To effectively treat eyelid dermatitis, modern medicine uses various creams and ointments. The disease is accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process, redness of the skin, swelling of the tissues, and severe itching. In the absence of comprehensive treatment, patients may be concerned about increased tearing, mucus discharge from the eyes, and the development of conjunctivitis.
Infections and allergic reactions can provoke the occurrence of eyelid dermatitis. The disease is accompanied by uncomfortable symptoms and can negatively affect visual acuity. Before using medications, the patient should consult with a qualified dermatologist, who will determine the diagnosis and also prescribe an effective treatment regimen.
Kinds
Dermatitis of the eyelids (treatment, ointments and creams can only be prescribed by a dermatologist, since an incorrectly selected drug can provoke a deterioration in the patient’s well-being and the development of adverse reactions) can be of several types, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
Before purchasing medications, the patient must undergo an examination so that a specialist can correctly determine the diagnosis and prescribe safe drug therapy.
Seborrheic dermatitis
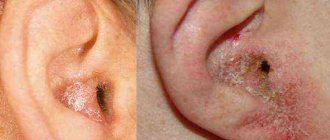
The symptoms of this form of the disease can easily be confused with blepharitis. The edges of the eyelids are covered with multiple yellow crusts and small white scales.
The skin takes on a red tint, there is severe itching and burning. If you have seborrheic dermatitis, the patient is concerned about increased dryness of the eyes, and eyelashes may fall out. Ignoring the disease is fraught with a decrease in visual acuity and the development of an inflammatory process in the cornea of the eye.
Eczematous dermatitis
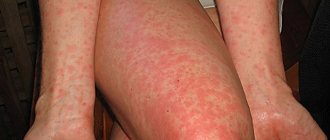
Eczematous dermatitis of the eyelids is diagnosed in isolated cases. This form of the disease develops rapidly as a result of long-term use of ophthalmic ointments with sulfanilamide or antibiotics.
Eczematous dermatitis can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as helminthic infestations present in the body. The disease is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the eyelids, and numerous rashes appear on the skin. The epithelium becomes painful, there is itching and burning.
Drug dermatitis
The disease develops as a result of long-term use of ophthalmic medications in the form of ointments and drops. The pathology quickly becomes acute. Frequent use of eye drops causes an intensification of the inflammatory process in the area of the inner corner of the visual organ. Uncontrolled use of ointments provokes inflammation of the eyelids and conjunctiva.
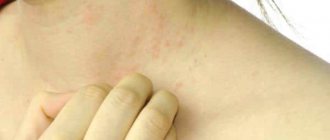
Allergic dermatitis
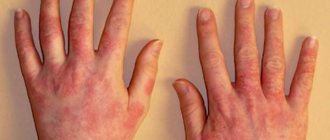
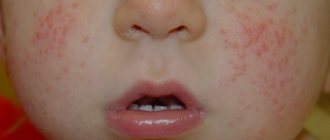
Allergens can include various decorative cosmetics (for example, eye shadow, mascara), household chemicals, medications, animal hair, pollen and insect bites. This form of the disease is characterized by severe hyperemia and swelling of the eyelids.
The discomfort increases several times as a result of mechanical scratching of the affected skin area. Allergic dermatitis is accompanied by severe itching and burning, tearing. As a result of a comprehensive examination, the patient may be diagnosed with conjunctivitis and rhinitis.
Atopic dermatitis
This form of the disease belongs to the category of chronic recurrent pathologies. The disease can be triggered by allergic reactions or infectious lesions of the eyelid epithelium. Pathology can also develop against the background of existing disorders in the gastrointestinal tract or due to damage to internal organs by helminthic infestations.
