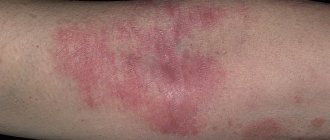
Fungal dermatitis is a chronic infectious skin disease. As a rule, inflammation is recurrent in nature with localization on the scalp and smooth surfaces of the skin.
Sometimes dermatitis has an allergic type of development, accompanied by characteristic symptoms that complicate diagnosis.
Causes and risk factors
For the development of the disease, a combination of two factors is necessary: the presence of a pathogen and conditions predisposing to the appearance of dermatitis.
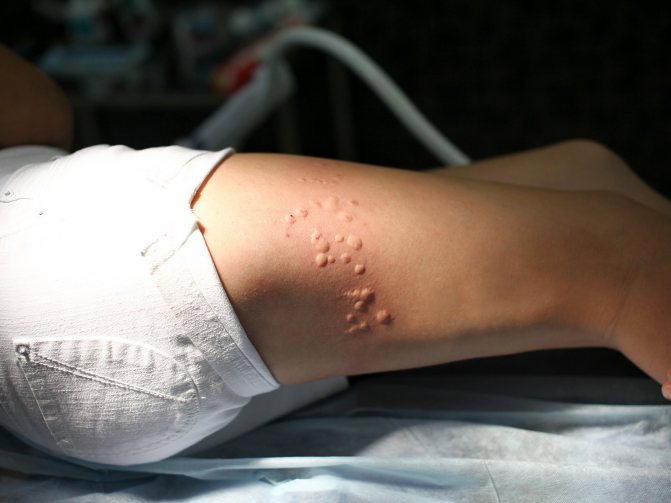
There are a great variety of fungi that can cause disease. Among the main culprits are:
- yeast-like fungi Candida . Conditional pathogens live under normal conditions on the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina and intestines. They cause inflammation only when immunity is reduced and the integrity of the integument is compromised. They are causative agents of candidiasis dermatitis, mucosal candidiasis (thrush), perianal fungal dermatitis;
- trichophyton . Pathogenic fungi of this genus cause trichophytosis of the skin and scalp, sycosis, rubrophytosis, favus;
- microsproroom . This fungus is responsible for the development of ringworm (microsporia) in children and adults.
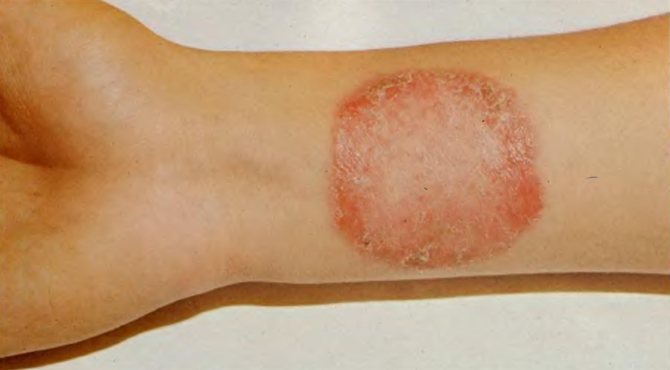
During normal functioning of the immune system, dermatitis pathogens are not able to penetrate deep into the skin. For the disease to develop, the presence of certain provoking factors is required:
- Regular, long-healing damage to the skin. This phenomenon can be observed with constant exposure to irritating substances, mechanical friction, strong high and low temperatures. Any skin disease accompanied by microtrauma and inflammation can be complicated by fungal dermatitis. Excessive dryness of the skin caused by frequent use of soap or disinfectant solutions also leads to the appearance of cracks.
- High humidity. Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating) is in many cases combined with skin mycoses due to the fact that a warm, moist environment is necessary for the favorable development of fungi. It can also be achieved by wearing thick, non-breathable synthetic clothing and low-quality shoes.
- Long-term use of medications. With long courses of antibiotics, the normal microflora of the skin and mucous membranes dies, which allows fungi to actively colonize. By a similar mechanism, the situation develops when taking corticosteroid drugs. They disrupt the hormonal balance in the body, which aggravates the course of mycoses.
- Metabolic diseases. A classic example of a disease that is often complicated by fungal dermatitis is diabetes mellitus. It is characterized by disruption of the functioning of all body systems, including the immune system, as well as increased skin susceptibility to pathogenic agents.
- Immunodeficiencies of various natures. Mycoses often appear in people with HIV, as well as those who have undergone chemotherapy or radiation for oncology.
