- July 23, 2018
- Dermatology
- Timoshenko Mikhail
Signs of ear dermatitis can appear suddenly, without obvious reasons. Without proper timely treatment, the rash can spread into the inner ear canal, causing serious health consequences. To avoid discomfort and prevent complications, it is worth understanding how ear dermatitis is treated in people, what are the causes of the development of the disease, and what are its main symptoms. The answers to these and other questions are presented in our material.
Causes of the disease
Dermatitis can occur due to the following factors:
exposure to chemicals on the external auditory canal; prolonged discharge of purulent contents and itching behind the ears; any types of dermatitis, especially seborrheic; decreased immunity; the presence of chronic infections in the body; allergic predisposition; symptoms of general intoxication of the body; metabolic disorders, etc.
In addition, the cause of the development of dermatitis can be scratching behind the ears and mechanical damage to the ear, which leads to secondary infection and the development of dermatitis.
Course of the disease in children
Symptoms of dermatitis in childhood can be observed due to the persistence of residual maternal hormones in the body of children. In addition, there is an opinion that seborrheic dermatitis, which often accompanies ear diseases, can be inherited by children.
The disease in children most often develops in the first months of life and, as a rule, goes away on its own. However, it should be understood that this does not mean that these symptoms in children can be ignored.
It is not difficult to identify the disease in childhood, since the ears are covered with greasy scales that constantly peel off onto clothing. Most often, the disease is accompanied by dandruff, which proves the relationship with the seborrheic form of dermatitis. Often, seborrheic and ear dermatitis leads to secondary infection, and if the child does not have preventive measures and appropriate care, antibiotic therapy may subsequently become necessary.
Treatment is carried out taking into account the general condition of the baby. In young children, treatment can be carried out externally, and in more severe cases, hydrocortisone ointment is recommended, which is considered the weakest hormonal agent and is quite suitable for children.
Causes of development of atopic ear dermatitis
The disease usually manifests itself in childhood. Most often, the disease affects people whose relatives suffer from asthma, suffer from rhinitis, and other disorders of a similar nature. According to recent research, atopic dermatitis of the ears may develop due to changes in the immunological balance in the body. With the latter, T-lymphocytes begin to significantly predominate in the composition of bodily fluids. The result is accelerated synthesis of interleukins, which leads to the appearance of a rash.
In general, there are several triggers for the development of atopic dermatitis of the ears. Among the most common causes of the disease it is worth noting:
- sudden changes in the environment;
- use of skin irritants;
- emotional instability, tendency to develop stress.
Symptoms of ear dermatitis
Characteristic signs of the disease are:
severe itching of the affected areas on the ears; the skin in the ear area is swollen and swollen; a weeping wound surface may appear; there is peeling of the skin in the area of the auricle; bubbles and hard crusts are found in the lesion; very often the disease is accompanied by the release of pus from the wound surface.
With the acute development of dermatitis, symptoms may occur suddenly and are characterized by a gradual increase until the pathological process spreads to the external auditory canal. In this case, the patient experiences excruciating itching, which forces him to scratch the area behind the ears, which can be complicated by the appearance of boils, which can lead to hearing loss.
Treatment of ear dermatitis
Dermatitis of the auricle must be treated comprehensively, using all necessary therapeutic measures.
Most often used for treatment:
Treatment of dermatitis should begin by wiping the inflamed area with 3% hydrogen peroxide or soap and soda solutions. This allows you to get rid of accumulated exudate in the ear canal with simultaneous disinfection; if acute symptoms of dermatitis are observed, it is recommended to take antihistamines (Loratadine, Zyrtec, Erius, etc.); in addition to antihistamines, treatment can be carried out with corticosteroids in the form of ointments (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Geocortone, etc.);
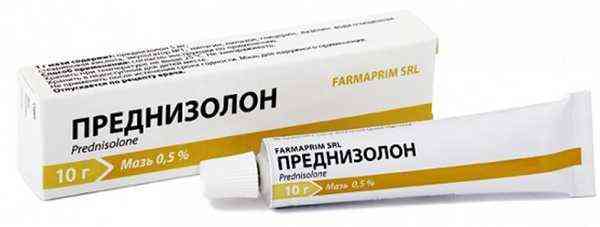
if symptoms of infection appear, antibiotic therapy is prescribed (Flucloxacillin, Erythromycin, etc.); To completely cure dermatitis on the ear, it is necessary to follow a hypoallergenic diet and include a large amount of fruits and fiber in the diet. Compliance with this condition is especially important for people with gastrointestinal diseases. In addition, the diet normalizes metabolic processes in children.
In addition, complex treatment involves physiotherapeutic measures (UV therapy, X-ray therapy and UHF).
Treatment methods
Dermatitis can be of different types and severity, so the selection of medications is individual in each case and is carried out directly by the doctor.
The initial stage of treatment is to eliminate the influence of factors that provoked the development of the disease, get rid of itchy skin and follow the prescribed diet.
It is recommended to daily wipe the outside and inside of the ear with hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, and a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Medicines are also used:
- Therapeutic shampoos for seborrheic dermatitis (Nizoral, Sulsena, Friederm, Sebozol) stop the process of fungal reproduction, promote the healing of damaged skin, and normalize sebum secretion.
- Ear drops (Polydex, Otofa) act on pathogenic organisms and relieve inflammation in the ears.
- Creams, ointments, gels (Fenistil, Losterin, Zinocap, Desyatin) dry the affected surface, reduce skin itching, and promote the healing of dermatological lesions.
- After drying the wet surfaces, use Bepanten, Solcoseryl, Actovegin. They improve nutrition and normalize the metabolism of skin cells, stabilize their division.
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Loratadine, Zodak) eliminate burning and itching, reduce swelling and reduce inflammation.
- Immunomodulators help the body successfully fight allergens and bacterial infections by strengthening the body's defense reactions.
- Enterosorbents (Enterosgel, Laktofiltrum, Polysorb) are used to remove allergens from the body and reduce intoxication of the body when taking medications.
- Emollients (vaseline, mineral oil, Emolium, Physiogel, Topicrem, Mustella) are used in children with atopic dermatitis to restore the fat layer and maintain the water balance of the skin. Apply to pre-moisturized skin.
- Glucocorticosteroids have varying degrees of activity and have many side effects, so they are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease.
- In complicated cases with concomitant fungal or bacterial infection, antibiotics are used.
As additional methods of treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out, including ultraviolet therapy and phototherapy.
To avoid relapse of ear dermatitis, you should complete the full course of treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Folk remedies
In addition to the pharmacological effect on the body in getting rid of the negative symptoms of the disease, therapy using traditional medicine recipes has shown good effectiveness. Among these methods, various lotions with anti-inflammatory decoctions are especially popular to relieve the acute process that develops in the ears.
