Allergic blepharitis is an acute bilateral eye disease. This pathology is considered one of the most common. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can become chronic, as well as a secondary infection or irreversible cosmetic defect. To prevent this from happening, you need to know how the pathology manifests itself and what to do when a violation is detected.
What is allergic blepharitis
Allergic blepharitis develops in patients against the background of increased sensitivity of the skin located in the eye area to certain allergic agents.
Pathology in 95% of cases affects both eyelids. However, the use of new cosmetics can lead to the development of a unilateral form of the disease, when pathological processes affect only the tissues of one eye.
Allergic blepharitis manifests itself with increased sensitivity of the skin located in the eye area, as well as with hypersensitivity of the eyelids, which react to the contact of pathogens on their surface.
Regardless of the cause of allergic blepharitis, the symptoms of the disease are almost always the same, but depending on the severity of the disease, they can be expressed clearly or less noticeably.
Important! Unlike other forms of blepharitis, this type of disease is often recurrent, and under certain circumstances can become chronic.
This usually occurs as a result of either ineffective treatment or the development of additional ailments and diseases that negatively affect the immune system.
The medical term blepharitis refers to an inflammatory reaction affecting the lower and upper eyelids. It is characterized by erythematous-exudative changes; the irritant is most often allergens acting at the local level.
It is possible that symptoms of pathology may appear in response to the introduction of allergens into the body along with food and medicines.
Consequences, prognosis
With correct and timely therapy, the prognosis for vision preservation is quite favorable. Otherwise, the disease can become chronic, protracted and lead to new pathologies. The most common complications are:
- barley;
- chalazion;
- increased lacrimation;
- "dry eye";
- corneal damage;
- deformation of the edges of the eyelids;
- trichiasis;
- chronic blepharoconjunctivitis;
- decreased visual acuity.
Causes of blepharitis
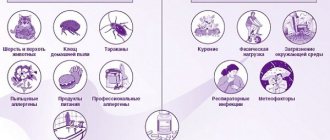
The main factor influencing the development of the disease is an allergen that enters the body and provokes a negative reaction. There are people who have a genetic predisposition to allergies. The main factors are:
- Use of various medications.
- In the apartment or house where the patient lives, there are flowers whose pollen causes allergies.
- Fur of animals, dogs or cats.
- Household chemicals.
- The use of cosmetics intended for eyelid skin care, the components of which can cause an allergic reaction.
- There is a lot of dust in the apartment, as a result of which mites appear.
These reasons are the main causes of this disease.
Allergic blepharitis is based on the patient’s increased sensitivity to certain allergens, which, when they enter the body, trigger a chain of pathological reactions.
Depending on the type of allergen, the disease is often seasonal. In such cases, exacerbations of blepharitis will develop during the flowering period of plants.
This disease can be caused by a number of reasons.
Thus, the edges of a person’s eyelids can become infected with demodex mites. Although in 80% of people these mites live in the sebaceous glands, in hair follicles and on the surface of the skin, but with a general decrease in the body's resistance (overwork, hypothermia, a consequence of past diseases), mites can become more active.
At the same time, they begin to multiply intensively and, getting on the surface of the eyelashes and the skin of the eyelids, can provoke the appearance of demodectic blefairt.
The main cause of allergic blepharitis is always an allergen, which can be of different origins, but always causes similar symptoms.
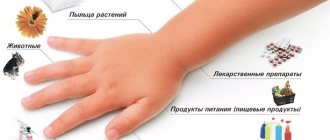
The following factors can contribute to the development of allergic blepharitis:
- A large number of plants and flowers, the pollen and smell of which can lead to irritation and allergies.
- The use of medications containing components that can cause an allergic reaction in a person.
- Pet hair.
- Use of household chemicals.
- Large amount of dust.
- Constant use of cosmetics.
Allergic blepharitis rarely develops as an independent disease.
It generally either accompanies other allergic diseases, or itself becomes a provoking factor for the development of other side ailments.
The main cause of the disease is an allergenic irritant for the body, in response to which the body develops a sensitization reaction. This leads to the destruction of the mast cell membrane and the release of inflammatory mediators.
Features of the disease
Blepharitis is a chronic, bilateral inflammation of the ciliary margin of the eyelids. Eyelashes begin to fall out, their growth is impaired, the patient feels photophobia, eye fatigue after minor exertion.
The disease is quite dangerous, complications are possible in the form of:
- chalazion;
- conjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- decreased vision.
