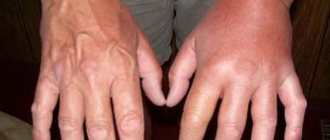
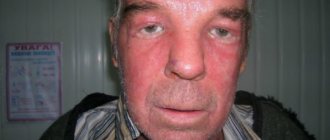
Symptoms
If the eye is swollen and red, but there are no other symptoms, the most likely cause is external factors, dust, wind, rain or sun. Under such conditions, there are no other symptoms other than lacrimation.
Depending on the cause of the disease, the following additional signs may appear:
- Itchy, gritty eyes and soreness are common signs of a condition called conjunctivitis. It is important to distinguish these signs from deep pain that occurs inside the visual analyzer, which indicates a more serious illness. For example, increased intraocular pressure or iritis.
- Nasal congestion, sneezing and watery eyes indicate allergic conjunctivitis. Increased sensitivity to light appears.
- A sore throat, general malaise, nasal congestion and watery eyes are associated with a cold or viral conjunctivitis.
- Vision is temporarily impaired if the cornea is obscured by fluid or pus. With conjunctivitis, visual perception does not change. Loss of acuity is often accompanied by pain in the eye, but there are exceptions such as blockage of blood vessels or hemorrhage.
Other signs include asthenopia, pain, burning, proptosis, and headache.
Photo
Types of edema
Swelling of the right and left eyes may have different origins and locations. First of all, let's talk about tumors that appear against the background of mechanical damage.
Swelling of the eye after a blow
With facial injuries caused by a blow, swelling and bruising occur in more vulnerable and tender places.
These include the area around the eyes. If the visual organs were not specifically damaged, then the swelling does not pose a danger.
The vessels and capillaries under the eye are not protected, so if damaged, hemorrhage occurs
Most often, the blow does not fall on the eyeball itself, but despite this, the tumor spreads to the area around the visual organ. Swelling does not always occur immediately after injury; it may even take several hours. Depending on the condition of the tissues and blood vessels, as well as the functioning of the regeneration mechanism, the tumor can resolve even without the use of special means.
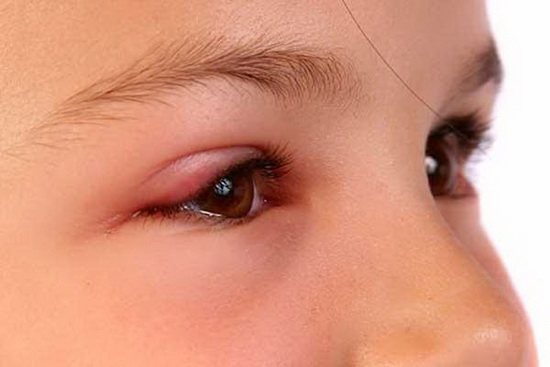
Traditionally, three to four weeks are required for complete recovery.
The first and most basic thing you should do after a blow is to apply something cool to the injury site. This could be frozen food, ice wrapped in cloth, or a heavy iron object. Cooling promotes the most accelerated blood clotting, so it will be released from the capillaries to the least extent.

Swelling of the eyeball
The corneas are responsible for accurately seeing objects. When the shell given to us swells, problems with light refraction appear.
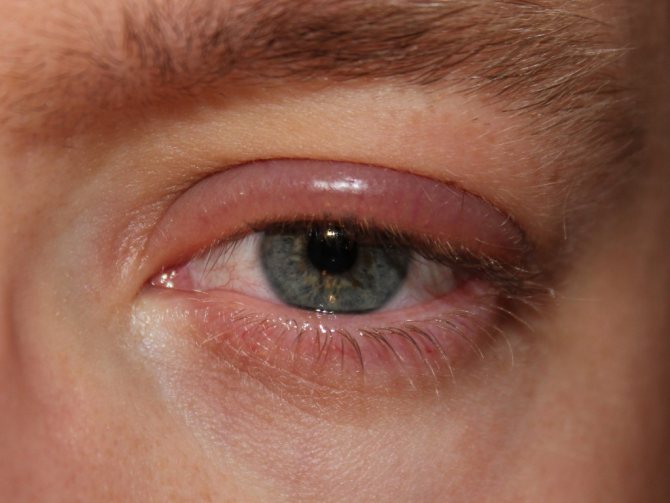
This causes the following symptoms:
- pain;
- photophobia;
- blurred vision;
- decreased visual acuity;
- distortion of objects;
- clouding of the eyeball;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body.
