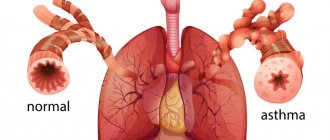
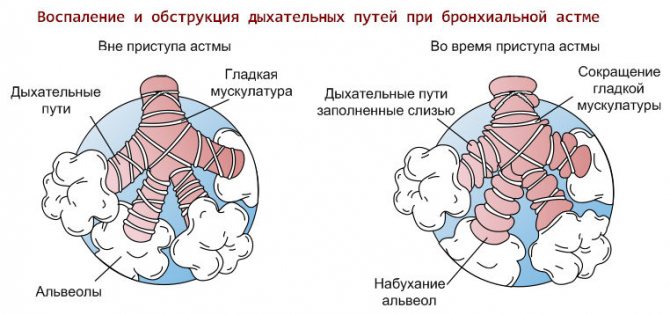
Bronchial asthma (BA) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways, which often causes bronchospasm. This happens under the influence of negative external factors.
They provoke the development of the disease and can also cause exacerbations. With such exacerbations, the patient exhibits symptoms of the disease in a very aggressive form. These events, called asthma attacks, are very dangerous and require urgent medical attention.
But the danger of the disease lies not only in its sudden and acute attacks. If there is no correct and effective treatment, bronchial asthma will lead to complications affecting not only the respiratory system, but the entire body as a whole.
- Types of respiratory complications
- Heart problems
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Complications in brain function
- Other consequences
The danger of bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma is a serious disease. The patient requires serious and long-term treatment. Only by following all the instructions of your doctor can you achieve a significant improvement in your condition. At the same time, the number of asthma attacks is reduced to a minimum, and it becomes possible to lead an almost normal lifestyle. At the same time, the patient constantly has to carry medicines with him to relieve an attack in case of exacerbation of the disease.
If medical prescriptions are not followed and the patient is not attentive enough to his health, dangerous complications may develop. First, the disease itself begins to progress. The intervals between attacks decrease, and the attacks themselves become more severe. There comes a time when independent measures no longer help, and urgent medical attention is required to save a life.
The consequences of bronchial asthma are the following types of complications:
- Pulmonary - damage to the respiratory system.
- Extrapulmonary - metabolic disorders, problems with the heart and blood vessels, brain damage, effects on the gastrointestinal tract and other pathologies.
Pulmonary complications Bronchial asthma can cause complications of varying severity. They are divided into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Why is asthma dangerous?
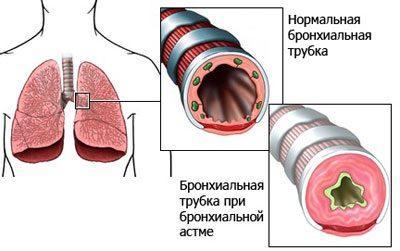
The patient's bronchial patency is impaired, which leads to constant oxygen deficiency. Treatment of asthma is long-term, but even the prescribed therapy will not lead to complete recovery, but will only alleviate the patient’s condition so that he can live a full life. Many people of different ages constantly carry a pocket inhaler with them in order to stop an attack if something happens. However, there are patients who do not take this disease seriously and completely ignore the instructions of specialists. They have absolutely no idea how dangerous this disease is and how complicated it can become.
In the absence of proper treatment, the disease gradually worsens, attacks of suffocation occur more often and, ultimately, status asthmaticus develops. In this case, the usual pocket inhaler cannot help, so serious treatment is required in a hospital setting. Bronchial asthma can also be complicated by individual systemic diseases, the treatment of which will take no less time than the asthma itself.
Asthma of allergic origin may not manifest itself for months or even years, but a disease of an infectious nature progresses very quickly.
Acute respiratory system disorders
Complications of bronchial asthma can manifest as acute symptoms. The patient's condition quickly becomes serious, and pronounced breathing problems are observed.
There are several possible complications:
- Asthmatic status.
- Acute respiratory failure.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax.
- Atelectasis of the lung.
- Pneumonia.
First of all, these complications are characterized by transience and pose a significant threat to life. It is necessary to urgently seek help from a medical institution.
Asthmatic status
The patient's life-threatening condition. The attack of suffocation lasts more than 30 minutes. Symptoms increase gradually. Medicines do not have any significant effect. Status asthmaticus cannot be stopped on its own.
