Even the smallest pets can cause serious illness. Thus, recently, experts have noted more and more cases in which both adults and children Allergy to hamsters is diagnosed.
Those who believe that the cause of the disease is only the hair of rodents are deeply mistaken. After all, the allergen that provokes the onset of the disease is also contained in the urine, saliva, and dander of a small animal.
Currently, this disease has been widely studied and researched. Therefore, if a person wants to find out whether there may be an allergy to hamsters, before purchasing these animals directly, they should consult an allergist. He will help him find out whether there is a danger of developing the disease and how to prevent the occurrence of serious health consequences .
The mechanism of development of an allergic reaction
It is believed that hamster allergies occur as a result of human contact with the pet's fur. However, this opinion is erroneous, since the immunological reaction is caused by skin flakes (the upper layers of the epidermis), which are found in large numbers on the hairs.
They contain a protein (immunoglobulin) that provokes a hypersensitivity reaction.
The highest concentration of immunoglobulins is in the sweat, saliva and urine of a hamster. These biological fluids fall on the exfoliated particles of the animal’s skin and fur, causing an immediate allergy.
The protein penetrates the body, activates the immune system, which thus reacts to the pathogen. The body produces histamine, which enters the bloodstream and causes allergy symptoms.
Important! Often adults and children are allergic to the Djungarian hamster. But the immunopathological process can be caused by representatives of different breeds: Syrian, Roborovsky, Campbell and others. There is also an allergy to hamsters, which naturally do not have hair.
To reduce the risk, a sensitivity test should be performed. This can be done at a specialized medical center.
It is important to check your body's reaction, as at first there may be no allergy symptoms. There are 3 stages of the immunopathological process:
- Immune – the allergen penetrates the human body.
- Biochemical - the body reacts to the protein, and the immune system rejects the foreign substance, antibodies begin to be produced.
- Clinical – symptoms of hamster allergy appear.
Since signs of a hypersensitivity reaction do not appear immediately after contact with an animal, people cannot accurately identify the allergen.
Preventive measures
An allergy to a hamster does not always force owners to part with their pet, so in such a situation it is necessary to take into account a number of preventive techniques that will help communicate with the rodent as painlessly as possible. So:
- After finishing feeding or after cleaning the hamster's cage, you should thoroughly wash your hands and thoroughly disinfect all exposed areas of the body. This can be done using special products or antibacterial soap. You cannot be near your pet for a long time.
- Regularly ventilate the room in which the rodent’s cage is located 2-3 times. It is advisable to dust and wet clean every day.
- When cleaning the cage, pay special attention to the sanitary area of the hamster, which must be washed with special care.
- If possible, it is better to entrust caring for a hamster to a family member who is not susceptible to allergies.
Do not ignore compliance with preventive rules when interacting with a rodent, since protective measures will help not only prevent the development of symptoms, but in some cases avoid unpleasant symptoms. If, while taking the necessary measures, a Syrian hamster or another breed of rodent causes an allergy, immediately seek medical help. A timely investigation and prescription of therapeutic therapy will save you from serious consequences while maintaining good health.
Are there allergies to hamsters?
5
(100%)
1
vote
Doctor
Factors contributing to allergies
The likelihood of an immunopathological reaction increases under the influence of the following factors:
- decreased immunity in humans;
- hereditary predisposition;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- the presence of chronic diseases;
- frequent contact with allergens.
Allergies can be caused by particles of keratinized skin, dandruff, saliva, urine, sweat, or animal excrement. The allergen enters the bloodstream after being bitten by a hamster that is playing or getting scared.
Most often, pet owners who are in constant contact with the pet suffer from the pathology. Laboratory or vivarium workers are also more likely to exhibit allergy symptoms. However, people who are not related to rodents in any way can also be allergic to hamsters.
In this case, the allergen enters the body through dust, skin particles on clothing or household items.
