Allergic laryngitis symptoms and treatment in adults vary. With this disease, damage to the mucous membranes located in the larynx area is observed. Allergic laryngitis can be caused by a variety of causes .
When the disease occurs, the tissue that lines the upper region of the throat is damaged. As the disease progresses, the patency of the paths through which air masses move is disrupted. Complications of a disease such as allergic laryngitis, symptoms, treatment in children are the subject of close attention of doctors.
Causes
In everyday life, symptoms of allergic laryngitis can be triggered in adults and children by: household chemicals (varnishes, paints, detergents); representatives of local flora (pollen); medications; food products (nuts, spices and herbs, sweets with honey or chocolate, seafood, some fruits and berries); dust, fluff, wool.
Especially often, the allergic form of the disease is diagnosed in adults who, by profession, are forced to breathe polluted air saturated with industrial waste, exhaust gases, dyes, varnishes and other harmful substances.
Forms of the disease
Allergic laryngitis in children and adults is divided into several types:
- Spicy. Occurs upon contact with an allergen, resulting in swelling of the larynx, in addition, laryngospasm may occur, which leads to breathing problems. Allergic laryngitis is especially dangerous in a small child, which is often complicated by croup and requires immediate medical attention.
- Chronic. It is characterized by a sluggish and long-lasting course, blurred symptoms are observed with prolonged contact with the allergen or with improper treatment of the acute form. People with a chronic form of the disease experience frequent exacerbations, sometimes the slightest hypothermia is enough. Along with the catarrhal form of the disease, a polypous form develops, in which the mucous membrane grows and forms tubercles; the patients’ voice is quiet and hoarse, and they are bothered by tickling and a dry cough.
What causes the development of allergic laryngitis?
Allergens that cause this disease most often enter the body aerogenously. The most common types of allergens include:

It is not homogeneous in its composition and contains a large number of different allergens. The main triggers of allergies are tiny mites of the genus Dermatophagoiges. They live in the upholstery of upholstered furniture, on curtains, carpets, soft toys, etc.
House dust also contains various chemicals, animal hair and dander, cockroach allergens, and mold. It is noteworthy that carrying out disinsection increases the number of allergens several times, because After the death of ticks, cockroaches and other insects, excrement, components of the chitinous shells of these parasites, which have antigenic properties, enter the air.

These include:
- wool;
- dandruff;
- epidermal particles;
- excrement;
- pet saliva;
- feather and down.
This species is highly active, especially the epidermis of the cat. Allergens attach to dust particles and are easily transferred to clothing.
The following have the greatest allergenic ability:
- cow's milk;
- nuts;
- citrus;
- chocolate;
- fish;
- eggs;
- black currant;
- strawberries;
- strawberry;
- grape;
- blackberry;
- raspberries;
- a pineapple;
- persimmon;
- cereals.
In children, the cause of allergic laryngitis can be sensitization to latex, from which pacifiers, nipples, and toys are often made. Latex intolerance may subsequently cause increased sensitivity to bananas, avocados, melons, chestnuts, and kiwis.

