Asthma is considered a serious chronic disease. It develops due to non-infectious inflammation of the bronchi. The main symptoms of asthma are difficulty breathing during an attack, tension in the chest muscles, wheezing, severe coughing and shortness of breath.
Patients with bronchial asthma complain of a feeling of tightness in the chest and the inability to cough completely.
Causes
As described above, this type of asthma is infectious in nature.
The causes of the development of pathology are the simultaneous action of external and internal factors. The latter include pathogenic microorganisms. Untreated bronchitis under the influence of external irritants develops into infectious-allergic asthma. The main reasons for the development of the disease, which doctors identify, are:
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic infectious process in the bronchi;
- bad ecology;
- professional activities that involve the presence of aggressive substances in the air;
- lung diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- excess weight.
Often the allergens are bacteria themselves and other microorganisms. This mostly applies to mold fungi. They tend to release spores, which, when they enter the human respiratory tract, cause suffocation. Attacks occur when the patient is in a room with mold.
Also, infectious-allergic asthma can be provoked by a long course of drug therapy. In this case, the respiratory muscles become tense, and the patient constantly coughs.
Often external irritants are nervous stress or strong physical exertion. In this case, the patient suffers from a dry cough, however, by taking only mucolytics, the process of further progression of this form of asthma can be accelerated.
Allergens
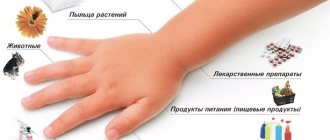
- Allergens localized in the room. Their source can be pets, insects, and fungi.
- Provocateurs located in open space. This list includes polluted air and pollen.
- Food. Antigens can be found in eggs, honey, some vegetables and fruits, milk, strawberries, peanuts and seafood.
Less commonly recorded are allergic reactions provoked by food irritants. It is quite difficult to cope with illness at home, so when the first symptoms appear, you need to call a doctor. If acute respiratory failure occurs, the patient is urgently hospitalized.
Respiratory tract infections
- infectious pathologies of the respiratory system;
- bad habits;
- bad ecology;
- poor nutrition;
- antisocial lifestyle;
- long-term drug therapy.
Heredity also matters. Asthma is not passed from parents to children. Only the appearance of a predisposition to the development of the disease is possible.
Based on the modern classification, there are several degrees of severity of atopic asthma, including mild, moderate and severe. The disease can move from the acute phase to the chronic phase in the autumn-summer period.
The first signs of bronchial asthma
The chances of successful treatment of the disease increase if the first alarming symptoms of asthma are recognized in a timely manner.
A number of early signs of a pathological condition include:
- shortness of breath, which can be disturbing at rest, during physical exertion, being in polluted air, in the spring during flowering vegetation, as well as when the ambient temperature changes;
- a dry cough occurs simultaneously with shortness of breath. By the end of the cough, a small amount of mucus is released, the cough becomes wet;
- shallow breathing and prolongation of exhalation. During this condition, it is difficult for asthmatics to fully exhale;
- Early asthma symptoms may also include wheezing and wheezing;
Sometimes it is not immediately possible to understand how asthma begins in adults, since the first symptoms may be vague. Over time they become pronounced. If the frequency of manifestations increases, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Etiology
Allergic bronchial asthma can develop as a result of many reasons.
- As a rule, atopic asthma is expressed by serious allergic manifestations, as well as a chronic inflammatory process of the upper respiratory tract. An obstructive process is observed in the bronchi, accompanied by suffocation, for which it is recommended to use an inhaler. Most often, atopic asthma appears if an unbalanced diet is used and the diet prescribed by the doctor is violated;
- Heredity is of great importance. However, it should be remembered that the medical history expresses only a predisposition to the appearance;
- the history of the development of allergic asthma may be complicated by infectious diseases of the respiratory system, which increase the sensitivity of the bronchial walls;
- An unfavorable environmental situation and activities associated with harmful substances can lead to an asthmatic attack. In addition, smoking in all its forms, including passive smoking, is not recommended. The history of medicine confirms the fact that smoking parents sharply increase the risk of allergic asthma in the baby;
- in some cases, the atopic form of bronchial asthma exhibits negative symptoms, which are provoked by poor diet and the presence of a large number of preservatives, aromatic and other additives. Therefore, if there is a predisposition to asthmatic manifestations, a special diet and careful handling of household chemicals are necessary.
