The larynx is one of the organs that is often exposed to allergens. When the laryngeal mucosa comes into contact with an irritant, capillary permeability is impaired, which ends in the release of transudate. This causes the development of laryngeal edema in children of allergic etiology.
The condition in question in children is not an inflammatory process, which is characterized by rapid development. In a very short time, the airways become greatly narrowed; in especially severe cases, everything can end up completely blocking them. Experts note that most often such a pathology in children appears as an allergy to certain foods and medications, although other allergens can provoke rapid swelling of the larynx.
This condition is most dangerous for young children - due to the natural narrowness of the respiratory tract, even slight swelling can cause suffocation.
Causes of a swollen throat
In case of symptomatic recurrence of edema, it is necessary to carry out a detailed diagnosis of the patient’s condition and keep at hand methods for quickly eliminating the pathology.
Among the main causes of impairment in adults are the following:
- oral diseases;
- purulent sore throat;
- phlegmous laryngitis;
- epiglottis abscess;
- purulent inflammation of the root of the uvula;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- kidney and liver diseases, including cirrhosis;
- allergic reactions;
- problems with blood circulation in the larynx area;
- pathological proliferation of lymphatic tissue;
- injuries to the throat, back wall and surrounding areas;
- cancerous tumors;
- postoperative period, especially in cases where a tube was inserted;
- infectious diseases;
- severe hypothermia of the patient;
- poisoning with toxic substances.
In a child, the cause of laryngeal edema can be the same factors as in adult patients. But in children, such conditions are much more acute , more complex and dangerous.
If swelling begins, you should immediately call emergency help.
Due to the characteristics of the respiratory system, children have weakness in the muscles of the respiratory organs, their passage is very narrow, and the mucous membrane is sensitive to the slightest irritants.
With a slight swelling of 1 mm, the clearance in the larynx is reduced by half, which can lead to shortness of breath and the inability to breathe at all .
There may be several reasons for this disorder, including infections, ingestion of hot foods, injuries, allergies, and angioedema.
Treatment of nasal swelling in young children
In childhood, as well as in adults, there are many reasons due to which swelling of the nasopharynx can develop. The most common are:
- allergic diseases,
- chronic runny nose,
- infectious processes,
- development of adenoids or polyps,
- various nasal injuries.
Based on the reasons, the small patient is prescribed competent therapeutic intervention. Medicines are often used as treatment. However, their choice should be approached with particular care, since many of them are contraindicated for use at a young age.
Redness of the mucous membrane and its swelling should be treated only after a full diagnosis and examination of the child by a medical specialist. According to the etiology, individual characteristics of the body and age, he will select the right remedy that will be the safest for the little patient.
During the initial stages of therapy, in no case should you treat the child yourself, give him antibiotics, vasoconstrictor drops and rinse the sinuses with a pear-shaped balloon.
Allergic swelling of the larynx
This process is a non-inflammatory process that occurs unexpectedly and develops quite rapidly , which poses a serious danger to the patient’s health.
Within a few minutes, the respiratory organs can narrow until breathing stops completely.
is especially dangerous in young children, as it can lead to suffocation.
There may be several reasons for this disorder:
- taking medications , especially when administered intravenously and intramuscularly
- eating intolerant foods , especially fish, nuts and eggs;
- contact with chemicals, including detergents;
- cold allergy;
- insect bites;
- house tick;
- dust, including book and street dust;
- fungi and mold;
- pet hair.
It is always necessary to keep a good antihistamine or tablet on hand if the patient has previously been diagnosed with an allergy, especially if there is frequent swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and throat.
Mechanism of edema development
Normally, lung tissue consists of many tiny air-filled bubbles called alveoli. If, in addition to air, liquid begins to accumulate in the alveoli - as a result of sweating from the circulatory and lymphatic systems - pulmonary edema occurs.
The mechanism of occurrence of this pathological condition is as follows:
- As a result of stagnation in the pulmonary circulation, the outflow of blood and lymph is disrupted and intravascular pressure in the pulmonary capillaries and lymphatic vessels increases.
- Blood and lymph accumulate in the vessels and begin to penetrate through their walls into the pulmonary structures of the alveoli - the so-called fluid effusion occurs.
- The liquid or transudate that has penetrated into the alveoli seems to displace air from them and significantly reduce their respiratory surface. The situation gets worse as the amount of transudate in the lungs increases - the effect of “internal drowning” is observed when the lungs fill with water and cannot fully function.
- Transudate is very rich in protein and therefore easily foams when in contact with air in the alveoli. The resulting foam makes breathing even more difficult.
- As a result, breathing becomes almost impossible, oxygen does not enter the blood, hypoxia and death occur.
1. Cardiogenic – that is, associated with diseases of the heart and blood vessels: acute heart attack, heart defects, cardiosclerosis, severe hypertension. In this case, stagnation in the pulmonary circulation occurs due to the fact that the heart cannot cope with its functions and is not able to fully pump blood through the lungs.