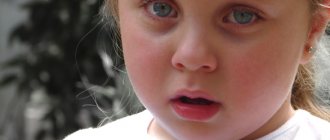
According to statistics, about 30% of the population suffers from allergic blepharitis. Most often, the disease is registered in children and middle-aged people (over 40 years old).
In children, the disease occurs frequently, which is due to the specifics of the growing organism and the still unformed immune system. Children at risk in this age category include:
- with congenital visual impairments, such as: myopia, astigmatism, strabismus, nasal infections and sinusitis;
- with helminthic infestations in the gastrointestinal tract;
- with allergic reactions: diathesis or atopic dermatitis, milk intolerance;
- with pathological conditions associated with malabsorption in the intestines, which is caused by the presence of worms.
The high probability of the disease manifesting itself in middle age is explained by the fact that during this period of life a person begins to experience disruptions in the body’s protective functions, caused by the presence of certain chronic ailments, as well as age-related changes.
The group with a predisposition to allergic blepharitis includes patients with various pathologies. The main ones:
- diabetes;
- chronic dental ailments: aphthosis, caries, pulpitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, enterocolitis, helminthiases;
- skin diseases and skin manifestations of pathologies associated with internal organs;
- HIV infection (primary immunodeficiency);
- secondary immunodeficiency - this includes patients who have had infections, surgical interventions, and also patients after anticancer therapy;
- harmful chemical exposure associated with a person’s profession;
- individuals with a tendency to allergies.
The disease is often registered in patients with such problems of the visual system as:
- excessive visual stress;
- chronic conjunctivitis;
- uncorrected refractive errors.
Types of blepharitis
Depending on the location, ophthalmologists distinguish the following forms of allergic blepharitis:
- Anterior edge form. The pathological process affects the tissue of the eyelid along the border of eyelash growth;
- Posterior marginal form. The disease is characterized by damage to the meibomian glands. In the absence of timely therapy, it can lead to the spread of the pathological process to the tissue of the cornea and the conjunctival membrane of the eye;
- Isolated (angular) form. The pathology is extremely rare and only affects the corners of the eyes.
It is also customary to distinguish acute and chronic forms of allergic blepharitis. In the first case, the disease develops suddenly, the pathological process immediately affects the eyelids of both eyes. Symptoms may be minor or cause severe discomfort, disrupting the patient’s ability to work and sleep.
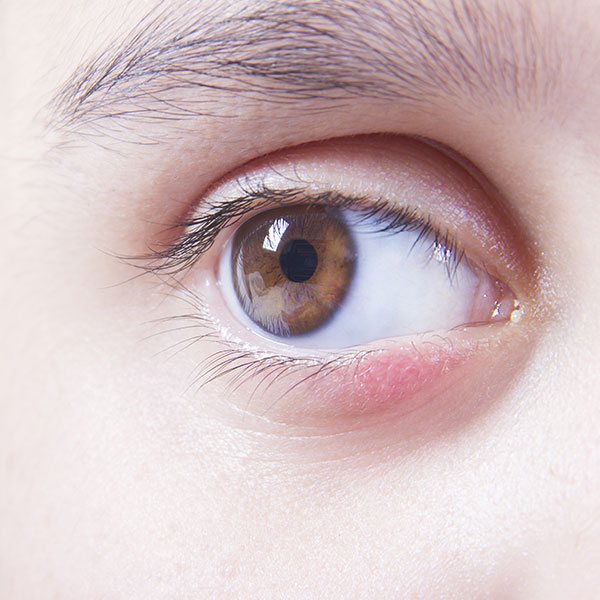
Allergic blepharitis spreads to 2 eyes at once, but inflammation can take different forms. There are 3 main varieties:
- Front edge. Violation occurs only at the border where the eyelashes grow.
- Isolated. Symptoms appear at the corners of the eyes, the pathology is often called angular.
- Posterior edge. The meibomian glands are most affected by this type of blepharitis. If there is an allergy, the process extends to the cornea and conjunctiva.
Most often, the allergic form of eyelid blepharitis is seasonal. That is, all manifestations of the disease begin to worsen during flowering of plants.
Allergic blepharitis affects both eyelids, but a one-sided form of the disease also occurs, for example, when using a new cosmetic product that causes allergies on only one side.
Depending on the anatomical structure, there are:
- Anterior marginal blepharitis, which affects the eyelid along the border of the eyelashes.
- Posterior marginal (occurs with characteristic damage to the meibomian glands, which can cause the pathological process to transfer to the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye).