An allergy attack with suffocation can increase during the interaction of the bronchial system with allergens, which are absolutely individual for each patient.nThe most common form of atopic bronchial asthma can be triggered by household allergens. There are often cases where atopic asthma occurs as a result of contact with fungal spores.
The main reason for the progression of the disease is immediate hypersensitivity. It is characterized by the rapid development of the disease as soon as the unfavorable allergen penetrates the human body. This entire process usually only takes a few minutes.
Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role in the development of this type of asthma. According to medical statistics, in 40% of cases, relatives of allergy sufferers have the same ailments.
The main factors contributing to the progression of atopic asthma:
- diseases of an infectious nature that affect the upper respiratory tract of a person;
- passive or active smoking;
- direct contact of the individual with allergens;
- taking certain medications for a long period of time.
In atopic asthma, the manifestation of symptoms occurs due to the fact that a person has been in contact for some time with allergens that entered the body during the act of breathing. Such specific substances can be divided into 4 groups:
- household This includes feathers from pillows, dust, etc.;
- epidermal. This group includes dandruff, bird feathers, wool;
- pollen;
- fungal.
Reasons for the progression of an attack of allergic (atopic) asthma:
- dust;
- smoke from fireworks, incense or tobacco;
- flavored substances included in perfumes, air fresheners, etc.;
- evaporation.
Pathogenesis of the disease

The mechanism of development of this disease has not yet been fully studied. But it has already been established that the reaction of the bronchi to an allergen occurs under the influence of various cells, structures and components:
- As soon as an allergen enters the body, special blood cells are activated. They produce active substances that are responsible for all inflammatory processes .
- The muscle mass in the walls of the bronchi of patients is especially predisposed to stable contraction, while the receptors located on the mucosa become susceptible to the effects of biologically active components.
- Due to these processes, bronchospasm begins, and at the same time, the lumen of the airways is noticeably reduced. In this case, the patient’s breathing is significantly impaired, severe shortness of breath occurs, which can be fatal.
Allergic asthma rapidly progresses, the condition of the asthmatic gradually worsens . A person with bronchial asthma is not difficult to recognize; he tries to take a comfortable position in which shortness of breath will be less pronounced.
Asthmatics very often feel that an attack of suffocation is approaching, usually this occurs within minutes after short contact with the allergen.

Allergic asthma occurs for a variety of reasons. Sometimes the cause of the disease is a combination of factors:
- Hereditary predisposition. Often, when interviewing a patient, you can find out that his close relatives suffer from allergic pathologies or bronchial asthma. Through research, it was revealed that if one of the parents suffers from allergic asthma, then the child’s chance of illness is 30% or more . When two parents are diagnosed with asthma, the child will get sick in 70% of cases or even a little more. You need to understand that allergic bronchial asthma is not inherited, children only receive a tendency to this disease.
- If a person often suffers from respiratory and infectious diseases, then the walls of the bronchi become thinner and become more susceptible to irritants.
- The disease often begins when the environment is poor in the place of residence or when working in industrial enterprises with large emissions of dust and other harmful substances.
- Abuse of tobacco products also leads to the development of the disease. Don't forget about passive smoking. People who smoke in the house significantly increase the child’s chance of developing bronchial asthma.
- Abuse of foods that contain a lot of preservatives, food colors and flavor enhancers.
Attacks of suffocation in allergic asthma begin after contact with some irritant. The susceptibility of each patient is individual, sometimes there are several allergens. The most allergenic substances are:
- pollen from vegetation, especially flowers from the Asteraceae family;
- particles of hair from different animals;
- fungal spores, mainly moldy;
- particles of house dust containing waste products of dust mites;
- cosmetics and some household chemicals, especially substances with a cloying odor that cause attacks;
- tobacco smoke and cold air.
Food rarely causes allergic asthma, but it does happen. The most allergenic foods are honey, chocolate, milk, eggs, nuts, crayfish, citrus fruits and tomatoes .
Dry fish food can trigger an asthma attack. If a person is predisposed to allergies, then the fish should be abandoned or fed with fresh food.