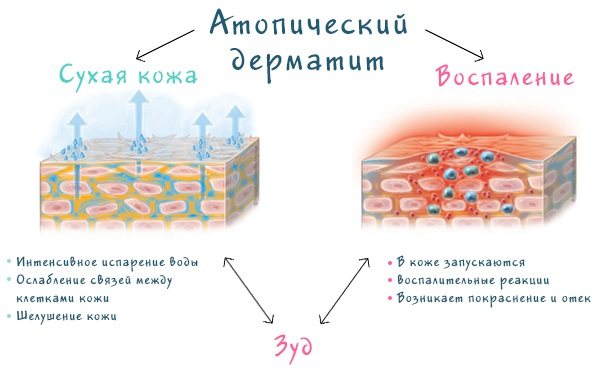
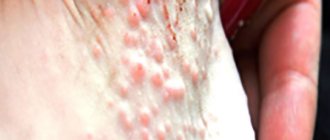
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by constant itching and burning of the skin of the eyelids. The epithelium may become covered with small vesicles that are filled with clear liquid. In the absence of drug therapy, the disease will progress, which can significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
Dermatitis of the eyelids: general description of the pathology
Eyelid dermatitis is inflammation of the skin around the eyes. This disease is observed in 27% of people suffering from dermatitis. The reasons for the development of this disease include the following pathologies:
- infections (herpes, measles, chicken pox and scarlet fever),
- allergies to medications, cosmetics, pollen, animal hair and food,
- physical factors (radiation, body reactions to cold),
- household chemicals, chemicals used in hazardous industries if work practices are not followed,
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands.
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs as a result of disruption of the endocrine system of the human body. The allergic form develops against the background of immediate or delayed hypersensitivity of the body. In the first type, symptoms are observed 15 - 30 minutes after the negative impact, and disappear after 1-2 hours. In the second case, the disease can be determined after 6-12 hours through examination, and external changes appear after a few days.
Stages and degrees
Dermatitis of the eyelids (treatment, ointments and creams are recommended to be chosen depending on the form of the disease and the general condition of the patient) has several stages of development, each of which can negatively affect the patient’s visual acuity. Self-medication of dermatological pathologies can provoke rapid progression of the disease and further deterioration of a person’s well-being.
Acute stage
Acute stage eyelid dermatitis develops rapidly and causes the patient a lot of discomfort, which is why drug treatment cannot be delayed.
Ointments and creams with bactericidal, immunostimulating, and analgesic properties are very effective. In the absence of therapy, the affected area will gradually increase, which is why the occurrence of concomitant pathologies cannot be ruled out.
The acute stage of eyelid dermatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling of tissues.
- Hyperemia of the skin of the eyelids.
- Increased body temperature.
- Dry skin.
As the disease progresses, the patient may experience painful tingling in the eye and increased tearing. Tissue swelling may increase. Severe dermatitis is characterized by chills, aching headache, and malaise. Treatment should be started immediately, as the pathology negatively affects the functioning of the visual system.
Chronic stage
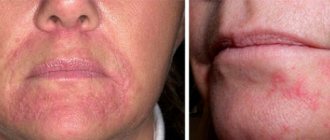
This form of dermatitis is characterized by rare relapses. The disease can bother the patient for several years, due to which the painful symptoms gradually intensify. A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it affects both eyes.
The pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Redness of the skin around the eyes.
- Swelling of the eyelids.
- Development of conjunctivitis.
- Dryness and flaking of the skin around the eyes.
- Thickening of the eyelids.
Dermatitis is not a life-threatening disease. But already at an early stage, this pathology can cause the patient a lot of discomfort, significantly worsening his quality of life. For this reason, at the first appearance of signs of eyelid dermatitis, you should consult a dermatologist.
Symptoms and signs
Dermatitis of the eyelids (treatment, ointments and creams will be effective only if the patient adheres to the treatment regimen recommended by the doctor) in 99% of cases is manifested by increased body temperature, chills, and redness of the skin around the eyes.
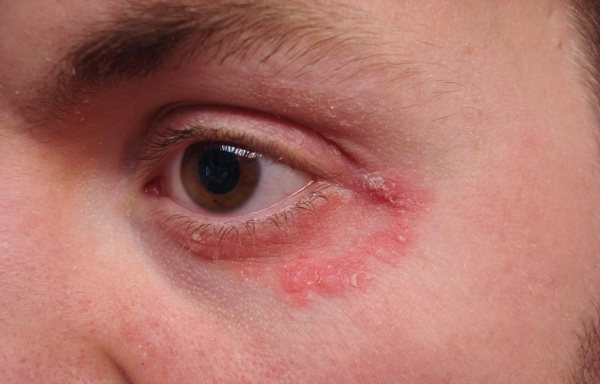
As a result of contact with the pathogen, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Profuse lacrimation.
- Pain in the eyes.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Formation of multiple bubbles with liquid on the eyelids.
- Severe itching and burning of the skin.
