Tylotic eczema is a skin disease that affects the hands and feet. It does not appear for one reason, but is a multifactorial disease. It is also called horny or callous, since the skin first cracks, then thickens, and dry calluses appear on it.
Without proper timely treatment, the disease can become chronic. There is a high risk that it will no longer be possible to cure it. The disease worsens and recurs in autumn and winter, and appears in people of any age, but more often in women during menopause. The pathology is accompanied by itching and burning, a decrease in a person’s nervous state and his overall quality of life.
Weeping and itchy skin on the face and hands
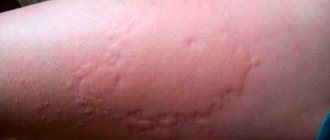
The appearance of multiple rashes on the skin in the form of blisters and bumps against the background of reddened skin may be a manifestation of true eczema.
Characteristic is the subsequent opening of the microvesicles with the release of serous fluid. The blisters are gradually replaced by shallow point erosions (ulcers). The released liquid dries, forming soft crusts. Content may be difficult to view
Constant accumulation in the area of the pathological focus leads to the fact that vesicles, ulcers, and crusts are simultaneously visible on the skin - this is the so-called polymorphism of elements. All skin rashes are accompanied by severe skin itching. Sometimes the itching is such a strong sensation of irritation that a person suffers from insomnia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wvm6x4pTtsA
Post-traumatic, varicose or microbial eczema most often appears on the legs. This is due to a higher incidence of skin injury on the legs, as well as chronic venous insufficiency; in 75% of cases identified in patients with eczema, women are women.
Eczematous rashes on the legs are most often localized in the area of varicose veins. They have a rounded shape and clear boundaries, where the skin is especially flaky. Sometimes there is a screening of several lesions along the periphery of larger and older ones, which is a characteristic sign of microbial eczema.
Quite often, microbial eczema manifests itself as many rounded lesions up to 3 centimeters in size that do not merge with each other. Due to its resemblance to a scattering of coins, this form is called coin-shaped or nummular.
Peeling skin with eczema is a sign of either recovery or chronicity of the process. Recovery is usually accompanied by the complete disappearance of skin manifestations of eczema. At the site of the lesions, skin remains that is lighter than the intact skin. This is a normal phenomenon called depigmentation, that is, a decrease in the amount of pigment. Typically, such depigmented spots disappear on their own within 3-5 weeks.
Occasionally, with true eczema, the opening of the vesicles does not occur; in this case, the lesions become quite weak, appearing only as multiple tubercles and papules. In this case, some experts talk about pruriginous eczema, distinguishing it as a type of true eczema.
Typical sites of localization of pruriginous eczema: extensor surfaces of the hands and face. Pruriginous eczema is also called dry, which is not entirely true, since isolated openings of the vesicles still occur.
Skin itching with eczema is most severe at the initial stage or during the period of additional eruptions, when there is active formation of fresh papules and vesicles. Itching also intensifies with the addition of bacterial flora, that is, a hyperemic and itchy area of skin with many rashes is a sign of either true or microbial eczema.
With varicose and post-traumatic eczema, similar symptoms appear mainly on the legs. With the professional variety of the disease, itching and hyperemia are a typical symptom. Their severity increases after repeated contact of the skin with the provoking agent. It is important that after eliminating the influence of the provoking factor, the symptoms of occupational eczema disappear on their own, even without treatment.
Redness of the skin and the appearance of purulent crusts around the edges indicate the development of microbial eczema. It appears in places where skin trauma occurs more often.
Usually, against the background of existing hyperemia with typical eczematous elements, the redness of the skin intensifies significantly, the transparent serous secretion on the surface of the lesions is replaced by a yellowish, purulent one. When the pus dries, it forms fairly rough crusts that are easily removed, exposing the skin that continues to become wet.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating microbial eczema are good as additional measures to combat this disease. Herbs and decoctions are suitable for internal use:
- A decoction of marigold flowers is prepared from 1 tablespoon of raw materials and 1 cup of boiling water. Take it after infusion 2-3 times a day.
- 1 tablespoon of sage flowers is brewed in 0.5 liters of water. The decoction is taken every 3-4 hours in small portions.
- The string and hop buds are brewed together. This decoction is very useful in healing wounds.
- 1 tablespoon of crushed elecampane root raw material per 1 cup of boiling water. Take in small portions throughout the day.
- Viburnum berries help cleanse the body of harmful substances and support the immune system.