To use traditional medicine, the following criteria are required:
advanced form of ear dermatosis. lack of the desired result with traditional treatment; the need for complex therapy; symptoms of dermatitis associated with deterioration of ear function must be present;
1. CREAM WITH WOOD. To obtain a greater effect, it is recommended to prepare a cream with elecampane. To do this you need to mix 2g. elecampane with pork or goose fat (100 g), then heat the mixture in a water bath. The mixture must be left for 2-3 days, then filtered and lubricated on the affected areas of the ear.

2. SOLUTION. Weeping rashes can be wiped with a solution prepared from a solution of pyoctanin, boric acid and 2% silver nitrate. All ingredients must be taken in equal quantities.
3. OINTMENT FROM STARCH. A medicinal ointment that is prepared from 2 parts starch, 2 parts zinc oxide and 1 part each lanolin and petroleum jelly has the same effect.
4. PHYTO TEA. In case of acute manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to take herbal tea from medicinal plants (juniper, soapwort, strawberry leaf, etc.) by brewing 1 tbsp. l. herbs 0.5 liters of boiling water.
It is important to remember that herbal medicine cannot replace traditional treatment. It is only an auxiliary method, complementing it.
Dermatitis of any nature means a disease of the skin that is caused by various physical, chemical, and biological factors. Dermatitis can take a variety of forms, ranging from harmless flaking of the skin to serious dysfunction of the skin.
Ear dermatitis is an inflammatory process that occurs on the outer part of the ear canal. The whole danger of this type of pathology lies in the fact that if left untreated, it can develop in the inner part of the ear. This in turn will cause inner ear dermatitis.
Causes
The following factors can cause the development of the disease:
- Headphones made of low-quality plastics and rubber.
- Hearing aids for the same reason.
- Various jewelry - low-quality metal earrings, clips; Some people have allergic dermatitis to gold jewelry.
- Improper cleaning of ears, use of cotton swabs, to which allergies are possible.
- Hair products (sprays, mousses) - in case of contact with the skin of the auditory tube or concha.
- Injuries, burns (fire, acids, alkalis, etc.).
- Sometimes the cause is autoimmune processes (for example, psoriasis.)
Inflammation can be of the following types: atopic, seborrheic, contact. Atopic is characterized by a triad of symptoms:
- Itching, which is localized behind the ear, around it.
- Redness in the itchy area.
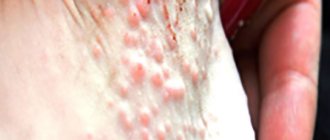
- Bubbles that burst and then constantly get wet.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wgDzoJDNvrI
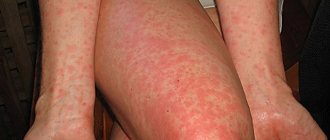
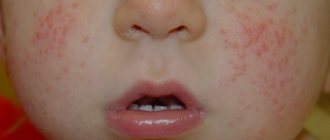
The atopic form is a manifestation of a systemic disease. It appears in childhood and is often combined with asthma and rhinitis of allergic origin. With constant scratching, the skin thickens and pigmentation increases. In addition, the lesion is localized on the face and neck in children, as well as on the arms and lower extremities in adults.
Direct manifestation of a contact allergic reaction when exposed to contact sensitizers. Here the triad of symptoms is different:
- Hyperemia, swelling of the skin near the auricle.
- Itching, milder than in the first form.
- Bubbles filled with liquid. Crusts form on them over time.
This form of the disease can be suspected by performing a simple skin test for allergens. Most often, allergens are various chemical compounds contained in rubber, plastic, metal of hearing aids, headphones, as well as various shampoos, gels, and perfumes. Cold air may also be the cause; read this article for details.
The etiology of seborrhea is always associated with a fungus. More than 80% of cases occur in infants. It is hereditary. Sometimes the cause is a lack of B vitamins. Symptoms are milder than in previous forms of ear dermatitis. This is itching, inflammation of the scalp around the ear, and dandruff.
Important! Only a qualified dermatologist has the right to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment of ear dermatitis can be divided into several lines. This is a conservative therapy using ointments, creams, drops, and other dosage forms depending on the form. The second is physical therapy, with the appointment of adequate procedures. Third - traditional medicine methods.
Before application, it is necessary to wipe the areas of inflammation with hydrogen peroxide (3% - solution). You can use soda and soap solutions. Local corticosteroids are used - prednisolone, hydrocortisone, clobetasol. Ointments help get rid of local symptoms: relieve swelling, redness, itching, and reduce inflammation.
For severe itching, antihistamine ointments are prescribed. They contain a drug that blocks histamine receptors, eliminating itching. Special creams are used to moisturize and soften the skin. They need to be used daily, in combination with ointments and drops. These include Vaseline, Bepanten, glutamol and others.
Bubbles in atopic and allergic dermatitis can be wiped with solutions of silver nitrate (2% solution), a solution of boric or picric acid. You can use ointments based on zinc oxide and starch.
In case of severe skin damage and the systemic nature of the disease, the use of systemic glucocorticoids and antibiotics is indicated. For seborrheic form, antifungal drugs are also prescribed for oral administration. And ointments containing drugs such as fluconazole, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole are used topically. The most common cream is Triderm, Trimistin.
For fans of oriental medicine, it is possible to use Chinese ointments, which you can learn about in this article.
Basically, to relieve inflammation inside the auricle and in the external auditory canal, drops based on anti-inflammatory drugs are used. The composition includes both conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (salicylates) and corticosteroids in combination with antibiotics. They are indicated when a bacterial infection is attached.
Physiotherapy
Today, physiotherapeutic procedures are a method of joint treatment. Here is a list of basic procedures:
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Phonophoresis with corticosteroids;
- Laser therapy;
- Electromagnetic radiation.
Ural irradiation improves metabolic processes and tissue trophism. Laser therapy affects areas of inflammation and leads to faster healing. Irradiate exposed affected areas with radiation from the red or near-infrared part of the spectrum. The latter is used already in the presence of crusts and scales. Phonopharesis based on corticosteroid ointments in the ear area eliminates itching, redness, and pain.
Home remedies include lotions and plant compresses. Rhubarb, juniper, strawberries, and black elderberry are often used. They are poured with boiling water at the rate of 1 teaspoon of dry matter per glass. Take 1 tablespoon several times a day.
Ointments are prepared to lubricate skin with areas of dermatitis. Elecampane root powder in the amount of 2 grams, one hundred grams of animal fat are mixed, placed in a water bath, then cooled. Apply 2-3 times a day.