Cause
Many people claim that the cause of allergies is animal fur. Some say that a severe form of allergy is caused by the Djungarian small hamster. In fact, the main cause is the animal's saliva and dander. Sometimes an allergy develops after a rodent bite. Allergens are also present in subcutaneous fat, and all hamsters can be dangerous, no matter how lush their fur is.

Currently, hamster allergies are not the most common. If a person has it, the quality of life noticeably deteriorates. It is important to establish in time the exact causes of the disease, and only then select treatment methods.
Clinical symptoms
At stage 3 of the immunopathological process, symptoms of an allergy to a hamster appear. Most often these are skin inflammations and breathing problems. But other dangerous signs may appear.
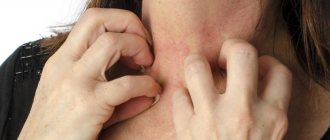
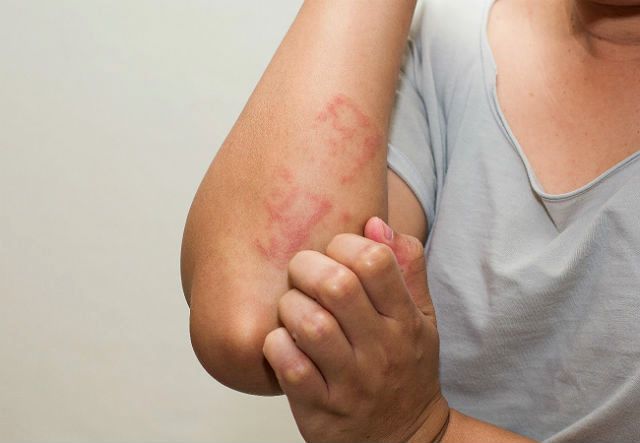
Skin reactions usually appear first at the site of exposure to the allergen. Then itching and redness, rash, and swelling of the skin occur. A person may experience individual symptoms or all of them at once, and their severity also varies.

Allergy to hamsters in adults and children is manifested by catarrhal symptoms. They are similar in that during their development the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and bronchi become inflamed. Breathing is often impaired.
When an allergen penetrates from the stomach into the small intestine, the digestion process is disrupted. This occurs due to damage to the villi of the jejunum. In this case, inflammation develops, flatulence, abdominal pain, and diarrhea appear.
The risk of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, erosions on the mucous membrane, and damage to the villous layer of the small intestine increases.
The most dangerous immunological reaction is anaphylactic shock. In 20% of cases it leads to death.
Under the influence of allergy mediators, blood circulation is disrupted, the stroke volume of the heart decreases, blood pressure drops, weakness is felt, and cold sweat is released. The person cannot breathe or speak normally and needs urgent resuscitation.
If the hamster's sensitivity to allergens is increased, the risk of developing vascular collapse increases. Then the vascular tone drops sharply or the mass of circulating blood quickly decreases. This leads to a decrease in venous flow to the heart, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the brain.
The person feels very bad, the pulse is thread-like, weak, and frequent.
Anaphylaxis requires long-term hospital treatment.
Important! All hamsters are allergenic, but most often the Djungarian hamsters cause an immunopathological reaction. The problem is that this breed is the cleanest. The Dzhungarik often washes its fur, so the allergen is constantly in the access zone and spreads in the environment.
From the respiratory system
Frequent manifestations of hamster allergies are sneezing and shortness of breath. A person sneezes when, during inhalation, irritants (for example, particles of a pet’s epidermis) enter the sensitive nasal mucosa.
The frequency and depth of breathing are impaired as a result of spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi, larynx or trachea. Then the volume of the lungs decreases, a feeling of lack of oxygen arises, and heaviness appears in the chest. Due to breathing difficulties, a person with a hamster allergy experiences anxiety and depression.
With high sensitivity to allergens, suffocation occurs and the risk of hypoxia (including brain tissue) increases.
An acute allergic reaction can lead to bronchial obstruction, when a person breathes heavily and develops paroxysmal coughing and wheezing. In such cases, it is necessary to take a drug to relax the walls of the bronchi and visit a doctor.