Medicinal plants used in the form of lotions and compresses on eczema lesions can have a good effect:
- Oak bark, St. John's wort, mint and string are brewed together. This decoction is used in the form of compresses.
- Black radish should be cut into thin slices and applied to wounds.
- Cucumber mugs are used for compresses. They can be wrapped around wounds with a bandage and left overnight.
- Fish oil lotions are used in liquid form to be applied to a bandage and applied to sore areas of the skin.
Baths have a good healing effect. Add 1 tablespoon of creolin to 7 liters of water.
Soak your hands or feet in the bath for 10-15 minutes. Then you need to let the skin dry without wiping it. The procedure can be repeated for three weeks.
Basic medications for treatment
Dermatosis occurs in most cases against the background of diseases and impaired functioning of internal organs, and also accompanies skin pathologies. Among the factors that can trigger the development of nipple eczema are the following:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and liver;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- problems with the metabolic process;
- long course of treatment with antibiotics and other medications;
- regular interaction with harmful chemicals that can provoke allergic reactions;
- infectious diseases (microbial, fungal);
- parasitic diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- psychosomatic reasons.
Drug treatment is individual for each patient, but the scheme by which all specialists prescribe their course of therapy is the same for everyone. So, first of all, antihistamine drugs are prescribed. Such medications eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Common antihistamines include the following:
- "Loratadine."
- "Pipolfen."
- Zyrtec.
- "Loratin."
- "Fenistil".
Some doctors consider it necessary to deal with intoxication of the body before treating eczema itself. To remove harmful substances, the following absorbents are used:
- "Multisorb".
- "Enterosgel".
- "Entegnin."
- "Atoxil".
In case of a complicated course of the disease and serious damage to the nipples, it will be necessary to include hormonal drugs in the treatment.
Eczema on the chest can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- genetic predisposition to inflammatory diseases;
- great emotional stress, constant stress;
- chronic fatigue and overwork;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases caused by infections;
- skin injuries in the chest area;
- allergic reaction to underwear or cosmetics.
For women who are breastfeeding, nipple eczema is a common problem. The localization of inflammation is mainly observed on the nipple halo. In this regard, difficulty may arise in feeding the child and, as a result, mastopathy (breast disease) may develop.
Quite often, nipple eczema is a post-traumatic complication of lactation. Nipples come into contact with the external environment and cannot be sterile. That is why microorganisms that get on the skin can cause eczema on the nipples and alveoli.
When examining women with this diagnosis, microflora of a nonspecific nature was very often determined. Such microflora can cause infectious pathologies in tissues and organs.
- – staphylococci;
- – proteus;
- – Escherichia coli;
- – bacteroids;
- – streptococci.
– Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis);
– actinomycetes (fungi);
– candida (pathogenic fungi);
– tuberculosis bacteria (Koch bacillus).
Eczema on the nipple: other causes
In addition, eczema on the nipples can develop due to other factors that may not be the cause of skin inflammation.
– state of stress. For example, caring for a child in the first months of his life;
– low amount of glucocorticoid production. This is a hormone of the adrenal cortex;
– change in diet;
– various infectious pathologies;
– contact with strong chemicals. This includes household chemicals;
– wearing very tight or tight underwear.
During lactation in the initial period, the mammary glands are not able to produce a sufficient amount of milk. The baby needs to make significant efforts to suck the milk. As a result, the alveolar area is injured and microcracks appear. When an infectious agent interacts, nipple eczema develops.
Female patients who have any allergic diseases are more prone to developing nipple eczema.
Stressful situations can also lead to the appearance of nipple eczema. During periods of stress, the tone of the sympathetic nervous system may increase. Because of this, additional portions of histamine are released into the blood, increasing inflammatory and allergic reactions. It is also worth considering caring for a child in the first months, when nervous tension increases. Nipple eczema in this case can also develop.
– chocolate;
– citrus fruits;
– fruits and red vegetables. It could be strawberries, tomatoes, bell peppers;
– smoked products. Fish, balyk, sausage.
The first manifestation of eczema on the nipples is associated with many factors, so the disease is considered polyetiological. The main reasons include:
- nervous system failures;
- genetic predisposition;
- allergies;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- problems with the digestive organs;
- weak immunity.
Eczema on the nipples mainly appears in the first month of breastfeeding, when mother and child are just learning to understand each other. An uncomfortable position for the baby forces him to make every effort to get milk. Because of this, the nipples are injured and cracks appear. Stress or the presence of other provoking factors push the progression of eczema. Dry skin on the nipples significantly worsens the situation.