Clinical picture and symptoms
A person suffering from allergic (atopic) asthma is hypersensitive to certain specific allergens. If these substances penetrate the respiratory tract, they immediately cause a reaction from the immune system. The body “responds” to the allergen with bronchospasm - the muscle structures located near the respiratory tract contract sharply. Inflammation develops, and a large amount of mucus forms in the bronchi. The following are specific symptoms of allergic asthma:
- breathing accompanied by whistling;
- cough;
- chest pain.
The above symptoms most often occur when the body is exposed to the following allergens:
- mold spores;
- plant pollen;
- field tick excrement;
- wool;
- saliva particles.
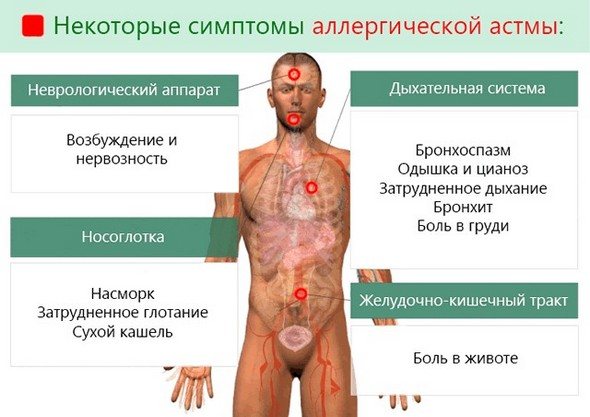
As a rule, at the first appointment, the doctor finds out the causes of the disease and characteristic signs. He is also interested in the patient's medical history. The symptoms of allergic asthma are not specific. They may not be different from asthma with a non-allergic etiology.
- First of all, asthma with a predominance of the allergic component is accompanied by paroxysmal cough, which does not provide relief. It remains possible that such symptoms arise as a result of concomitant diseases;
- when coughing, the release of a minimal amount of glassy (transparent) sputum with increased viscosity is typical;
- wheezing and asthma attacks due to allergies. Allergic asthma with shortness of breath appears a few minutes after direct contact with allergens, as well as during severe physical exertion. These symptoms result from narrowing of the airways through which air passes;
- asthma with a predominance of the allergic component forces the patient to take a specific position during an attack so that it can be relieved as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient rests his hands on a wall, table or window sill;
- Typically, atopic asthma lasts with varying frequency and duration, depending on the type of allergen with which contact occurs. For example, this allergen may be pollen from flowering plants, which is typical for seasonal exacerbations.
Severe symptoms require emergency care. If the attack is not treated, the patient may fall into a coma as a result of insufficient oxygen supply.
Symptoms of the infectious-allergic form of bronchial asthma develop as the provoking factors actively act. There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- At the first stage, the disease has all the signs of rhinitis: the patient feels severe discomfort and itching in the nose, suffers from frequent sneezing and congestion.
- Under the influence of external stimuli, the symptoms of the disease manifest. At this stage, there is severe shortness of breath, cough, difficulty breathing when exhaling, sputum does not come out, and the patient suffers from attacks of suffocation.
- At the stage of weakening of the symptoms of the disease, a productive cough with the release of large amounts of sputum is observed. The patient feels much better, suffocation and other unpleasant sensations disappear. As a rule, this stage is achieved only with the help of medication.

A peculiarity of the course of this pathology is that coughing attacks become more active at night, when the patient assumes a horizontal position. Because of this, he cannot get enough sleep and becomes irritable. Often the next morning your head starts to hurt badly, and other signs of fatigue appear.
It is worth noting that during an acute attack the patient’s temperature may rise slightly. After coughing, the patient has difficulty breathing, wheezing and chest pain are clearly visible.
If an allergen enters the body of a patient suffering from asthma, symptoms such as:
- cough;
- pain in the abdominal cavity;
- wheezing;
- chest discomfort;
- dyspnea;
- increased breathing;
- runny nose;
- bronchospasms;
- wheezing in the lungs. Dyspnea
The intensity of allergic asthma symptoms increases in the afternoon. The clinic varies depending on the type of illness. Intermittent asthma is quite rare. Persistent disease is activated much more often. This causes problems with sleep.
Atopic asthma of moderate severity provokes the appearance of general malaise. At this stage, the therapeutic regimen must include measures to prevent the development of serious complications. In severe forms, asthma attacks occur both during the day and at night. The patient practically does not rest, which causes loss of ability to work.