An allergy to a hamster often manifests itself with catarrhal symptoms: rhinitis, bronchitis. In the first case, the nasal mucosa becomes inflamed, in the second, breathing becomes difficult, swelling of the bronchi begins, coughing, and pain in the chest begins.
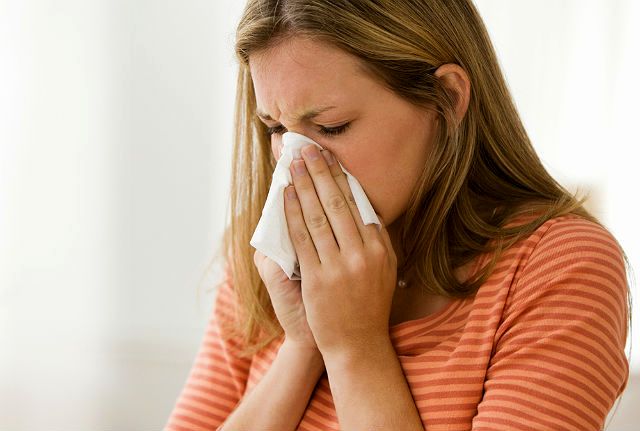

Many people mistakenly confuse allergies with ARVI and independently carry out symptomatic treatment, which does not produce results.
Urticaria and allergic conjunctivitis
A common hypersensitivity reaction to hamsters is urticaria. Then red spots or light pink blisters appear on the skin on the mucous membranes. Such formations can be single or merged, and they can also be of different sizes. In acute allergies, urticaria lasts about 2 weeks, but sometimes longer.
In rare cases, hamsters provoke the development of specific dermatitis. Atopic eczema is manifested by redness, rash, and peeling of the skin. Skin changes associated with contact dermatitis range from erythema to blisters and ulcers.
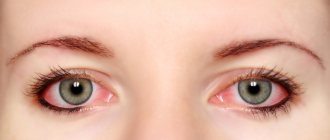
Often, if you are allergic to a hamster, the conjunctival membrane becomes inflamed. At the same time, the sensitivity of the eyes to light increases, itching, pain occurs, and tearing increases.
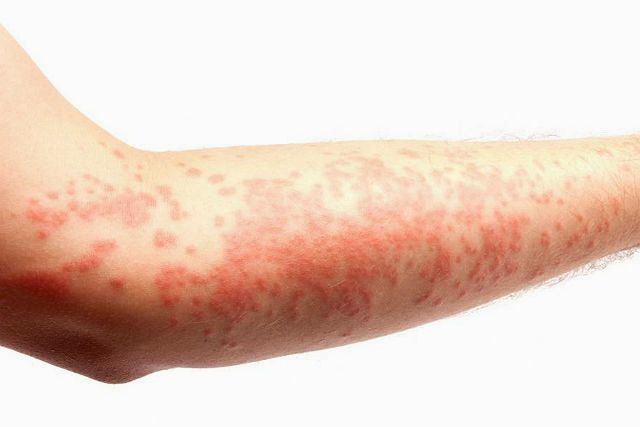
Quincke's edema
There is another dangerous reaction to the action of an allergen - Quincke's edema (angioedema). Immediately after contact with the irritant, areas with developed subcutaneous tissue rapidly swell - fluid accumulates in the area of the lips, eyelids, cheeks, and oral mucosa.
The most dangerous is swelling of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi. This symptom can lead to suffocation, so when the first signs of Quincke's edema appear, the victim must be hospitalized immediately.
Persistent allergic rhinitis
The symptoms of a runny nose are well known to everyone and do not frighten anyone. Most often we are talking about a common cold in the off-season. As doctors joke, if you treat it, your runny nose will go away in a week, and if you don’t treat it, it will go away in seven days.
What to do if the disease becomes chronic? Do not self-medicate under any circumstances and be sure to consult a doctor. It is likely that we are talking about persistent rhinitis.