There are 3 main groups:
- tree pollen (alder, birch, maple, oak, hazel, willow, ash, buckthorn);
- cereals (bluegrass, timothy, rye, oats, wheat, buckwheat);
- weeds (wormwood, nettle, dandelion, quinoa, ragweed).
A feature of pollen allergies is the seasonality of manifestations.
Spring exacerbations occur with an allergy to tree pollen, a reaction to cereals makes itself felt in the beginning and middle of summer, and a reaction to weeds manifests itself towards the end of summer or the beginning of autumn.
In addition, there is cross-allergy between pollen and certain foods. Sensitization to birch pollen can cause intolerance to apples, pears, cherries, and carrots.
- Air pollutants and production factors
- Medicines, vaccines.
Factors predisposing to the development of this disease:
- hereditary predisposition (bronchial asthma, various allergic diseases in close relatives);
- presence of signs of atopy (dermatitis, diathesis);
- massive intake of the allergen, or prolonged contact with it;
- exposure to polluted air, active and passive smoking;
- frequent acute respiratory infections;
- irrational use of drugs, especially antibiotics.
The development of the disease is based on an immediate allergic reaction.
Upon initial contact with an allergen, the body begins to synthesize immunoglobulin E, which is then fixed on the mast cell membrane. This process is called sensitization. Upon repeated contact, the allergen binds to immunoglobulin E, which leads to degranulation of mast cells and the release of special inflammatory mediators, which trigger various reactions in the body.
In the first few minutes, under the influence of mediators, there is an increase in vascular permeability and their expansion, clinically this is manifested by subglottic edema of the larynx. Due to edema, the glottis narrows, preventing the passage of air.
The degree of narrowing of the larynx is the determining factor in the clinical picture of acute allergic laryngitis. In addition, mediators irritate sensitive nerve endings, provoking a reflex cough.
After 6 to 12 hours, more than half of people with allergic diseases develop a delayed allergic reaction. Its manifestation is associated with the attraction to the site of inflammation of eosinophils, CD4 lymphocytes, basophils, which synthesize highly toxic proteins that can damage the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, smooth muscles, blood vessels, and lymphoid formations
Swelling and infiltration of the laryngeal mucosa serves as the basis for the development of chronic inflammation in it, which in turn contributes to the formation of hypersensitivity, when even minor irritating factors can cause laryngospasm or swelling of the larynx.
Quite often, especially in young children, the development of allergic laryngitis is preceded by a viral or bacterial infection of the respiratory system.
Infectious inflammation significantly reduces the protective properties of the mucous membrane, so allergens can easily penetrate the body. In addition, sensitive receptors are exposed, the irritation of which leads to hyperreactivity of the airways.
Acute allergic laryngitis is essentially angioedema that extends to the larynx area. The clinical picture is determined by the severity of edema and the degree of narrowing of the larynx.
- Compensated. It manifests itself as hoarseness of voice, a dry hacking cough that turns into a barking cough. There are no signs of respiratory failure, or they are minor and appear only during physical exertion, screaming, or crying.
- Incomplete compensation. Anxiety appears. Shortness of breath with difficulty breathing. Breathing is noisy and can be heard from a distance. Additional respiratory muscles take part in the act of breathing, the wings of the nose swell, the intercostal spaces and supraclavicular jugular fossae are drawn in. Mild perioral cyanosis appears.
- Decompensated. The patient is in serious condition, anxiety gives way to adynamia. The skin becomes sharply pale with perspiration. Cyanosis increases. There is a bluish coloration of the nasolabial triangle, tip of the nose, ears, fingers and toes. Blood pressure decreases and heart failure develops.
- Asphyxia. Total cyanosis. There is a pronounced depression of cardiac activity and respiration until they stop completely.
Signs
Symptoms of acute allergic laryngitis in adults and uncomplicated laryngitis in children are as follows: a feeling of a lump in the throat and painful sensations when swallowing, difficulty breathing, slight shortness of breath, a hoarse voice; dryness and burning in the throat, scratching or soreness; sometimes accompanied by painful coughing attacks; often the disease is complicated by rhinitis or pharyngitis. Sick children and adults may experience cyanosis (blueness) of the lips and nasolabial triangle.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease depends on its form (acute, chronic). If a person has acute allergic laryngitis, the symptoms will be as follows:
- dyspnea;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- dryness, burning inside the throat;
- difficulty breathing. It is provoked by a narrowing of the glottis;
- hoarseness. The voice becomes hoarse;
- sore throat;
- pain while swallowing. They appear due to inflammation of the posterior wall of the larynx, epiglottis;
- coughing fit, regular coughing.
With a weakened immune system, prolonged exposure to an allergen on the body, or the presence of a chronic infection inside the nasopharynx or oropharynx, infectious laryngitis may develop against the background of an existing allergic laryngitis.
With infectious laryngitis, there will be a cough with sputum, pain in the throat, a rise in temperature, and signs of general intoxication. When you stop exposure to the allergen, the disease will go away in a few days (literally 7 - 10).
If the irritant repeatedly affects the body, the patient will experience a new attack of laryngitis. The disease will become chronic. Symptoms of the disease after chronicity are the same as in the acute form of the pathology. The clinical picture of the disease disappears during the period of remission.
If the cause of allergic laryngitis is any food product, the patient will have the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- soreness;
- cough;
- slight sore throat.
These signs of the disease usually go away on their own after some time. If the concentration of the allergen in the blood increases, the patient will experience a repeat attack of allergic laryngitis.
Diagnostics
The medical history tells the doctor a lot. To unambiguously establish an accurate diagnosis, detailed diagnostics will be required:
- Blood for total IgE.
- Laryngoscopy.
- General clinical studies.
- Allergy tests.
Complications
Allergic laryngitis in children can cause serious complications - severe swelling develops, muscle spasms occur, and breathing problems begin. In a child under 5 years of age, the larynx is small, so swelling spreads much faster than in adults.
As the disease develops, the child develops other symptoms - attacks of a dry barking cough, shortness of breath, wheezing in the throat, cyanosis. Stenosis may develop - blocking of the glottis, followed by asphyxia and cardiac arrhythmia, including coma and death. Attacks of suffocation that occurred in a child with this disease can occur again with a second relapse, so all efforts of parents should be aimed at ensuring that the symptoms of the disease do not recur.
In adults, the allergic form of the disease is usually not as severe as in children, since the size of the larynx is larger, but sometimes cases of angioedema or anaphylactic shock occur, which are also fatal and require immediate medical attention.
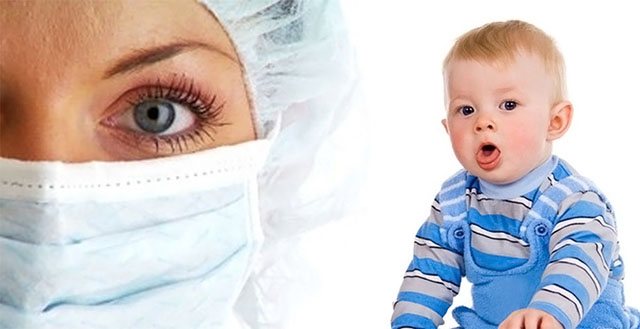
Diagnostics
At an appointment with an otolaryngologist, the patient will undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- Physical examination and interview.
- Laryngoscopy, which is performed using a special instrument - a laryngoscope. The procedure is unpleasant, but absolutely safe and extremely necessary, since without this device the doctor will not be able to fully assess the condition of the larynx and vocal cords.
When undergoing an examination by an allergist, if the etiology of the allergy that led to the development of laryngitis has not been established, the patient is prescribed allergy tests. They are carried out in several ways:
- Several shallow scratches are made on the patient's hand, into each of which a small amount of liquid containing the allergen is dripped. The substance with which the wound is swollen and red is the cause of the allergic reaction.
- The second method of conducting an allergy test involves collecting venous blood. A sample of biological material is divided into several portions, and a separate allergen is added to each portion. Based on the blood reaction, the laboratory technician can judge how sensitive the human body is to a particular substance.
Often, an allergy test with venous blood sampling for allergic laryngitis or other diseases with a similar etiology is carried out in pregnant women. However, it can only be performed if the patient does not have a risk of developing laryngeal stenosis, and the pathology itself is relatively mild.
An integrated approach to diagnosis helps prescribe the most effective treatment to the patient, especially if a child is suffering from the disease.
Drug treatment of the disease
Treatment of allergic laryngitis should be carried out by an otolaryngologist together with an immunologist and an allergist. It is important to prevent complications of the disease with cardiac dysfunction and severe shortness of breath.
Allergic laryngitis of mild (first) degree is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a doctor: Diazolin and Diphenhydramine are prescribed, calcium gluconate injections, sedatives and antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil), drinking plenty of alkaline mineral waters, soda rinses, warm baths.
For grades 2-4 of the disease, hospital treatment is indicated. Typically, antispasmodics (No-shpa), antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin), sedatives (Seduxen, Relanium), injections of calcium gluconate solution, inhalations with a 5% soda solution are prescribed. In severe cases, treatment with glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) and diuretics (Lasix) is prescribed. In case of asphyxia, specialists perform resuscitation measures - tracheal intubation or tracheotomy.

