Physiologically active substances enter the infant’s body with mother’s milk, adapted formulas, and complementary foods. An allergy to vitamin D in infants can occur due to an excess of this important regulator of calcium metabolism and the functioning of the immune system. In the future, hypo- and hypervitaminosis lead to problems in the development of the child’s cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems.
Causes of allergies
A true allergy to vitamin D is extremely rare, since this substance is not foreign to the human body. In most cases, a negative reaction from the immune system of newborns is provoked by the excipients included in such medications. The most popular among pediatricians and parents is Aquadetrim, which contains vitamin D3. This solution contains potential allergens:
- sucrose;
- lemon acid;
- anise flavor;
- benzyl alcohol;
- Cremophor EL (macrogol glyceryl ricinoleate).

Somewhat less frequently, other drugs are prescribed that help compensate for cholecalciferol deficiency, one of them is Oxydevit. Its main active ingredient is an analogue of vitamin D3 (alfacalcidol). In addition, this product contains the auxiliary component ionol. Also, to treat or prevent rickets in a child, the drug “Vigantol” may be prescribed. In addition to vitamin D3, it contains only triglyceride fats.
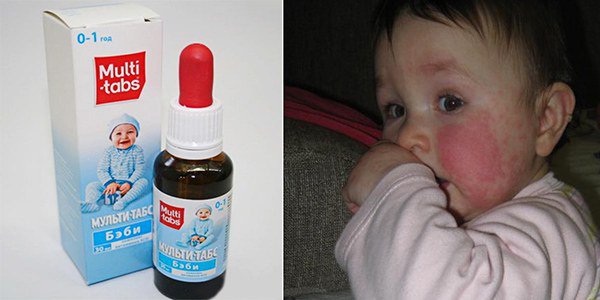
A child is also often allergic to Multi-Tabs Baby, because vitamin D is not the only active ingredient in its composition. This drug includes many other biologically active and additional substances:
- vitamin A;
- ascorbic acid;
- sucrose;
- Cremophor EL;
- hydrochloric acid.
Sometimes children are recommended to take ergocalciferol - vitamin D2. Previously it was believed that it is absorbed worse than vitamin D3, but the main difference between them is the form of release. Vitamin D3 and its analogues are usually available in the form of aqueous solutions, while ergocalciferol is dissolved in oils. Dosing an oil-based drug is more difficult than an aqueous solution. In this regard, ergocalciferol is not prescribed if there are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or metabolic disorders due to renal or liver failure.
Why do pediatricians prescribe it to babies?
Breastfed children receive only 4% of the vitamin D dose that should enter their body. He does not produce it himself.
In the summer, the problem with calciferol deficiency resolves itself. With regular walks in the fresh air, the microelement is synthesized in the baby's body under the influence of sunlight. This does not happen in the autumn-winter period. To compensate for the lack of vitamin D, doctors prescribe it to babies in the form of drops or other forms of medicine.
Attention! Children who are bottle-fed receive microelements from adapted mixtures.
Vitamin D is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of rickets. The main functions of the substance include:
- Calcium absorption by infants.
- Strengthening bone tissue.
- Strengthening the nervous system.
- Participation in processes such as: formation of the immune system; metabolism; cell division.
Microelement deficiency in a baby’s body can lead to softening of bones and autoimmune diseases.
Women who are breastfeeding are advised to consume:
- seafood. For example, salmon, fish oil, cod liver, herring;
- potatoes, sunflower seeds and parsley;
- eggs, cottage cheese and milk.
To compensate for microelement deficiency, children are usually prescribed:
- "Calcium D3 Nycomed".
- "Multi-Tabs Baby".
- "Osteotriol".
- "Aquadetrim".
- "Vigantol."
The medicine must be selected by the pediatrician individually for each child.
Allergy or overdose?
The symptoms of an allergic reaction and an overdose are very similar. Moreover, an allergy to vitamin D in many cases is caused by excess intake of this substance into the body. Often, parents do not even know about the causes of overdose in infants, and there may be several of them at once.
- Independently changing the drug and incorrect dosage regimen for a long time. For example, one drop of Viganol contains approximately 670 IU of the vitamin, and a drop of Aquadetrim contains 500 IU.