- Less common is isolated blepharitis of the corners of the eyes (the so-called angular form of the disease).
The disease can be seasonal with constant exacerbations during the bloom of plant allergens or appear only once in a lifetime with individual sensitivity to eyelid skin care products.
Depending on the main localization of allergic manifestations, blepharitis is divided into three:
- ANGULAR OR OTHERWISE ISOLATED. All symptoms of the disease affect the eyelids only in the area of the corners of the eyes;
- FRONT EDGE. The tissues of the eyelids from the outside are involved in the inflammatory process;
- POSTER MARGINAL. The affected area includes the thickness of the eyelid, in which the eyelash growth area is located. It is considered the most severe form of an allergic reaction.
Blepharitis is a fairly large group of eye diseases that affect the eyelids, namely their edges. Inflammation causes the eyelid to swell. The symptoms are extremely unpleasant and interfere with normal life. Inflammation is always serious, so treatment must be immediate and, what is also important, effective and competent.
Clinical picture
Unlike other types of diseases, allergic blepharitis begins suddenly, which is associated with the negative impact of allergens on the mucous membrane of the eyes. Most often, the disease affects both eyelids at once, but in rare cases, unilateral forms of pathology also occur. The external manifestations of the disease largely depend on the location of the inflammation. In this regard, the following types of allergic blepharitis are distinguished:
- angular – inflammation is localized mainly in the corners of the eyes;
- posterior marginal - the inflammatory process begins in the thickness of the eyelid in the region of the ciliary zone;
- anterior marginal - foci of inflammation arise on the outside of the eyelids.
In case of exacerbation of the disease, the following clinical picture is often observed:
- hyperemia of inflamed skin;
- itching and burning in the eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- circles under the eyes;
- photophobia;
- eyelash loss.
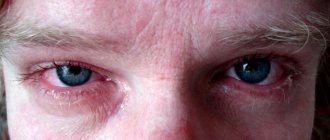
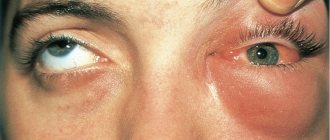
As can be seen in the photo, allergic blepharitis can be accompanied by telangiectasia, i.e. expansion of blood capillaries in the sclera of the eye and on the eyelids. As a result, vascular networks appear on the mucosa. Dry eye syndrome can also signal the development of pathology. This is due to inflammation of the tear ducts and insufficient hydration of the eye mucosa.
Allergic blepharitis in children
If a child becomes ill with a similar illness, the doctor prescribes the following preventive actions:
- Avoiding contact with the allergen.
- Washing the eyelids with water and soap.
- Using eye cream.
- Application of a vitamin-mineral complex.
To prevent children from getting sick, their immune system must be normal, otherwise they can easily catch this disease.
Allergic blepharitis is also possible in young children. The disease is treated according to the same principles as in an adult, but for small patients, medication dosages are selected taking into account their age.
It is also necessary to correctly select systemic and local medications, since some of them are contraindicated for use before the child reaches a certain age.
Caution should be exercised when using corticosteroids. For children they are prescribed for up to 7 days. It is important to observe the frequency of instillation of drops and application of glucocorticosteroid ointments. When acute symptoms decrease, steroids are discontinued and switched to safer drugs.
A sick child needs to boost his immunity. This is achieved by taking vitamin complexes, rational nutrition, and hardening. If necessary, immunomodulatory agents are prescribed.
Prevention
When the doctor tells you how to treat blepharitis, you can also ask him about prevention methods. The first thing you should do is follow basic hygiene rules: do not wipe your face with someone else's towel, wipe your eyes with a handkerchief, or rub your eyelids with dirty hands.
If one of the family members has contracted blepharitis, he should have personal means of care: a towel should be stored separately from others, a pillow should be intended only for the patient. If the patient is conscious, infection of other family members can be prevented.
Signs
Allergic blepharitis has general and specific manifestations. First, we will look at the symptoms that are characteristic only of this form of the disease.