2. Non-cardiogenic:
- Hydrostatic edema occurs due to increased intracapillary pressure in the lungs as a result of pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax, tumors, bronchial asthma, and foreign objects entering the respiratory tract;
- Membranogenic edema develops when the permeability of pulmonary capillaries increases as a result of respiratory distress syndrome (sepsis, chest trauma, pneumonia), aspiration syndrome (vomit or water enters the lungs), inhalation and intoxication syndromes (poisoning with toxic substances, including endotoxins) .
Symptoms and signs
In the first stages, it is difficult to identify the cause of throat swelling, since all disorders have similar symptoms:
- the soft palate, tonsils and uvula begin to become inflamed, slightly swollen and red;
- at first it is difficult for the patient to exhale, after which the same difficulties arise when exhaling;
- breathing begins to become more frequent, as the patient cannot inhale enough air;
- Mild shortness of breath may occur.
In the absence of an allergic reaction, the patient’s condition deteriorates quite slowly and it is possible to deliver him on time to the hospital, where all the necessary assistance is provided.
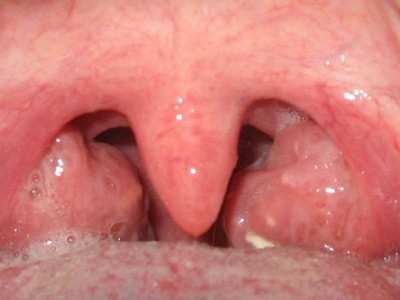
- it hurts to swallow, and the hardness of the food does not matter;
- the characteristics of the throat change, it becomes hoarse and deaf;
- acute lack of air begins , including signs of suffocation;
- the throat becomes dry and begins to become irritated;
- there may be a sensation of a foreign body in the larynx, the voice becomes hoarse;
- due to dry mucous membranes, a barking cough occurs;
- the pulse increases significantly , shortness of breath no longer disappears;
- the skin becomes pale, cyanosis may appear;
- active sweating is noted, especially in the last stages of throat swelling;
- it is difficult to breathe, and the breathing becomes not only heavy, but also noisy;
- mucous membranes begin to turn blue ;
- body temperature rises slightly;
- the patient may begin to panic.
In severe cases, laryngeal edema can develop into angioedema, which is characterized by severe swelling of the face and neck. An attack of suffocation begins. Due to laryngeal stenosis, the patient may lose consciousness and will not return to normal until he receives emergency help.
First aid
If a person’s larynx begins to swell, they should immediately call an ambulance and begin taking independent measures to eliminate the symptom:
- free your throat from a scarf, tight shirt and other objects so that the respiratory organs function at maximum capacity;
- if a person is exposed to an allergen from the external environment, contact should be stopped immediately and, if possible, the patient should be taken out into fresh air ;
- it is permissible to immerse the patient in a hot bath or to begin with, do this with the upper or lower extremities, this will significantly improve the condition of the victim;
- you can rinse your mouth with adrenaline hydrochloride;
- Introduce a nasal spray into the nasal sinuses to facilitate breathing; if the attack is allergic, antiallergic drops ;
- if there is a doctor in the house, administer an antihistamine drug intravenously ; at home, Suprastin or Diphenhydramine is usually used.
If an attack of acute edema was provoked by insect venom due to their bite, a tourniquet should be applied as quickly as possible a few centimeters above the site of the lesion. This will prevent toxins from spreading through the bloodstream.
How to help a patient - what you can and cannot do
The algorithm of actions for providing first emergency aid for pulmonary edema consists of performing the following emergency measures:
- Call an ambulance . You cannot ignore complaints and wait for the condition to worsen - pulmonary edema can lead to death almost instantly.
- Reassure the patient : use valerian or motherwort.
- Unbutton all clothing that restricts breathing.
- Sit on a chair, lower your legs down . Such a patient should not be placed in a horizontal position.
- Before the doctor arrives, you can apply tourniquets to the limbs that compress the veins. It is important not to allow the pulse to disappear on the clamped limb. The tourniquets are applied for 15-20 minutes and then removed. After some time they can be applied again. Thus, the heart is unloaded - it requires less effort to pump blood to the periphery of the body.
- You can give the patient 1 tablet of nitroglycerin sublingually.
- If possible, use an oxygen mask.
- If a large amount of foam is released during a cough , you should use antifoaming agents. At home, this can be ordinary alcohol: a towel soaked in vodka or medical alcohol is periodically applied to the patient’s nose and mouth. It is better not to use expectorants if the cough has already become wet with copious sputum.
- To prevent swelling from spreading, you should warm the patient’s back : apply mustard plasters.
It is important not to ignore the first symptoms of pulmonary edema, but to take timely measures to eliminate it and professional treatment in a hospital setting.
Treatment methods
Therapy to eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat, larynx or epiglottis should take into account the origin of the disease .
But due to the complexity of diagnosing the disease, even with a detailed examination, treatment usually begins according to one algorithm.
- The patient should be seated or his body should be given a reclining position .
- You should also be sure to take an antihistamine . Patients can be offered Zodak, Diazolin, Suprastin, Cetirizine, Zyrtec, Tavegil and others.