- Mom taking vitamins. Almost any substance that enters the body of a nursing woman can pass into breast milk, and then into the baby’s digestive system.

- Feeding with artificial formulas. Manufacturers add vitamins to most nutritional mixtures, including cholecalciferol.
It must be remembered that in a child with chronic diseases, the removal of the vitamin from the body occurs slowly, so some of it accumulates. For such children, the dosage of any medications should be selected with extreme caution.
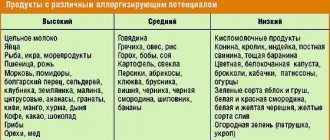
Allergenic foods during breastfeeding: stop list and menu for a nursing mother
Why diet is important
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Alergyx to treat allergies. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention.
Clinicians argue about the effect of maternal diet on the prevention of allergies in children of the first year of life. A 2008 study in the journal Pediatrics reported that including common allergens (peanuts and chicken eggs) in mothers' diets did not affect children's health. Later, medical journals published articles linking early manifestations of atopy with the consumption of certain foods by women during lactation.
Today, a direct connection has been established between the composition of breast milk and the condition of the gastrointestinal tract of the newborn.
For the baby's well-being, intestinal barrier function must be established in the first months. This is possible if you receive with meals:
- bacteria Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium;
- IgG and sIgA antibodies;
- unsaturated Omega-3 acids;
- vitamin D.
Symptoms of a vitamin D allergy
Symptoms of a vitamin D allergy usually appear within a few hours or days after taking the drug and disappear if use is stopped. The disease manifests itself as follows:
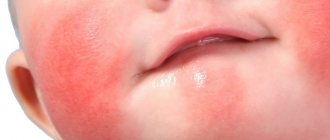
redness, peeling and rashes in the form of small blisters in the area of the child’s cheeks, neck, forearms, buttocks and legs;
- insomnia and restlessness of the baby due to itching;
- decreased appetite;
- runny nose, sneezing and nasal congestion;
- lacrimation, redness of the eyes.
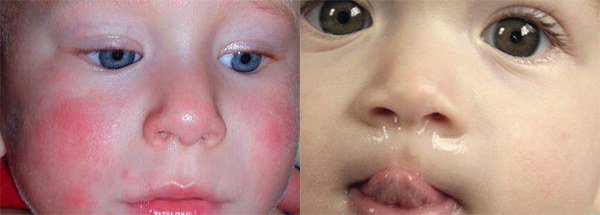
In severe cases of vitamin D allergy, difficulty breathing, coughing, swelling of the face, arms and legs develop, and crying becomes hoarse. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately call a doctor. If the disease manifests itself with frequent regurgitation, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, then there is a high probability of acute intoxication. Chronic overdose may be indicated by lethargy, sleep disturbance, increased irritability, too rapid closure of the large fontanel and impaired renal function, which will be shown by a urine test.
What is rickets?
Rickets is a disease that occurs due to a pathological deficiency of vitamin D in the body. The disease affects young children and infants. When a child becomes ill, the formation of bone tissue is disrupted and there are insufficient minerals in it.
The disease was first identified and studied by doctors back in the 17th century. At the beginning of the 20th century, doctors found a direct relationship between cases of rickets and eating foods containing vitamin D. Then it became fashionable to give fish oil to children.
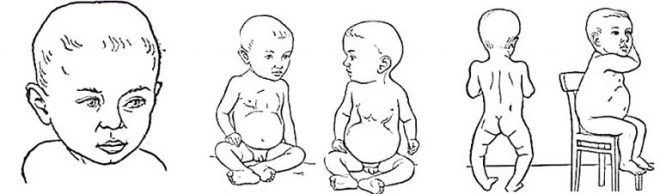
The most susceptible to the disease are children who are rarely exposed to the sun, receive insufficient nutrition, premature babies, babies with endogenous problems, if the absorption of vitamin D in the intestines is disrupted, as happens with a number of liver and kidney diseases, as well as children of the Negroid race.
Children whose mothers breastfeed are less likely to suffer from rickets, since they absorb about 70% of calcium through breast milk, while artificial babies can absorb only 30%.
The process of disease development is very complex. As a result of metabolic disorders caused by hypovitaminosis D, the work of other systems also changes - the production of enzymes and the nervous system suffers, but rickets still inflicts the most significant blow on the condition of the bones of the child’s musculoskeletal system.