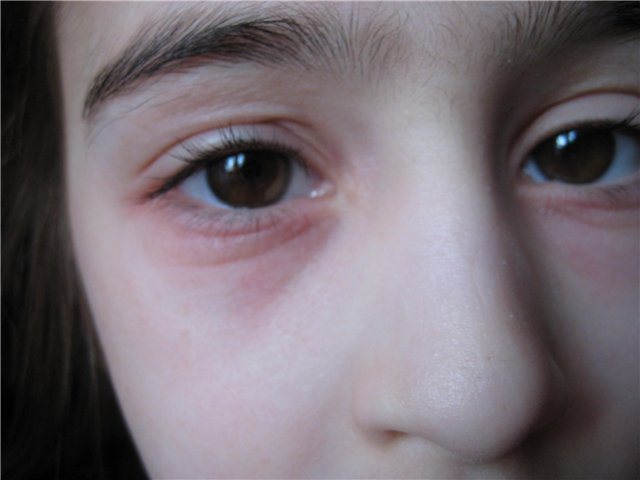
All patients report pronounced inflammation of the eyelid. Severe swelling and itching cause a lot of discomfort, which provokes nervous tension. If the patient scratches the eyelid, the condition will only worsen. In addition, high sensitivity to light, the presence of mucous discharge and constant tearing of the eyes are diagnosed.
This disease, unlike all other forms of pathology, is accompanied by intense peeling of the eyelids. Most of the scales are observed near the eyelashes. In addition, the eyelids may darken; ophthalmologists call this phenomenon “allergic bruising.” Most often, this symptom occurs in young patients. You can see in the photo the main symptoms of this disorder.
If blepharitis does not respond to treatment for a long time, the infectious-allergic effect intensifies and visual acuity begins to decrease.
Common symptoms of the disease include irritation, burning sensation, and the sensation of a foreign object. People who spend a lot of time near a computer or TV may experience dry mucous membranes.
The complicated form of the disease is accompanied by high fever, general weakness and clumping of the cilia. If a person wears lenses, then during inflammation they will cause severe discomfort.
Disease prevention
To prevent allergic blepharitis (ICD code 10 H01.1), the following rules must be followed:

Symptoms
Like any disease, allergic blepharitis has certain symptoms, namely the following:
- Swelling of the eyelids. They are characterized by swelling or severe swelling. With this disease, the eyeball becomes invisible.
- Burning and severe itching in the organs of vision. With such symptoms, the patient begins to scratch his eyes, and as a result of these actions, some kind of infection may develop.
- Tearing and fear of light. With this disease, the cornea of the eye becomes irritated, severe lacrimation occurs, and a fear of light appears. The patient experiences a feeling of discomfort when looking at a bright light.
- Eyelashes fall out. This only occurs in cases of severe allergic blepharitis.
If at least one sign of the disease appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In the process of numerous studies and observations, it was found that symptoms of blepharitis in patients are observed against the background of various diseases:
- chronic and inflammatory;
- diseases of a hormonal and psychological nature;
- against the background of cardiac pathologies.
How to make a diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, the patient should consult an ophthalmologist. The specialist will conduct a visual examination and study the anamnesis of the pathological condition (patient complaints, specific symptoms).
Diagnostic tests for adults include:
- bacteriological scrapings that are taken from eyelashes;
- tests to identify the irritant substance;
- blood tests;
- biomicroscopic eye examination.
An ophthalmologist conducts a thorough examination of the eyelid mucosa using a special (slit) lamp to prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnostic principles
To conduct a differential diagnosis and accurately determine what type of blepharitis the patient has, an eye biomicroscopy procedure is performed. Thanks to this method, the possibility of making an erroneous diagnosis is eliminated, and the course of preventive measures will be prescribed correctly. To relieve symptoms and treat allergic blepharitis, the following drugs are used:
- Antihistamines: Opatanol, Spersalerg, Suprastin, Zyrtec.
- Glucocorticosteroid agents: Cortisone, Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone.
- Antibacterial ointments containing dexamethasone and gentamicin.
- Decongestants: Metrogyl, Visine, Cetirizine.
All medications, as well as their dosage, should be prescribed only by an ophthalmologist. If the patient self-medicates such a serious illness, his condition may worsen and this will lead to complications.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the clinical picture.
The diagnosis of blepharitis is made by an ophthalmologist after biomicroscopy (examination of the patient at a slit lamp). Chronic blepharitis, which does not respond to traditional methods of treatment, necessarily requires a biopsy. This procedure is necessary to exclude eyelid tumors, the presence of which can stimulate the disease.
The symptoms and treatment of allergic blepharitis can only be determined by an ophthalmologist. If there is such a form of the disease, the patient will first need to consult with an allergist and identify what the body gave such a reaction to.
To confirm the diagnosis, you need to collect anamnesis and conduct research. If the patient’s inflammation has become chronic, then a biopsy must be performed. This procedure will eliminate eyelid swelling, which can also cause problems.