What it is
Allergic persistent rhinitis is a chronic disease, the symptoms of which appear all year round, regardless of the season.
They may not be as obvious as in acute rhinitis, but they always manifest themselves in the classic trinity:
- persistent heavy nasal discharge (rhinorrhea);
- sneezing;
- difficult nasal breathing.
Progressing, constant inflammation of the delicate nasal mucosa can lead to loss of smell.
Reasons for appearance
The main factor provoking the development of the disease is the presence of strong allergens in the air.
The most severe situation occurs if the patient is constantly in contact with household allergens.
Adults and children are susceptible to the disease, but it is in children that manifestations of chronic runny nose of an allergic nature most often lead to the development of concomitant diseases.
Some of the most common household allergens include:
- biological fluid and pet dander;
- dust mites;
- pollen and plant aroma;
- mold.
There are also external factors that cause the development of constant inflammation of the nasal mucosa: insects and plant pollen.
Finally, in rare cases, adults develop a runny nose of an allergic nature associated with professional activities.
It can be caused by constant contact with one type of dust or another.
Flour, wallpaper glue, latex, animal hair, formaldehyde, sawdust, cement dust - all this can trigger the development of the disease.
Variants of the course of persistent allergic rhinitis
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa caused by the presence of allergens in the environment can have different courses.
The disease can manifest itself differently throughout the year, which is associated with changing concentrations of allergens and varying degrees of contact with them.
We should talk about several variants of the course of the disease:
- mild degree of inflammatory manifestations;
- moderate inflammation;
- severe form of rhinitis with the development of concomitant diseases.
With minimal manifestation of persistent rhinitis, the main symptoms are mild or completely absent.
However, even in this case, inflammatory processes in the nasal mucosa certainly persist.
A runny nose causes discomfort and can affect the quality of night sleep, since due to swelling of the mucous membrane, the functions of nasal breathing are disrupted.
Moderate severity of inflammation seriously affects daytime performance and quality of night sleep.
A person cannot engage in usual work, sports, rest or study.
In severe cases, allergic rhinitis is complicated by concomitant diseases of the nasopharynx, ears, and even the bronchopulmonary system. Symptoms of the disease become painful.
Video: Important points
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of the disease is characterized by a long course.
At least two striking symptoms must appear for at least an hour during the day, more than four days during the next exacerbation of the disease, and the total duration of symptoms is at least four weeks a year.
The disease manifests itself as disturbances in sleep and daytime activity due to nasal congestion, excessive discharge, and sneezing attacks.
We should talk about two variants of the clinical manifestation of the disease: exudative and obstructive. They differ in the severity of the main symptoms.
A number of manifestations are characteristic of exudative rhinitis.
The main ones:
- frequent, paroxysmal sneezing;
- watery, thin discharge;
- constant itching in the nose;
- periodic nasal congestion;
- often the development of conjunctivitis;
- relief during the day, worsening at night.
The clinical picture looks different in the obstructive form:
- sneezing is practically absent or very slight;
- a thick secretion is released from the nose;
- no itching;
- the nose is constantly stuffy, the degree of stuffiness is high;
- no conjunctivitis;
- The course of the disease is the same for night and daytime hours; the condition may worsen at night.
Often, upon examination, doctors discover chronic foci of infectious inflammation and moderate-severe diseases of the upper respiratory tract in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis.
Thus, persistent allergic rhinitis in a child is usually accompanied by sinusitis and otitis media. In adult patients, sinusitis and pharyngitis are diagnosed.
How to make a diagnosis
To diagnose persistent rhinitis, clinical and laboratory research methods are used. Doctors must collect a thorough medical history, analyze complaints and symptoms, and conduct general and local tests.