- In many cases, antihypoxants and antioxidants . These include Actovegin, Vixipin, Confumin.
- The patient should be kept warm at all times ; it is recommended to apply mustard plasters to the calf area.
- Inhalations using solutions cope well with edema . The exact dosage should be selected under the supervision of a physician.
- If the problem is caused by an infection , antibiotic therapy should be taken. It includes medications such as penicillin and streptomycin.
- In severe cases, an immediate tracheotomy is performed , which can only be done by experienced doctors.
During rehabilitation, the underlying disease must be treated.
It is important to adhere to a diet in which it is recommended to consume only liquid and semi-liquid foods. It should be at room temperature and not contain any flavoring spices or vinegar dressings.
Principles of treatment
Any pathology of the respiratory tract requires complex treatment prescribed by an experienced specialist. Treatment includes taking special medications that facilitate the passage of mucus, antibiotics and inhalation of airway dilators.
If a doctor has diagnosed an allergic disease, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating the effect of the allergen. Treatment may include taking antiallergic and hormonal medications.
In order for treatment to be successful, it is extremely important to participate in activities that enhance immunity. This includes an active lifestyle, regular sleep, healthy eating and giving up bad habits.
Dangers and Consequences
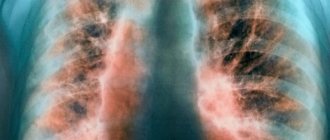
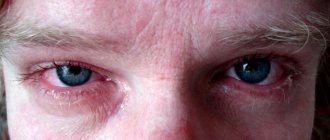
The main danger of throat swelling is its effect on respiratory function.
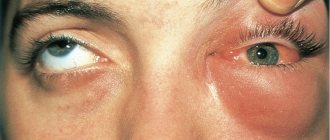
When the lumen narrows, breathing becomes difficult, which causes acute oxygen starvation .
The photo on the left shows just such a case.
Organs begin to reduce their function, which worsens the general condition of the patient.
In severe cases, as already described above, the patient may simply die from lack of air.
In a severe allergic reaction, dangerous symptoms can develop in just a few minutes. This usually happens when drugs are administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
You should not think that you can cope with swelling without the use of medications. Usually this can only be done if the problem is not associated with a severe allergic reaction.
Refusal or unwillingness to undergo therapy using antihistamines can lead to dire consequences.
In addition, it is very important to undergo treatment to eliminate the underlying disease , this applies to heart disease, kidney disease, liver disease and infectious lesions.
How to relieve swelling of the nasopharynx?
Treatment for adults and children differs depending on the patient's condition.
In children, symptoms are relieved with medications intended for children or medications for adults, but in a lower dosage.
Features of treatment for nasopharyngeal swelling:
- Swelling should be treated with vasoconstrictor drops. They are effective for 6–12 hours. Vasoconstrictor drops relieve swelling, eliminate nasal congestion and prevent swelling of the walls of the mucous membrane. But the drops cause dryness in the nose, so after instillation it is advisable to lubricate the nose with ointment. The course of treatment is no more than 7 days. With prolonged use of drops, addiction to the drug occurs and its effect on the body decreases. Drops are used with extreme caution for the treatment of young children. Sanorin, Tizin, Nazivin drops have proven themselves well.
- If the symptoms of swelling are caused by an allergic reaction, then antihistamines are used for treatment. They relieve inflammation, swelling, redness of the eyes and nose, and make breathing easier. If possible, you need to identify the allergen and try not to come into contact with it. Effective antihistamines are Diazolin, Loratadine, Cetrin, Erius and Zyrtec.
- Homeopathic medicines, for example, Euphorbium Compositum or Edas-131, help eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Euphorbium Compositum is taken every 15 minutes in the first stages of the disease. The advantage of homeopaths is that they are harmless to the body and are not addictive, unlike vasoconstrictor drops. Homeopathic medicines relieve congestion, relieve inflammation and improve breathing.
- During therapy, it is important to pay attention to strengthening the immune system. Throughout the illness, while the body fights pathogenic microorganisms, the immune system is weakened and requires additional support.
- If swelling of the nasopharynx was caused by a viral infection, then antiviral drugs are instilled into the nose along with antihistamines and homeopathic drops. The drug Grippferon is effective. The area above the nasolabial triangle is lubricated with ointments based on essential oils.
See also
What to do if a subcutaneous pimple pops up on your nose and it hurts, how to treat it?
Read
- Massaging the bridge of the nose using an asterisk will help. The ointment warms the mucous membrane and eliminates the symptoms of pathology. Essential oils make breathing easier. The bridge of the nose is lubricated with a small amount of ointment and rubbed into the skin in a circular motion.
- At high temperatures you need to take antibiotics. Only a doctor should prescribe them, since antibiotics are difficult to choose and the dosage should be different for each individual case. The course of treatment is no more than a week. If there is no improvement after taking medications, then you need to return to the clinic.