- Eyelash loss.
In chronic dermatitis, the pathology develops slowly, and the occurrence of conjunctivitis is possible. The skin around the eyes gradually becomes rougher, cracks, and peels. The eyelids become covered with a rash. The disease affects both eyes, causing the patient to experience severe itching and burning of the eyelids.
If the inflammatory process was provoked by bacteria, then the crust on the papules acquires a characteristic yellowish tint. When mechanically scratching the skin, re-infection occurs and ulcers form.
Causes
The skin around the eyes is highly sensitive, and it is not protected from external irritants. For this reason, dermatological diseases can develop under the influence of allergens.
Laboratory studies have shown that the following factors can provoke the occurrence of eyelid dermatitis:
- Infection. Dermatitis of the eyelids can develop as a result of damage to the skin by a virus or fungus, which is transmitted through contact with a carrier of the infection, as well as after using personal hygiene items from a stranger.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract can provoke the occurrence of dermatological diseases.
- Contact with allergens. Dermatitis can be caused by poor-quality cosmetic products, the use of medications, and frequent use of aggressive household chemicals. This category also includes seasonal allergic reactions and the body's response to pet hair.

- Autoimmune diseases. Disturbances in the protein compounds of body cells can provoke the development of atopic dermatitis of the eyelids.
Medical statistics confirm that dermatological diseases are increasingly being diagnosed in patients who live in a region with poor ecology. If the patient has swelling of the eyelid, then you should not try to eliminate it yourself. Before using medications, you need to undergo the necessary examination so that the doctor can determine the diagnosis.
Which doctor should I contact?
Dermatitis of the eyelids (treatment, ointments and creams will help get rid of the skin disease only if the patient refuses cosmetics during the therapeutic course and strictly follows all the recommendations of the dermatologist) will not provoke the development of complications only if promptly seek help from a qualified physician.
Otherwise, the patient's condition will rapidly deteriorate. At the first suspicion of eyelid dermatitis, you should contact a dermatological clinic. After the initial examination, the doctor prescribes an examination for the patient and writes out a referral for consultation with specialists.
For example:
- An allergist helps to exclude or confirm that a patient has an allergic reaction to food, medications, animal hair or cosmetics.
- Consultation with an infectious disease specialist is necessary if a rapid development of an infectious disease is suspected.
- An ophthalmologist examines your vision.
- Contacting an immunologist will help you find out the patient’s exact immune status.
Only based on the results of an examination of the patient, a dermatologist can correctly determine the diagnosis.
Diagnostics
To correctly determine the diagnosis, the dermatologist prescribes the necessary diagnostic procedures to the patient.
In 99% of all cases, diagnosis of the disease consists of the following steps:
- A dermatologist examines a patient. Often this is enough to correctly identify the disease. Collecting a detailed medical history helps the specialist find out whether the patient has a genetic predisposition to dermatitis. The doctor draws conclusions about the frequency of relapses of the pathology.
- The patient must undergo a complete blood test for eosinophils.
- Based on the data obtained, the dermatologist excludes ophthalmological and dermatological pathologies. In each case, the set of laboratory tests is individual.
- Additionally, skin tests can be performed to find out which allergens are present in the patient’s body.
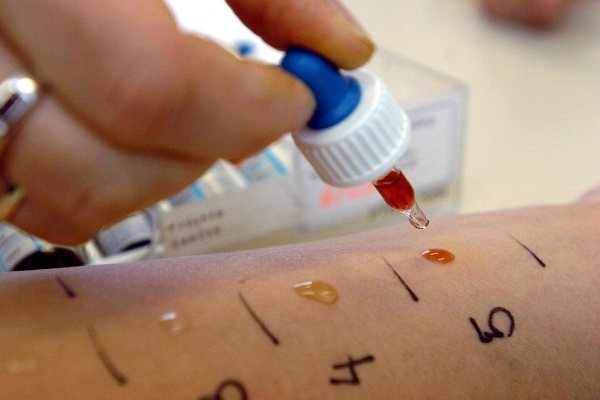
Enzyme immunoassay is very effective, thanks to which it is possible to determine the intensity of the development of the inflammatory process. PCR analysis helps to find out whether the viral load on the body is exceeded in cases where there is a suspicion of the infectious nature of eyelid dermatitis.