In the absence of proper treatment, the entire period of lactation becomes more complicated or even natural feeding of the child becomes impossible.
Rubbing nipples against underwear and clothing causes pain, interfering with the mother's ability to get a good night's rest, which in turn increases stress and symptoms.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are carried out based on the specifics of the disease. Eczema is the most popular dermatosis. But there are a lot of reasons for its development, and not all of them have an explanation.
The presence of a pathological process can be detected by clinical symptoms. An external examination of the patient and clarification of the medical history is enough for the doctor. The examination can be carried out in a laboratory setting. This process is lengthy and may not yield results.
First, tissue and scrapings are diagnosed under magnification. Such an analysis will make it possible to detect any changes in tissues, processes characteristic of eczema on the nipples.
A general immunogram helps to fully assess the state of immunity. Thanks to her, it is possible to select the appropriate therapy. In addition to this diagnosis, auxiliary diagnostics are prescribed.
Instrumental diagnostics
This type of examination is multifaceted and consists of several procedures. First, the patient must submit a culture, which is taken from the damaged areas. Thanks to such diagnostics, it is possible to check susceptibility to antibacterial agents, as well as to inflammatory agents.
On this topic
- Eczema
All about tylotic eczema
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 11, 2020
This makes it possible to choose the appropriate therapy. Coprogram involves the study of feces. Such diagnostics provide a complete picture of the patient’s well-being and hidden difficulties in the body.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity helps detect changes in organs, which can trigger the formation of dermatosis. Allergic skin reactions are carried out in order to identify the allergen.
Differential diagnosis
First, a scraping is performed. This will make it possible to study damaged tissues and determine the nature of inflammatory processes.
A general blood test shows the severity of inflammation. A biochemical blood test makes it possible to detect disorders that are associated with metabolism.
It is necessary to determine the content of immunoglobulins; their significant increase indicates the nature of the disease. If worm eggs are found in the feces, then this will be the main provoking factor of eczema.
Correct diagnosis facilitates the selection of appropriate therapy.
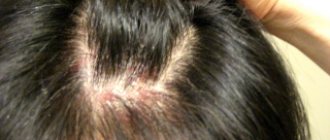
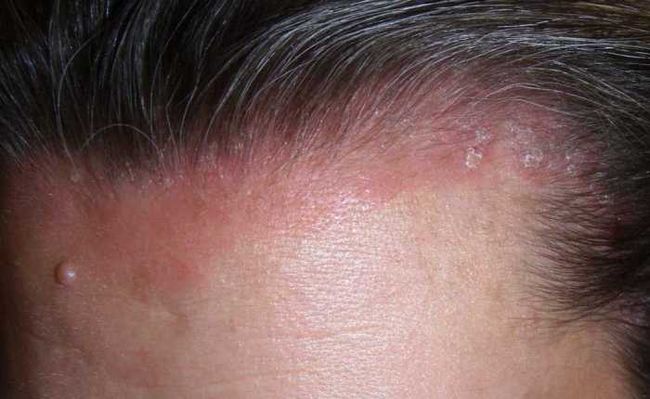
Scaly layer at the border of the scalp
The so-called seborrheic eczema often appears in the scalp area. At the initial stage, it looks like single yellowish nodules. The number of these nodules is rapidly increasing, they merge into spots, on the surface of which whitish scales form.
The merging of individual foci of seborrheic eczema often leads to the formation of a “seborrheic crown” at the border of the hair - a continuous scaly ring, along the edge of which areas of hyperemic skin are visible. In the absence of treatment, in advanced cases, this form of eczema spreads from the sides of the head to the folds behind the ears, and from the back to the neck.
Seborrheic eczema is very difficult to distinguish from true seborrhea, and some experts consider seborrheic eczema only as a type of seborrhea with some nuances in the course of the pathological process.
Forecast
The prognosis for nipple eczema depends on many factors. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the patient’s body condition. This applies to its nervous system and immune functions of the body. The duration of the disease, the frequency of relapses, and the patient’s working conditions are important.
Exacerbation of the pathological process has a more favorable prognosis. It is difficult to cure idiopathic and priuriginous forms of pathological processes. And yet the likelihood of healing is high.
The prognosis will worsen significantly when the pathogenesis develops in children and the elderly. This appears against the background of failures of protective functions in the body. Mostly, the prognosis completely depends on how soon the patient went to the doctors.
His well-being and prescribed therapy are of no small importance. It is impossible to eliminate the chronic form of eczema on the nipples; exacerbations will occur frequently. The pathogenesis continues for years, and the prognosis will be unfavorable.
