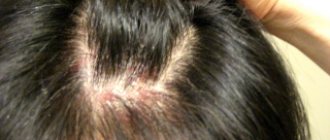
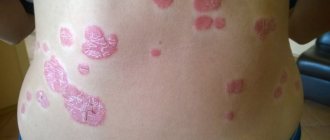
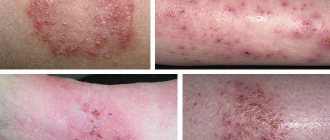
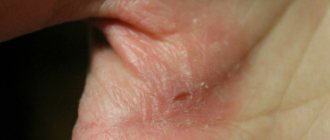
Types of eczema on the face
There are several types of eczema that are often found on the face. Each type has individual characteristics.
| Type of eczema | Description |
| Seborrheic | It usually affects the entire surface of the head, not just the face. More often, the rash forms on the hairline, on the forehead, near the lips. It is distinguished by the presence of a crust with red edges. Over time, the rash merges into a single focus and has no clear boundaries. |
| getting wet | It is characterized by frequent exacerbations and the formation of symmetrical inflammatory foci. The second name is true eczema. A characteristic feature is that the surface of the skin is wet, there are many erosive wells on it. In advanced stages, it can spread to other parts of the body. |
| Dry | Unlike wet eczema, it has a dry surface. Cracks and peeling form on the skin. Treatment is carried out using moisturizing ointments. |
| Microbial | It often forms in the area of the chin and upper lip. The onset of the disease is accompanied by swelling, redness and itching. Then purulent foci and a wet surface form on the affected area. As it progresses, inflammation increases. |
| Allergic | Develops as a result of prolonged contact with an allergen (internal or external). It is a violent reaction of the body to an irritant. May appear as dry or wet lesions. For treatment, it is important to identify and eliminate the allergen. |
Treatment for eczema is complex and differs depending on its type. The treatment method is selected only by the attending physician!
Treatment in Russia (Moscow, St. Petersburg)
Persons suffering from any form of eczema must be registered with a dermatologist. If the pathological process worsens, there is no need to delay visiting a medical facility. To achieve maximum effect, specialists will select an individual treatment regimen taking into account the severity of inflammation, the type of dermatosis and the characteristics of the patient’s body. All efforts will also be directed towards eliminating the cause of the emerging pathology.
Many modern clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg combine traditional proven techniques - conservative and physiotherapeutic - with innovative foreign trends, including those that came to us from the East. These are pharmacopuncture, acupuncture, plasma lifting and moxotherapy. Many of them involve non-drug treatments for eczema. Which clinics can you go to today?
Clinic “Paramita”, Moscow, Shmitovsky proezd, 16. The center offers a free initial appointment with diagnostics and selection of effective treatment tactics. Treatment of eczema in the clinic is carried out using oriental, innovative and traditional methods. Doctors try not to include hormones and other strong drugs in the treatment regimen unless necessary. Each center specialist has a Russian diploma and internship experience abroad. The cost of treatment depends on the amount of medical care required, on average it ranges from 15 thousand rubles.
Let's look at the reviews for the Paramita clinic:
Medical, St. Petersburg, st. Odoevskogo, 28. At the clinic you can undergo a comprehensive examination and learn everything about your diagnosis and how you can cope with it from qualified specialists. Within the walls of the medical institution, successful therapy of all types of dermatoses is carried out at a very reasonable cost. The average course of treatment for lip eczema ranges from 9 thousand rubles.
Let's look at the medical reviews:
What does eczema look like on the face?
Symptoms of the disease may differ depending on the cause that provoked it. Common signs of the disease include:
- skin redness;
- rash;
- development of edema;
- formation of watery vesicles, cracks;
- intense, painful itching;
- temperature rises;
- there is a loss of appetite;
- peeling appears;
- a dense yellowish crust may develop;
- If the wound is infected, pus is released from the vesicles.
Is eczematous cheilitis contagious?
If we talk about the contagiousness of eczematous cheilitis, then there is no simple answer regarding its contagiousness.
If the pathological process is provoked by unfavorable environmental factors, allergens or internal somatic diseases, it is impossible to transmit it to another person.
With microbial and mycotic forms of eczema, infection is possible, but in this case it is not the dermatosis itself that is transmitted, but the viruses, fungi and bacteria that led to its progression. Therefore, conditionally in such clinical situations the disease is considered contagious.
Stages of disease development
The development of eczema is divided into 4 main stages:
| 1 (erythematous) | The characteristics are similar to dry eczema. Differs in the beginning of development:
|
| 2 (papulovesicular) | The formation of microvesicles is observed, which contain serous exudate (initially non-infectious). |
| 3 (wet) | After opening the vesicles, erosions and ulcers are formed. |
| 4 (secondary dry) | Wound healing is observed, a dense crust forms, and tissue scarring may develop. The disease returns to the first stage. |
Causes
To find out the etiology or origin of the disease, first of all, when searching for provoking factors, doctors evaluate the climatic conditions in which the person constantly lives. Environmental influences can negatively affect the delicate skin of the lips and face in general. External causes that contribute to the development of eczema on the lips can only work against the background of a weakened immune system. These include:
- excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- sudden change of cold and heat;
- prolonged exposure to the wind.