A special scraping of biomaterial for histological examination is carried out in order to confirm or refute the presence of seborrhea or any other fungal disease.
The results of differential diagnosis of pathology are of great importance, since in dermatology there are a large number of diseases with similar symptoms. For example, erythroderma, toxicoderma, eczema. To combat these diseases, completely different treatment regimens are used.
In clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg, a PCR test costs from 260 to 680 rubles. For a general blood test you will have to pay from 560 to 800 rubles. Skin tests for allergens cost from 120 to 450 rubles.
What is eczema and why does it appear on the eyelids?
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by the appearance of rashes of various shapes on the upper and lower eyelids.
The cause of the disease is considered to be:
- congenital predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- allergies to chemicals and pollen;
- long-term use of medications for chronic diseases.
Eczema on the eyes can occur in response to internal and external factors. It appears completely unexpectedly. The easier it is to treat eczema, the sooner the cause of the disease can be identified.

The appearance of eczema around the eyes as a reaction to an allergen requires avoiding contact with this allergen. Then the use of local ointments will very quickly cleanse the skin of the eyelids.
If this is a reaction of the human body to long-term therapy for chronic diseases, the treatment protocol should be reconsidered. Things are more complicated if there is a genetic predisposition to this disease, but even in this case, an experienced dermatologist will select a therapeutic technique.
Treatment methods
To prescribe an effective treatment regimen for eyelid dermatitis, the doctor first determines the cause that triggered the development of the disease. In contact forms of pathology, it is necessary to block the action of the irritating substance. In 95% of cases, this is enough to overcome painful symptoms.
An important therapeutic measure is the abolition of allergenic cosmetics and medications, as well as the protection of the skin of the eyelids from the negative effects of the environment. Complex treatment of dermatological diseases involves the use of medications, the use of traditional medicine recipes, treatment of inflamed skin areas and diet.
Ointments and creams
Inflamed areas of the skin of the eyelids can be treated with Solcoseryl or Fenistil-gel. The antiseptic Wundehil perfectly disinfects the epithelium and heals existing microcracks. Dermatologists recommend choosing for treatment those ointments and creams that contain natural ingredients. Propolis, yarrow and sophora are very effective.
| Drug name | Description |
| Lipikar | This cream is indicated for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, restoration of the natural protective barrier of the epidermis from the negative effects of the environment, as well as for the individual patient’s tendency to have an allergic reaction. Contraindications include: pregnancy, lactation, intolerance to the components of the dermatological product. To achieve a positive therapeutic effect, Lipikar cream must be applied to the eyelids once a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the dermatologist on an individual basis.
|
| Sinaflan | This ointment is indicated to combat acute and chronic inflammatory pathologies of non-microbial etiology, which are accompanied by increased dryness of the skin (neurodermatitis, dermatitis, psoriasis, sunburn, eczema of various origins). The drug Sinaflan should not be used for skin manifestations of syphilis, skin tuberculosis, as well as during pregnancy and lactation. This ointment is not prescribed for the treatment of children under 2 years of age. The drug is applied to skin pre-treated with an antiseptic 2-4 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the form of the diagnosed disease. The maximum course of therapy is 25 days. |
| Diprolene | Indications for use: dermatitis, diffuse neurodermatitis, lichen, urticaria, eczema, discoid lupus erythematosus, generalized erythroderma. Diprolene is prohibited for use in cases of melanoma, hemangioma, trophic ulcers of the leg, tuberculosis of the skin and increased sensitivity of the body to the components of the drug. The cream should be applied to the eyelids 2-6 times a day in an even, thin layer. The duration of treatment is determined by a dermatologist. |
| Betamethasone | This medicine is used by dermatologists to treat psoriasis, dermatitis, eczema, necrobiosis lipoidica and erythroderma. Betamethasone is contraindicated in the presence of the following diseases: varicose veins, acne, bacterial and viral skin lesions, plaque psoriasis. To achieve a positive therapeutic effect, it is recommended to apply the ointment to cleansed eyelid skin in the morning and evening. The standard course of treatment lasts 1-2 weeks.
|
Before using the drug, you should consult a dermatologist and study the instructions for the drug to eliminate the possibility of contraindications.
Traditional medicine recipes
By combining traditional medications with traditional medicine, the final therapeutic effect of the combination treatment can be significantly increased. Time-tested recipes help stop the inflammatory process, eliminate itching and burning, and also overcome dryness and flaking of the skin.
