Dermatological problems quite often become the cause of both physical and psychological discomfort. Vesicles, the appearance of which is characteristic of dermatoses, crack over time, and ulcers and wounds appear in their place. A particular danger is the addition of a bacterial infection; such complications require treatment with antibiotics.
Eczema on the legs is one of the forms of the disease that affects the skin of the lower extremities and feet. In most cases, eczema of the legs develops against the background of varicose veins, so as a preventative measure, dermatologists recommend using comfortable shoes and following the principles of proper nutrition to prevent the occurrence of problems with excess weight.
The article provides information about the causes of eczema on the legs, symptoms of the disease, as well as what types of eczema on the legs are most common. In addition, the material contains information about methods of treating eczema on the hands and feet, both with the help of medications and through the use of alternative techniques.
Important! The therapeutic course is based on the use of traditional methods; treatment with folk remedies is allowed as an additional technique, the use of which is possible only after consultation with a dermatologist. In the traditional treatment of eczema on the hands and feet, herbal infusions, decoctions and healing ointments are usually used.
Causes of eczema on the hands and feet
What causes eczema on the legs? With eczema on the legs, the cause of the disease is quite difficult to determine. The pathology is neuro-allergenic in nature, and a predisposition to its development can be inherited. There are many factors that contribute to the manifestation of the disease, but in most cases it is impossible to establish the true cause of its manifestation, so the issue of the etiology of eczema on the legs is quite relevant in modern medicine.
Eczema on the heels and lower extremities is a relatively young disease that was isolated from a number of other types of dermatoses not so long ago. The disease is one of the serious dermatological diseases, the treatment of which requires the use of serious drugs and proven techniques.
Additional Information! According to medical statistics, every 15 children and 30 adults on the planet suffer from eczema, so preventive measures are strongly recommended by dermatologists. After all, as practice shows, curing eczema is much more difficult than preventing its manifestation.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of eczema on the leg:
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
Many parents suffering from dermatological diseases wonder: how to get rid of eczema and prevent the likelihood of its occurrence in a child? The answer is obvious: it is necessary to follow the principles of proper nutrition, avoid eating allergens, especially for infants, spend more time in the fresh air and avoid damage to the epidermis.
- leg injuries;
- the body's sensitivity to chemically active substances;
- excessive use of cosmetics and detergents, which should not be done for dermatitis;
- overweight and varicose veins.
Additional Information! Patients with diabetes mellitus, as well as those suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia and disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are more often susceptible to the disease.
Causes
Eczema is a chronic neuro-allergic disease. The etiology of its appearance has not yet been fully elucidated, but the genetic predisposition of the body to react to various stimuli plays an important role.
Both external and internal factors can trigger the onset of the disease. These include:
- allergies to certain foods, medications, chemicals, dust;
- neuropsychic disorders, stressful situations;
- the presence of chronic pathologies of the digestive system (gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis);
- endocrine diseases, including diabetes;
- mechanical and thermal damage to the skin;
- past infections;
- helminth infection;
- hormonal imbalance.
The cause of eczema on the legs can be varicose veins - dilation of the venous vessels, leading to their thinning and lengthening, as well as the formation of varicose nodules.
