
Even hereditary predisposition is not a 100% indicator that the baby will definitely get a serious illness; parents can prevent this. There are a number of preventive measures that can help avoid the development of psoriasis in infants, these include:
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- adherence to sleep and diet;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- observing the rules of baby hygiene;
- washing underwear and bed linen with hypoallergenic detergents;
- calm and friendly atmosphere in the family.
To minimize the risk of the disease and prolong the period of remission, follow simple rules:
- When bathing, do not use aggressive agents or hard washcloths;
- teach your child to avoid cuts, burns, and skin injuries;
- keep your child away from direct sunlight;
- give preference to clothes made from natural fabrics;
- monitor your child’s diet;
- carefully select medications;
- try to ensure that the child has a positive emotional state.
If you have the slightest suspicion that your child has psoriasis, consult a dermatologist. This is a serious disease, so only a competent doctor can tell you how to treat it. Do not self-medicate, because the sooner you undergo effective therapy, the faster you will be able to achieve a state of stable remission. Despite the fact that psoriasis cannot be cured, with the right and timely approach, the number of relapses of the disease can be minimized.
What can be used besides medications
For the treatment of psoriasis in children, medicinal cosmetics have appeared on the market, which are more convenient for treatment, especially if only some not very large areas of the skin are affected. An example is the “Psorilom” series, consisting of shower gel, shampoo, spray and cream.
The gel contains tar, sapropel extract and chaga extract. The shampoo has antiseptic properties, the spray contains zinc pyrithione and is convenient for localizing the rash in the folds.
There are also ointments and creams made on the basis of vitamins A, E and D and stimulating keratinization and regeneration of the affected areas. But using them for a long time is not recommended, as they can cause hypervitaminosis.
In addition to products containing medications, you must not forget about the most important thing:
- protect affected areas of skin from scratching;
- take care of sufficient hydration of the skin;
- give children with psoriasis baths made from medicinal herbs;
- exclude sweets and foods containing unnatural ingredients from the diet;
- Provide the sick child with sufficient and comfortable sleep.
Diagnosis of childhood psoriasis
It is difficult to diagnose a child under one year of age based solely on external examination and general symptoms. Psoriasis in children occurs without the characteristic psoriatic triad, expressed by the appearance of a thermal film and pinpoint hemorrhage when the scales peel off.
Infants may not have peeling in the first days of illness. The suspected diagnosis is confirmed by examining a scraping taken from the surface of psoriatic elements.
Elucidation of hereditary predisposition and past infections is important in diagnosis. During examination, it is necessary to differentiate psoriasis from dermatoses that have a similar clinical picture.
While some people think whether psoriasis occurs in children or not, others begin to quickly solve the problem that has arisen. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis - this axiom does not require proof. In the case of psoriasis, this is a dermatologist. The disease is so obvious that a standard medical examination is enough for a specialist.
1. so-called phenomenon stearin stain - peeling and shavings and a yellowish tint;
2. the so-called phenomenon pinpoint bleeding - if you scrape off the tops of the scales, drops of blood will appear;
3. so-called phenomenon terminal film - the surface of the papules under the scales is glossy, even and smooth.
- the whole body is covered with small plaques of red or bright pink color;
- psoriatic plaques affect the scalp, areas of the elbow and knee joints, and the inner thighs.
For 100% accuracy, the young patient is sent for general blood tests, urine tests, a biopsy of the affected skin areas, and blood biochemistry; coagulogram. Psoriatic arthritis is determined by radiography. To complete the picture, an immunogram and allergen testing are performed. Histology of skin scraping is prescribed.
Take into account
Doctors strongly advise taking children to exercise therapy and sports clubs. The disease is not transmitted by contact, touching or through the air, but physical activity will come in very handy.
At the first manifestations of psoriasis in a child, it is necessary to seek medical help. The specialist will assess the condition of the rash and make the necessary appointments. In addition to the external examination, when making a diagnosis, the doctor is guided by:
- the presence of the psoriatic triad - a number of signs characteristic only of psoriasis;
- results of blood, urine and scraping tests.
In children under one year of age, there are often no signs of the psoriatic triad, so the dermatologist focuses on the result of the scraping analysis.
Useful video
Psoriasis is a rather severe and unpleasant disease, especially for infants. Unfortunately, the disease is chronic, but with the right approach to treatment and supporting the child’s immunity, the likelihood of relapse can be significantly reduced.
Minimum diagnostic features: typical symmetrically distributed erythematous scaly plaques.