In this case, the formation of edema in the tissues of the bronchi and a significant accumulation of sputum are observed. All this causes suffocation and, as a result, hypoxia.
The patient remains conscious until the third, most severe, stage of the complication occurs, during which consciousness fades and convulsions begin. Emergency treatment involves the administration of corticosteroid drugs and diuretics. Medicines are also prescribed to help with sputum removal. The third stage of the complication requires artificial ventilation.
Acute respiratory failure
It is diagnosed when there is an almost complete cessation of air flow into the lungs.
Symptoms of this complication:
- rapid, shallow breathing;
- severe, sometimes painful cough.
- the appearance of fear of death;
- gradually increasing suffocation.
Acute respiratory failure threatens the patient's life and requires emergency medical intervention. To alleviate the condition, it is necessary to increase the supply of oxygen to the body at any cost. For this use:
- artificial supply of air to the lungs;
- administration of hormonal drugs and diuretics;
- use of bronchodilator drugs.
During an attack, most often the patient takes a position characteristic of this pathology, aimed at alleviating the condition and improving the flow of air into the lungs. To do this, the patient rests his hands on a table or other hard surface and leans slightly forward.
Spontaneous pneumothorax
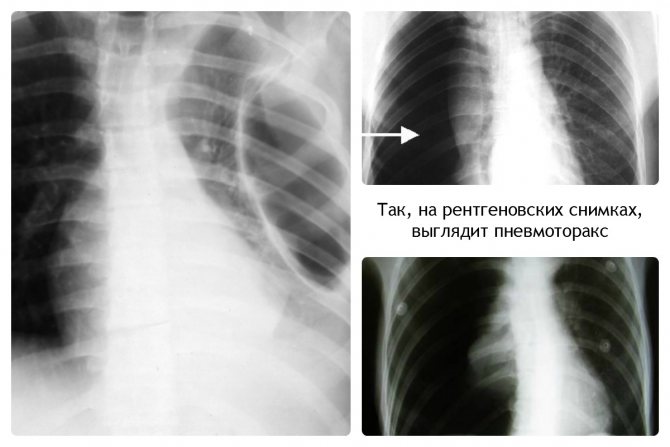
A very serious complication characterized by damage to lung tissue. As a result, air accumulates in the pleural cavity. In this case, the patient experiences severe pain. Urgent surgical intervention is required to remove air and restore the integrity of the lung.
Most often, this pathology occurs during prolonged and severe attacks of bronchial asthma.
Atelectasis of the lung
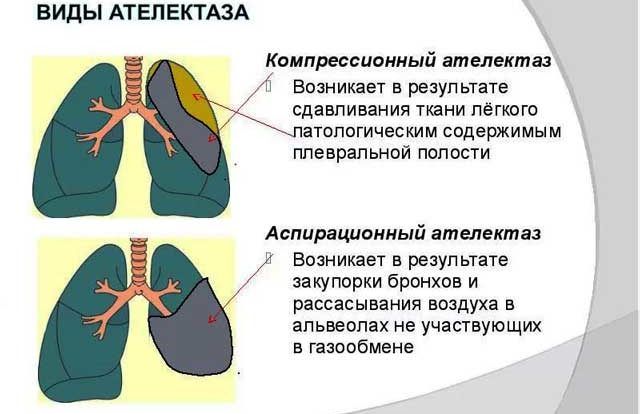
If, during asthmatic attacks, sputum is formed with a sufficiently dense and viscous consistency, there is a risk of it blocking the lumens of the bronchi. In this case, the lung decreases significantly in size, and collapse may develop.
The first sign of complications is shallow breathing. Gradually, the condition worsens, the patient finds it difficult to breathe, and chest pain occurs. The symptoms of the attack are similar to those of a normal attack, but the condition does not improve after taking conventional medications.
Pneumonia
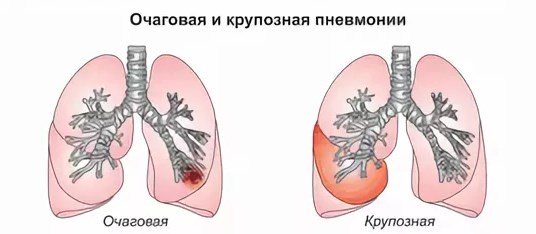
With pneumonia, inflammation develops in the lungs. Children are most often affected by the disease. In children, this complication occurs in a more severe form and requires more thorough treatment.