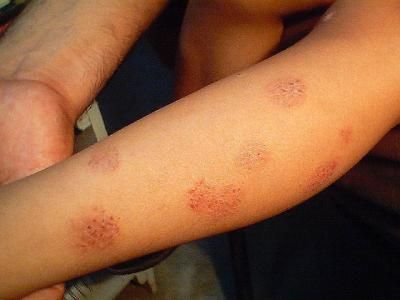
Round rashes on the skin of the hands
Itchy and itchy rashes on the upper extremities can be symptoms of a wide range of diseases. One of them is eczema on the hands, in 80% of cases this localization is characteristic of true eczema, another 15% is due to occupational eczema and the remaining 5% to other varieties.
Round shapes are characteristic of eczema at the initial stage; as the disease progresses, they lose their regular shape. The roundness of the outline is also characteristic of mycotic eczema, in which the primary lesion has large scalloped edges.
The skin around wounds on the legs and arms festers and itches
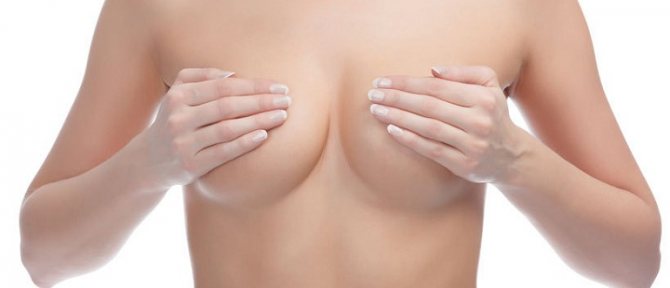
Mostly in women, extremely rarely in men, eczema can affect the skin around the nipple. In women, this process is quite often associated with injury to the nipples due to improper breastfeeding. In men, nipple eczema can develop against the background of scabies.
Typical manifestations are the appearance of crimson lesions near the nipple, often covered with crusts or large scales. Wetting is noted, and quite deep cracks often appear. When cracks appear, in addition to itching, severe pain also occurs.
The addition of a bacterial infection often leads to the fact that nipple eczema is microbial in nature. Difficulties in treating eczema of this localization in women are associated with the process of lactation, against the background of which inflammation is excessive.
Disease in pregnant and lactating women
Many breastfeeding women are susceptible to eczema. The fact is that during breastfeeding, the baby can injure the nipple, which can cause the development of the disease. The maculopapular rash, which is characteristic of the early stages, develops into blisters and small erosions filled with liquid after a couple of days. Then the affected areas are covered with crusty scales of a light brown shade.
Pregnant women can also experience this disease quite often. Low immunity and a weakened body lead to easy penetration of various infectious diseases. If a woman already has chronic pathologies of the skin, there is a risk of developing nipple eczema. If a girl suffers from chronic dermatosis, then an aggravation in the form of dermatological problems with the nipples is quite understandable. Treatment of the disease in this situation is very limited, since it is extremely undesirable for active drugs to enter the body.
Preventive measures
Prevention of this disease in most cases is aimed at preventing relapses. First of all, the patient must change his diet.
A special diet prescribed by a doctor minimizes or completely eliminates the consumption of foods that are dangerous allergens. Special attention should be paid to personal hygiene.
Due to the increased secretion of sebum, it is necessary to take a shower with warm water several times a day. Hygienic products must be designed strictly for sensitive skin.
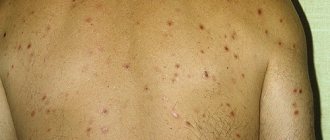
Skin thickening on the arms and body
The symmetry of the lesion is more characteristic of true eczema. Despite the fact that the disease most often manifests itself with the appearance of a rash on the extremities, in some cases the lesions initially appear on the body.
In the initial stages, these lesions have the typical appearance of “boiling skin.” With a long-term recurrent (repeating) course, weeping lesions are replaced by areas of thickened skin with lichenification (increased skin pattern). With long-standing eczema, the lesions during the healing stage are covered with flaky skin, their weeping is significantly reduced - in this case they speak of dry eczema.
In the initial stages of any eczema, the skin is swollen and hyperemic, but in consistency it differs little from healthy skin. The appearance of foci of compaction may indicate transformation of the disease into a chronic form.
This process is characterized by a decrease in the process of weeping and the appearance of large areas of thickened and flaky skin. During the healing process, all manifestations regress - the foci of eczema disappear completely.