For antiseptic purposes, lotions based on infusions of lingonberries, walnut leaves, sage, and chamomile are used.
One possible cause cannot explain the disease. As with other dermatitis, here it is a combination of internal (genetic) and external factors (acquired).
The main reasons are as follows:
- This ear infection is a syntropic disease. – This means that it manifests itself together with other allergic inflammations of the skin and mucous membranes. – This disease is often observed in combination with atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis. – Syntropic diseases are caused by syntropic genes. – These large genetic complexes can be transmitted through both parental lines.
- A particular manifestation of psoriasis, which is currently classified as an autoimmune pathology.
- An infection in the outer ear or ear canal. – The lesion can be provoked, for example, by Staphylococcus aureus, meningococci, group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, etc. – An additional factor is the depressed state of the immune system.
- Hypothermia. It is often a concomitant symptom of cold otitis media.
With allergic sensitization of the body, dermatitis is provoked by:
- jewelry - earrings containing nickel;
- cosmetics - shampoos with a high concentration of lauryl sulfates.
The signs of a diseased ear affected by dermatitis are recognizable, the symptoms are characteristic and the treatment is determined.
Symptoms of the disease are revealed during the initial examination of the patient:
- The skin in the area of the outer ear, earlobe, and pinna is hyperemic and swollen. – There is pronounced dry peeling of the epidermis, externally similar to hyperkeratosis.
- Vesicles and papules sometimes appear behind the ears; weeping, characteristic of an eczematous lesion, is much less common.
- There is slight pigmentation behind the auricle.
- The ear canal is inflamed, there is excessive secretion of sulfur, sometimes mixed with pus and mucus (especially if there is a secondary infection).
- A feeling of itching and burning, also inside the ear canal, a feeling of ear congestion.
- With severe inflammation, systemic signs may be observed, for example, evening low-grade fever.
Ear dermatitis is a chronic disease that worsens when exposed to triggering factors or seasonally.
Before starting any therapy, it is necessary to eliminate possible triggering factors:
- aggressive cosmetics;
- jewelry and ear piercings.
Treatment of ear dermatitis is conservative and does not require hospitalization (unless there are some serious complications, such as the spread of the inflammatory process to the membranes of the brain).
Main methods of therapy:
- drug systemic and local therapy (tablets, creams, ointments, gels);
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- methods of traditional medicine.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy - comes down to various options for the impact of electromagnetic radiation on the body, including directly on the affected areas.
We suggest you read: My wife has thrush - how to treat her husband: ointments, tablets, folk remedies
This effective treatment is based on several methods:
- Ultraviolet irradiation with different wavelengths (short, medium, long waves). – Long-wave ultraviolet stimulates cell division in the epidermis and melanin synthesis. – Medium wave ultraviolet leads to the release of vasoactive mediators in the dermis, which improve capillary permeability. – Short-wave ultraviolet light has a pronounced mycocidal, antiviral and antibacterial effect.
- Electrophoresis. – All biochemical reactions in the body are reactions of ions. – Any drugs that enter the body also turn into ionic form. – In an electromagnetic field, charged particles begin to move. Consequently, with the help of electromagnetic radiation it is possible to accelerate and enhance the penetration of drugs deep into tissues.
- Exposure to weak currents of variable frequency. – Significantly enhances regenerative processes, stabilizes cell membranes, and in particular, the ion balance of sodium and potassium.
- Inductothermy. – With dermatitis, the most common area of influence is the adrenal glands. – The bottom line is that a magnetic field with variable parameters enhances the production of hormones of the adrenal cortex (its own corticosteroids), which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
- Laser therapy. – The biochemical mechanisms of action are similar to those that occur during treatment with weak alternating current, but the zone of influence is targeted.
- This ear infection is a syntropic disease. – This means that it manifests itself together with other allergic inflammations of the skin and mucous membranes.
– This disease is often observed in combination with atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis.– Syntropic diseases are caused by syntropic genes.
– These large genetic complexes can be transmitted through both parental lines.
- A particular manifestation of psoriasis, which is currently classified as an autoimmune pathology.
- An infection in the outer ear or ear canal.
– The lesion can be provoked, for example, by Staphylococcus aureus, meningococci, group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, etc. – An additional factor is the depressed state of the immune system. - Hypothermia. It is often a concomitant symptom of cold otitis media.
Ear dermatitis ICD 10
According to ICD 10, dermatitis combines a whole group of skin diseases (seborrheic, atopic, dysmenorrheic, allergic, etc.). In the case of ear dermatitis, we are talking about a painful process that occurs strictly within the auditory canal.
This problem is not as harmless as it might seem. In some cases, dermatitis can go away on its own, but this does not always happen. Often, ear dermatitis seriously bothers both adults and children, annoying with constant itching, peeling of the skin, and irritation.
Ignoring symptoms leads to dermatitis progressing. Within a short period of time, it will be possible to observe a full-fledged inflammatory process, which will require more serious and high-quality treatment.
Causes
Ear dermatitis is directly related to a person’s attitude towards himself. Often the cause of the disease is a careless attitude to hygiene, to the selection of jewelry, glasses and other personal items.
In second place are health problems. However, it must be remembered that sometimes completely unpredictable factors can cause an inflammatory process:
irritation due to exposure to chemicals; incorrectly selected glasses frames; decorative cosmetics; wearing headphones, hearing aids; incorrectly selected ear jewelry; allergic reaction; reaction to purulent discharge that appears as a result of an illness in the inner ear canal; cosmetics for hair styling.
The onset of the disease can be triggered by a wide variety of medications (side effects), allergens, especially food ones. If you notice suspicious redness and peeling, you should consult a dermatologist for advice to avoid complications.
Also, mechanical damage to the skin can often cause the inflammatory process. This includes not only specific contact of the skin of the ear with any object, but also the bite of an animal, as well as an insect.
The following can become a catalyst for the occurrence of ear dermatitis:
low protective abilities of the immune system; chronic diseases of various types; metabolic disorders; tendency to allergies; intoxication; work in hazardous production; unfavorable environment.
Special attention should be paid to the irritation that children have. In this case, you absolutely cannot hesitate, since the infection has an extremely negative effect on the condition of delicate, baby skin.
Until you go to the doctor, you should not treat the skin, comb it, or try to remove flaking skin. Some measures taken independently can have an extremely negative impact on the general condition of the epidermis.
Symptoms
The main and most important symptom of ear dermatitis is a change in the color of the skin of the ears. On examination, there is obvious hyperpigmentation and the top layer of skin is noticeably thickened. The patient develops unbearable itching, which he strives to constantly eliminate, which is absolutely forbidden to do.