Against the background of reduced immunity in asthma, secondary infections may occur, which also worsens the patient’s condition.
For treatment, the doctor prescribes drug therapy:
- antibiotics;
- mucolytics;
- bronchodilators.
Treatment at home is dangerous and requires hospitalization.
Complications and consequences of asthma: extrapulmonary diseases, respiratory failure
Bronchial asthma is characterized by increased production of viscous sputum and periodic bouts of coughing, which are a consequence of bronchospasm and swelling that occur under the influence of provoking factors.
Chronic obstruction of bronchial patency leads to the development of compensatory mechanisms that are aimed at maximizing lung ventilation and oxygen supply to tissues. Gradually, the reserve capacity weakens, and asthma complications affect not only the respiratory system, but also affect other body systems.
The consequences are especially pronounced in people suffering from a hormone-dependent form of the disease, since glucocorticosteroid drugs gradually lead to addiction and require a constant increase in dosage.
The most common complications of asthma are effects on the respiratory system. A decrease in pulmonary ventilation and an increase in resistance in the bronchi lead to disruption of physiological functions and cause the formation of secondary pathology. All complications can be divided into acute and chronic:
- The first type of disorder develops in a short time, progresses quickly and directly threatens the patient’s life, and therefore requires emergency treatment.
- Chronic complications develop over a long period of time as a result of profound changes and are accompanied by structural and functional disorders, but at the same time they provide time to make a decision and choose a treatment regimen.
The consequences of bronchial asthma are easier to prevent, so it is important to take medications prescribed by your doctor and undergo diagnostic procedures in a timely manner.
Acute
A direct threat to life as a result of acute complications requires competent recognition, rapid response and first aid to an asthmatic. Regardless of the type of pathology, all the consequences of this group are characterized by a similar pathogenesis, when, due to impaired lung function, the body experiences a sharp lack of oxygen.
The main task, which is determined based on the presumptive diagnosis, is the speedy restoration of respiratory ability, improvement of bronchial patency, getting rid of edema and normalizing the functioning of the respiratory system.
In addition, asthmatics who are dependent on medications should always carry first aid supplies or have a doctor's note with them.
Atelectasis
Asthma is accompanied by increased production of thick and viscous mucus, which leads to increased stress on the bronchi. As a result of prolonged stretching of the bronchial structures, protrusion occurs in the most vulnerable place. Sputum accumulates in this depression, which gradually blocks the lumen of the bronchus.
Bronchiectasis often complicates the course of chronic bronchitis, and also becomes a consequence of allergic bronchial asthma. Typical symptoms of atelectasis include acute pain, difficulty breathing, bluish skin, severe wheezing and a semi-sitting position of the patient.
These manifestations resemble a prolonged asthma attack, and the main difference is the impossibility of relief with conventional medications.
Upper respiratory tract infections
People with this disease are especially susceptible to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. A common cold or flu often causes complications, leading to impaired respiratory function. A child or elderly person exposed to a viral or cold infection should be under the close attention of doctors until complete recovery.
Chronic
Bronchial asthma is a chronic disease that is accompanied by inevitable changes.
Chronic complications are not considered emergency conditions, but over time they worsen a person’s quality of life and lead to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
The lungs are the first to suffer, since excess load on the bronchi disrupts physiological functions. Proper treatment and careful attention to your own health can slow down negative reactions.
Extrapulmonary complications
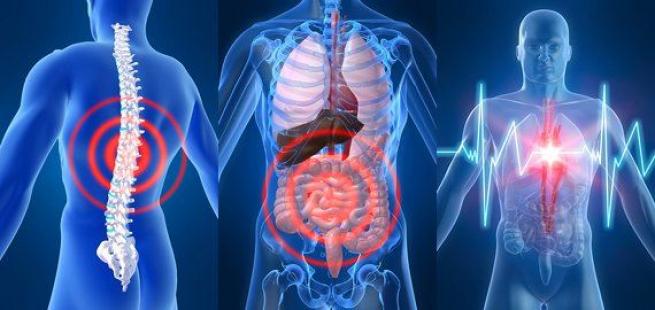
The consequences of bronchial asthma are manifested not only in disruption of lung function. Many other organs and systems may also be affected.