In addition, the following studies are being conducted:
- eyelash examination under a microscope;
- bacteriological culture;
- scraping;
- biomicroscopy.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the patient’s complaints, medical history and characteristic clinical picture. For differential diagnosis with other forms of blepharitis, eyelash examination (to identify mites), eye biomicroscopy and bacteriological culture from the conjunctiva may be required.
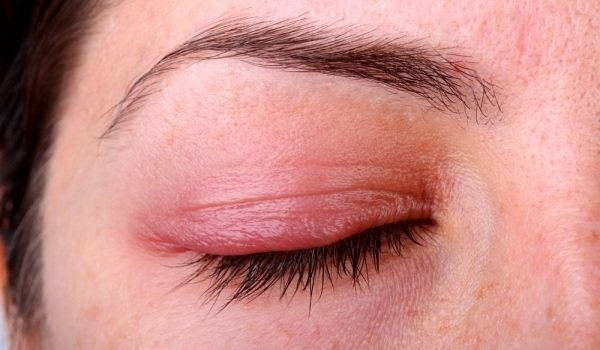
The main aspect of treating the disease is eliminating or maximizing contact with the allergen. Often, this measure alone helps minimize painful symptoms and promote recovery.
Drug treatment for allergic blepharitis includes:
- Antihistamines (Zodak, Tavegil, etc.).
- Antiallergic eye drops (allergodil, lecrolin, etc.).
- Glucocorticosteroid ointments for the eyes (hydrocortisone ointment, etc.).
- Antibacterial drops for the development of conjunctivitis (Normax, Tobrex, etc.).
- Severe forms of allergic blepharitis in combination with other allergic reactions may require the administration of systemic hormones.
Medicines and dosages are prescribed by an ophthalmologist, taking into account the patient’s condition and concomitant pathology.
For endogenous causes of allergy development, such as helminthic infestation, gastritis, diabetes mellitus and other conditions, adequate treatment with appropriate medications is necessary.
After the acute manifestations of blepharitis subside, treatment can be supplemented with a course of physiotherapeutic procedures to quickly resolve the inflammatory process (UHF, electrophoresis, darsonval, etc.).
In addition to the use of medications, you should adhere to general recommendations for eyelid skin care during allergies:
- Protect your eyes from dust, pollen, and fur.
- During seasonal flowering, try not to go outside and regularly do wet cleaning at home.
- Use vacuum cleaners with HEPA filters.
- Avoid bright light and wear sunglasses.
- Do not use mascara, eye shadow and other cosmetics and eye care products.
- Stick to a hypoallergenic diet.
- Wash your eyes with warm water and wipe with chamomile infusion.
- Maintain proper sleep and rest.
- Do not use contact lenses during exacerbation of pathology.
Treatment of the disease is conservative and requires timely and persistent therapy, this is the only way to avoid unpleasant complications (deformation of the eyelids, blurred vision, chalazion).
If the eyelids are inflamed, the patient should consult an ophthalmologist; if necessary, the doctor will refer the patient to a consultation with an allergist.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of complaints, external signs and diagnostic procedures, among which the following are of primary importance when allergic blepharitis is suspected:
- Bacteriological culture of scrapings from the conjunctiva and eyelashes;
- Biomicroscopy is an examination of the anterior area of the eye using a slit lamp. Allergies are indicated by swelling, hyperemia, and formation of skin folds;
- Skin tests to identify the causative allergen;
- Complete blood count and immunoglobulin E test.
Evaluating the results of all studies allows the doctor to accurately determine the type of blepharitis, which is necessary for selecting the correct therapy.
READ ON THE TOPIC: How else does allergies manifest themselves on the eyelids.
Only an ophthalmologist can reliably establish a diagnosis after conducting a thorough comprehensive examination.
During the examination, the doctor will check the acuity of visual functions and perform a biomicroscopic examination of the eyes, which helps to objectively assess the condition of the tear film, conjunctiva, eyelid margins, and cornea.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a swab is taken from the surface of the conjunctiva and bacteriological culture is carried out in order to detect a specific pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Useful tips
People prone to allergic reactions need to be careful when coming into contact with any irritants. The eyes are the organ that may be the first to become inflamed. You need to follow some rules to prevent aggravation of allergies:
- protect the organs of vision from allergens;
- wear sunglasses in summer;
- monitor the humidity level in the house;
- get rid of dust accumulation;
- make lotions with chamomile or calendula to prevent inflammation;
- use hypoallergenic eye cosmetics;
- strengthen immunity;
- Healthy food.