The following recipes are most often used to treat eyelid dermatitis:
- Lotions based on chamomile decoction. To prepare a healing remedy you need to take 1 tbsp. l. chamomile flowers and pour 120 ml of hot water over them. The product must be brought to a boil and left on the fire for another 5 minutes. The broth should be allowed to cool. The product should be filtered through a piece of gauze and used for lotions, washing the eyelids 3 times a day until complete recovery.
- Compress of chamomile and string. For this recipe you need to take dried string and chamomile flowers in a 1:1 ratio. The components are mixed and poured with 200 ml of hot water for 5 minutes. After this time, the flowers of medicinal plants should be squeezed out and wrapped in a clean piece of gauze. It is recommended to apply the compress to the eyelids for 30 minutes. With regular use of this recipe, you can eliminate itching and burning of the skin of the eyelids, as well as overcome irritation and dryness of the epithelium, and stop the inflammatory process.
- Use of tea tree oil. To combat eyelid dermatitis, you need to take 5 ml of refined sunflower oil and add 6 drops of tea tree oil to it. Using a cotton pad, the resulting product should be treated with the inflamed area of the skin in the morning, afternoon and evening for 1-2 months. This recipe is in great demand due to its antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.

Additionally, dermatologists recommend that patients observe the rules of personal hygiene, regularly perform wet cleaning of living quarters, strengthen the body’s immune system and undergo a comprehensive examination of the body 2 times a year.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis in the eyes
The manifestation of one of the types of dermatitis requires immediate action. The patient should first visit a dermatologist and therapist. Then you may need to contact an ophthalmologist, allergist, endocrinologist, or gastroenterologist to identify the true causes of the disease. An examination is prescribed to the patient after an external examination and anamnesis. Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- blood test (check the level of eosinophils, leukocytes, red blood cells);
- tear fluid samples;
- scraping to identify pathogens;
- biomicroscopy (non-contact examination of the eye with a slit lamp).
After diagnosing dermatitis and identifying the form of the pathology, the doctor prescribes treatment. In addition to drug therapy, patients are advised to eliminate the allergen and stop using decorative cosmetics for a while. The eyes are washed daily with boiled water and furatsilin solution. After this, the affected areas are treated with antifungal ointments. When treating the disease externally, blindfolds are not applied to the eyes. A positive effect is provided by lotions with tea or infusions of medicinal herbs.
Patients are often prescribed corticosteroid drugs for external use. Treatment lasts up to 14 days, depending on the specific case. In addition to ointments against eye dermatitis, drops are prescribed (solution of prednisolone, adrenaline hydrochloride and others). Additionally, patients may be prescribed restorative medications (calcium chloride intravenously). Patients are advised to cleanse the body and adjust their diet.
- Ointment for sprained ligaments and muscles
- Wisteria beads
- Cindy Crawford - the secret of an ideal figure, shaping lessons, video. Workouts with Cindy Crawford in video lessons
Antihistamines
The basis of treatment for allergic eye dermatitis is the use of antihistamines. This group of drugs, after entering the body, relieves external symptoms caused by the effect of the allergen on the patient’s body (lacrimation, rash, itching, bronchospasm). Antihistamines are available in tablets, drops, syrups and are used only after a doctor's prescription. Popular drugs in this group:
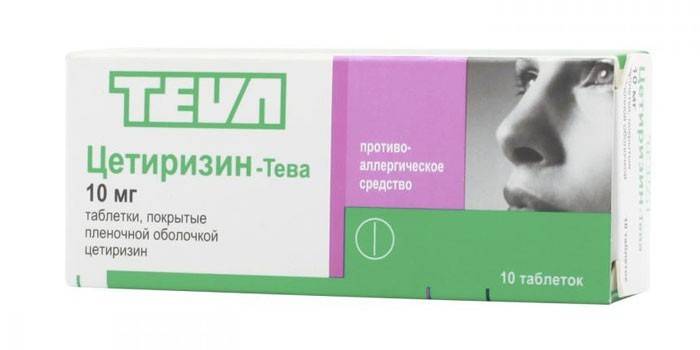
- Cetirizine has a gentle effect on the patient’s body and has virtually no contraindications. The effect of the drug becomes noticeable 1.5-2 hours after use. The medicine relieves itching, lacrimation, and helps fight conjunctivitis.