Diagnosis of allergic chronic rhinitis includes the following methods of physical, laboratory and instrumental studies:
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity) to identify characteristic changes in the mucous membrane and the degree of their severity;
- identifying the level of allergen-specific IgE in the blood;
- mucosal smear to determine the level of eosinophils, goblet cells and mast cells;
- computed tomography of the nasal sinuses to differentiate the variants of persistent rhinitis;
- X-ray of the nasal sinuses to exclude dangerous complications.
Thus, the diagnosis of chronic inflammation of the nasal mucosa is carried out comprehensively, with the participation of allergists, otolaryngologists and immunologists.
Treatment options
Particularly difficult is the treatment of young patients diagnosed with persistent rhinitis. Treatment makes sense only if it is carried out comprehensively and continuously.
The role of parents in this situation is very important, since it is they who will be responsible for the competent and timely implementation of the treatment measures prescribed by the doctor.
Directions for the treatment of chronic allergic rhinitis are as follows:
- exclusion, if possible completely, of contact with identified allergens and constant monitoring of the state of the air environment;
- use of pharmaceutical drugs;
- specific immunotherapy, or allergy vaccination.
To reduce the concentration of allergens, daily wet cleaning is used.
If the cause of the reaction is a pet, plant, or mold, you should get rid of them immediately.
The patient's bed linen should be made of material that provides maximum protection against the penetration of allergens.
Children's allergists recommend using natural flax, in the fibers of which dust mites do not live.
During the treatment of persistent rhinitis, pencillin antibiotics, aspirin, and sulfonamides should not be used, as these drugs have a high sensitizing activity.
To relieve severe symptoms of the disease, an allergist prescribes the following medications:
- antihistamines (azelastatin, suprstin, tavegil, etc.);
- local or systemic glucocorticosteroids (beclomethasone);
- vasoconstrictors (naphthyzin, xylene);
- drugs that block cholinergic stimulation (ipratropium bromide);
- leukotriene receptor blockers (zafirlukast, montelukast).
Allegovaccination is a complex and unsafe method of introducing microscopic doses of allergens into the body according to a certain pattern in order to gradually develop resistance to them.
This treatment continues for several years.
Comprehensive treatment of persistent rhinitis leads to an improvement in the patient's condition. The resulting remission allows the nasal mucosa to recover; further treatment consists of preventive measures.
Prevention
The only possible method of prevention is to avoid contact with the identified allergen.
It will not be possible to achieve a complete or maximum reduction in its concentration right away, because wool and pollen remain on furniture upholstery, fabrics used in the interior, etc. Therefore, sometimes it takes several months to remove the allergen.
A common problem in the treatment of chronic allergic inflammation of the nasal mucosa is polyvalent sensitization, that is, a reaction to more than one allergen at once.
However, in the absence of constant contact with identified allergens, the patient’s condition improves significantly, which makes it possible to gradually reduce the doses of medications taken.
A preventive measure is to follow a diet that excludes the use of allergenic foods in the diet.
This is an important point, since with cross allergies, exacerbations of rhinitis are possible precisely against the background of eating certain foods.
Useful tips
Complications of persistent rhinitis are unlikely to be avoided, especially if it is caused by external factors. However, there are ways to minimize the harm that allergenic substances can cause to your health.
What can be done:
- Avoid drying clothes outdoors: on the balcony, in the yard. This recommendation is especially important during the flowering period of plants that can potentially cause an allergy attack. It is better to always dry children's clothes at home to prevent the penetration of mineral dust and plant components;
- arrange ventilation of living rooms after rain. At this moment, the concentration of plant allergens in the air is minimal;
- carry out daily wet cleaning in the room where the sick person spends the most time;
- do not use chemical air fresheners, substances with a strong odor, including aroma lamps, if an allergy sufferer lives in the apartment;
- At night in the summer, close the windows tightly to prevent insects and pollen components from entering the room. In the early morning hours, the concentration of harmful, potentially dangerous components of plant origin in the air is highest.
Persistent allergic rhinitis is a chronic disease that can seriously affect a person's quality of life and health.