Most often the disease affects:
- cardiovascular system;
- metabolism;
- CNS;
- Gastrointestinal tract.
Main types of complications
Complications of bronchial asthma can be divided into several groups that relate to different organs.

Among them are:
- respiratory (acute or chronic type),
- heartfelt,
- gastrointestinal problems,
- brain,
- others.
Knowledge of these complications is necessary for patients, since not everyone considers it necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations. Sometimes patients believe that asthma cannot be cured, so there is no need to even try. But, knowing the consequences of bronchial asthma, which can be very large-scale, people become more responsible in relation to their health.
Types of respiratory complications
Complications of bronchial asthma, characteristic of the respiratory system, can be acute and chronic. Among the acute ones we can highlight:
- Asthmatic status. This problem is an acute attack of suffocation. This attack is characterized by duration; during it, the bronchioles swell and sputum accumulates in them. It is impossible to get rid of this pathology on your own; urgent help from a qualified specialist is needed.
Respiratory failure. In the presence of this pathology, almost no oxygen enters the lungs during breathing, which causes suffocation, and also increases the load on other organs and systems (due to oxygen starvation).- Spontaneous pneumothorax. It is characterized by rupture of lung tissue, which causes air to accumulate in the pleural cavity. In addition, the patient experiences severe chest pain.
- Atelectasis. This condition is characterized by impaired ventilation. It occurs due to the fact that the alveoli do not function properly, forming and accumulating dense mucus in the bronchi. In its manifestations, this disease is similar to an attack of asthma, but it lasts too long and cannot be controlled with conventional medications.
The main chronic respiratory diseases arising from asthma:
- Hyperinflation of the lungs. This diagnosis refers to the tendency of the lungs to become full of air. In this case, the patient cannot completely empty the lungs during exhalation, which means the respiratory system is not functioning properly.
- Emphysema. In this case, expansion of the bronchioles and modification of the alveolar walls occurs. Lung function is impaired. Frequent symptoms of the disease are cough and shortness of breath.
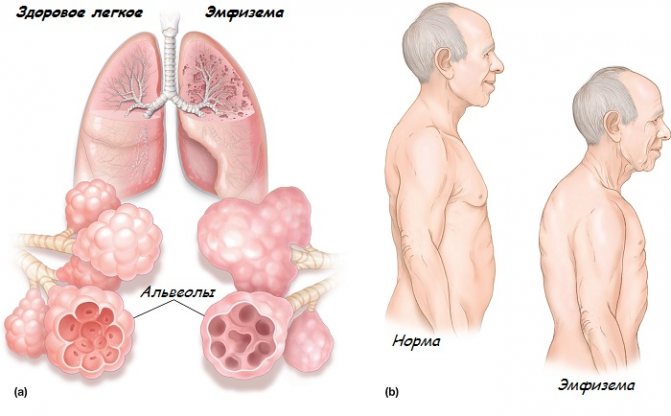
Emphysema
- Pneumosclerosis. In the presence of this disease, part of the active lung tissue may be replaced by inactive tissue. This leads to disturbances in the functioning of the organ, chest pain, constant shortness of breath and cough.
Heart problems
With bronchial asthma, the patient's body may experience oxygen deficiency, which impairs the functioning of many organs. First of all, this affects the heart, which is forced to contract more intensely in order to supply the body with useful substances.
If this phenomenon occurs too often, irreversible changes may occur in the functioning of the heart. The most common occurrence in this case is the development of cor pulmonale in the patient. This is a pathology in which the walls of the organ thicken, and the organ itself increases in size. The patient experiences weakness, loss of appetite, frequent headaches, and decreased performance. Fainting is often observed with this pathology.
Another problem is excessive stress on the vessels, which leads to their thinning and increased pressure.
Gastrointestinal problems
Complications in the gastrointestinal tract do not arise due to bronchial asthma itself. Illness is only an indirect stimulus. The fact is that the treatment process for asthma is long, and the patient is forced to take medications daily.
Despite the fact that bronchial asthma is neutralized with the help of medications, their frequent use causes consequences that are unfavorable for the body.
This manifests itself not only in digestive disorders - in some cases internal bleeding may begin. Therefore, efforts should be made to prevent this complication.
Complications in brain function
This type of consequences is the most severe, since the brain affects the functioning of all other organs. Brain complications of bronchial asthma are due to the fact that brain function is adversely affected by any changes in the composition and quantity of blood.