Swelling of the nasopharynx is a serious disease that, without proper treatment, leads to complications. In severe cases of sinusitis, if conservative treatment does not help, a puncture is performed. A special needle is inserted into the nose and the accumulated contents are pierced, which prevents normal breathing. The procedure is simple but painful. The punctured area hurts for some time.
Video on the topic
Find out more about the structure of our respiratory organs - the throat and larynx, as well as what to do if there is swelling due to allergies.
The larynx is one of the organs that is often exposed to allergens. When the laryngeal mucosa comes into contact with an irritant, capillary permeability is impaired, which ends in the release of transudate. This causes the development of laryngeal edema in children of allergic etiology.
The condition in question in children is not an inflammatory process, which is characterized by rapid development. In a very short time, the airways become greatly narrowed; in especially severe cases, everything can end up completely blocking them. Experts note that most often such a pathology in children appears as an allergy to certain foods and medications, although other allergens can provoke rapid swelling of the larynx.
This condition is most dangerous for young children - due to the natural narrowness of the respiratory tract, even slight swelling can cause suffocation.
Symptoms of allergic laryngeal edema in children
The clinical picture for the condition in question will depend on how narrowed the airways are. At the first stage of development of allergic laryngeal edema in children, the following symptoms will be noted:
- deepening of breathing;
- slight shortness of breath;
- reducing pauses between inhalation and exhalation;
- decreased breathing rate and heart rate;
- difficulties with inhalation; a little later, the same problems arise with the exhalation process.
If the body’s allergic reaction is more intense, then doctors will talk about the second stage of allergic edema in children. This condition will be characterized by the following symptoms:
- dry throat;
- increased sweating;
- excessive pallor of the skin;
- hoarseness/hoarseness of voice;
- complaints of a feeling of lack of air, sometimes suffocation develops;
- breathing becomes noisy and difficult;
- the child claims that he has a foreign body in his throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- coughing attacks with characteristic hoarseness (barking cough);
- increased heart rate;
- the skin and mucous membranes begin to acquire a bluish tint;
- Body temperature may increase, but not critically.
The often described condition is accompanied by Quincke's edema, when there is rapid swelling of the face and neck. When it develops, children may lose consciousness, and if urgent qualified medical care is not provided, everything can end in death.
Symptoms of allergic laryngeal edema in children can develop quite slowly, or they can be rapid. In the first case, the baby will show anxiety. If he is not talking yet, parents may notice causeless crying and frequent movements of his legs and arms. If the child is already talking, then he will come up and tell you about his unpleasant feelings.
Allergic edema in childhood can be acute or chronic. The first option is more common, goes away quickly with proper medical care, but can occur again the next time the allergen appears in the child’s body.
Reasons for development
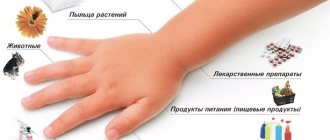
Symptoms of the disease in question appear only if the child’s body is exposed to some kind of allergen. Of all the known irritants that can provoke allergic swelling of the larynx, the following can be distinguished:
- food products: honey, cocoa, chocolate, strawberries, citrus fruits, peaches;
- house dust;
- fluff - in children, symptoms of laryngeal edema often appear at night, when they are in direct contact with pillows;
- animal fur and their saliva are extremely rare, but there are cases of recording allergic swelling of the larynx to such irritants;
- some medications, especially with forced long-term use.
In addition, plant pollen is a fairly strong allergen, and in this case, in children, the symptoms of allergic swelling of the larynx will be especially intense when going outside if it is spring/summer.
It is worth knowing that if the symptoms of the condition in question already exist, you should immediately contact your pediatrician, this specialist will refer the child to an allergist. Even if the baby is forced to take some kind of medication, it must be stopped immediately and the situation explained to the doctor - he will either completely change the treatment regimen or simply reduce the dosage of the drug.
Swelling in the throat area occurs with various pathologies. Therefore, laryngeal edema in a child is treated in such a way as to eliminate the very cause of its occurrence. The severity of the process largely depends on the condition of the mucous membrane, the child’s immunity, his reaction to the disease and medications.
Symptoms: from the first signs to a dangerous form
Harbingers of pulmonary edema in an adult are the following symptoms and signs:
- the appearance of shortness of breath and suffocation, which do not depend on physical activity;
- coughing or chest discomfort at the slightest physical exertion or while lying down;
- orthopnea is a forced vertical position of the patient, which he takes because lying down he cannot breathe fully.
As edema and dysfunction of a larger area of the lungs increases, the patient’s condition quickly deteriorates and first “blue” and then “gray” hypoxia may occur:
| Symptoms | "Blue" hypoxia | "Gray" hypoxia |
| General state | Severe, severe weakness and restlessness. Consciousness is preserved. Forced vertical position of the body. Swollen blood vessels are visible on the neck. There may be nausea and vomiting, and high fever. | Extremely difficult. Consciousness is confused until it is completely lost. Apathy. |
| Localization of pain | Behind the sternum | Severe squeezing pain behind the sternum |
| Breath | Difficult, frequent (30-60 per minute) and superficial | Rare and arrhythmic. You can hear wheezing in your lungs. |
| Cough | At first dry and painful, then with copious foam-sputum. Feeling of liquid bubbling inside. | With abundant foamy liquid of a pinkish tint. |
| Condition of the skin and mucous membranes | The mucous membranes and skin on the fingers are blue | Sallow skin, covered in cold sweat |
| Pulse | Frequent, up to 100 per minute, but weak | Weak, almost unpalpable |
| Urination | Very rare, even completely absent | Absent |
| Forecast | If assistance is provided in a timely manner, favorable | Adverse |
What should be the treatment after a myocardial infarction, the drugs prescribed by doctors, the correct lifestyle - find out everything on the pages of our website.