Treatment of the allergic form of laryngitis in children under 2 years of age is carried out only in a hospital. Treatment for a child usually involves the same methods as for adults using inhalations, medications and other measures. A month after the acute attack of the disease has stopped, studies are carried out: an allergy test is performed and a general immunogram is compiled.
The progression of chronic allergic laryngitis in children can subsequently become a cause for the development of bronchial asthma, so due attention should be paid to examining the child. With the right treatment tactics, the prognosis is good, symptoms disappear within 5-7 days of therapy.
Prevention

To prevent the primary development of allergic laryngitis or its relapse, it is necessary to find out which substances can cause an acute reaction in the human body and completely eliminate contact with them.
If this cannot be done, the patient should always have an antihistamine with him, the use of which will prevent the spread of the pathological process to the throat.
You should ventilate the room where the child or adult is located more often. Don't forget about air humidification.
If the humidity outside is too low, you can purchase a special device - an air humidifier, which will spray water at certain intervals (in some devices you can set the intervals between sprays yourself).
Daily wet cleaning and regular removal of dust from the surfaces of home furniture is another condition, observing which you will not be afraid of developing an allergy that can lead to such a dangerous disease as laryngitis.
General measures and folk remedies
Patients suffering from an allergic form of laryngitis are advised to follow a gentle diet with the exclusion of irritants, completely eliminate smoking and alcohol in adults, maintain silence and cleanliness in the room, maintain a temperature range of +19+25 degrees with humidity levels at 60%. A plentiful drinking regimen is recommended to moisturize the mucous membrane of the larynx - you can drink plain water, unsweetened tea, or alkaline mineral water.

Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out very carefully: essential oils, honey and other substances can provoke a new allergic reaction, so patients are advised to steam inhalation with boiled potatoes, gargling with potato and carrot juice or soda solution.
We recommend reading: What is the treatment of laryngitis?