Signs of the disease include the following changes:
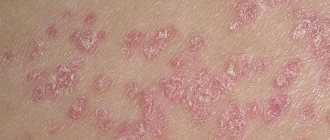
swelling; swelling; redness; peeling; the presence of wet areas of the skin; release of exudate; the presence of warts (in the chronic form of the disease).
In some cases, with ear dermatitis, hard crusts and blisters can be found. Sometimes the common form of ear dermatitis can progress to a weeping stage, which contributes to the appearance of wounds, pus and an unpleasant odor.
Itching in the ears as a symptom of dermatitis:
Forms and symptoms
Inflammation can be of the following types: atopic, seborrheic, contact. Atopic is characterized by a triad of symptoms:
- Itching, which is localized behind the ear, around it.
- Redness in the itchy area.
- Bubbles that burst and then constantly get wet.
The atopic form is a manifestation of a systemic disease. It appears in childhood and is often combined with asthma and rhinitis of allergic origin. With constant scratching, the skin thickens and pigmentation increases. In addition, the lesion is localized on the face and neck in children, as well as on the arms and lower extremities in adults. The blisters are intact at first, but when scratched they burst, become wet, and do not heal for a long time. A secondary infection may occur, then the patient’s condition worsens. Symptoms include fever and general malaise. You can read more about the disease in children here.
Allergic dermatitis
Direct manifestation of a contact allergic reaction when exposed to contact sensitizers. Here the triad of symptoms is different:
- Hyperemia, swelling of the skin near the auricle.
- Itching, milder than in the first form.
- Bubbles filled with liquid. Crusts form on them over time.
This form of the disease can be suspected by performing a simple skin test for allergens. Most often, allergens are various chemical compounds contained in rubber, plastic, metal of hearing aids, headphones, as well as various shampoos, gels, and perfumes. Cold air may also be the cause; read this article for details.
Seborrheic dermatitis in the ears
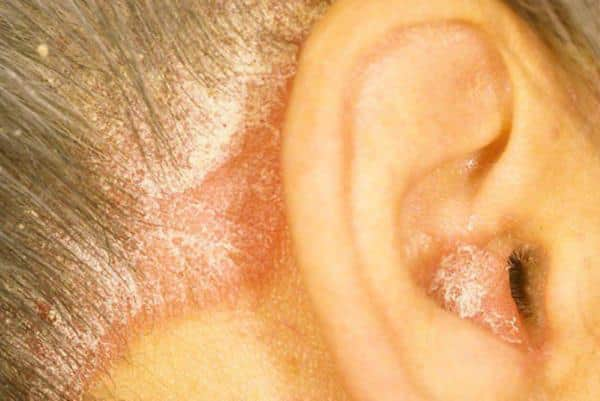
The etiology of seborrhea is always associated with a fungus. More than 80% of cases occur in infants. It is hereditary. Sometimes the cause is a lack of B vitamins. Symptoms are milder than in previous forms of ear dermatitis. This is itching, inflammation of the scalp around the ear, and dandruff. Oily, white-gray scales appear that constantly peel off.
Treatment
Treatment of ear dermatitis should be comprehensive and only under the strict guidance of a doctor. The main basis is built on the use of various ointments and creams. In difficult cases, antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed.
The patient also needs to remember that dietary adjustments are recommended for treatment. The therapeutic diet involves the exclusion of possible allergenic and heavy foods, as well as sweets and flavorings. Such nutrition additionally allows you to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Medication
Drug treatment is prescribed only by the treating dermatologist. Having familiarized himself with the existing diagnosis and its form, he makes the necessary appointments. In the standard version, the patient receives the following list:
ointments and creams to combat ear dermatitis; antibiotics; drinking medicinal mineral water; physiotherapy, consisting of x-ray therapy, UHF and UV.
Treatment of dermatitis should be carried out according to a strictly prescribed scheme. Departure from the doctor’s recommendations may provoke an increase in
painful symptoms
, which will reduce all expended forces to zero.
Folk remedies
Natural substances are excellent in helping to cope with ear dermatitis. They have excellent antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. The main problem is to choose exactly the tool that will be useful specifically in your case.
So, for help, you can turn to the same doctor with whom you are being treated or use special medical literature.
Folk remedies help perfectly in such cases:
lack of quick results through drug treatment; chronic dermatitis; acute dermatitis or advanced disease.
Properly made product allows you to achieve good results within a short period of time. After the first use, the patient feels significant relief, itching goes away, redness and swelling go away.
Herbal medicine cannot be taken as a basis in the treatment of dermatitis. In more advanced cases, it will not bring results, but will only worsen the situation.
For simple forms of ear dermatitis, it is best to use:
strawberry leaves; juniper; anise; elder; centaury; smoker; beans; celery; Tartar; chamomile; Oak bark; thuja; sorrel; bedstraw.
It is best to use medicinal herbs as tea. They will strengthen the immune system, improve metabolism and help speedy healing of dermatitis. In some cases, lotions are indicated for treatment. But it is better to discuss their use with your doctor.
Possible complications
Complications from ear dermatitis are quite rare, but they do occur. The thing is that if left untreated, dermatitis spreads extremely quickly, affecting healthy areas of the epidermis. This brings many unpleasant symptoms, ranging from itching to severe inflammation and swelling of the affected areas.
When scratching, there is a high probability of infection entering the ear. This, in turn, is fraught with the appearance of an inflammatory process directly inside the ear canal. This greatly complicates the treatment process.
Inner ear dermatitis is incredibly difficult to tolerate, as it causes severe itching, redness and unpleasant pain.
How to recognize dermatitis in children, watch our video:
Prognosis and prevention
With a correctly selected treatment regimen and timely consultation with a doctor, ear dermatitis can be quickly eliminated. It may take some time for the tissue to completely heal and restore the natural color of the skin.
In case of chronic dermatitis, it is necessary to take a more careful approach to treatment, following all the instructions and recommendations of the dermatologist. You should choose the optimal diet for yourself and avoid inappropriate jewelry made from gold, plastic, or low-quality metal.
Preventive measures for the usual form of dermatitis include being more careful with your body. So, it is necessary to protect yourself from low-quality jewelry, cosmetics, and accessories. The diet should not include excessive amounts of potentially allergenic foods.
To avoid any skin disease, including dermatitis, you should protect yourself from stress. Contact with chemicals that can cause burns and irritate the skin is unacceptable.
Inflammatory diseases of the skin can sometimes develop in people in places of the body that are difficult to access for visual inspection and treatment. Dermatitis that develops in the ear canal and on the auricle itself belongs to such diseases. Ear skin irritation is divided into atopic dermatitis, contact and seborrheic; these ailments have similar symptoms, but different provoking factors.