The following pathological processes can cause swelling of the protein:
- uveitis;
- glaucoma;
- injuries;
- allergy;
- viral and bacterial lesions of the visual organs.
Sometimes the eye becomes swollen after surgical interventions or incorrectly selected contact lenses.
In some cases, pathological changes in the cornea are asymptomatic, which is why the person is not even aware of the problem.
Macular edema
The macula, or yellowish spot, is a small element that is responsible for central visual perception. Swelling in this part for us develops against the background of ophthalmological diseases or injuries. The problem is reversible and has a suitable prognosis. But in the absence of timely treatment, the situation can end in complete loss of vision.
At the initial stages of the pathological process, clinical symptoms may be completely absent.
In some cases, the patient experiences a short-term loss of central vision. This phenomenon lasts only a few seconds, which is why it is most often ignored.
In the initial steps, conservative treatment may bear fruit. Clients are prescribed hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs. In languid versions the operation is shown.
Causes of a swollen eye
If the eye is swollen and watery after hypothermia, due to prolonged work at the computer or due to chapping, there is no serious cause for concern.
It is worse if these signs appear due to the development of an inflammatory or infectious pathology. In this case, suspicion falls on the following diseases:
- Contact allergy. Dust, pollen, or pet hair getting into the eyes can cause minor irritation that leads to swelling. If there is no general allergic reaction, swelling and itching will go away on their own.
- Eye irritation. If particles of makeup or dirt get into the eye, it irritates the eye socket. Manifested by redness and swelling.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the glands at the edge of the eyelid. The condition is usually associated with seborrheic dermatitis or allergies, in the latter case conjunctivitis may be seen. With blepharitis, peeling is pronounced, and the degree of redness depends on the severity of the disease.
- A chalazion is an enlargement of the sebaceous gland. Typically affects only the right or left eye. It looks like a small mound.
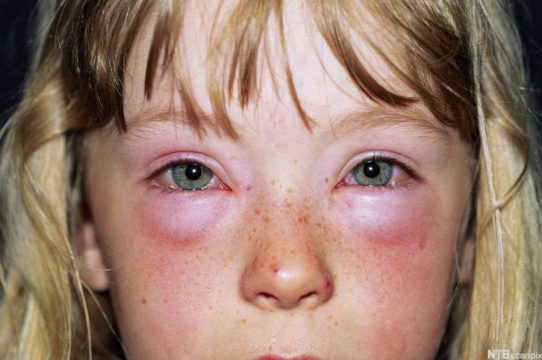
- Conjunctivitis is the most common cause of redness and swelling. It affects both visual organs. In both allergic and infectious diseases, the protein is red, hyperemia spreads to the inner surface of the eyelids. If you pull the eyelid down, you may see a red and swollen conjunctiva. In the infectious form, purulent discharge is observed. A common cause is Staphylococcus aureus.
- Iritis is inflammation of the iris. More often the disease is unilateral. Other structures are involved in the process; when the ciliary body is involved, iridocyclitis develops. Symptoms include blurred vision, redness, swelling, and blurred vision.
- Shingles is the same virus that causes chickenpox. In rare cases, a facial rash may appear, causing the eyes to become red and swollen.
- Orbital cellulitis is an infection of the tissue behind the orbital septum. Affects the eyelid, cheeks and eyebrows. The eyes become very swollen, the conjunctiva becomes red. The development of the disease begins with one organ of vision and gradually moves to the second.
- Preseptal/periorbital cellulitis - Like orbital cellulitis, this is an infection, but it occurs around the outside of the eye rather than in the internal tissues. Accompanied by pain and increased body temperature.
- Hypothyroidism is an underactive thyroid gland. Causes fatigue, weight changes, eyes become swollen and congested.