- Lifestyle. Constant stress, poor nutrition, and bad habits undermine the body's defenses, increasing its susceptibility to pathogens of skin diseases.
- Perianal fungal dermatitis in infants can be caused by prolonged exposure to a diaper soiled with feces, which compromises the integrity of the skin and leads to infection. The immune system of babies is too weak to resist pathogenic fungi.
How to cure allergic dermatitis
To cope with allergic dermatitis at home, in addition to identifying and eliminating the allergen, an herbal mixture that is drunk a quarter glass four times a day will help to overcome the symptoms of the disease. The folk remedy is prepared as follows:
- Take a teaspoon each of chamomile, string, viburnum bark, currant;
- four - licorice root;
- pour a liter of boiling water;
- leave for about an hour;
- filter.

The beneficial properties of this product are well known. It improves blood circulation, promoting healing, relieves irritation, and has an anti-inflammatory effect. It is important to make sure that tar soap will not cause allergic reactions. When treating dermatitis at home, a liquid composition is very convenient to use, which additionally includes concentrates of medicinal herbs.
Alcohol tinctures
Allergic (contact) dermatitis is popularly treated this way. Prepare a mixture: 1 teaspoon of lemon juice, 2 teaspoons of eggshell powder, 1 teaspoon of vodka (alcohol, moonshine). Twice a day you need to take a teaspoon of this remedy. The dermatitis will go away quickly.
Folk recipes suggest treating dermatitis of any etiology with celandine. There are many different recipes, but this one is the most suitable. Take 50 grams of fresh plant and 50 ml of alcohol. Celandine is ground in a meat grinder or using a blender. Squeeze out all the juice through cheesecloth and pour it into a glass bottle. Place the tightly closed bottle in a dark place. The juice must “ferment” for 7 days. The bottle should be opened daily to release any accumulated vapor. After a week, the juice must be combined with alcohol and the “compound” allowed to brew for another day. The prepared tincture is used to wipe the areas of dermatitis twice a day. The treatment is long-term. The minimum course of such therapy takes at least 30 days.
How to cure a disease with folk remedies
Treatment of contact dermatitis begins, first of all, with eliminating the cause of the disease. Classical therapy includes the use of antihistamines and corticosteroid ointments.
There are many folk remedies that will help cure contact dermatitis:
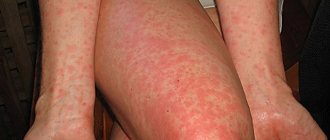
Contact dermatitis (simple dermatitis) is a type of allergic disease that manifests itself as inflammation of the skin when it is directly exposed to an irritating substance. Therefore, in medicine this disease is also called allergic dermatitis.

Its symptoms: swelling, itching, rashes on the skin in the form of blisters filled with liquid, redness of these areas of the body. In the future, weeping lesions and erosions may form. This type of dermatitis can occur when the skin comes into contact with physical irritants: temperature, radiation, current, friction, diaper rash, etc.
External remedies - baths and lotions
- At the first symptoms of the disease, you should prepare a bath with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (the water should be slightly pink). Next, you should immerse yourself in warm water and lie in it for at least 15 minutes.
- It is beneficial for the skin with contact dermatitis to take a bath with a decoction of oak bark. It will relieve itching, swelling and inflammation.
- For allergic (contact) dermatitis, you need to apply lotions to the areas of the skin affected by rashes - an infusion of strong tea. Thanks to tannin, which is part of black and green tea, itching, inflammation and swelling of the skin goes away. For weeping dermatitis, tea infusion has an antimicrobial and drying effect.
- Periwinkle helps in the treatment of contact dermatitis. You need to take a glass of well-dried leaves of the plant, grind them and pour 2 liters of boiling water. Next, put the composition in a steam bath and simmer for 10 minutes. The strained product is poured into the bath. The water procedure is carried out for at least 15 minutes. The plant mass is spread and compresses are made on the affected skin. During treatment, drink tea with lemon balm.
- For allergic dermatitis, you can relieve itching, inflammation and irritation of the skin with a decoction of birch buds. Take two tablespoons of plant material per glass of boiling water. Boil the composition in a steam (water bath). Wipe all sore spots with the prepared extract.