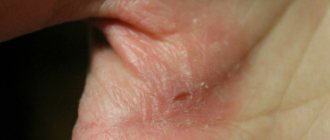
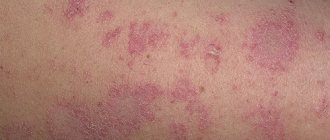
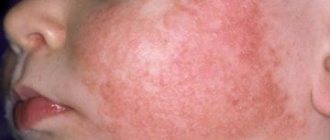
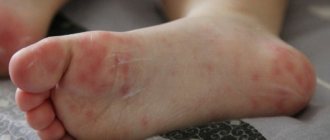
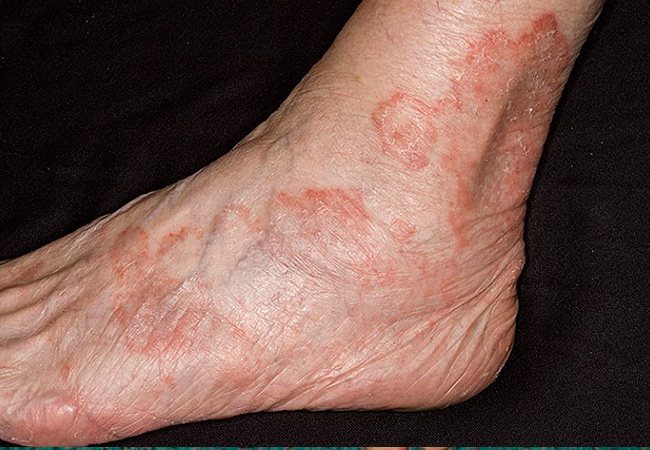
Eczema on the arms and legs, what eczema looks like
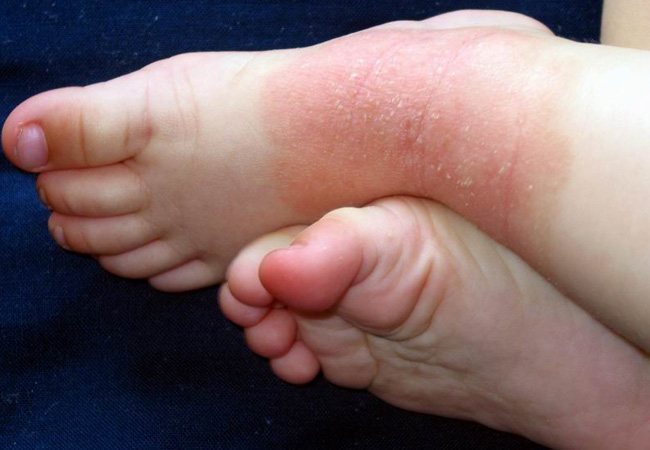
Eczema of the legs is accompanied by the appearance of a rash. Vesicles formed in problem areas burst over time and weeping appears in their place. Infectious eczema is dangerous because a bacterial infection is added to the underlying disease. In advanced cases, the rash spreads to other areas of the skin, forming peculiar foci.
Timely use of remedies for eczema on the legs helps reduce the symptoms of the disease and achieve significant remission. The disease is recurrent in nature and is also characterized by seasonal exacerbations.
Eczema on the sole of the foot causes particular discomfort; the foot may become covered with cracks, which is accompanied by pain. To prevent the development of pathology, dermatologists recommend using comfortable low-speed shoes made from natural materials that do not cause allergic reactions.
Therapeutic treatments
Often, the use of medications is not enough to get rid of eczema on the legs. A dermatologist may prescribe a course of hardware therapy. These methods help speed up the healing and restoration processes of the skin of the legs. For this illness it is best to use:
- electrophoresis sessions,
- phototherapy sessions,
- cryotherapy,
- laser irradiation.
Single sessions of hardware treatment for eczema are not effective. Systematic application of such methods is necessary. Typically, 7 to 10 sessions are prescribed to restore the skin.
Symptoms and signs of eczema on the legs
Symptoms and treatment of eczema on the legs are interrelated concepts, since, as a rule, dermatologists prescribe therapy after examining and determining the stage and type of pathology. For more severe symptoms, serious general medications are prescribed, mainly in the form of tablets and capsules. You can get rid of the manifestations of the disease at the initial stage with the help of external local remedies, and sometimes only with the help of folk recipes.
Signs of eczema on the legs:
- formation of fluid-filled pimples (vesicles) on the skin;
- the appearance of burning and itching;
- the temperature of the affected areas increases, skin color changes;
- vesicles burst, and oozing forms in their place;
- the temperature rises, the patient’s general well-being worsens;
- dry eczema on the legs and arms is characterized by the appearance of cracks, not accompanied by the formation of wet spots;
- the appearance of swelling.