Since in asthma there is often a deficiency of oxygen and oversaturation of the blood with carbon dioxide, pathological processes may occur in the brain tissue. This causes disturbances in memory function, and it is also much more difficult for a person to concentrate. Disorders of consciousness are not uncommon, which manifest themselves in the form of excessive irritability, frequent mood swings, and aggressiveness. A person is characterized by depressive thoughts, emotional instability, and decreased performance.
One of the brain complications of asthma is called bettolepsy. It occurs as a reaction to a failure in the process of cerebral blood supply. A severe cough provokes an increase in pressure in the chest area, due to which consciousness may be briefly impaired during such an attack.
Other consequences
These complications include those associated with diseases accompanying bronchial asthma. These consequences rarely occur, but if they occur, it is not easy for a person.
The main ones:
- Urinary and fecal incontinence. During aggressive coughing attacks, intra-abdominal pressure may increase. If the patient is characterized by such a feature as sphincter weakness, there is a possibility of these problems occurring.
Uterine prolapse. The same reasons as in the previous case, combined with a weak perineal muscle, can lead to this phenomenon. Rectal prolapse also sometimes occurs.- Hernias of various types. They occur during severe asthmatic attacks.
- Ruptures of internal organs, internal bleeding. This type of complication occurs rarely; it is provoked only by very severe bronchial asthma.
Cardiovascular disorders

First of all, the cardiovascular system reacts to a lack of oxygen. She suffers especially severely during attacks, when the air supply is severely limited. Also, the functioning of the heart is affected by drug therapy, which doctors are forced to prescribe to relieve the symptoms of bronchial asthma.
Complications associated with the functioning of the heart and blood vessels are characterized by the following symptoms:
- During an attack, blood pressure drops significantly. This may lead to loss of consciousness.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle contribute to the development of myocardial infarction. Possible cardiac arrest.
- Patients who have suffered from asthma for many years have an increased risk of developing a complication called cor pulmonale. In this case, changes occur in the tissues of the heart, leading to disturbances in its functioning.
You should also take into account the effect of the disease on blood vessels, which become less durable due to increased load.
Metabolic disorders

One of the most severe complications of bronchial asthma is metabolic pathology. First of all, this affects the composition of the blood. A lack of potassium and oxygen with an excess of carbon dioxide is a standard clinical picture in such patients. All this causes disruptions in the functioning of the body.
The most common pathologies of metabolic disorders:
- Hypokalemia. Lack of potassium in the body. Patients in this case complain of increased fatigue and insufficient performance. Pain in the arms and muscle cramps may occur. In advanced cases, all human organs are affected. Paralysis may develop.
- Metabolic acidosis. With this complication, the internal environments in the body begin to acidify. The patient experiences nausea, sometimes vomiting, drowsiness, and a change in breathing rhythm. If measures are not taken, arrhythmia may occur, and in the most severe cases, coma.
- Hypercapnia. Characterized by excess carbon dioxide in the blood. At the same time, the heart rate increases and blood pressure rises. Possible arrhythmia. The skin color changes and acquires a bluish tint. Headaches and various disturbances of consciousness are possible.
Almost always, complications of asthma associated with metabolic disorders are treated in a hospital setting, since they can lead to irreversible consequences for the body.
Gastrointestinal disorders

With asthma, complications associated with the functioning of the digestive system are common. Vital medications, especially glucocorticosteroids, have a detrimental effect on the walls of the stomach and intestines.
The most common pathologies are:
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Damage may affect either one organ of the digestive system or both at the same time. Due to improper metabolism, the mucous membrane is destroyed. This causes long-term pain. Nausea, vomiting and significant weight loss may occur.
- Perforated ulcer. If a peptic ulcer is not treated promptly, the walls of the stomach or intestines can become thinner and rupture, causing gastrointestinal contents to leak into the abdominal cavity. The condition is life-threatening for the patient. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
When treating asthma, it is important to monitor the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and provide supportive therapy.
Effect on the digestive organs

Patients often suffer from frequent abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea. Problems with stool are possible when the patient cannot go to the toilet for several days or, conversely, has diarrhea. This condition is very exhausting for an already weakened asthmatic and can provoke more and more new attacks. With such complications, there is a high probability of developing internal bleeding. If internal bleeding opens, then emergency medical attention is needed. This condition can quickly lead to a heart attack and death. The patient should be alerted by scarlet blood in vomit or feces.