You need to take 40 grams of propolis and pour it with sea buckthorn oil (120 ml). Heat this composition in a “bath”, stirring occasionally. It is enough to warm up for 10 minutes. After this, the composition is allowed to brew and cool for another 20 minutes. Treatment: lubricate the sore spots or make applications on them, moistening the bandage in this product.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
Clinical picture of the disease
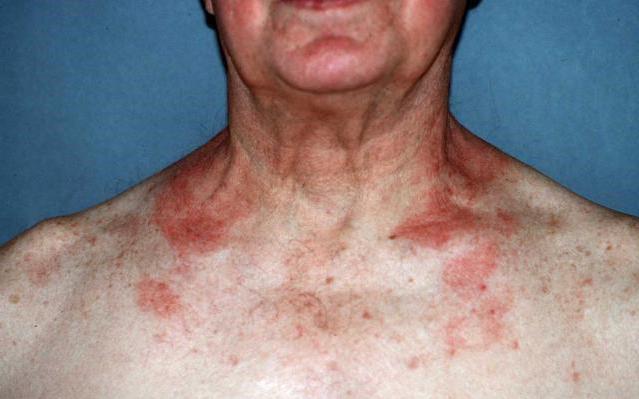
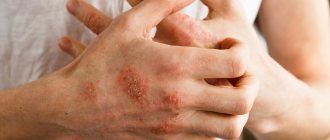
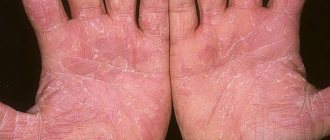
Despite the variety of pathogens and different localization of the lesion, fungal dermatitis, as can be seen in the photo, has a typical clinical picture. It is characterized by the spread of an itchy, allergic rash on red, flaky skin. The rash can be located either near the source of penetration of the pathogen or spread throughout the body. The elements of the rash are small blisters that open, forming crusts and weeping wounds.
Another characteristic symptom is clear foci of inflammation that tend to merge with each other. At the border of healthy and damaged epidermis, an inflammatory ridge of small bubbles appears.
Candidal dermatitis provokes the development of weeping areas - inflamed, swollen and moist areas of reddened skin. Other pathogens, on the contrary, increase peeling of the skin and contribute to the formation of crusts and scales. But at the same time, the overall moisture content of the skin always increases.
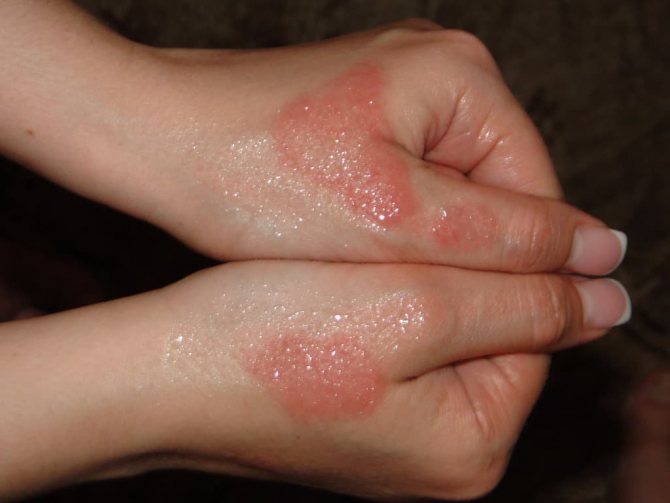
Inflammatory elements cause itching of varying degrees of intensity and a burning sensation. When the deep layers of the epidermis and dermis are affected, pain occurs. In advanced severe cases of the disease, a purulent bacterial infection or herpes virus may occur and symptoms of general intoxication may appear: fever, weakness, lack of appetite, drowsiness.
Fungal dermatitis can also occur in a chronic form (photo). In this case, the infection spreads to the skin appendages: the nails turn yellow and thicken, hair growth is disrupted and alopecia (baldness) occurs.