- Chloropyramine provides antiallergic and sedative effects. Not for pregnant and nursing mothers.
- Cetrin is prescribed to patients over 2 years of age and is a histamine blocker. Produced on the basis of cetirizine, it has a gentle effect and eliminates the effects of allergies.
- Tavegil - a drug in tablets is prescribed to adults and children. It has a gentle effect, soothes, relieves swelling and itching.
- Suprastin has many contraindications due to its toxicity. Prescribed for serious forms of the disease. After taking the tablet, eye swelling and other symptoms of allergic dermatitis subside within 10-15 minutes.
- Zyrtec is a second generation drug based on Cetirizine. Included in the group of selective histamine blockers. Quickly relieves symptoms of dermatitis by blocking histamine receptors.
- Levocetirizine is available in the form of syrup or tablets. It acts in 15-20 minutes, relieves swelling, itching, and rash.
Creams and ointments
In addition to antihistamines, patients with allergic eye dermatitis are prescribed external treatment agents. Below are popular ointments and creams to combat this disease:
- Advantan is a medicine in the form of a cream based on methylprednisolone aceponate. After application to damaged areas of the skin, the drug quickly suppresses inflammatory and allergic reactions, eliminates swelling, itching, and relieves inflammation. The cream is prescribed to children from 4 months and adults.
- Zinc ointment is an inexpensive, effective remedy for the treatment of skin diseases based on zinc oxide. The drug relieves inflammation, provides an astringent effect, and kills bacteria.
- Celestoderm is a betamethasone-based ointment that provides anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects. Contraindicated for children under 6 months and pregnant women.
Eye drops
To speed up the recovery process and improve the patient’s condition with allergic eye dermatitis, drops can be prescribed as part of complex therapy. This form of medication quickly affects the body, relieves swelling and itching, and prevents further development of pathology. Below are the popular drugs in this group:
- Opatanol – drops based on olopatadine hydrochloride. The product is a selective inhibitor of histamine receptors, suppresses the effects of allergens on the body, eliminates inflammation of the conjunctiva and lacrimation. The effect is observed 2 hours after applying the drops.
- Olopatadine is an analogue of Opatanol. It has a double effect, relieving allergy symptoms and affecting mast cells, which prevents the development of the disease. It has virtually no contraindications or side symptoms. Prescribed for adults and children.
- Allergodil is a drug based on azelastine hydrochloride. It has an antiallergic effect on the patient’s body, strengthens the membranes of eye cells, and relieves allergy symptoms. Not for children under 4 years of age, pregnant women, or nursing mothers.
- Azelastine, a drug in the form of drops, is a phthalazinone derivative. After use, the medicine provides membrane-stabilizing, antiallergic, antihistamine effects. Not prescribed during lactation, during pregnancy and for children under 4 years of age.
- Cromohexal is a product based on cromoglicic acid with disodium salt and benzalkonium chloride. The drug provides stabilization of mast cell membranes and relieves allergy symptoms. The effect of the medicine is observed only after 3-5 days, so it is prescribed more often for prevention or as part of complex therapy.
- Lecrolin is an inexpensive product containing sodium cromoglycate. The drug is an antihistamine, relieves the symptoms of the disease, eliminates inflammation from the membrane of the eye. Prescribed to patients with allergic dermatitis over 6 years of age.
Possible consequences and complications
To reduce the likelihood of progression of eyelid dermatitis, experts recommend abandoning the idea of hiding the affected areas of the skin using cosmetics.
Otherwise, re-infection may occur, which is difficult to overcome even with modern medications. Without effective treatment for ocular dermatitis, the likelihood of developing serious complications increases significantly.
In such a situation, it is possible that an inflammatory process may occur in the area of the cornea of the eye, which will contribute to a rapid decrease in visual acuity. At the early stage of development of eyelid dermatitis, properly selected ointments and creams help to cope with the disease in 15-20 days.
Prevention
To avoid eyelid dermatitis, you should follow tips including:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- careful selection of cosmetic products;
- in case of hay fever during the flowering period of plants, carry out wet cleaning frequently;
- do not use other people’s decorative cosmetics;
- when working with potentially allergenic compounds, use appropriate personal protective equipment;
- Follow the rules for using contact lenses.