That is why you should treat the symptoms of the disease with extreme attention, identify the allergen with the help of a specialist, follow all the doctor’s recommendations and, if possible, avoid contact with allergenic substances.
Hamster allergy in a child
Children are more likely to suffer from hamster allergies as they spend more time with the pet. In addition, their body is weaker than that of adults. Allergy to hamsters in children is manifested by the symptoms described above. But the signs may be more pronounced in contrast to older pet owners.

An immunopathological reaction can occur even in infants who do not come into contact with animals. It is enough that the cage is in the same room as the child. Allergens enter the baby's body through dust particles or during contact with parents.
Intolerance

Allergies to rodents are common. Many people feel unwell after interacting with these animals. Watery eyes intensify, a runny nose and cough appear, spots appear on the allergy sufferer’s body, sometimes a rash appears, and itching is felt. Many people are familiar with these symptoms firsthand.
Sawdust is the most popular filler for the cage where the hamster lives. The huge advantages of wood shavings are ease of use, as well as the price of the sawdust itself.
Interesting! Allergies are caused by mold fungi contained in wood filler particles.
Diagnostic methods
An allergist will help you find out whether you are allergic to hamsters or not. For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- Skin testing. A little allergen (hamster biological fluids) is applied to the skin of the back or arms. Sometimes, before applying the irritant, the skin is lightly scratched or a shallow injection is made. If after 25-30 minutes redness or itching appears at the affected area, then there is an allergy. You can test about 15 allergens at one time. Skin testing is inexpensive and easy to perform. However, this method is not always accurate.
- Blood test for immunoglobulin E. This method allows you to identify specific antibodies that react to the pathogen. The study gives an accurate result. Sometimes it is done to confirm skin testing.
- Provocative tests. This method is used if skin testing and blood tests do not clarify the picture. During the procedure, a potential allergen is injected into the patient’s nasal mucosa, under the tongue, or into the bronchi. Testing is carried out in stationary conditions, since the reaction to the stimulus can be vivid.
- Elimination test. This diagnostic method is used if a person is unable to visit a medical facility. Its essence is that a potential allergen, for example, hamster, is removed from everyday life. If after a few days the symptoms disappear, then the causative agent of the immunological reaction has been identified.
The tests described above are prescribed after allergy symptoms appear. To prevent the immunopathological process, they are carried out before contact with the suspected allergen.
If there is a hereditary predisposition to allergies, the child must undergo testing. Also, studies are prescribed for continuously recurrent respiratory diseases without periods of remission.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is the most dangerous immunological reaction, since out of ten cases, two are fatal. It develops rapidly, causing impaired blood circulation, a decrease in the stroke volume of the heart and a decrease in blood pressure.
The first symptoms in a child are usually a runny nose, sneezing, dry cough, hoarse voice, and red eyes. Children often complain that their eyes are itchy, they don’t feel like eating, and their condition is usually weakened. If you suspect an allergy in a child, it is very important to immediately exclude contact with a rodent and seek help from a doctor.
Parents should refuse to buy a rodent if:
- the child has a predisposition to allergies;
- he often suffers from colds;
- The allergy has occurred previously to other animals.

- the child has a predisposition to allergies;
- he often suffers from colds;
- The allergy has occurred previously to other animals.
Hamsters are often found in apartments where small children live. They love to communicate and play with them. But sometimes cute animals bring problems. The most common is an allergy to hamsters. It is very important to notice the symptoms of the disease in time and consult a specialist. This is the only way to avoid serious consequences.
Allergy treatment
To eliminate the immunological reaction, elimination and antihistamine therapy is carried out. Treatment can be supplemented with folk remedies only after the doctor’s approval.
First of all, a person with allergy symptoms should avoid contact with the allergen (hamster biological fluids). This is elimination therapy. The patient delegates the responsibility for caring for the animal to relatives or friends (without allergies).
The cage with the pet must be moved to another room; it is forbidden to pick up the hamster or bring it to your face. It is also necessary to change the toilet filler as often as possible.