Clinical characteristics
The disease manifests itself as erythematous plaques with silvery scales on the surface. Typically, the extensor surfaces of the knee and elbow joints and the scalp are symmetrically affected. After removing the scales, a smooth shiny surface is formed with droplets of blood on it.
Characteristic is the positive Koebner phenomenon (isomorphic reaction) - the appearance of psoriatic rashes at the site of irritation (scratch, abrasion). The course is usually recurrent. Nail atrophy may occur. Microscopically, parakeratosis, epidermal hyperplasia and a slight inflammatory process are detected.
Generalized exfoliative erythroderma with hypoalbuminemia and hypothermia, generalized pustular psoriasis, and joint damage are possible. The etiology is multifactorial.
Population frequency is 1:100.
The sex ratio is M1:W1.
Differential diagnosis: seborrheic dermatitis.
Features of the treatment of psoriasis in children
When choosing a method for treating childhood psoriasis, the oldest principle of medical ethics of the chief physician of the civilization, Hippocrates, is especially relevant: “Do no harm,” or primum non nocere. Therapy should be effective and efficient, but at the same time facilitated, in some way, gentle.
To get positive dynamics, in practice, dermatologists use an integrated approach. Typically the treatment process includes the following activities:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- treatment with plasmapheresis, ultraviolet light;
- sanatorium-resort recovery - you should give preference to holiday homes with good mineral springs; water saturated with minerals is especially effective in the fight against illness.
External remedies from the category of drug treatment have their own classification.
Traditional therapy
To relieve inflammation in the initial stages, drugs based on urea, salicin, and tar are prescribed. But their effect is observed only with an integrated approach. Vitamin therapy plays an important role. High dosages of vitamins of groups B, PP, A, E, C are successfully used. Tar and sulfur-salicylic ointments are effective when localized on the palms and soles: they are usually applied under a bandage.
Topical steroids
- mometasone;
- clobetasol;
- betamethasone;
- hydrocortisone.
Steroids are hormonal drugs: they act quickly and effectively. But there is a significant drawback: there is a high risk of complications - withdrawal dermatitis and complete skin atrophy. They have a very strong effect. In European countries they are not available without a prescription. Self-medication is fraught with serious consequences.
You can take topical steroids for 5 days. Do not apply to large localizations, sensitive areas and use very often. Violation of intake leads to addiction and exacerbation. Some dermatologists believe that the prescription of glucocorticosteroid drugs is completely unsafe for children’s fragile bodies. Growth retardation, weight loss, increased blood pressure, hypopigmentation and skin breakdown may occur.
- calcipotriol - a substance that prevents rapid cell division (suitable for children over 6 years old);
— zinc pyrithione, or active zinc, is a substance that has many beneficial properties, reduces itching, restores the dermis and its protective functions (prescribed to children from 1 year).
Some doctors believe that non-hormonal treatment is no less effective than hormonal treatment, and is much safer.
Vaccinations and dermatitis
Skin pathologies often serve as a reason to refuse vaccination. Parents of sick children avoid vaccinations, fearing that the disease will worsen. The consequences of refusing to vaccinate can cause serious health problems.
Let's figure out whether it is possible to get vaccinated for atopic dermatitis, as well as for an allergic skin reaction, without increasing problematic rashes and redness.
When to do it
The first thing to do for any type of dermatitis is to relieve the relapse condition.
During exacerbations, vaccination is contraindicated; allergic or atopic dermatitis may worsen after vaccination.
It is better to wait for remission and only then begin the vaccination procedure.
During dermatological exacerbations, the body fights this disease, and a new burden is added to it in the form of the introduction of pathogenic elements, which it also needs to fight by producing antibodies.
Often the load is too great for a small body to cope with.
Atopic dermatitis
Vaccinations for atopic dermatitis in children are best done in a hospital under the supervision of doctors.
At the same time, visual observations are made, regular tests are performed, and the temperature is measured.
It is very important to observe the child for the first 3 days after vaccination. Usually in hospitals, vaccination is carried out together with antihistamine cover.
The step-by-step procedure for children in the hospital is done as follows:
- Preliminary tests and examination by specialists take place.
- After positive results, the baby’s temperature is measured in the morning (vaccination is given in the morning).
- Antihistamine injection.
- Repeated temperature measurement.
- After 2 hours, control temperature change.
- Graft.
- After 1.5-2 hours, the temperature is measured.
- In the evening, an antihistamine injection.
- Injections of antihistamines over the next 2 days.