Today, allergic blepharitis is becoming increasingly common among different age groups. This is due to the increasing appearance around us of products and substances that tend to cause allergies. When any substances come into contact with your eyes, you need to make sure that they are safe and will not cause inflammation.
Below is a video about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for allergic blepharitis:
Treatment
Treatment methods for allergic blepharitis that exist in traditional medicine are also very effective. One of the most popular is calendula tincture with chamomile or thyme. It can rid the body of infection that helps the disease develop.
If the inflammatory processes are caused by a tick, then apply foam from laundry soap to the affected area, then wash the eyes and lubricate the surface of the eyelids with Vaseline. Aloe and red clover juice also helps a lot in the treatment of allergic blepharitis.
Effective remedies for tearing are decoctions of cornflower and eyebright flowers. They are dripped immediately before going to bed and in the morning after getting up. This folk method has proven itself well.
Often, when treating allergic blepharitis, specialists use an integrated approach, which consists of prescribing medications and physical therapy. This allows you to significantly shorten recovery time and reduce the risk of exacerbations.
Physiotherapeutic methods have a restorative, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect on the eye mucosa. Therapy is not recommended during the acute phase of the disease, since the procedures can only worsen the patient’s condition.
However, after reducing the severity of symptoms, physiotherapy will help not only eliminate inflammatory processes, but also refractive errors.
As part of the treatment of allergic blepharitis, the following health procedures are used:
- Electrophoresis. Allows you to eliminate foci of inflammation, increases local immunity;
- Darsonvalization. Current pulses eliminate inflammatory processes, reduce the intensity of eyelash loss;
- UHF. The procedure improves blood microcirculation and accelerates recovery processes;
- UV therapy. The method leads to the destruction of allergens, bacterial agents, toxins, and increases the intensity of tissue restoration.
When choosing physiotherapeutic techniques, the specialist must take into account the patient’s age, symptoms of the disease, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Scientists have made great strides in developing methods for treating blepharitis of various etiologies. At the moment, a number of physiotherapeutic procedures have been developed and effective medications have been created.
Treatment for this disease is usually quite lengthy. Improvement in the condition occurs slowly, since effective treatment requires elimination of the very cause that caused the disease.
Treatment is approached in a comprehensive manner and, in addition to correcting refractive errors, consultations are carried out (if necessary) with an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, dermatologist and allergist, and unfavorable exogenous and endogenous factors are also eliminated.
Like other types of allergies, blepharitis is treated by avoiding contact with the irritating allergen. To do this, a thorough diagnosis is carried out to identify the allergen. The following studies are prescribed:
- blood test for immunoglobulin;
- dermal cell allergy tests;
- biomicroscopy of the eye;
- special examination of eyelashes;
- taking a smear;
- taking a scraping;
- biopsy.
When the causative agent of the allergy is found, it will be necessary to create a treatment program that aims to reduce the body's sensitivity to allergens.
Treatment with medications
| glucocorticosteroid ointments | hydrocortisone ointment |
| antiallergic drops | allergodil, lecrolin, etc. |
| antihistamines | tavegil, zodak, etc. |
| in case of conjunctivitis - antibacterial drops | Tobrex, Normax, etc. |
| in case of severe form of leakage | systemic hormones |
The type of medications, as well as their dosage, should be prescribed by an allergist and ophthalmologist. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the general health of the patient, the type of allergen, the possibility of developing associated abnormalities and other nuances. Self-treatment is strictly not recommended!

After completing a course of medication, physical therapy may be prescribed. Use one of four methods:
- Electrophoresis is a classic technique that destroys pathogens that cause allergic blepharitis, and also has a general strengthening effect on the immune system.
- Darsonvalization is the effect of a low-pulse electric current on the affected areas. Prevents eyelash loss.
- Ultraviolet therapy - disinfection of problem areas of the skin, destruction of allergy pathogens. It has a general health effect and helps to cope with the disease faster.
- Ultrahigh-frequency therapy accelerates blood microcirculation in disease-affected tissues. Accelerates cell regeneration, which results in the formation of a new, healthy layer of epithelium.
The above physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of allergic blepharitis have practically no contraindications and, at the same time, have proven effectiveness in practice. Such methods simultaneously relieve symptoms and help the body fight the disease. Therefore, they are recommended to all patients who are faced with such a problem.
Often, not one procedure is used, but several. In combination with drug treatment, you can count on quick relief from blepharitis. In some cases, only taking medications will be sufficient.