Additional Information! Associated symptoms that appear in the absence of timely treatment for eczema on the legs include headache, increased anxiety, nervousness, inattention and irritability. This is not to mention the fact that the disease has a rather unaesthetic appearance, which is fertile ground for the development of complexes.
Treatment
Treatment of eczema on the legs begins with removing the possible allergen or irritant, eliminating stressful situations, direct sun, synthetic clothing and hypothermia. For all forms of the disease, hyposensitizing therapy is used.
Medicines
The basis of systemic treatment for eczema of the legs are antihistamines. The patient is prescribed:
- Acrivastine.
- Clemastine.
- Mebhydrolin.
- Chloropyramine.
- Hifenadine.
- Dimetinden.
In the presence of severe inflammation, corticosteroid drugs are used: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Betamethasone disodium phosphate. To relieve severe itching, psychotropic drugs with an antihistamine effect, for example, Hydroxyzine, are used.
To treat microbial eczema with fever, antibiotics are prescribed:
- Cefotaxime.
- Ofloxacin.
- Levofloxacin.
- Doxycycline.
- Ampicillin + clavulanic acid.
External therapy includes antiseptics (brilliant green solution, fucorcin, Chlorhexidine) and hormonal ointments: Alclomethasone dipropionate, Mometasone furoate, Clobetasol propionate. Oxycyclosol and Oxytetracycline + hydrocortisone aerosols work well with weeping eczema.
After the inflammatory process subsides, ointments with ichthyol, naftalan oil, and birch tar are prescribed. For microbial eczema, antibacterial gels are used: Muliricin 2%, Fuzidin, Gentamicin, Clindamycin. Mycotic eczema on the feet is treated with antifungal agents - Miconazole, Exoderil, Clotrimazole.
In case of severe swelling of the legs, it is possible to use diuretics; venotonics and antiplatelet agents can help prevent varicose eczema.
Traditional methods

It is recommended to supplement drug treatment with alternative medicine recipes. Raw potatoes are good for itchy skin. You can make a paste from the vegetable, which is applied to the affected areas, or squeeze out the juice.
Fresh cranberry concentrate is also used for compresses for eczema. There may be a slight tingling sensation, but it goes away quickly.
For oral administration, it is easy to prepare a decoction of dandelion and burdock roots. The dried and crushed raw materials are mixed in equal proportions and poured with boiling water. For 1 tbsp. l. mixture take 250 ml of water. Boil the mixture for 10 minutes and take ½ cup in the morning and evening.
According to traditional healers, eczema of the feet can be easily eliminated with a solution of gasoline and engine oil. The mixture is applied to areas with severe itching and peeling.
Nutrition
Foods that can provoke an exacerbation of eczema are excluded from the diet of patients:
- citrus;
- sweets, sparkling waters, chocolate;
- legumes;
- canned food and marinades;
- mushrooms;
- tomatoes, spinach, radishes and radishes;
- alcohol;
- hot seasonings, mayonnaise, horseradish and mustard;
- seafood.
For eczema, a dairy-vegetable diet, boiled chicken meat, grains, apples and their juice, and compotes are welcome. It is advisable to limit fluid intake. This will help prevent swelling and make it easier to put on your shoes.
Types of eczema on the legs
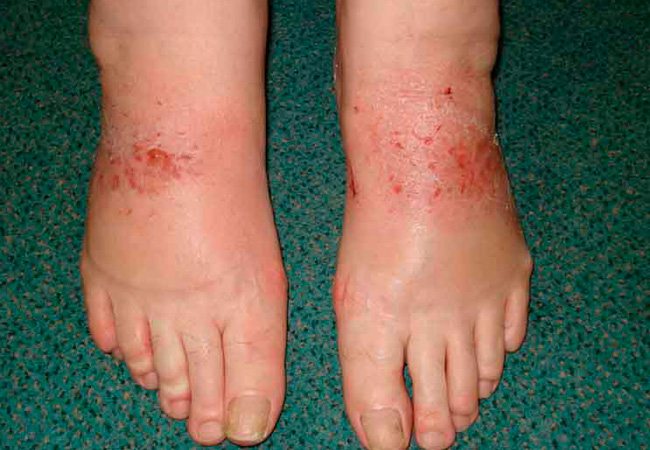
There are several types of foot eczema. Before treating a disease, a dermatologist must determine the type of pathology and differentiate it from other types of dermatoses that have similar symptoms. To achieve this goal, specialists carry out diagnostic measures.