If the baby is breastfed, the mother also needs to take antihistamines orally.
Types and doses are selected individually for each little patient and his mother.
When asked about the advisability of vaccinations for atopic dermatitis, the opinions of doctors are as follows:
- Here it is necessary to take into account not only the patient’s age, but also the capabilities of his body.
- Medical opinions on vaccinating children with similar diagnoses vary.
- Some believe that most vaccinations should be done after a year.
There is another opinion, for example, Komarovsky considers vaccinations for atopic dermatitis safe at any age, but emphasizes the need to continue remission for at least a week.
Allergic dermatitis
Before getting vaccinated for allergic dermatitis, you need to take a number of steps.
The vaccination order is determined in a timely manner, so you need to prepare for vaccination in advance and carry out appropriate treatment in order to achieve remission.
- Eliminate all allergenic foods from your diet.
- Bedding and accessories, as well as clothing and personal items must be hypoallergenic.
- It is necessary to exclude all irritating factors. It should be remembered that natural materials are not a panacea for allergies. Many people have a negative reaction to wool, cellulose, plant elements, etc. You need to find and remove the allergen. Only then will vaccinations for allergic dermatitis remain without consequences.
- Take antihistamines orally, such as Fenistil, Zyrtec for 4-5 days.
- Polysorb and Enterosgel will help remove poisons from the body. They should be treated for at least a week.
- Normalize intestinal function with Lactulose. Some sorbents may cause constipation.
- Moisturize the skin with emollients and moisturizers.
- Water procedures should only be taken at medium temperature, preferably in the shower. This should be done no more than 2 times a week.
Answering the question whether it is possible to get vaccinated for allergic dermatitis, we touched upon the topic of measures before the vaccination procedure. Now we need to consider the aspect after the vaccination period.
As a rule, vaccinations such as BCG and against hepatitis B do not cause any special consequences for the allergy sufferer’s body.
In some cases, vaccinations provoke atopic dermatitis or skin allergies.
- It should be noted that the presence of allergens cannot be allowed even after vaccination.
- The body is weakened after vaccination and is susceptible to spots, rashes, and blisters on the skin much more than before.
- After vaccination, you should not wash for 3 days.
Do not use corticosteroid drugs or antibiotics. An increase in temperature is a normal phenomenon, so it can only be reduced after 38.5.
Be sure to moisturize your body with cream, but it should not contain dyes or fragrances.
Traditional methods of treating psoriasis in children
Traditional treatment does not involve following whisperers and other concepts of alternative medicine. Treatment always helps well in combination. And here the best assistant is nature.
The following remedy is suitable for lubricating plaques: burn the dried bark of linden branches in a fireproof container. The result is a semi-liquid resinous substance. Use it to lubricate the reddened areas twice a day. Everything is good in moderation. After a course of linden branches, a 7-day break is taken.
Another remedy is being prepared. Cranberries are squeezed through a sieve. The juice is boiled for several minutes, a piece of lard or fat and a few drops of fish oil are added. Mix everything, cool. Keep refrigerated. Lubricate at the initial stage of psoriasis in children.
There is another good remedy. The alcoholic extract of the string is mixed with Vaseline. Alleviates the condition during the acute stage.
Herbal decoctions for oral administration are not recommended for children. It is better to do baths or lotions. The following plants help well: sage, plantain, violet, nettle.
For psoriasis on the scalp in children, you can add juniper or tea tree oil to your regular shampoo.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine helps improve the child’s well-being by reducing itching, reducing peeling, and prolonging remission.
External means
- Apply crushed celery root to the plaque area every day for 2 hours. Course - 2 months.
- Wash the kalachoe leaves, chop them and wrap the resulting pulp in a gauze swab. Then attach it to the sore spot with an adhesive plaster for 30 minutes.
- Soak a cotton pad with sauerkraut juice and apply to the plaques overnight.
- Apply linseed oil to the affected areas to soften hardened skin and prevent the formation of cracks.
- Combine 100 g of butter with 15 g of propolis, add 5 drops of vitamin A oil solution. Make applications with gauze soaked in this mixture.
Herbal decoctions for oral administration
- Pour a tablespoon of birch buds into a glass of boiling water. After half an hour, strain, drink 50 ml before meals.
- Brew a tablespoon of dried clover flowers with a glass of boiling water. After an hour, the infusion is ready. Take 50 ml 3 times a day.
At home, baths with herbal decoctions, sea salt and table salt help a lot.
Traditional methods are used in children only with the permission of a doctor.