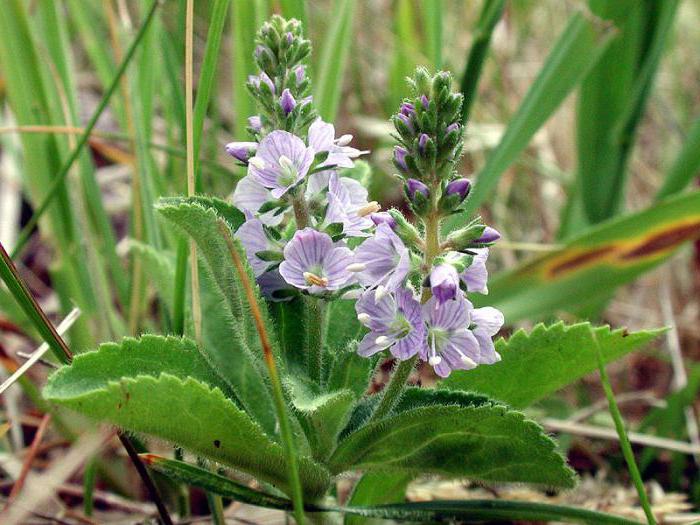
Veronica officinalis lotion
Treatment of atopic dermatitis with folk remedies in adults and children is impossible to imagine without the use of external drugs. They can also be made at home from medicinal herbs. For example, from the leafy tops of Veronica officinalis. This plant contains substances that help treat bronchial asthma, skin itching, and inflammation. The lotion is prepared as follows - 2 teaspoons of raw materials are placed in a glass or earthenware cup, poured with 2 cups of boiling water. The dishes are covered with a towel and left to cool and infuse at room temperature. Then the resulting infusion is filtered through cheesecloth and squeezed out. Using a cotton or gauze swab, apply this lotion to areas with rashes 5-7 times a day. This remedy is absolutely harmless, and can be used even by pregnant women and children.

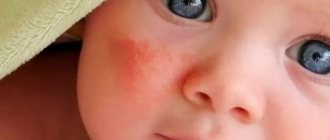
Manifestations in children
The most common mycoses in infants are candidiasis, seborrheic and perianal fungal dermatitis.
Fungi of the genus Candida infect the oral mucosa with the formation of a cheesy, whitish coating on the cheeks, tongue and gums. Hence the popular name for the disease – thrush. They do not cause discomfort to the baby.
- The seborrheic form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of greasy, yellow scales on the head, eyebrows, and sometimes on the face. They can cause itching and irritation of the skin;
- perianal dermatitis develops with prolonged wearing of soiled diapers, poor hygienic care of the baby's skin, and disruption of the digestive system. In the genital area, on the abdomen and thighs, hyperemic, merging spots appear. Large, fluid-filled blisters form under the skin, which soon burst, forming weeping wounds. The affected area hurts and itches very much, which affects the baby’s well-being. With extensive foci of inflammation, the general condition may deteriorate, body temperature rises, sleep and appetite are disturbed.
Non-infectious nature
You can get dermatitis not only in case of infection. This disease can be triggered by systemic diseases that occur in the body.
Allergic
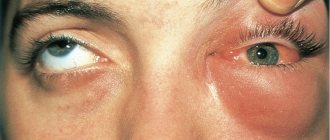
Allergic inguinal dermatitis is the most common non-infectious form. The disease can be caused by direct contact with an allergen (for example, when wearing synthetic underwear) or by eating certain foods, interacting with chemicals, pollen, etc.
Diagnostics
A dermatologist examines patients with suspected fungal skin diseases. The first stage of diagnosis is a visual examination of the affected skin and illumination of the lesions with a Wood's fluorescent lamp. Many mycoses give a characteristic glow. To determine the type of causative agent of fungal dermatitis, the method of microscopy of skin scrapings and the cultivation of fungi on special nutrient media are used.
To establish provoking factors, the patient is carefully questioned, and additional diagnostics are carried out to exclude immunodeficiency and metabolic diseases.
Treatment
Therapy for cutaneous mycoses consists of a combination of external and systemic antifungal drugs. Before carrying out treatment, it is necessary to establish the type of pathogen, as well as eliminate possible provoking factors.
External therapy
The most effective drugs for the treatment of various fungal dermatitis are imidazole derivatives (Clotrimazole, Ketaconazole, Miconazole) and allylamine (Terbinafine, Naftifine). They are produced in the forms of cream, ointments, shampoos and sprays for the convenience of treating different parts of the body and scalp.
In case of severe inflammatory process, it is possible to prescribe combined ointments containing antimycotic and hormonal components (Travocort, Dermozolon). When a bacterial infection occurs, agents that combine antifungal and antimicrobial effects are used (Betaderm, Triderm).