If the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms. If internal bleeding occurs, then the help of a surgeon is necessary.
Pathologies of the central nervous system
Attacks of bronchial asthma cause severe forms of complications associated with the functioning of the central nervous system. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain leads to the following disorders:
- Respiratory encephalopathy. Brain tissue is affected. Symptoms are: headache, extraneous noise in the ears, changes in sensitivity. Possible loss of vision and hearing.
- Bettolepsy. Fainting associated with painful cough. Loss of consciousness can be either short-term or long-term.
- Brain dysfunction. Various changes occur related to the functioning of the brain: behavioral disorders, decreased or changed sensitivity, and so on.
Brain diseases
In the absence of normal therapy, bronchial asthma is complicated by brain diseases. These are the most severe consequences that asthmatics can have. The danger is explained by the following factors:
- With asthma, the amount of blood and its qualitative composition decrease slightly, which can affect brain tissue.
- There is a lack of oxygen, due to which the brain works worse.
- The blood contains a high content of carbon dioxide, which also negatively affects brain function.
Because of all this, the consciousness of the sick person is disturbed and memory suffers greatly. The patient may become extremely aggressive and irritable for no apparent reason. An asthmatic suffers from fatigue, mood swings and frequent depression.
If the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, betolepsy occurs. During severe coughing attacks, when very little oxygen reaches the brain, fainting may occur.
To eliminate these phenomena, special blockers, hormonal drugs and analgesics are prescribed. Treatment usually takes at least 3 months, but this period may vary depending on the age of the patient and the severity of his condition.
Treatment of complications of bronchial asthma is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. If the prescribed therapy does not produce an effect, the treatment regimen is reviewed.
Complications of asthma in children

Complications of bronchial asthma also occur in children. The most common symptom is atelectasis, among other things. Emphysema, diagnosed using an x-ray, is also possible. If in children, during a laboratory study of mucous secretions from the bronchi, not bacterial components are diagnosed, but eosinophils, this shows that the disease is not of an infectious nature, it is atopic.
If the child is not treated on time or does not follow the doctor’s recommendations, bronchiectasis may develop. It is characterized by a purulent inflammatory process occurring in the tissues of the bronchi. Cases of pneumosclerosis have also been recorded.
Preventing complications in children is an important component of the treatment of bronchial asthma.
What are the complications?
Complications of bronchial asthma can be different. Doctors distinguish 6 categories of such consequences - respiratory, cardiac, digestive, metabolic, cerebral and others. In addition, the disease can quickly be complicated by status asthmaticus, oxygen deficiency and spontaneous pneumothorax. With asthmatic status, a prolonged attack of suffocation occurs, which is very difficult to relieve with conventional methods. This is explained by severe swelling of the bronchi and adjacent tissues.
With oxygen deficiency, not enough oxygen enters the lungs, so all organs work under wear and tear, with increased load. This phenomenon can be eliminated only with the help of drugs that relieve spasm from the bronchi.
In spontaneous pneumothorax, lung tissue suddenly ruptures. This is accompanied by pallor, unbearable pain in the sternum and a disturbance in the general condition of the patient.
In addition, pneumomediastinum may develop, a condition in which air collects in the mediastinum. Severe pneumonia can also occur against the background of bronchial asthma. This occurs due to the fact that when the immune system is weakened, a secondary infection occurs.
Asthma is sometimes complicated by atelectasis. In this condition, attacks are especially long-lasting and stopping them with usual medications is quite problematic.
Preventing asthma complications
Complications from bronchial asthma always have serious consequences for the patient. And, like any other disease, they are easier to prevent than to treat.
First of all, it is important to prevent exacerbations of the underlying disease. For this it is recommended:
- Follow all doctor's instructions.
- If possible, eliminate the risk of contracting acute respiratory diseases. To do this, there is a whole range of measures related to both strengthening the immune system and personal hygiene.
- Eliminate bad habits. Smoking is especially dangerous.
- Watch your diet. Products containing allergens can trigger an attack.
- Do breathing exercises every day.
It is important to understand that by taking measures to prevent exacerbation of the disease, you can significantly improve your quality of life, reduce the negative impact of the disease on the body and avoid serious complications.