Types of eczema of the lower extremities
- true. As a rule, the causes of this type of disease are internal causes, in particular dysfunction of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, metabolic disorders;
- mycotic eczema. The disease manifests itself as a result of exposure to a fungal infection;
- callosal. The localization of the disease in the case of callous eczema is the feet. On the skin of the soles, keratinized areas are formed that are susceptible to inflammatory processes;
- varicose eczema. The etiology of this disease is based on impaired blood circulation in the lower extremities and the occurrence of blood stagnation. As a result, varicose veins develop, which contributes to damage to the legs.
How to treat eczema on the legs? Causes and treatment of eczema in the initial stage
Eczema is one of the most common dermatological pathologies. It is a skin lesion of an allergic nature. Most often the disease is chronic. It can affect different parts of the body.
In elderly people, infants, and also in people working in hazardous industries, it is often located on the lower extremities. With eczema of the legs, the top layer of skin suffers: first it cracks and then becomes covered with a weeping crust.
Despite the fact that at first glance eczema is an external lesion, in most cases it has internal causes. That is why the disease requires careful diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
What it is?
Eczema is a chronic disease predominantly of an allergic nature. As a rule, it is characterized by a wide variety of skin rashes and a long course.
Causes of eczema on the legs
The development of eczema on the legs is based on a whole complex of neurogenic, infectious-allergic, endocrine-metabolic and immunological mechanisms. In particular, the factors provoking the occurrence of the pathological process are:
- 1) Heredity.
Eczema is not necessarily hereditary, but the possibility exists. It is difficult to calculate and impossible to prevent. Eczema on the legs is not a contagious or infectious disease, so it is not transmitted to relatives through contact or air. - 2) Stress, depression, nervous breakdowns.
In this case, people with and without chronic disorders of the nervous system are affected by eczema. A simple prolonged disorder, pessimistic thoughts, or a depressed mood can become a source of illness. - 3) Allergy.
It could be for soap, or maybe for some ingredient in the products consumed. The first step in treating a disease is to determine the element that causes conflict in the body or is not accepted by the skin. - 4) Environmental impact.
Mechanical impact, temperature, chemical is a good stimulus for eczema. Uncomfortable wool socks or constant hypothermia, inappropriate foot gel or tight shoes create a reliable basis for the development of the disease. - 5) Hormonal imbalances.
More typical for the fair sex. Young mothers often suffer from eczema, in whom serious changes in the body are added to the restructuring of the psyche. - 6) Dysbacteriosis, diseases of the digestive system.
An incorrect diet and disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract can be reflected externally. The skin is a mirror that instantly reacts to the slightest change in norms within the body. Often with eczema. - 7) Medicines. There are cases when eczema is caused by medications. Caution must be exercised with antibiotics.
In some cases, the cause of eczema of the lower extremities can be varicose veins of the legs.
Classification
Experts identify the following types of eczema on the legs:
True eczema, which is characterized by the appearance of symmetrical lesions with unclear boundaries, with weeping and swelling of the skin. Nodules and pustules rarely appear with this type of disease.
The following subtypes of true eczema may occur on the legs:
- 1) Dyshidrotic with a predominant location on the feet (with severe itching, weeping, with dense blisters);
- 2) Puriginous with a predominant location on the bends of the legs (without weeping with blisters, nodules and severe itching);
- 3) Horny or tylotic with a predominant location on the heels (with hyperkeratosis of the skin, with the formation of cracks and itching).