The allergist prescribes medications to the patient that block histamine receptors. These medications reduce or remove the sensitivity of the body and receptors to the allergen.
For severe immunological reactions, medications from the group of glucocorticosteroids are used. Immunomodulators increase the body's resistance to allergens. Enterosorbents cleanse the body of toxins and reduce allergy symptoms.
After the doctor's approval, the patient can use herbal remedies. However, this must be done carefully, since some plants themselves can provoke allergies.
Antihistamines
There are 3 generations of antihistamines that are used to treat hamster allergies:
- Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenistil. These drugs relieve angioedema and symptoms of anaphylaxis. However, they depress the functioning of the nervous system, so they are prohibited for pregnant women and children.
- Claritin, Allergodil, Zyrtec. These medications are distinguished by their selective action on H1 receptors, practically do not disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system, and therefore are suitable for longer-term use. However, they can negatively affect the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract (including the liver) and the cardiovascular system.
- Levocetirizine, Desloratadine, Fexofenadine. These are modern medications that help eliminate allergy symptoms (itching, swelling). It is believed that they are the safest, practically do not interfere with the functioning of the heart, central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and do not interact with other medications. Adverse reactions (insomnia, nausea, headache) occur rarely.
For severe allergies, which are accompanied by serious dysfunctions of the body, steroid drugs are prescribed, for example, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Hydrocortisone.

They are used for medical reasons in limited quantities, as they disrupt hormonal levels, have many contraindications and can cause serious adverse reactions.
Enterosorbents cleanse the body of toxins and reduce the symptoms of hamster allergy. For this purpose, Polysorb, Lignin, Smecta, Atoxil, Enterosgel are often used.
To strengthen the immune system, doctors prescribe immunomodulators in the form of drops in the nose or eyes. Timolin, Derinat, Likopid, Imunofan and some others are used as part of complex therapy.
The decision to prescribe drug combinations and the regimen of use is made by the attending physician.
Traditional methods
If an allergy to hamsters is accompanied by rhinitis, then it is necessary to use a nasopharyngeal rinse. To do this, use saline solution, infusion of butterbur, calendula or chamomile.
Warm liquid is drawn into a syringe without a needle, injected into the nasal passage, and then exhaled with force, while closing the other nostril. This allows you to clear the nasal passage, wash away allergens from the mucous membrane to ease allergy symptoms.
The patient can drink herbal teas. They relieve spasms, symptoms of inflammation, have a sedative effect, and accelerate the removal of sputum.

To eliminate catarrhal symptoms, inhalation is carried out with herbal decoctions or essential oils (for example, eucalyptus). The following will help relieve allergy symptoms:
- olive oil;
- peppermint;
- chamomile;
- horseradish root.
But you should use folk remedies only after consulting an allergist, since some herbs do not cause a therapeutic effect or provoke negative reactions. In addition, the effectiveness of non-traditional remedies has not been proven.
Prevention
Patients predisposed to allergies are better off abandoning the idea of buying a hamster.
If you have already acquired an animal, then it is advisable to have minimal contact with the pet (bites are especially dangerous, since in this case saliva enters directly into the blood), seek the help of loved ones to clean its cage, regularly ventilate the apartment and keep the room clean.
From all that has been said, two conclusions can be drawn. First, hamsters, like other animals, can provoke allergic reactions, and some of these immunological manifestations are life-threatening. Secondly, if symptoms of the disease are detected, it is recommended to contact a qualified specialist as soon as possible.
Characteristic symptoms and treatment methods for parrot allergies.
What reaction can a simple insect bite cause?
Our smaller brothers do not cause runny nose, cough and itching.
Symptoms, prevention and treatment of the disease.
Of all the types of pet allergies that are common in the world, allergies to cats or dogs are the most common. But sometimes there are other manifestations of it, for example, now you can increasingly find an allergy to a hamster. Why such a problem develops, how such an allergy manifests itself and whether it can be overcome - you will learn about all this further.