Forms
When pathological processes are mild, pale pink spots will remain on the epidermis. Severe cases are characterized by a dark red color.
The skin is covered with rough crusts, and after final removal the dermis will remain rough and rough. Sometimes peeling, pigmentation may develop, and the color of the skin may change.
Dermatosis disrupts the integrity of the skin. Therefore, viruses, microorganisms and bacteria penetrate through it. The development of infectious diseases is possible.
On this topic
- Eczema
How to recognize and quickly treat plaque eczema
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 24, 2020
This will significantly complicate the progression of eczema on the nipples. Pathological processes can affect the central nervous system, causing disorders in its functioning. As a result, the person develops insomnia.
A severe form of the disease can become chronic. This worsens the patient’s quality of life for a long time. Getting rid of the disease is extremely difficult. New wounds form on the affected areas.
Over time, the skin may become completely affected and become very sensitive. In view of this, it is easier to prevent eczema on the nipples than to later counteract its adverse consequences.
Possible complications
Usually, it is not difficult to get rid of a disease that has a mild course, but even after effective and efficient treatment, patients can often still have spots on their chest. After complications, serious redness remains “as a souvenir.” However, this is far from the most unpleasant thing that pathology can leave behind. A more serious consequence of eczema is the development of a secondary bacterial infection.
Of particular danger is herpetic breast eczema, which develops together with the human herpes simplex virus that has entered or is activated in the body. Accompanying eczema, the infection carries a great risk for pregnant women and their babies. The difficulty is that recognizing the presence of herpes in the body is very difficult, since viral vesicular rashes are almost no different from the symptoms of eczema. The only sign of a secondary infection may be complicated symptoms such as fever.
The situation becomes significantly more complicated when a herpes, staphylococcal or streptococcal infection is added to the eczematous processes. Inflammation and rashes spread more widely over the skin, the resulting crusts acquire a yellow tint, and body temperature rises.
The disease itself is difficult to treat, and the emergence of complications makes this process even more difficult, because now you have to not only relieve the symptoms of eczema, but also get rid of the infection.
Constant itching with nipple eczema is typical during the acute phase of the disease and during the period of exacerbation. The disease can affect the emotional state of the patient. A woman may become irritable and have a bad mood. In addition, tearfulness is observed. Since the itching is worse at night, nipple eczema can be affected by long-term chronic sleep deprivation.
In some cases, nipple eczema can be complicated by a secondary bacterial infection or mastitis. Increased body temperature, weakness, chills, high fatigue, decreased appetite. Rare consequences may include pale spots appearing in the areola area.
Bibliography
- Current problems of dermatovenerology [Text]: materials of the conference. / State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education SamSMU. - Samara: SamSMU, 2007. - 132 p.
- Baumann, L. Cosmetic dermatology: principles and practice [Text] = Cosmetic dermatology: principles and practice / L. Baumann; lane from English; edited by N. N. Potekaeva. - Moscow: Medpress-inform, 2012. - 688 p.: ill.
- Skin diseases [Text]: atlas / ed. N. V. Kungurova; Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Federal State Budgetary Institution Ural. Research Institute of Dermatovenereology and Immunopathology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. - Ekaterinburg: Publishing house "VIP-Ural", 2014. - 176 p.: ill.
- Macharadze, D. Sh. Atopic dermatitis in children [Text] / D. Sh. Macharadze. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 392 p.: ill. - (Current medical issues).
- Morgan, M. B. Atlas of deadly skin diseases [Text] = Deadly dermatologic diseases / M. B. Morgan, B. R. Smoller, S. K. Somach; lane from English; edited by A.V. Molochkova. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2010. - 304 p.: ill.
- White, G. Atlas of dermatology [Text] = Color atlas of dermatology / G. White; lane from English N. G. Kochergina; edited by O. L. Ivanova, N. G. Kochergina. - Moscow: GEOTARMEDIA, 2009. - 384 p.: ill.
- Dermatology [Text] = Dermatology. Vol. 1./ed. by Jean L. Bolonia; associate and artwork ed. JV Schaffer; section ed. JP Callen. — 2nd ed. - London: Mosby Elsevier, 2008. - ill.
- Fitzpatrick`s dermatology in general medicine [Text] = Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. Vol. 2. / ed.: K. Wolff. – 7th ed. – N.York [etc.]: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2008. – ill.
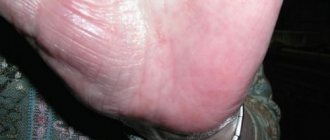
Callus-like rashes on the palms
Eczema can affect not only the soft skin of the body; its foci also appear on the rough skin of the palms and feet. Due to the peculiarities of the skin structure in these places, eczematous lesions take the form of small whitish tubercles.