Why they take a general blood test, interpretation of results in adults and children, norms by age and much more are discussed in detail here.
What should the ESR be in a blood test: the norm for women and men by age is presented in the table in this article.
What are the signs of throat swelling?
The larynx is located in the front of the neck, just behind the hyoid bone. Through this inlet from the nasopharynx, air from the environment passes into the trachea, bronchi and lungs. The larynx is formed by a frame of cartilage, the largest of which is the epiglottis, which, like a petal, closes the lumen of the trachea during swallowing food and drink. Other parts of the larynx are ligaments, muscles and the vocal apparatus.
In case of inflammation or injury to the epiglottis, the entrance to the trachea narrows or is completely blocked, and acute respiratory failure develops.

Symptoms of laryngeal edema in children:
- fast, shallow, intermittent, labored breathing;
- hoarseness (if the vocal cords are affected);
- neck muscle tension;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- feeling of lack of air;
- pain in the neck.
The narrowness of the airways in children aged 1 to 7 years is one of the reasons for more frequent swelling of the larynx at this age. The mucous membrane is more prone than in adults to allergic reactions and swelling. The lumen of the larynx decreases by half when the mucous membrane thickens by only 1 mm.
Signs indicating the possible development of throat swelling in a child:
- increased heart rate and irregular heartbeat, decreased blood pressure;
- urticaria, itching, redness of the skin of the face, neck;
- conjunctivitis and rhinitis (watery runny nose);
- excessive sweating (“hail sweat”);
- wheezing, chest tightness, cough;
- swelling of the skin around the mouth, nose, and eyes;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- swelling of the lips and tongue;
- dizziness;
- fainting.
Due to swelling of the throat, children may experience neuropsychiatric symptoms. The child becomes excited and restless. Suddenly your head begins to feel dizzy, your speech becomes slurred, and convulsions appear. In case of unfavorable development - confusion, fainting.
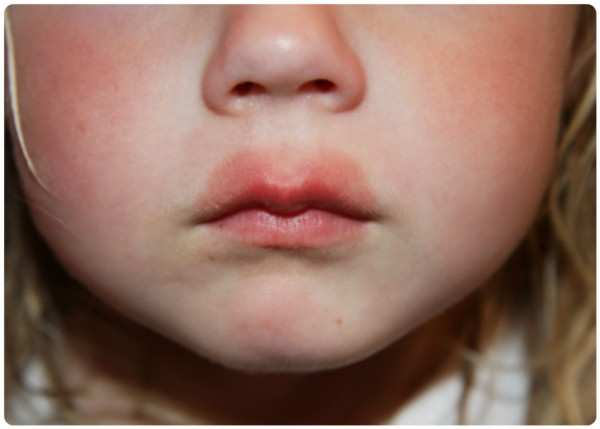
Why does throat swelling occur?
The most common causes of swelling of the larynx are allergic and inflammatory processes. As a result, breathing problems may occur. Obstruction or obstruction of the upper respiratory tract often accompanies angioedema in the oral cavity and larynx.
Children react to various natural factors, irritating substances in food, medicines, and inhaled air. Sometimes there is a strong rush of blood to the tissues and swelling of one organ (eyelids, lips, cheeks, palms). This enlargement of any part of the body as a result of an unusually strong reaction to familiar stimuli is called “Quincke’s edema.”
Other causes of swelling in the larynx (except allergic reactions):
- inflammation of the epiglottis involving surrounding tissues (epiglottitis);
- reaction to examining the throat with an endoscope;
- burns of the pharyngeal mucosa (chemical, thermal);
- acute tonsillo-laryngitis;
- laryngospasm;
- neck injuries;
- croup
With various infectious and inflammatory diseases, as well as throat injuries, the development of acute respiratory failure poses a great danger to life.
The doctor examines the child's throat and uses a laryngoscope to determine the degree of swelling in various areas. The mucous membrane of the larynx swells and turns red as the inflammatory process develops; a rash appears (not always). In the area of the larynx, the glottis narrows, the epiglottis thickens and the arytenoid cartilages enlarge.
Swelling of the upper and lower respiratory tract
One of the most common respiratory pathologies is bronchial edema.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to those of other diseases. Swelling of the trachea and bronchi is usually associated with infectious inflammation, allergies and the harmful effects of various irritants (nicotine, dust, gas) on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. As a result of their harmful effects, inflammation develops, which is accompanied by swelling, cough, pain and production of copious sputum. The nature of the sputum can be either light or viscous, difficult to expectorate.