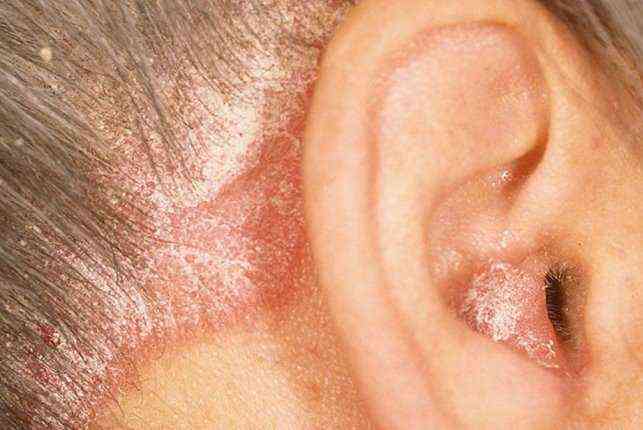
Ear dermatitis: description of the disease and methods of treatment
Dermatitis translated from Greek means inflammation of the skin.
Auricular dermatitis is an inflammation of the epidermis of the external auditory canal or pinna due to exposure to external and internal irritants.
The disease poses a danger of spreading to the internal auditory canal with possible complications such as damage to the eardrum, hearing loss, and therefore requires urgent diagnosis and timely treatment.
general characteristics
A distinctive feature of ear dermatitis is the difficulty of access to topical medications due to the location of the process. The deeper the inflammation penetrates into the ear, the more difficult diagnosis and treatment becomes. To make the correct diagnosis, depending on the type and severity, consultation with a dermatologist and otolaryngologist is necessary.
Ear dermatitis can have different etiologies - mechanical damage, burns, exposure to irritants, allergic reactions. To eliminate the disease if the process is not started, it is enough to solve the problem of skin moisture - the main factor that provokes dermatitis.
Depending on the type of disease and the causes that caused it, drug therapy is prescribed, supported by folk remedies and lifestyle correction.
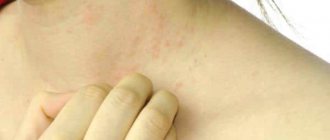
To more quickly recognize the disease, you can see examples of ear dermatitis in the following photographs:
Violation of normal moisture levels of the skin in the auricle, caused by external and internal influences, is the result of the disease. The main reasons are as follows:
- purulent discharge from the outer, middle and inner ear due to infectious and inflammatory processes;
- overheating, burns, including sunburn, leading to dry skin;
- prolonged contact with chemicals that come into contact with the skin;
- the presence of dermatitis on any other part of the body, since the infection can spread to the ear area;
- weakening of the body’s immune system, leading to a decrease in defenses and susceptibility to disease;
- the presence of allergic reactions or predisposition, since the allergic nature of dermatitis is possible.
Various types of diseases have additional causes that lead to the development of pathologies. The following types of ear dermatitis are distinguished:
- Allergic contact dermatitis is the result of hypersensitivity after a person comes into contact with an allergen. For the ear form of dermatitis, the allergens are objects that are in physical contact with the ears - earrings, clips, eyeglass frames, hearing aids. An allergic reaction occurs as a result of incompatibility of the materials that form the basis of the objects with the skin of the ear. In addition, allergies can be triggered by individual intolerance to cosmetics and hygiene products.
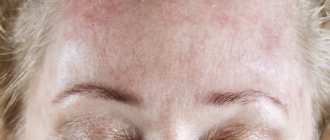
- Atopic dermatitis is a systemic disease of hereditary nature. It first appears in children under the age of two; during adolescence it can disappear without a trace or enter a stage of exacerbation. The etiology has not been fully studied, but laboratory studies show the spread of the disease in families with a high predisposition to allergic diseases - bronchial asthma, rhinitis of allergic origin, chronic diseases that weaken the immune system. The ear involvement is part of a process involving the face and neck.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a concomitant disease that occurs as a result of the presence of another skin disease caused by fungal infections or the entry of microorganisms into a wound in the ear. In infants, it can manifest itself due to the residual presence of maternal hormones in the child’s body. Without constant prevention, a relapse is possible, even if the disease itself passes without treatment.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The symptoms of different types of ear dermatitis are similar, despite the fundamental difference in the triggering factors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2UXuc6UbdQ
Since allergic contact dermatitis is caused by external factors, clinical manifestations are most pronounced on the outer side of the auricle and ear canal.
Main symptoms:
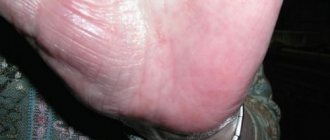
- redness and swelling in the ear area;
- itching of the shell, which in case of complications extends to the ear canal;
- fluid released from small blood vessels at the same time as the rash;
- formation of crusts on the auricle.
Since atopic dermatitis is caused by long-term chronic diseases of internal organs and the presence of allergic reactions, the main manifestations will be inside the ear canal and accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unbearable itching of the inside and surrounding area;
- pronounced overflow of blood in the ears, accompanied by redness;
- the appearance of nodules with purulent contents, which, when ruptured, cause the formation of weeping spots, causing additional discomfort;
- skin pigmentation.
Since the causative agent of seborrheic dermatitis is a fungus that acts in conditions of excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands, the main symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of plaques covered with a yellow or gray greasy crust;
- rash spreading around the ear due to fat;
- the appearance of falling off scales.
Ear dermatitis can have an acute and chronic form. In the case of an acute course, the inflammatory process begins spontaneously, quickly spreading and affecting new areas. Itching is accompanied by pain with the formation of fresh blisters that become crusty.
Over a short period of time, the crusts turn into boils, causing infectious processes inside the ear that can lead to inflammation of the eardrum and hearing loss.
Diagnostic measures involve collecting anamnesis, examining the patient, studying and analyzing chronic diseases. In order to determine the type of disease, samples are taken from the affected areas for laboratory testing. After identifying the type of disease and its causative agent, therapy is prescribed.
To successfully treat ear dermatitis, it is necessary to use an integrated approach, which will prevent a secondary relapse of the disease:
- The beginning of therapy consists of disinfecting the ears with a 3 percent solution of hydrogen peroxide. It is possible to use a soap or soda solution. In case of localization on the inner surface, it is recommended to instill boric alcohol inside.
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiallergic drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments for external use - corticosteroids. Ointments induce the formation of proteins with anti-edematous activity and reduce inflammatory infiltrates at the cellular level.
- In the case of an acute form of the disease antihistamines to reduce itching and pain and have a sedative and calming effect.
- If ear dermatitis is accompanied by infection, then antibiotics are included in the therapy to eliminate foci of infection.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, which have a positive effect as part of complex therapy.