In addition to environmental factors, according to dermatologists, the eczematous form of cheilitis is provoked by an allergy that manifests itself on the face, including in the lip area, to irritants of various origins. In this case, the oral mucosa, as a rule, is not subject to a pathological process, but if you delay in contacting a doctor, the disease can spread from the nasolabial triangle to the surface of the lips. Provoking factors in this clinical situation are:
- low quality cosmetics, such as cheap lipsticks;
- individual hypersensitivity to toothpastes and mouth rinses;
- intolerance to dentures;
- food allergy.
Pills
To eliminate negative symptoms caused by allergies, antihistamines are prescribed:
- Pipolfen;
- Suprastin;
- Cetrin;
- Diazolin;
- Claritin;
- Tavegil;
- Zyrtec.
To combat weeping eczema, antiseptic agents will help:
- Fukortsin;
- Tsindol;
- Calamine.
Antiseptics help dry wet eczema and protect the skin from the development of pathogenic microorganisms. The use of antibiotics, antiviral, and antifungal agents is also possible. Immunomodulators are used to strengthen the immune system. Vitamin and mineral complexes will help speed up the healing process of damaged tissues
For allergic eczema, it is not recommended to choose vitamin complexes on your own - they can provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
Forecast
Early consultation with a doctor and treatment of the pathological process under his supervision are considered the main conditions for recovery. Only in such a situation are there chances that eczema will not become chronic.
Self-medication or prolonged ignoring of the resulting cheilitis leads to the spread of inflammatory foci to other areas of the skin, which aggravates the course of the disease and becomes the cause of incurable recurrent dermatosis. In this case, the prognosis for a person’s life is favorable, but for health it is negative.
Ointments and creams
Effective hormonal ointments include Prednisol and Soderm. These drugs have a beneficial effect on the skin and eliminate the negative manifestations of the disease. The use of ointments based on corticosteroid hormones is necessary only for severe forms of the disease.
This is due to many contraindications and side effects. It is not recommended to choose such remedies on your own - it is better to consult with your doctor.
The most effective non-hormonal agents include:
- Skin Cap;
- Aurobin.
These drugs have a minimum of side effects and contraindications. Help eliminate inflammation and speed up the regeneration process of damaged skin. Most effective in the early stages of eczema.
Zinc ointment shows high therapeutic results in the treatment of eczema. Helps cope with the disease within a week.
Complications
With the first signs of dermatosis on the lips, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist and begin the necessary treatment. This is due to the fact that eczema quickly develops and becomes chronic, provoking constant tension on the part of the immune and nervous systems and contributing to the formation of the following complications:
- The addition of a bacterial infection with the development of purulent inflammation, which aggravates the clinical picture of the disease, sometimes even to the point of sepsis, especially when the body’s defenses are weak.
- The formation of erythroderma is an extensive inflammatory process covering most of the body area.
To prevent these complications, it is important to treat even mild forms of dermatosis under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Traditional methods of treating eczema on the face
Traditional recipes are an effective addition to basic therapy, but are not able to cure the disease on their own.
It is important to note that in addition to the beneficial properties, traditional therapy methods have certain contraindications, which are important to consider before starting treatment. Otherwise, complications may develop.
| Recipe name | Cooking method |
| Potato compress | Grind two raw potatoes, mix with honey until smooth and thick. Apply to affected skin for 2 hours. You can also use potato juice to lubricate the rash with vesicles. |
| Propolis-based ointment | Mix 150 g of melted butter with 20 g of crushed propolis. Cook in a water bath, stirring constantly. Cool and apply on damaged skin before bed. |
| Berry compress | Grind 200 g of strawberries, mix with linseed oil (20 g). Use as a compress 2 times a day. |
Eczema on the face is a serious dermatological disease that requires timely medical attention. If the disease is advanced, it will regularly recur, cause serious complications, and be accompanied by the development of secondary infections.
Diagnostics
First of all, the dermatologist must conduct an external examination of the patient. In addition to the neck, you also need to examine the back and abdomen to rule out eczema in other parts of the body.
After a visual examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease based on the patient’s complaints, scrapes the affected epidermis to examine for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, for example, fungi or opportunistic microflora.
As additional studies, immunological and hormonal statuses are determined.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is careful care of the oral cavity and lips, aimed at maintaining their healthy condition. To do this, it is important to brush your teeth daily, visit the dentist on time and, if necessary, eliminate identified diseases (caries, stomatitis, etc.), prevent dry lips, and give up the habit of licking and biting them.
Thanks to these measures, it is possible to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microflora onto the surface of the lips with the subsequent formation of cracks. You also need to avoid spicy and sour foods, which irritate the skin and contribute to the development of cheilitis. Additionally, as a preventive measure, it is recommended to comprehensively strengthen the immune system, avoid potential allergens and monitor your own health.
At the first signs of irritation and inflammation in the lip area, you should not expect complications. You need to consult a specialist and eliminate any negative motives in the situation, and if necessary, undergo the recommended treatment.
source