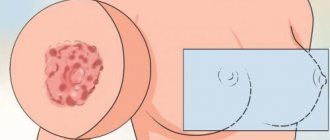
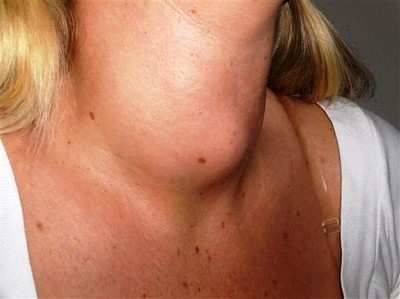
Causes of lumps in the neck area
The most common cause of tumors in the front of the neck is tonsillitis. Inflamed tonsils become enlarged and feel like a lump in the throat. Swelling under the jaw closer to the ears can be caused by infection and inflammation of the salivary glands.
The lipoma can easily move under the skin if you press lightly with your finger. It is painless and does not pose a danger in terms of oncology. Atheroma is a dense, elastic, painful tumor of the sebaceous gland on or below the neck. It is more common in adolescents who have entered puberty. The formation has clear contours and is mobile. As the tumor suppurates, the pain intensifies and the body temperature rises.
When the lymph nodes become enlarged, there is also pain and a lump in the throat. The causes of swollen lymph nodes are tonsillitis, dental diseases, abscesses, and mononucleosis. Enlarged lymph nodes or lymphadenitis caused by a bacterial infection can lead to serious complications - an abscess, cellulitis of the neck.
Lumps and tumors in the throat appear due to diseases of the thyroid gland. It is necessary to undergo an ultrasound of the neck and be tested for thyroid hormones.
Some lumps under the skin remain the same size, others increase in volume. Some tumors in the neck area may be cancerous. Lymphoma is characterized by the spread of the malignant process to healthy lymph nodes. Carrying out differential diagnosis in the clinic helps to identify the initial cause of swelling in the throat.
What does the larynx look like with epiglottitis?
Inflammation of the epiglottis, as well as surrounding tissues, can cause airway obstruction. Acute epiglottitis most often develops in children aged 2 to 4 years. The disease in a child under 3 years of age usually manifests itself as irritability, fever, loss of voice, and hearing loss. The baby takes a characteristic pose: he sits, leaning forward, saliva flows from his mouth. Symptoms in adolescents include an increase in sore throat, drooling, bluish lips and shortness of breath. Causative agents of epiglottitis:
- Pneumococcus;
- streptococci A, B and C;
- bacterium Haemophilus influenzae;
- yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida;
- Varicella zoster virus (the causative agent of chickenpox).
With the edematous form of epiglottitis, severe pain in the throat appears when swallowing, and intoxication develops. The temperature rises, the epiglottis increases in size, and the mucous membrane becomes bright red. If epiglottitis is not treated, acute airway obstruction occurs. Death in this case occurs within a few hours.
A child with symptoms of epiglottitis should not be given drugs with a sedative effect - valerian, motherwort tincture, antihistamine drops or tablets.
Acute epiglottitis is treated in the intensive care unit, where it is possible to ensure the patient can breathe freely. The patient is given antibiotics and given an intravenous infusion of saline and nutritional fluids. The child is in the hospital for a week, then he is transferred to outpatient treatment.
What should parents do if their child has laryngeal swelling?
The larynx is anatomically and functionally connected to the oral cavity, oropharynx, and laryngeal part of the pharynx. The appearance of edema in each of these sections threatens the child’s life. Narrowing or obstruction of the laryngeal opening or compression of the carotid artery by swollen tissues is dangerous. Parents are interested in how to relieve swelling in children, but it is much more important to first determine the root cause of this condition. Only a doctor will determine exactly what the child is sick with and prescribe adequate therapy.
Laryngeal edema with acute respiratory failure is a condition requiring immediate medical attention.
In acute tonsillitis, laryngitis, and colds, the temperature rises sharply. Difficulty breathing occurs, the voice becomes muffled, wheezing and coughing appear. If there are problems with breathing, the child is not given food and drink, and an ambulance is called.
Allergic swelling of the larynx is treated with antihistamines, and in severe cases with glucocorticoid drugs. With the use of these groups of drugs, the child’s condition quickly improves.
Edema of the larynx occurs with such a “forgotten” disease as croup - inflammation in the throat of an infectious nature. There are three main symptoms: stridor or noisy breathing, hoarseness, and barking cough. Most often, children aged 1–6 years suffer from croup.
For croup, the child is given valerian tincture and an ambulance is called. Treatment of laryngeal edema in a hospital involves restoring the patency of the laryngeal opening. The little patient is prescribed interferon drugs, antipyretics and antihistamines, vasoconstrictor nasal drops, and inhalations with mucolytic solutions.
Swelling inside the throat is a condition that requires immediate medical attention, as it is life-threatening.
This symptom often accompanies severe allergies.