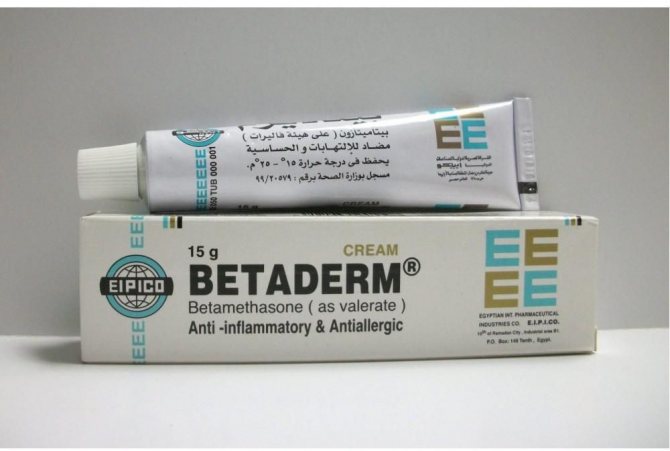
To disinfect weeping wounds, lotions of aqueous solutions of antiseptics are used: chlorhexidine digluconate, miramistin - and only then antifungal drugs are applied.
Systemic therapy
General antifungal agents are prescribed for extensive and deep skin lesions, as well as for hair involvement. The required drug and the regimen for its administration are chosen depending on the type and resistance of the pathogen and the severity of the process.
The most common drugs for the systemic treatment of fungal dermatitis are Griseofulvin, Itraconazole, Flucanazole, Terbinafine. These drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, because they have many contraindications and side effects; their incorrect use will lead to extremely adverse consequences.
To relieve itching and redness, antihistamines (Suprastin, Zyrtec) are used. For severe inflammation, a short course of corticosteroids may be used.
How to treat dermatitis at home
Folk remedies for combating dermatitis at home include herbal decoctions and teas for internal use to strengthen the body. For external use, oils, creams, ointments, and infusions are used. These folk remedies are used as:
- superficial application to problem areas;
- applications;
- lotions;
- compresses;
- baths;
- bandages.

Baths for dermatitis
An excellent healing effect comes from using baths to treat the skin, especially if a significant part of the body is covered with dermatic rashes. It is advisable to carry out the procedure every day for 15 minutes. After using them, itching decreases, peeling and redness disappear, and the skin becomes clean. You need to do at least 10 sessions, changing the composition for the bath. For cooking use at home:
- chamomile decoction;
- succession leaves;
- pine buds;
- oak bark;
- bay leaf decoction;
- Birch buds.
Baths with medicinal herbs effectively reduce the symptoms of dermatitis. You can pour 200 ml boiling water over two tablespoons of calendula, cook for 10 minutes, strain. Pour the composition into the bath. When treating dermatitis at home with folk remedies, the herbal composition perfectly relieves inflammation, itching, and irritation. The dry mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for two hours. According to the recipe it includes in teaspoons:
- nettle – 2;
- valerian – 2;
- cornflower – 3;
- chamomile – 3;
- oregano – 1.
Prevention
Basic measures to prevent fungal dermatitis:
- careful body hygiene;
- following a diet with a reduction in the amount of sugar, fatty and smoked foods consumed;
- long courses of antibiotics are combined with pre- and probiotic drugs to eliminate possible dysbiosis;
- preventive courses of antifungal drugs are prescribed if long-term use of hormonal drugs is necessary;
- identifying and eliminating the causes of increased sweating;
- control over chronic and immunodeficiency diseases, regular preventive examinations with specialized doctors;
- In infants, it is possible to prevent the development of fungal dermatitis by carefully caring for the baby’s skin, timely changing diapers and maintaining a properly balanced diet.
Inflammatory skin diseases caused by fungi can be effectively treated and disappear without leaving a trace if the first symptoms are quickly identified and timely contact a dermatologist.
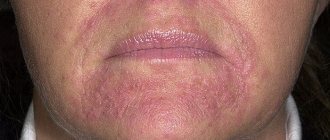
Forms of atopic dermatitis
So, more details. Atopic dermatitis is often associated with other chronic inflammatory diseases such as allergies. For example, bronchial asthma, hay fever, rhinitis. The complex of atopic dermatitis, hay fever (hay fever) and bronchial asthma is called the atopic triad. Medicine divides atopic dermatitis as follows:
- infant;
- children's;
- teenage.
This is a non-contagious disease that manifests itself in a person prone to it with a certain frequency. Medicine does not yet know a specific way to permanently rid a patient of this problem, and therefore therapy comes down to stopping exacerbations and prolonging periods of remission. Look how unattractive atopic dermatitis looks (photo). Treatment with folk remedies helps, in combination with traditional medical methods, to reduce the manifestations of the disease.