- Graves' disease is the opposite of hypothyroidism. The condition involves an overactive thyroid gland caused by an immune problem. Protruding eyes, double vision, anxiety, weight loss and rapid heartbeat are all symptoms of Graves' disease that can only be diagnosed by a medical professional.
- Systemic disorders (preeclampsia, kidney disease, cardiovascular disease and liver failure) - lead to swelling and fluid retention in the body. Diseases affect the entire body.
- A subconjunctival hemorrhage (caused by a ruptured blood vessel) appears as a red spot and can completely cover the white of the eye.
Causes and treatment of eyeball swelling
Due to some external influences or pathologies, swelling of the cornea occurs, which leads to unpleasant and painful symptoms.
By finding out the causes and coordinating the treatment of swelling of the eye mucosa, there is a chance to get rid of the problem and restore vision. Treatment is not easy, especially if it occurs against the background of glaucoma.
And if a person values one of his senses, he should visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Symptoms of edema
In the visual organ there is no mucous membrane similar to the one that lines the internal cavities. When talking about swelling of the mucous membrane of the eyeball, we are talking about the cornea, formed by the inner surface of the upper and lower eyelids and conjunctiva.
When the cornea edema, the state of the organ of vision changes: the tissue thickens, folds and compactions form, which disrupts the normal refraction of light. During this process, the following metamorphoses occur:
- distortion of objects in the field of view;
- decreased vigilance;
- a feeling of fog before the eyes;
- reaction to exposure to bright light;
- feeling of sand or foreign body;
- corneal clouding;
- pain;
- spider veins or redness of the conjunctiva.
With secondary infection, purulent discharge is possible along with swelling. Sometimes there is dryness of the cornea and peeling of the skin of the eyelids.
Note: With swelling, pain in the eyes is not always pronounced, which makes diagnosis difficult. Redness is noticeable on the eyeball and upon careful examination there is a violation of the structure of the cornea.
Causes of swelling in the eyeball
The causes of swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye are different. Unilateral swelling is possible as a result of injury to the eyeball, the development of dry conjunctivitis, and manifests itself as a consequence of surgical interventions. Bilateral edema occurs after a hypertensive crisis or a fracture at the base of the skull.
Infections of various kinds
Inflammatory diseases of the eyeball can cause microorganisms that settle on the conjunctiva, capturing the cornea area and causing swelling.
Bacteria or viruses quickly infect both eyes and are easily transmitted from person to person.
Swelling of the white of the eye occurs under the influence of streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, viruses, fungi, and the normal microflora of the cornea is replaced by pathogenic ones.
Inflammation and swelling of the conjunctival mucosa is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the eyeball visibly swells due to inflammation;
- irritation from bright light is expressed;
- white or yellowish discharge from the eyes is observed;
- blurred vision, poor visibility.
The main symptoms of conjunctival irritation are a feeling of pain and the discharge of pus, which causes the eyelids to stick together in the morning. The infection is accompanied by redness due to dilated vessels of the eyeball.
The following can cause conjunctivitis and edema:
- microtrauma of the eyeball;
- violation of eye care rules;
- low immune defense;
- infectious lesions of the nasopharynx.
Violation of hygiene rules when wearing contact lenses can also provoke infectious swelling of the eyeball. But the most unpleasant thing is that the infection manifests itself through purulent discharge, which can be quite copious.
Principles of treatment of edema
Treatment of swelling of the eye mucosa begins with finding out the cause of the development of the pathology. Even knowing the nature of the disease, be sure to consult with an ophthalmologist. The disease is diagnosed, as well as the removal of the discharged contents of the eyeball (tear fluid, purulent discharge, film on the surface of the cornea).
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor draws up a treatment plan:
- In case of infection, antibiotic drops or antibacterial ointments are administered: Albucid, chloramphenicol ointment. For viral infections, Acyclovir and Zovirax are prescribed. If purulent discharge appears, the eyes are washed with a solution of potassium permanganate and furacillin.