Treatment of allergic blepharitis is carried out comprehensively: both physiotherapeutic and medicinal methods are used.
And if in the second case the actions are aimed at eradicating the disease, then physiotherapy mainly contributes to the general strengthening of the protective properties of the visual organs, and also helps to eliminate the further development of inflammation and the formation of new lesions.
Physiotherapeutic measures include:
- Darsonvalization. In this case, the inflamed eyelids are exposed to electric current, which leads to a decrease in the number of eyelashes that fall out.
- Electrophoresis. A standard procedure that helps increase local immunity and destroys infections that cause allergies.
- UHF therapy. The method helps improve blood microcirculation in tissues affected by inflammation. As a result, the processes of formation of a new layer of epithelium in place of the affected one are restored.
- UV therapy. The procedure helps to get rid of allergens that accumulate in the mucous membrane of the eye, which has a general healing effect and accelerates the healing process.
Important! As means used for drug treatment, a number of medications are used that eliminate symptoms and normalize metabolic processes, speeding up treatment.
Among the main drugs are:
- the anti-allergenic drug “Zodak” helps relieve external symptoms such as inflammation of the eyelids, swelling and itching;
- "Tavegil" also helps eliminate external symptoms and has a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane of the eye;
- "Allergodil" (local drops that quickly relieve inflammatory processes by blocking histamine receptors);
- "Normax" (an effective antibacterial agent that prevents the formation of suppuration and generally prevents the transition of allergic blepharitis to a severe form).
We can talk about quick and successful treatment when using a combination of these methods, although drug treatment is often sufficient.
Symptoms of allergic blepharitis will decrease only if one condition is met - repeated contact with the identified allergen should be completely excluded or minimized.
To eliminate the inflammatory reaction, local and systemic antihistamines, agents that improve metabolic processes, and, if necessary, antibacterial drops are prescribed. Complex treatment is complemented by physiotherapy and traditional methods of therapy.
Physiotherapeutic treatments
Scientists have made great strides in developing methods for treating blepharitis of various etiologies. At the moment, a number of physiotherapeutic procedures have been developed and effective medications have been created.
When treating blepharitis, a diet is recommended, since the patient must receive enough vitamins (especially A, D, B), proteins and unsaturated fatty acids from the diet. It is recommended to include in the menu:
- fish and seafood;
- meat and liver;
- dairy products and eggs;
- cereals, legumes;
- nuts, dried fruits, mushrooms;
- vegetables - potatoes, carrots, cabbage, beets, bell peppers;
- fruits - melon/watermelon, pomegranate, apricot/peach, citrus;
- onions, garlic and herbs - lettuce, dill, spinach, horseradish;
- any compotes and natural juices.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
To eliminate allergic blepharitis, specialists use comprehensive approaches that include the use of medications and physical therapy. The main goal of physiotherapy is to provide a general strengthening, anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect on the mucous membrane of the eye. Wellness procedures help eliminate not only foci of inflammation, but also refractive errors that arose during the development of the disease.
For exacerbation of allergic blepharitis, the following types of procedures are indicated:
- electrophoresis – helps eliminate infections in the conjunctiva and increase local immunity;
- darsonvalization - when the affected areas of the eyelids are exposed to pulsed currents, inflammation subsides and the process of eyelash loss stops;
- UHF therapy helps improve blood microcirculation in the affected tissues, which accelerates the process of their epithelization.
To prevent the development of bacterial infection in allergic blepharitis, UV therapy can be used. It helps eliminate pathogens in the eye mucosa and accelerate skin regeneration processes.
Allergic blepharitis is an erythematous-exudative pathology characterized by the appearance of foci of inflammation on the skin of the eyelids. The main reason for the development of the disease is hypersensitivity of the skin and a tendency to allergic reactions. Exacerbation of blepharitis can be provoked by medications, food, household dust, decorative cosmetics, etc.
The disease occurs as a response to the action of a particular allergen. Inflammation can be triggered by contact with household chemicals, cosmetics, animal hair, dust, pharmaceutical drugs or pollen from flowering plants. Subsequently, inflammation occurs in the mucous membrane of the eye and ciliary glands, which provokes redness and severe itching.
Allergic pathology is characterized by a recurrent course, so it often takes on a chronic form. In the absence of adequate treatment, deterioration of peripheral vision may occur.
Etiological factors provoking the development of the disease include:
- hypovitaminosis;
- decreased immunity;
- allergic diseases;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- anemia;
- chronic infections;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system.