In case of significant thickening of the skin and coverage with warts, the option of surgical intervention is considered.
Folk remedies
In combination with traditional medicine, various infusions and lotions based on natural ingredients are used to treat the disease.
Traditional methods:
- Medicinal plants are used as antipruritic auxiliaries - elderberry, strawberry, celery, juniper.
- Lingonberries, walnuts, sage, chamomile, and St. John's wort have antiseptic properties Lotions will produce the maximum effect.
- An ointment based on elecampane in combination with lard, infused in a water bath, is effective in eliminating rashes and residual manifestations of dermatitis.
Folk remedies are not an alternative to medications; they are used only in combination with the agreement of the attending physician.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures are effective both to eliminate the likelihood of the disease and as a complex therapy.
These include:
- a diet that includes a vitamin complex in the form of vegetables and fruits, freshly squeezed juices, rosehip decoctions;
- exclusion of sweet, fatty foods, carbohydrates, foods that cause an allergic reaction;
- review of cosmetic and hygiene products, selection of shampoo, soap, creams with antiallergic effect;
- consumption of vitamins A and E, which are involved in the construction of skin cells;
- caution in the selection of jewelry;
- strengthening the immune system.
Due to the fact that the inflammatory process occurs in a hard-to-reach place and can develop rapidly, becoming chronic, it is best not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a specialist. This will completely defeat ear dermatitis at the initial stage and maintain the health of the immune and nervous system.
We recommend other articles on the topic
Source: https://allergia.life/zabolevaniya/dermatit/ushnoj.html
Causes and symptoms of atopic dermatitis of the ear
The causes of atopic dermatitis in the ear and auricle area are often long-term chronic diseases of internal organs, a predisposition to allergic reactions, intolerance to certain foods, and intestinal dysbiosis. Ear skin dermatitis can be either mild with symptoms of mild itching or severe inflammation, the main symptoms of which are:
Unbearable itching of the ear canal, the skin of the organ itself and the area of the body around it; Skin hyperemia; Formation of nodules with serous contents, when opened, they cause the formation of weeping spots.
Constant exposure to the cause leads to a change in the normal color of the organ, hyperpigmentation and thickening of the upper layer of the epidermis are observed. Unbearable itching of the ear canal forces the patient to scratch the skin with cotton swabs, some resort to using sharp objects. This cannot be done, as microcracks form in the ear canal due to trauma, which can cause a secondary infection.
Treatment of the atopic form of dermatitis should be comprehensive; antihistamines are prescribed to relieve itching, and anti-inflammatory drops are instilled into the ear canal. Following a hypoallergenic diet and intestinal cleansing will help to quickly reduce the symptoms of the disease; enterosorbents and therapeutic fasting can be used for these purposes. It is necessary to treat exacerbations of diseases of internal organs and dysbacteriosis. For external remedies, drying ointments are used for weeping spots, and softening ointments for dry crusts.
Methods of treatment and prevention of ear dermatitis in humans
› Dermatitis
09.02.2019
Ear dermatitis in humans is not a single disease, but in fact, a complex of several. They can appear singly or simultaneously. Treatment is also carried out comprehensively.
The ear form of dermatitis can be of the following types:
- regional allergic (contact) dermatitis;
- systemic allergic (atopic) dermatitis;
- a consequence of autoimmune disorders (psoriasis);
- a consequence of chronic microbial infection (chronic external otitis);
- variant of eczematous lesions of the auricle.
Diagnostics
Dermatitis in the ear is diagnosed in 95% of all cases during an initial clinical examination by an otolaryngologist or dermatologist.
Skin scrapings, blood tests, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - all this is carried out only for clarification. For example, skin lesions are often associated with chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
They examine not only the external structures, but also the inside of the external auditory canal - for this they use the classic Hartmann ear specula.
Features of the etiology of auricular dermatitis in standard diagnostics are not so important. Since a secondary severe infection requiring antibacterial therapy is easily determined by the formation of pus.
Treatment methods
Before starting any therapy, it is necessary to eliminate possible triggering factors:
- aggressive cosmetics;
- jewelry and ear piercings.
Treatment of ear dermatitis is conservative and does not require hospitalization (unless there are some serious complications, such as the spread of the inflammatory process to the membranes of the brain).
Main methods of therapy:
- drug systemic and local therapy (tablets, creams, ointments, gels);
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- methods of traditional medicine.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy - comes down to various options for the impact of electromagnetic radiation on the body, including directly on the affected areas.
The exact method to treat dermatitis is determined individually.
This effective treatment is based on several methods:
- Ultraviolet irradiation with different wavelengths (short, medium, long waves). – Long-wave ultraviolet stimulates cell division in the epidermis and melanin synthesis. – Medium-wave ultraviolet leads to the release of vasoactive mediators in the dermis, which improve capillary permeability.
– Short-wave ultraviolet light has a pronounced mycocidal, antiviral and antibacterial effect. - Electrophoresis. – All biochemical reactions in the body are reactions of ions. – Any medicine that enters the body also turns into an ionic form.
– In an electromagnetic field, charged particles begin to move. Consequently, with the help of electromagnetic radiation it is possible to accelerate and enhance the penetration of drugs deep into tissues. - Exposure to weak currents of variable frequency. – Significantly enhances regenerative processes, stabilizes cell membranes, and in particular, the ion balance of sodium and potassium.
- Inductothermy. – For dermatitis, the most common area of action is the adrenal glands.
– The bottom line is that a magnetic field with variable parameters enhances the production of hormones of the adrenal cortex (its own corticosteroids), which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. - Laser therapy. – The biochemical mechanisms of action are similar to those that occur during treatment with weak alternating current, but the zone of influence is targeted.
For cold otitis media, dry heat treatment may sometimes be indicated.
Drug therapy
Ear dermatitis can usually be resolved with basic treatment.
Such therapy includes:
- softening nourishing creams;
- analgesic gels;
- anti-inflammatory hormonal and non-hormonal ointments.
Doctors prescribe the following medications:
- Anti-inflammatory hormonal ointments: – Triderm; – Akriderm; – Sinaflan; – Hydrocortisone; – Methylprednisolone; – Advantan;
- Elokom. - Anti-inflammatory non-hormonal ointments: – zinc ointment; – Fastum-gel;
- Exoderil. - Softening, moisturizing, nourishing creams: – Bepanten; – Sudocrem; – Topicrem; – Emolium; – Zinocap;
- La-cree. - Pain relieving gels: – Fenistil;
– D-Panthenol. - Antihistamines in tablet form: – Diphenhydramine, Clemastine, Suprastin, Promethazine (first generation, many “side effects” such as drowsiness, headache, nausea); – Loratadine, Azelastine, Cetirizine (second generation, “side effects” are minimized, efficiency has increased );
– Erius (Desloratadine, third generation, which has an additional advantage - the synthesis of histamine itself is inhibited). - In case of a very severe allergic reaction, systemic hormonal drugs may be prescribed.