- If the inflammation is not caused by an infection, then treatment involves eliminating the inflammation itself and relieving swelling. In this case, non-hormonal decongestants are used: Indanazoline, Xylometazoline, Tetrizoline, Naphazoline. They cause vasoconstriction and reduce swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose, throat and eyeball.
- For allergic eye swelling, antihistamines are prescribed and allergy tests are performed, identifying a compound that can cause a negative physiological reaction. It is important not to come into contact with the allergen during treatment. Antihistamine and desensitizing drugs include: Claritin, Cetrin, Tavegil, Suprastin.
First aid for edema of various etiologies
If there is sudden and rapid bleeding of the eyes, the likely cause is an allergy. A cold compress is applied to the eyelids, the patient is given an antihistamine and as much fluid as possible. Useful activated carbon to remove the allergen from the body. With allergies to the eyes, Quincke's edema often develops, which is especially dangerous.
How to relieve swelling of the eyes due to a bruise? Any cold substance is applied to the wound site, for example, ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle of cold water. This leads to rapid blood clotting and the formation of a smaller hematoma. They use badyaga (water moss), which quickly relieves swelling from the eyeball. The product can be used for bruises and bruises under the eyes.
Note: If the cause of swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye is stress, insomnia, tears, or a cold, then cosmetic procedures will help solve the problem of dull eyes: massage, masks, compresses.
Traditional medicine in the fight against edema
How to remove swelling and swelling, how to relieve corneal irritation? If the eyeball is slightly damaged, but swelling causes unpleasant symptoms, use folk remedies:
- eyes and eyelids are washed with an infusion of black, cold tea, which is a good antiseptic;
- a compress of grated, raw potato gruel is applied to the eyelids, which can alleviate the condition and alleviate the pain of swelling;
- washed with warm infusion of propolis or honey if the cornea is injured;
- apply lotions to the eye socket area from infusions of chamomile, linden, and sage; lotions provide relief from inflammatory processes caused by conjunctivitis.
You can try infusions of agrimony, cornflower, dill seeds, and aloe juice for swelling on the eyeball. The number of “grandmother’s” recipes is simply huge, but this is not a panacea for all ills. An examination by an ophthalmologist is required to determine the stage of the disease and its course.
Postoperative period
After eye surgery, the mucous membrane of the eye remains swollen for some time. This condition causes certain inconveniences. To make eye swelling go away faster, you should listen to some tips:
- During sleep, the head should be higher than the level of the legs so that blood flows away from the organs of vision.
- Reduce the number of television viewings, reducing eye strain.
- Use dark glasses in the sun to avoid causing inflammation of the cornea.
- You should not visit saunas, steam baths, or swimming pools, as this can cause additional infection.
- Limit any physical activity while the recovery period is underway.
Sometimes in the postoperative period swelling of the fundus occurs. At the same time, fluid accumulates in the organs of vision and image clarity is lost. Treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at restoring blood microcirculation and outflow of ocular fluid.
Prevention against swelling
To avoid swelling, it is important to follow some rules:
- choose hypoallergenic cosmetics from reliable manufacturers;
- use protective equipment in the sun and during work hazardous to eyesight;
- after forty years, undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist due to age-related changes;
- choose the right contact lenses based on the recommendations of specialists.
Massage and a set of exercises help relieve swelling caused by an irrational lifestyle. But for serious pathologies, these measures are ineffective. In some cases, hospitalization and drug treatment are necessary.
Conclusion
If swelling of the eye mucosa occurs, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. The consequences of self-medication or inaction will affect the quality and acuity of vision. Do not underestimate the disease, which can lead to subsequent complications. And then there is a chance to maintain sharp vision and observe the world around us in bright colors.
Causes and treatment of eyeball swelling Link to main publication
Source: https://OtekOff.ru/otek/otek-litsa/otek-glaznogo-yabloka
Treatment
Seek help if symptoms do not go away within 2 days or new signs appear. If redness and swelling do not go away within 1 week using home remedies, consult an ophthalmologist. Some chronic diseases do not cause other symptoms and continue to progress.