People suffering from gastritis, cholecystitis, colitis, etc. are at risk of developing allergic blepharitis. But most often the pathology develops in people who abuse alcohol and smoking.
Medication therapy
To start using medications, the effect of allergens must be excluded. This will make the disease much easier to treat. To cure allergic blepharitis, the following remedies will help:
- "Ophtimol" - eye drops that help with chronic blepharitis.
- “Zodak” is a blocker that eliminates itching and swelling of the eyelids and is an antiallergic drug.
- "Normax" - has an antimicrobial effect. Prevents the development of corneal ulcers.
- “Allergodil” - one drop into a sore eye eliminates an allergic reaction and any manifestations of inflammation.
- "Tavegil" - eliminates swelling of the eyelids, relieves itching, and also eliminates dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes. It is an antihistamine.
Allergic blepharitis is a recurrent disease and it can worsen. To get rid of its symptoms, anti-inflammatory antihistamines and physical therapy are used.
To get rid of such a disease, you need to use an integrated approach, namely, combine medications and physical therapy. It strengthens the body and helps relieve inflammation from the mucous membrane of the eye. If allergic blepharitis has worsened, then they resort to the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis - eliminates infection in the conjunctiva and helps improve immunity.
- Darsonvalization - helps eliminate inflammation of the eyelids and stops eyelashes from falling out.
- UHF therapy improves blood circulation in the affected eyelids, thereby accelerating the epithelization process.
In some cases, UV therapy is used for prevention purposes. It helps speed up the regeneration processes of the eyelid skin and eliminates pathogenic microorganisms in the mucous membrane of the eye.
Treatment of the allergic form of blepharitis is aimed at eliminating or at least minimizing contact with the allergen.
General therapy will not give a positive result, since the cause of inflammation will remain. First of all, the patient will need to carefully monitor personal hygiene. If possible, it is necessary to cure all chronic diseases, since they inhibit the body's protective functions.
You will also have to reconsider your diet, exclude fatty and spicy foods from your diet, and try to eat as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible. To supply the body with vitamins, special complexes can be recommended.
What local treatment will be depends largely on the characteristics of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the general condition of the patient. In the initial stages, you can perform massage to normalize the functioning of the glands. It must be performed with a special glass rod for 2 weeks.
Comprehensive drug treatment is mandatory. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Antihistamines, which negatively affect the allergen and strengthen the immune system. Thanks to them, you can very quickly eliminate itching, swelling and rash. For this purpose, Tavegil or Zodiac may be prescribed.
- Eye drops are faster than other medications in eliminating symptoms because they act instantly. Their only disadvantage is that they are very quickly washed out of the eyes along with tears. Lecrolin and Allergodil are good for allergies.
- If, in addition to blepharitis, other concomitant diseases have been identified, then antibacterial agents are prescribed. They may recommend Tobrex or Normax.
- For the purpose of daily treatment, elimination of discharge and crusts on the eyelids, Miramistin is prescribed. It can be used up to 3 times a day.
If the listed medications do not achieve improvement, then treatment of allergic blepharitis is carried out using hormonal agents.
Regular eyelid hygiene
This is the most important part of treating and preventing blepharitis. The main purpose of regular eyelid hygiene:
- Calm the eyelids
- Relieve blocked meibomian glands
- Clear any stagnant oily secretions from these glands
Daily eyelid care is necessary, consisting of three parts - heat, massage and cleansing. Daily and proper eyelid hygiene can help relieve the symptoms of blepharitis and prevent future occurrences.
Follow these steps to keep your eyelids clean:
- Apply a warm compress . Every day (up to 4 times a day) apply a warm (not hot) compress to closed eyelids for 5 - 10 minutes in order to easily cleanse the gland ducts of stagnant fatty secretions. For compresses, a small container of warm water wrapped in a flannel cloth is suitable, or you can use special eye bags that are heated in the microwave.
- Clear blocked meibomian glands . Gently rub vertically and horizontally across closed eyelids using your finger or cotton swab to help loosen any crusts and dislodge any accumulated oily secretions from the gland ducts.
- Clean your eyelids . Use a cloth or cotton swab soaked in warm water and a small amount of cleanser and gently clean the edges of the eyelids. When cleaning the inside of the eyelid, try to avoid touching the eye, as... this may irritate him.
In the acute phase of the disease, these actions should be performed twice a day, and after improvements occur, they can be performed once daily. Avoid using eyeliner and mascara as this may worsen the symptoms of blepharitis. But if you do wear eye makeup, make sure it's one that comes off easily.