If fever occurs, use NSAIDs.
Folk recipes
The achievements of traditional medicine should be used only after consultation with your doctor. Chronic dermatitis in the ears is successfully controlled by such prevention.
Examples:
- mix 5 ml of whole milk and 5 ml of simple medical glycerin, add rice starch until a paste forms, apply overnight;
- Mix 50 ml of freshly squeezed cranberry juice with Vaseline (200 grams), apply overnight;
- Pour 3 tablespoons of grated St. John's wort with 250 ml of sunflower oil, leave in a dark place for 20 days, shake periodically while infusing, strain, pour into a dark glass container, smear overnight;
- Grate peeled, raw fresh potatoes on a fine grater, apply the paste to the affected area of skin, secure with a bandage, and leave for at least 2 hours.
When turning to traditional medicine, care should be taken not to cause a new allergy.
Complications during treatment
One of the complications can be considered the transition of acute ear dermatitis to a chronic form.
This happens when:
- untreated dermatitis;
- ignoring the disease.
The disease can provoke other ear diseases. First of all, secondary infection.
During an infectious process, a purulent abscess may form in the ear. To prevent this, it is necessary to carry out antibacterial therapy, i.e. use of local and systemic antibiotics (beta-lactams, macrolides, etc.).
Diet
There is no strict diet for these pathologies. Here everything is determined exclusively individually.
If the condition worsens after eating certain foods, they are excluded from the diet.
Foods that are considered classic allergens:
- eggs;
- citrus;
- honey;
- nuts;
- mushrooms;
- Red caviar;
- most berries;
- pineapples;
- tomatoes;
- peaches;
- apricots;
- seasonings
Preventive measures
The health of a person’s ears also depends on his lifestyle.
Here we can recommend:
- balanced diet with vitamin complex;
- moderate physical activity in the fresh air;
- sufficient sleep;
- living in an environmentally friendly region;
- avoiding stress;
- maintaining skin hygiene, using hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- protection from aggressive environmental factors (frost in winter, sunlight in summer).
Self-observation and monitoring of your own health is also important.
Conclusion
Ear dermatitis, although it is chronic and can sometimes be quite an unpleasant disease, is completely controllable. You just need to take adequate treatment measures in a timely manner.
Author of the article. Practicing doctor
Methods of treatment and prevention of ear dermatitis in humans Link to main publication
Source: //GribokBolezn.ru/dermatit/lechenie-ushnogo-dermatita-u-lyudej.html
Course of the disease in children
Ear dermatitis may appear in a child if a lot of mother’s hormones have accumulated in the baby’s body, which are allergens for him. This disease occurs more often in infants.
Seborrhea may be the cause of dermatitis in children.
Treatment involves the use of creams and ointments. In severe cases of the disease, the doctor prescribes hydrocortisone topical medications.
Treatment
The disease responds well to treatment if the infection does not spread to other areas of the skin.
When choosing medications to treat ear dermatitis, it is important to know the cause, consider the symptoms and extent of the damage.
The affected skin should be regularly wiped with hydrogen peroxide to disinfect it. It is better to treat wet areas with a solution of boric acid, and then with Zinc ointment.
To reduce itching, you should take antihistamines. Cetirizine, Zodak or Suprastin will do.
How and how to treat ear dermatitis depends on its type. In any case, treatment must be comprehensive. For atopic type, therapy looks like this:
- taking antihistamines orally - Suprastin;
- application of local antiallergic agents – Fenistil gel;
- instillation of drops that have an anti-inflammatory effect into the ear canal - Sofradex or Polydex;
- application of hormonal creams and ointments Geokrton (for children), Lorinden;
- the use of drying ointments (for dry crusts) – Zinc ointment;
- application of moisturizing creams and gels (for weeping spots) – Aqualan L, Mustella.
To remove allergens from the body, it is necessary to take enterosorbents. Be sure to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Treatment of contact dermatitis is similar, but it is imperative to eliminate the irritant that causes the allergic reaction.
In the treatment of seborrheic type it is necessary to use antifungal drugs. Hygiene procedures are very important. The treatment looks like this:
- wash your hair with antifungal shampoo Nizoral or Skin-cap;
- use antifungal ointments, for example, Mycospor, Lamisil or Bifisam.
The ear canal, sink and area behind the ears must be carefully cleaned of crusts and pus. If you have seborrhea, you need to follow a diet. It is necessary to exclude sweet, fatty and spicy foods from the diet. It is useful to eat vegetables, fruits, rosehip decoction, and also drink vitamin complexes containing vitamins A, E and B.
In addition to drug therapy and diet, doctors can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF and UV. They enhance the effectiveness of treatment and help restore the skin.
Complications
Complications from dermatitis are rare. With seborrheic appearance, there is a high probability of developing dermatosis of the ear. The disease can spread to the neck and cheeks. Other types of ear canal dermatitis can develop into eczema without treatment.
Complications can arise due to severe itching. When scratching, there is a high risk of infection. If the infection gets inside the ear, the inflammatory process of the ear canal will begin. This consequence significantly complicates the treatment process.
Prevention
Preventive measures include proper nutrition and the exclusion of low-quality jewelry and cosmetics.
You should avoid contact with possible allergens and chemicals. You should lead a healthy lifestyle and protect yourself from stressful situations. Treatment of ear dermatitis should be carried out under the strict supervision of a dermatologist, since complications of the disease can affect not only the skin, but also the hearing aid.
Source: //dermatologiya.pro/dermatit/ushnoj-dermatit.html
Manifestations of contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis of the hearing organ develops under the influence of external factors. This could include materials used to make eyeglasses, jewelry, cosmetics, dyes and hair styling gels. In some patients, dermatitis first occurs when using a telephone headset or hearing aids.
Signs of an allergic reaction are:
Swelling and redness of the ear; Itching of the ear canal and the organ itself; Rashes of various shapes, blisters with serous exudate; Crust formation.
Treatment of contact dermatitis of the skin of the ear must begin with the complete elimination of the influence of the allergen, after which external and internal medications are used. In case of acute development of the process, severe itching and swelling, treatment includes the use of systemic antihistamines and ear drops. Glucocorticosteroids relieve skin itching and swelling well; they can be used both in the form of drops and ointments. Treatment with hormones should not be long-term; it is usually prescribed for the first days of the disease, and then switched to non-hormonal agents.