Treatment and prevention of allergies
The first thing to do is to temporarily stop taking the drug. If you have a severe allergy to vitamin D, your pediatrician may prescribe oral antihistamines (Simprex, Kestin, Xizal). If angioedema has developed, the doctor will use systemic corticosteroids. To eliminate the symptoms of dermatitis, anti-inflammatory creams (Bepanten, Bübchen, Epidel) are used. To relieve itching and reduce rashes, an ointment with an antiallergic effect (Fenistil-gel, Advantan) can be used.
You should carefully choose allergy creams, as many of them contain large doses of hormonal substances that are unsafe for children. To cleanse the body of protein molecules that cause a negative reaction, some doctors advise doing a cleansing enema.
Once allergy symptoms subside, it may be worth trying other vitamin D supplements if needed. A good alternative would be regular fish oil or Devisol, which contains only oil and alpha-tocopherol as excipients. If a nursing mother eats properly and introduces complementary foods into the baby’s diet in a timely manner, the child’s body will receive all the necessary substances. However, for the synthesis of vitamin D, the baby needs regular exposure to the sun. To reduce the risk of developing a vitamin D allergy, follow certain rules.
- Walk with your child every day; even in cloudy weather, a certain percentage of ultraviolet rays hits the skin. If you live in an area where sunny weather is very rare, try to spend your holidays in the southern regions.
- As an alternative to medications, heliotherapy or ultraviolet irradiation of children under a special lamp is performed.
- Choose drugs with a minimum amount of substances in the composition. The wider the list of ingredients, the more potential allergens there are in the medicine.
- You should not give your baby multivitamins without first consulting a specialist. A child's body does not always need all the substances that are there. In addition, the need to absorb several vitamins at once can provoke the development of a negative reaction from the immune system.

- Avoid taking vitamin D during pregnancy unless there is a real need (indications from a gynecologist). Even a slight excess of this substance in the body of a pregnant woman can cause sensitization in the fetus and allergies in the future.
Remember that allergic reactions in children are often temporary, because the child’s immunity continues to develop. After a few months, the allergy may disappear on its own. However, the appearance of pathological symptoms requires a mandatory visit to the pediatrician, especially if the child’s condition does not improve.
Do not try to diagnose yourself, because taking vitamin preparations can be accompanied not only by allergies, but also by overdose or side effects. Each of these conditions manifests itself in a similar way, and only a doctor can tell the difference.
How to quickly cope with an allergic reaction
First of all, you need to stop taking medications containing vitamin D. Then seek help from a pediatrician, who, depending on the severity of the disease and the patient’s age, will prescribe therapy.
It may include:
- Antihistamines: if the baby is already a month old, he will prescribe Fenistil, Suprastin or Cetirizine; if infants are more than 6 months old, then medications such as Zodak, Claritin, Cetirizine, Zyrtec or Kestin.
- Ointments with an antihistamine effect. For example, “Gistan”, “Vundehil”, “Desitin”, “Bepanten” or “Fenistil”, “La-Cri”.
- Enterosorbents. They are necessary to remove toxins from the body. "Polifepan", "Smecta", "Enterosgel" or "Polysorb" can be used.
- Corticosteroids if the child develops angioedema.
Only a doctor should select medications to relieve an allergic reaction.
If the baby has an allergy, then the breastfeeding mother is advised to review her menu and remove foods that contain vitamin D from it. If the baby is bottle-fed, then you need to look at the composition of the formula. If there is calciferol in it, then it must be replaced. To more quickly remove the allergen from the child’s body, you should give him as much fluid as possible.
Komarovsky about the problem
Rickets itself is not as terrible, according to Evgeniy Komarovsky, as our attitude towards it. Doctors just can’t get over how to make a diagnosis based on symptoms, and therefore they “register” as rickets sometimes completely healthy children who simply have excessive sweating or have slow growth.

Evgeniy Olegovich urges colleagues not to rush to conclusions, and parents not to panic and remember that therapeutic doses of vitamin D are more preventive. If they are given to a healthy child who has been misdiagnosed, the consequences can be very, very serious: loss of appetite, convulsions, severe arrhythmia, nausea, vomiting, impaired respiratory function, and death.