Microbial eczema, which most often appears near damaged areas of the skin, such as burns, cracks, scratches, etc. Areas of inflammation become wet, covered with a large number of crusts, and are characterized by peeling of the epidermis. The following subtypes of microbial eczema that can appear on the legs are distinguished:
- 1) Intertriginous, which can appear in the inguinal folds (characterized by severe redness, cracks, itching, weeping);
- 2) Nummular in the form of round areas of inflammation with vesicles, papules, crusts;
- 3) Fungal or mycotic eczema can affect the feet and nails (may be accompanied by weeping and itching);
- 4) Varicose, which is located in places of varicose veins (most often this type of eczema occurs with varicose veins, complicated by sclerosis of the skin and ulcerative processes.
Occupational eczema occurs due to frequent contact of the skin of the feet with various chemicals. Clinical signs are similar to true eczema, but can quickly resolve on its own in the absence of a potential irritant.
Seborrheic eczema can occur in the groin folds, since this is where most of the sebaceous glands are located in a person (if we consider the lower extremities). This type of disease is characterized by the appearance of oily plaques with yellowish crusts.
Symptoms and photos
The first symptoms of eczema on the legs in the initial stage (see.
photo), common to all types:
- the appearance of various rashes, in the form of bubbles, vesicles, scales, crusts;
- an inflammatory process characterized by swelling and redness of the skin;
- burning and itching of areas affected by eczema on the legs;
- with inflammation subsiding, the formation of scales, dryness and flaking of the skin;
- sleep disturbance and nervousness due to severe itching.
To accurately determine the type of eczema and prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to separate the stages of the disease.
- 1) Acute. It is characterized by itching, redness and swelling of the skin.
- 2) Papulovesicular. Formations appear in the form of nodules, vesicles form
- 3) Getting wet. Liquid leakage from opened bubbles.
- 4) Cortical. Drying of erosive areas, formation of crusts.
- 5) Subacute. The extinction of the inflammatory process, dry skin, the appearance of scales and cracks.
- 6) Chronic. Dryness, swelling and pigmentation of the skin.
The dermatologist examines the patient, establishes provocative factors, and, if necessary, prescribes a biochemical blood test, allergen tests, a stool test for helminths, and an immunogram.
Treatment of eczema
Effective treatment of eczema on the legs will differ somewhat depending on what type of disease worries a particular patient, the severity of the pathological process, and the presence of a secondary infection. It will not be possible to get rid of the problem if you do not get rid of the cause that provoked eczema on the legs.
Therefore, existing diseases of the endocrine, nervous, and digestive systems should be eliminated. How to treat eczema in the initial stage? Therapy begins with the doctor’s recommendations, which are mandatory for the patient to follow:
- 1) Control of sweating, careful hygiene of the skin of the feet.
- 2) Room ventilation. Maintaining optimal levels of humidity and temperature.
- 3) Elimination of irritants and allergens. These include: animal hair, dust, synthetics, woolen fabrics, pillows, detergents, pollen, mold, chemicals.
- 4) Limitation of psycho-emotional and physical stress, correction of work and rest schedules, adequate sleep.
- 5) Avoiding injury to affected areas.
- 6) Hypoallergenic diet.
- 7) Vaccination and administration of serums, taking medications - with caution.
Among the external treatments for this pathology, the most popular are the following:
- 1) For dry eczema on the legs in the initial stage, moisturizing ointments containing glycolic, lactic acid and petroleum jelly are used.
- 2) When the inflammatory process spreads, anti-inflammatory ointments, creams, pastes based on corticosteroid and hormonal drugs are used: Elokom, Advantan, Lokoid, hydrocortisone, prednisolone ointment, as well as Soderm ointment.
It is important to know that medications containing corticosteroids thin the skin and weaken its immune status, so fungal as well as bacterial infections are often added to the underlying disease. These medications should be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision, since these medications, despite their effectiveness, have a number of side effects. - 3) The use of non-hormonal medications: “Dermasan” (the drug is not recommended in the presence of open wounds and ulcers, pregnancy, breastfeeding; “Skin-Cap” is used for infectious eczema. Suitable for all categories of patients, as it does not provoke side effects; “Aurobin” » is used in the initial stages of the disease.