As the disease progresses, the bumps come together to form blisters that may burst. As a result of the opening, quite extensive ulcers are formed on the palms and soles, constantly secreting serous fluid. The described phenomena are called dyshidrotic eczema.
The appearance of callus-like rashes on the palmar surfaces of the hands in places where the appearance of calluses is uncharacteristic is a sign of tylotic eczema. In this case, hyperemia due to the thickness of the stratum corneum is not very noticeable, but vesicles continue to appear, and they may not open due to the thickness of the skin.
Recommendations for effective treatment of eczema
- If the general condition of the nipples is extremely severe and painful, it is better for the nursing mother to stop breastfeeding.
- If the disease is chronic, it is better to switch to a special hypoallergenic menu, consisting mainly of plant foods and foods high in protein.
- When purchasing underwear, pay special attention to the materials from which they are made. So, it is better to choose a bra from natural, cotton fabrics; avoid wool, flannel and synthetic products.
- Be sure to change your underwear every day.
- Body care products should consist of hypoallergenic components.
- During an exacerbation of the disease, it is advisable to perform water procedures less frequently.
Prevention
There are several main preventive measures regarding pathological processes of the skin. First of all, you should avoid working in hazardous industries. This mainly applies to those who have a hereditary predisposition to eczema. It is necessary to limit contact with allergenic substances and irritants.
You need to follow the rules of hygiene. A balanced diet and an active lifestyle will make it possible to strengthen the body. Stressful situations and nervous tension should be excluded. It is optimal to choose clothes and underwear made from natural materials. Tight shoes, gloves and should also be excluded.
It is necessary to timely treat diseases, in particular those that can provoke the formation of eczema on the nipples. It is necessary to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco. A woman should lead a healthy lifestyle after childbirth. Following preventive measures will make it possible to avoid such an unpleasant disease.
Where to start treatment?
Getting rid of spots on the chest and other symptoms of eczema takes quite a lot of time, as well as effort and patience, since it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Sometimes specialists are in no hurry with drug treatment in the hope that the body will be able to overcome dermatological pathology on its own. If after some time no positive results are observed, the doctor prescribes a special course of treatment.
Naturally, you will not be able to get rid of the pathology on your own if it is fungal or bacterial in nature. In any case, before curing eczema, you must first change your lifestyle and review your diet. It is worth excluding from the daily menu those foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
Multiple bumps on the face and hands without weeping or crusting
The appearance of vesicles in the axillary region with a hair piercing them in the center is a sign of sycosis - a specific lesion of the hair follicles. The spread of this process beyond the abundant hair growth is called sycosiform eczema.
For sycosis, itching is an atypical symptom, so its appearance indicates that the process has transformed into eczema. In addition to the armpits, sycosiform eczema can appear on the pubis, upper lip and chin.
Diet
- Those who are interested in how to cure eczema should include more dairy and fermented milk products in their menu.
- It is recommended to eat plenty of vegetables and fruits to supply the body with missing vitamins and microelements.
- It is important to eat protein products of animal origin, and their fat content should be within achievable limits. These include chicken, rabbit, turkey and beef.
- It is recommended to eat river or sea fish at least twice a week.
- Be sure to include whole grain cereals in your menu, such as oatmeal, buckwheat, and brown rice.
Also during treatment you should avoid spicy, smoked, salty and fried foods. Eliminate sweet foods, baked goods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, and coffee from your menu. Very often, in addition to drug therapy, they resort to other types of skin treatment. For example, after consulting with your doctor, you can try treating eczema with folk remedies at home. A comprehensive and comprehensive fight against pathology should bear fruit.
There is no way to determine how quickly the disease will subside. This mainly depends on the general well-being and strength of the body, the duration of the disease and the frequency of relapses (if we talk about chronic pathology). The disease is especially complex in older people. The sooner the patient seeks medical help, the easier and faster the course of treatment will be.
Diet or proper nutrition
Compliance with certain dietary rules helps alleviate the course of the disease and avoid its exacerbations. Doctors recommend reducing, or better yet completely eliminating, potato dishes, sweets, fruits rich in vitamin C, and alcoholic drinks.
Especially harmful for eczematous rashes is eating smoked, fried and fatty foods, as well as those containing preservatives, dyes and large amounts of spices. Vegetables, fruits, cereals, lean meats, any fish, and low-fat dairy products are allowed for consumption.