About this type of dermatitis
Dermatitis is a skin disease that occurs under the influence of external factors. Can form anywhere on the body. Ears are no exception. Appears in the middle of the auricle, behind the ears. The risk is hearing damage. The advanced form causes complications in the form of partial hearing loss. Occurrence on the face constitutes an eye hazard.
It is worth starting treatment immediately. The launched form will remind you every day. Further elimination will be difficult. Penetrating deep into the auricle, treatment becomes difficult to reach and practically impossible. There is a risk of eardrum damage and hearing loss. If you notice the initial symptoms, go to the doctor immediately. Troubleshooting should begin immediately. Solving one question automatically solves the second.
Causes
Dermatitis of the auricle occurs due to:
- chemical damage;
- purulent discharge;
- decreased immunity;
- metabolic dysfunctions;
- heredity.
People working in chemical plants and places where products are manufactured are susceptible to various ailments associated with skin disorders. May consist of an allergic reaction, dysfunction of the auditory and visual apparatus. Chemicals that come into contact with the skin during operation remain in place. After passing the incubation period, they begin to negatively affect the body, manifesting themselves in the form of a skin disease.
There are problems directly related to the ears. Inflammation and various formations lead to the release of pus. The substance is released from the affected area and flows out. It tends to dry out. Contains a lot of toxic substances. Remaining at the site of the lesion, it irritates the epidermis, causing itching and discomfort. When scratching, a rash and inflammation appear. A skin infectious disease occurs, which is associated with a large lesion at the site of formation.
May appear due to weak immunity. A weakened system guarantees the rapid emergence of infectious diseases. The most common acute respiratory infection is influenza. A weak immune system can result in insufficient vitamins in the blood. To strengthen your immune system, you should take a course of vitamins every two months. Protection from illness never hurts.
Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and gallbladder are obvious causes of dermatitis. The above organs, together with feces, remove toxic substances from the body. Violation of one organ contributes to an increase in harmful substances in the body. The immune system is not able to cope with the large processing of toxins, it turns on a protective reaction, bringing the result to the dermis.
Genetic predisposition is the main reason for the manifestation of the disease. Most often transmitted from the mother. Contact with the child is closer than with the father. It appears when exposed to a source of inflammation. Stops when the allergenic factor is eliminated. Has an incubation period of two weeks. With repeated contact, the consequences will be worse. The process has a name - remission. Elimination of a problem with a quick acute manifestation.
Symptoms
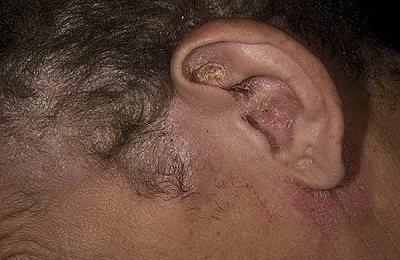
The symptoms are not complicated, the disease is easy to recognize:
- Itching.
- Swelling.
- Wet surface.
- Peeling.
- Blisters.
- Discharge of pus.
Itching is definitely the first thing to appear. The feeling is incomparable. The affected area is constantly itching. Redness occurs after scratching. What follows are the remaining unpleasant aspects of the disease. The itching cannot be tolerated without scratching. Few people can avoid touching an irritated area.
Swelling occurs due to an infectious disease. Bacteria spread, causing allergic processes. The resulting swelling provokes the formation of pus. There is a blockage of sulfur, an inflammatory process appears, causing the release of a purulent mass. The skin becomes more irritated. Blisters appear. Papules burst, forming wet spots. The areas dry out, forming a brown crust. The affected area hurts and itches. Combing the crust, the process begins again. Circular repetition is a characteristic feature of ear diseases, not only. The process is repeated at any site of inflammation, affecting nearby organs.
Seborrheic dermatitis progression
Seborrhea is a chronic skin disease with a hereditary predisposition. The causative agent is a conditionally pathogenic fungus that develops its negative activity in the ears under conditions of excessive sebum secretion. Most often, seborrhea of the ear begins after the appearance of inflammation on the head; emotional stress, taking certain medications, and a lack of vitamin B can provoke an exacerbation.
Symptoms of skin irritation due to seborrhea are the appearance of plaques covered with a greasy yellowish crust. When scratching, a large number of scales are separated; seborrheic dermatitis can occur both in the ear itself and around it, spreading to the neck and skin of the cheeks.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis should be aimed at suppressing the activity of the fungus, for which antimycotic external agents are used. During an exacerbation, it is advisable to immediately start washing your hair with shampoos containing ketoconazole, such as Nizoral. Such activities will reduce the likelihood of inflammation of the scalp and help eliminate irritation in the ears.
Treatment of seborrhea also involves following a diet excluding sweets, carbohydrates, fatty and spicy foods. Including vegetables and fruits and rosehip decoctions in the diet helps to cope with the acute period of the disease in a minimum period of time. Vitamin complexes containing vitamins A and E, that is, those substances that are involved in the construction of skin cells, are well suited for the treatment of seborrhea. For mild cases, sometimes it is enough to use medicated lotions for wiping, maintain a diet and take vitamins.
In severe cases, antifungal agents are prescribed; in cases of secondary infection, antibacterial ointments and tablets are prescribed.
If any dermatitis occurs in the area of the hearing organ, testing is indicated to identify the causative agent of the disease, which will help the doctor choose the right treatment tactics.
Therapy
Treatment of dermatitis in the ears begins with wiping off the inflammation. To do this, use a solution of soda or hydrogen peroxide. If there are wet spots on the ear, they are treated with boric acid and dried with zinc ointment or baby powder.
To relieve itching, tablets, drops or syrups from the group of antihistamines are prescribed. Children are prescribed Cetirizine or Parlazin in drops, adults are prescribed Suprastin, Loratadine, Zodak.
If the diagnosis of ear dermatitis sounds like atopic, treatment is carried out comprehensively. Drops containing antibiotics and steroids are given. They relieve itching, swelling and inflammation.
A corticosteroid ointment should be applied to areas of the skin affected by the disease, and a complex ointment supplemented with antibiotics should also be used.
When the disease is caused by an allergic reaction, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen. For seborrheic dermatitis, additional cleansing procedures are performed. Hair washing is done using antifungal shampoos or shampoos containing zinc. Antifungal ointment is applied to the wound, and crusts and pus are removed from the ear canal and sink.
The exclusion of citrus fruits, gluten-containing products, coffee, and cocoa is indicated. The growth of the fungus is suppressed by following a diet and limiting sweets. B vitamins, vitamins A and E are prescribed to improve the regenerative ability of the skin. In case of calcium deficiency, calcium gluconate is taken, if necessary, in combination with vitamin D. Physiotherapeutic procedures are sometimes prescribed, which include UHF and UV therapy.