The components of the ointment are capable of healing the skin well; zinc ointment has the same good healing properties. However, this remedy should not be used for acute purulent processes, especially for allergy sufferers.
Treatment of eczema on the legs with folk remedies
At first, at home, the disease allows the use of traditional medicine methods. They can also become a supplement after the main symptoms have subsided. Here are some recipes:
- Raw potatoes. You can peel one potato and grate it on a coarse grater, apply the mixture to the affected area 3-4 rubles. per day, or you can soak gauze in potato juice and apply it as a compress to the eczema.
- Sulfur. Mix 100 g of homemade butter with 70 g of sulfur powder and leave for 7 days in a warm place, and then put it in the refrigerator. Apply this ointment to the areas of skin affected by eczema, then cover with cling film and leave overnight. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks. Kalanchoe and aloe help in curing weeping eczema. Apply a leaf of the selected plant, cut lengthwise, with the flesh side down, onto the affected area, or squeeze the juice onto a cotton swab and thoroughly treat the eczema; there may be a burning sensation.
- Tar. Mix 1 tbsp. pure tar with 3 tbsp. fish oil and 1 tbsp. natural 6% apple cider vinegar - mix well. Apply the product to a linen napkin, apply it to the affected area, cover with film and secure with a bandage.
- Poplar buds. Prepare an ointment from them: fill a half-liter jar with poplar buds, collected in the spring before they bloom, and fill them with melted pork fat. Place the jar in a water bath for 3-4 hours. Strain and get a greenish ointment with a pleasant smell. Store the ointment in the refrigerator in a dark container. It is possible that a course of treatment may require not one such jar of the drug, but two. This ointment will also be very effective for bites, bruises, cuts and joint pain.
- Celandine. Quickly helps relieve itching. The easiest way is to soak a cotton pad or a sterile piece of gauze in celandine juice and lubricate the affected area with it. When treating eczema on the legs at home, you can prepare an ointment based on celandine. Mix fresh, crushed leaves of the plant with lanolin and petroleum jelly in a 2:1:1 ratio. Lubricate dry and cracked skin with this mixture several times a day.
- Sea salt and licorice. Take salt and dry licorice herb in equal proportions - grind and apply dry to the affected areas, bandage (do not tighten too tightly) and hold for 2 hours. Remove the remaining mixture with apple cider vinegar. Carry out the procedure for 3 days in a row, then take a break for 3 days, etc.
Remember that many traditional medicine recipes have contraindications; before use, it is better to agree on the chosen remedy with your doctor.
Prevention of occurrence
To prevent the development of the disease, you need to avoid stressful situations and get proper rest. If you are prone to allergic reactions, follow a hypoallergenic diet. Give preference to clothing only made from natural fabrics.
Avoid sudden changes in temperature and high humidity. And in case of the slightest damage to the skin, treat the wound with an antiseptic drug. If you follow all the recommendations, you will not have to deal with the disease and treat it for a long time.
Which doctor should I contact for treatment?
If, after reading the article, you suspect that you have symptoms characteristic of this disease, then you should consult a dermatologist.
Source: //MyMedicalportal.net/529-ekzema-na-nogah.html
Stages of pathology development
For eczema on the legs, treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease; the more advanced the form of the disease, the more serious the medicine will be required.
Stages of the disease:
- eczema of the legs (photo), initial stage. This stage is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin, which is accompanied by burning, itching, and swelling;
- the papulovesicular stage is characterized by the formation of vesicles at the affected sites;
- wet stage. The vesicles gradually burst, and oozing appears in their place;
- crust-forming stage. Wet spots dry out and become crusty;
- The subacute stage is characterized by subsidence of symptoms, dry skin, and peeling;
- chronic stage. Characteristic signs: dry skin, the presence of cracks, age spots and swelling.