With constant contact with an irritant allergen, the permeability of the capillary wall is disrupted, as a result of which transudate or edematous fluid begins to be released in the cells of the throat mucosa.
How to find out in a timely manner, not to confuse it with other diseases
If the swelling develops gradually, then the stage of imaginary well-being can take about a day.
Sometimes the pathology occurs in an erased form , in which hypoxia is not very pronounced. This happens more often in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Alarming symptoms that require immediate medical attention are:
- shortness of breath at rest;
- difficulty breathing, with the patient complaining of a feeling of “bubbling” in the chest;
- inability to breathe “fully” - when trying to do this, the patient coughs and feels pain;
- increased breathing - as compensation for its insufficient depth;
- a feeling of compression and discomfort behind the sternum;
- dry continuous cough;
- inability to lie down - the patient gets worse in a horizontal position;
- weakness and weakness;
- blue lips and fingertips.
Main allergens, dangerous record holders
There are many factors that provoke an allergic attack. Basic:
- dust;
- plant pollen;
- Food;
- medicines;
- pet hair.
In most cases, allergic reactions occur as a result of taking honey, nuts, citrus fruits, and seafood.
Allergies to insect bites, chemicals (paints, laundry detergents, personal hygiene items), petroleum products, and decorative cosmetics are common.
The symptoms are clear, unpleasant and powerful
The intensity of the symptoms depends on the state of the immune system and the degree of narrowing of the upper respiratory tract. Almost always at the first stage the following symptoms of laryngeal edema are observed with developing allergies:
- pulse quickens;
- slight shortness of breath appears;
- difficult to breathe, take a deep breath;
- swelling of the palate and tongue becomes noticeable.
With a more intense reaction, additional signs appear:
- hoarseness of voice;
- noisy breathing;
- bluish skin;
- constant thirst;
- heavy sweating;
- feeling of lack of oxygen;
- pain in the throat area;
- severe shortness of breath, even in an immobilized state.
In rare situations, a person may experience a slight increase in body temperature.
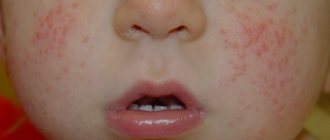
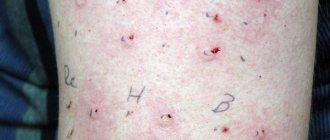
The photo shows signs of swelling with severe allergies:
Allergic swelling may be accompanied by Quincke's edema. In this case, the face and throat swell. You can suffocate and die.
Therefore, it is important to know, especially for allergy sufferers, the symptoms of swelling in the throat area due to allergies.
The danger of the phenomenon is that the symptoms appear suddenly. It's scary with an unpredictable ending. If the swelling is extensive, the likelihood of mortality in this case without the help of doctors is quite high.
The risk is much higher if the disease occurs in a child because their body contains more water than an adult, which affects swelling.
To minimize the likelihood of the worst outcome, you need to know what to do if your throat becomes swollen due to an allergy.
Major diseases
Swelling of the respiratory tract is usually caused by tracheitis, bronchitis, bronchial asthma, edema and pneumonia.
Tracheitis
The inflammatory process in the trachea is called tracheitis. Inflammation of the trachea, which is an ENT pathology, is characterized by the presence of edema and redness of the mucous membrane. Pathology often occurs against the background of allergenic and viral exposure. Often, inflammation of the trachea is accompanied by pathologies such as rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Changes are also possible against the background of pneumonia and influenza.
Bronchitis
The basis of the pathology called bronchitis is the inflammatory process that occurs in the mucous membrane of the bronchi. It can also be chronic or acute, caused by viruses, bacteria and chemical irritants. Signs of acute inflammation of the bronchi often occur against the background of an inflammatory process in the larynx and trachea. A specific sign of this pathology is the presence of attacks of dry or wet cough.
Bronchial asthma
The risk group for this disease includes both heavy smokers and people suffering from allergic diseases. The main reasons for the development of bronchial asthma include:
- allergic reaction;
- use of certain medications;
- consumption of certain foods;
- the presence of increased physical activity;
- use of food additives;
- nicotine abuse.
Pulmonary edema
In this case, there is an accumulation of excess tissue fluid in the lungs and its sweating into the lumen of the lung tissue. This occurs due to high pressure in the pulmonary vessels or damage to the lung tissue, it depends on the type of pulmonary edema. Pulmonary edema often occurs as a complication of cardiac pathology and in most cases is associated with heart failure.
Other causes of pulmonary edema include:
- pneumonia;
- thrombosis of pulmonary vessels;
- kidney diseases;
- liver diseases;
- presence of extensive burns.
During the examination, the patient often exhibits symptoms such as rapid breathing and an accelerating pulse. In addition, when listening to a patient, the doctor often detects the presence of abnormal sounds and swollen neck veins.
If the pathological condition of the lungs is acute, then the following symptoms are observed:
- labored breathing;
- coughing;
- secretion of sputum (foamy) with blood;
- increased heart rate;
- bluish skin;
- increased sweating.