Antibacterial eye drops and ointments
The preferred treatment for infectious conjunctivitis is Chloramphenicol. Active against bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci and Haemophilus influenzae and should improve the condition within 48 hours and completely eliminate a simple infection within 5 days. Chloramphenicol is sold as eye drops or ointment to treat acute bacterial conjunctivitis in adults and children over 2 years of age.
The use of antibacterial drops is effective against viral infections. They will prevent secondary bacterial infection, eliminate redness and swelling. Propamidine is also used for conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
Contact lens wearers should take care to ensure that infection is not caused by the lens itself. Lenses must be removed for the entire period of treatment with antibacterial drops, as they can cause the development of keratitis.
Soft lenses also cause preservatives to build up, resulting in increased irritation. An eye ointment containing dibromopropamidine is prescribed for use at bedtime to treat conjunctivitis.
Scales or pus stuck to the edges of the eyelids are removed with antibacterial eye ointment and by rubbing the edges of the eyelids with diluted, non-irritating baby shampoo.
Other anti-inflammatory drugs
The cause of allergic conjunctivitis, such as pollen or cosmetics, should be identified and, if possible, eliminated. Symptoms are mediated by histamine receptors in the mucous membrane of the eye.
The use of eye drops containing either a single antihistamine (Levocabastine) or a combination (Antazoline) along with a vasoconstrictor (Xylometazoline) is effective in providing rapid symptomatic relief.
If nasal symptoms are present, as in allergic rhinitis, oral antihistamines should be taken in addition to eye drops.
Eye drops containing sodium cromoglycate, a mast cell stabilizer, provide symptomatic relief of allergic conjunctivitis caused by seasonal allergies. Use 4 times daily to maintain their effectiveness.
Other treatments
If blepharitis is associated with seborrheic dermatitis, treatment of the skin disease may be carried out simultaneously with topical treatment of the eyelids.
If you suspect a blockage of the nasolacrimal duct (as with excessive tearing), you can try to relieve the problem by pressing one finger on the tear sac in the inner corner of the eye and gently massaging the duct underneath it.
In general, people should be reminded to take reasonable steps to reduce irritants from environmental factors such as dust, cosmetics, smoke and chlorine in swimming pools.
How to quickly remove puffy eyes
The following procedures will help relieve swelling from the eyes:
- folk remedies, mainly contrast and salt compresses;
- pharmaceutical preparation - Lyoton gel, used for severe swelling, applied in the form of a thin layer on the surface of the eyelid;
- Torasemide tablets, a diuretic, are prescribed according to the recommendations of doctors; use during pregnancy is prohibited.
How to relieve swelling from the eye after an injury
Swelling of the eye after an impact occurs due to rupture of blood vessels. The affected area swells and hurts.
If a person is hit hard and a bruise or hematoma appears, you need to apply something cold to the area of the bruise or swelling. An excellent “medicine” in this case is an ice cube. It is best to wrap a piece of a cold object in a rag and apply it to the eye like a compress.
How to remove swelling from the eyes after crying
In this case, it is possible to quickly remove swelling from the eye area using the same ice. Folk remedies, which will be discussed in the section below, will also remove the unfortunate swelling after tears.
How to quickly relieve swelling of the eyes after alcohol
Massaging the swollen area for 15 minutes will help quickly relieve swelling from the surface of the eyes after drinking alcohol. After massage actions, blood circulation is restored and swelling subsides.
How to quickly relieve swelling of the eyes
Visine drops and folk remedies help to quickly remove swelling from the eye area. The main components for preparing a folk remedy against swollen eyelids
- cucumber;
- potato;
- chamomile infusions;
- greenery;
- massage the affected area;
- exercises.
Traditional medicine based on such components not only removes bags under the eyes, but also prevents the appearance of swelling.
Prevention
To prevent your left or right eye from becoming too swollen before going to the doctor, it is recommended to take measures to help avoid worsening the condition. These same measures are a preventive measure against re-swelling and hyperemia. These include:
- maintain a sleep schedule;
- do not drink a lot of liquid after 18.00;
- remove makeup before going to bed;
- take breaks from work.
This condition can be prevented if eye diseases are treated promptly.