Symptoms
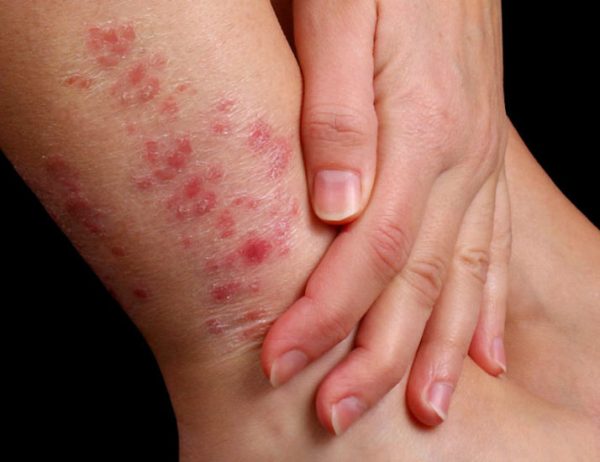
The classic sign of any eczema is itching. The manifestation of other symptoms will depend on which variant of the disease affects the limb.
True eczema is characterized by a varied clinical picture. The pathology begins acutely and develops in spurts, with frequent relapses and remissions. Microscopic bubbles with liquid contents appear on the skin of the legs, which quickly burst, forming small erosive lesions with drops of exudate.
As the eczema subsides, the microvesicles dry out and peeling crusts form on the surface of the skin. The patient is bothered by moderate itching, cracks and thickening of the stratum corneum appear on the foot, and symptoms of infiltration increase.
Mycotic eczema on the heels manifests itself as redness with clear edges and the subsequent appearance of papules. Opening up, they merge into wet areas, forming erosive wells and cracks. The pathological process is accompanied by severe scratching and soreness of the skin, and long healing.
Microbial eczema is typically characterized by an asymmetrical lesion with a purulent focus in the center and serous crusts. After their removal, an inflamed surface with erosive wells is exposed. The rash is accompanied by severe itching.
Occupational eczema on the legs has absorbed all the symptoms in its most severe manifestations. On the affected areas of the skin, blisters, vesicles, papules, peeling crusts and erosions are simultaneously observed. Bright erythema is accompanied by severe itching and irritation. The patient cannot sleep peacefully, since discomfort increases noticeably at night and often becomes the cause of neurological disorders.
Traditional approach to treating eczema on the legs
How to treat eczema on hands and feet using traditional methods? The most common methods are the use of general medications and topical external agents.
The general action drug allows you to get rid of the internal causes of the disease, while local remedies relieve skin irritation, promote its regeneration and healing.
General medications:
- antihistamines (Diazolin, Tavegil);
- sedatives (“Persen”);
- diuretics (Duphalac);
- corticosteroid drugs (“Prednisolone”);
- drugs to enhance immunity;
- enzymes for disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
External local agents:
- creams;
- ointments, in particular based on tar, ichthyol;
- alcohol solutions;
- compresses.
Eczema on the legs: treatment with folk remedies
The following traditional medicines have a beneficial effect on the skin of the feet with eczema:
- lotions based on medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, millennial);
- baths;
- decoctions:
- ointments made from propolis, vinegar, vegetable oils, honey;
- compresses from fresh cabbage, grated carrots;
- rub of garlic and honey.
How to prevent eczema on the legs, preventive measures?
To prevent the manifestation of pathology, dermatologists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- adhere to the rules of foot hygiene;
- reduce the amount of overexertion and stress to a minimum;
- control sweat loss;
- walk more in the fresh air;
- follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- Avoid contact with animals and other external irritants that can cause an allergic reaction.
One of the reasons for the occurrence of eczema on the legs and other parts of the body is the patient’s reduced immunity, so proper fortified nutrition, exercise and hardening also help prevent the development of pathology. Following the recommendations of dermatologists and nutritionists helps to significantly reduce symptoms and achieve remission.