Considering that the heart begins to pump a small amount of blood, the (blood) pressure decreases and the patient’s pulse takes on a thread-like character.
We provide first aid
It is very important to remember that even minor swelling of the throat can lead to death. For this reason, it is necessary to clearly know not only the main symptoms when the throat is swollen, but also the rules of first aid:
- call an ambulance;
- rinse the stomach with a solution of potassium permanganate or just water if the allergy is caused by food;
- drink activated carbon;
- if the problem is caused by an insect bite, you need to remove the sting and apply a tourniquet to prevent the spread of the allergen (poison);
- if possible, place the person on the floor and place something like a pillow under his feet;
- make sure that the tongue does not roll back, provide the person with air;
- apply something cold to your throat - this will help relieve swelling and inflammation a little;
- drip a vasoconstrictor drug into the nasal cavity;
- give an intramuscular injection of an antihistamine or give a medicine to drink;
- Until doctors arrive, drink more plain water.
Effective treatments
Surgical
If a person’s general condition rapidly deteriorates, attacks of suffocation begin, and a tracheostomy is performed. The main goal is to make a small incision in order to form the so-called anastomosis of the trachea and its surrounding tissues.
This method is carried out using a special tube, which is directly inserted into the trachea.
Only a specialist should perform a tracheostomy.
Medication
To carry out drug therapy, you need to know which allergen caused such a violent reaction. Occasionally, after several days after the first signs of the disease, slight swelling goes away on its own, but more often the swelling can only be removed with the help of doctors and the necessary medications.
The first task of drug treatment for allergic laryngeal edema is to remove it as soon as possible and normalize breathing. To achieve this, the following measures are being taken:
- Parenteral use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs (Penicillin, Cephalosporin).
- Use of antihistamines by injection (Zyrtec, Tavegil).
- If there is no positive effect, corticosteroid hormones (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) are administered.
- Doctors often use dehydration drugs intravenously or intramuscularly (Veroshpiron, Furosemide).
General recommendations:
- Maintain bed rest for the entire treatment period.
- Follow the course of taking antihistamines.
- Minimize contact with the allergen.
- Use prescribed antihypoxants and antioxidants.
- Stay warm all the time; on the recommendation of a doctor, you can put mustard plasters on the calf area.
Inhalations using adrenaline and ephedrine cope well with edema.
Folk
Folk remedies can only be an addition to the main treatment of allergic edema. They are recommended to be used after consultation with a doctor.
Some useful recipes:
- Gargling frequently with a baking soda solution. To prepare this product, you need to take one teaspoon of baking soda and stir it in a glass of warm water. The procedure must be carried out until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
- For rinsing purposes, you can use tinctures based on various medicinal herbs such as chamomile and calendula.
- A mixture of carrot juice and honey. You can take 100 milliliters orally three times a day. Must be consumed immediately after preparation.
- In order to reduce the area of damage, you can periodically apply ice wrapped in gauze or a thin towel to the neck.
- To remove the disease, you can take rosehip decoction without sugar and honey instead of tea. This method will help quickly eliminate all signs of allergies.
Traditional recipes for treating nasal swelling
The cause of swelling of the nasopharynx can be cured using folk recipes. But they must be used with caution and under the strict supervision of the attending physician. It is advisable to consult a doctor before use.
Alternative medicine methods for the treatment of infectious and allergic inflammation of the nose:
- Relieves swelling by rinsing the nasopharynx with saline solution. Dissolve 25 g of table salt in 150 ml of warm water. Stir until the salt crystals dissolve. The temperature of the solution should be comfortable for the mucous membrane. To rinse your nose, you need to take a syringe without a needle, draw up the solution and rinse each nostril one by one.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, eucalyptus, sage) are also used to rinse the nasopharynx, provided that they do not cause an allergic reaction. Baking soda is effective. It kills germs and washes away accumulated mucus from the mucous membrane.
- For sore throat and sore throat, gargling with herbal decoctions and soda is useful. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, tablets (Strepsils, Hexoral or Doctor MOM) are dissolved.
- Cut off an aloe leaf and mash it, mix with a teaspoon of honey until smooth. Place 2-3 drops into each nostril. After 20–25 minutes, the swelling should go away.
- An effective remedy for eliminating the symptoms of the inflammatory process is Kalanchoe juice. Mash the freshly cut leaf, squeeze out the juice and put it into a pipette. Place a few drops into your nose.
For therapy, you need to use only proven traditional medicine recipes. Otherwise, the disease may worsen and the condition will only get worse. It is better to immediately consult a doctor rather than treat yourself.
We don’t give the problem a chance to exist.
In order to prevent swelling of the airways, it is necessary to avoid any contact with the allergen. It is important to carefully read the instructions for any medications. We must not forget about strengthening the immune system.
For prevention purposes, you should adhere to the following simple rules:
- drink enough water;
- avoid severe stress;
- maintain a daily and sleep schedule;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- eat only healthy foods;
- Do light exercise every day.
It is important for allergy sufferers to be examined by an allergist-immunologist at least once a year, even if the throat usually does not swell with a negative reaction to irritants.