What is bronchial asthma
This disease can be diagnosed in people of different ages. To date, effective treatment programs have been developed to relieve asthma symptoms and relieve bronchospasm.
Patients with bronchial asthma show signs of airway obstruction for the following reasons:
- the lumen of the bronchi narrows due to spasm of smooth muscles;
- due to increased secretion production, clogging of the bronchi occurs;
- in the advanced stage, muscle tissue is often replaced by connective tissue.
Asthma with symptoms of suffocation in an adult reduces his ability to work.
Diagnostics
Allergy tests
- blood test for immunoglobulins;
- allergy tests;
- clinical study of urine;
- general and extended blood test;
- sputum microscopy;
- bac sowing
At the third stage of diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a chest x-ray and an ECG. Using the latter method, diseases of the cardiovascular system are excluded. If symptoms characteristic of atopic asthma appear, the patient should visit a general practitioner, allergist and pulmonologist. The child is examined by a pediatrician.
The infectious-allergic form of bronchial asthma is very difficult to diagnose. The doctor who treats her is called a “pulmonologist.” At the first symptoms, you should immediately contact him for advice. After a visual examination and history taking, the patient is prescribed a number of mandatory studies:
- laboratory blood tests to identify a possible infectious process;
- listening to the patient's breathing (a patient with asthma has a clear wheezing breath);
- bacteriological examination of sputum;
- allergy tests.
One of the informative diagnostic methods is peak flowmetry. Using a special device, the patient's breathing rate as he exhales is measured. In addition to basic research, it is very important to carry out differential diagnosis and exclude the presence of diseases with similar symptoms (pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, etc.).
It is worth noting that this disease is seasonal, and acute symptoms are observed in the cold season.

If a person shows signs of this disease, he should immediately contact a medical professional. institution. Such people are supervised by an allergist-immunologist and pulmonologist. It is important to identify allergens that trigger an asthma attack as quickly as possible. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed tests to determine sensitivity to allergens. After identifying the aggressive agent, treatment is prescribed.
How to treat allergic asthma?
Treatment of asthma should be carried out by a qualified specialist, since self-therapy with medications and folk remedies can only aggravate the course of the disease. To treat this type of asthma, the same drugs are used as for other types of disease, but it is important to take into account the allergic nature of the disease.
Timely intake of antihistamines can reduce the severity and manifestations of asthma. With the modern development of pharmacology, the drug market offers a wide selection of similar drugs, so finding a suitable medicine will not be difficult. Antihistamines block receptors, which is why either the release of histamine into the blood is completely absent, or its dose is so small that it does not provoke any reaction.
If a situation arises when it is impossible to avoid contact with the irritant, it is necessary to take an antihistamine in advance, then the risk of an acute reaction is significantly reduced.
- Modern medicine offers a technique that involves introducing an allergen substance into the body with a gradual increase in dosage. In this way, a person’s sensitivity to the irritant is formed, thereby reducing the risk of allergy attacks.
- The most common way to combat allergic asthma is the use of beta-2 adrenergic blockers and inhaled glucocorticoids. This is a basic treatment that promotes long-term control of the disease.
- Immunoglobulin E antagonist antibodies help eliminate the high sensitivity of the bronchi, as well as prevent possible exacerbations for a sufficiently long period of time.
- In the treatment of asthma in children, drugs from the cromona group of drugs are actively used. However, treatment of the disease with these drugs in adult patients does not bring the required result.
- For exacerbation of asthma, methylxanthines are used. They act very quickly by blocking adrenergic receptors. The active substances of this group of drugs are oral glucocorticoid and adrenaline.
Compared to medications, inhaled drugs that penetrate directly into the respiratory tract of a patient suffering from atopic asthma, using a special device, have a higher priority. At the same time, a therapeutic effect is produced. Another important advantage of inhalations is the absence of side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Atopic asthma can and should be treated, but the course of therapy must be structured in such a way that the characteristics of the course of the disease in a particular patient are taken into account. This can only be done by a qualified doctor, who, when prescribing, is based on diagnostic tools, clinical picture and medical history. Untimely or incorrect treatment increases the risk of developing pathological conditions in the body, as a result of which allergic asthma can take a severe form and lead to death.
In general, with a competent approach to treatment, a fairly favorable prognosis is offered. The main complications of atopic asthma are emphysema, heart and lung failure.
Degrees
Atopic asthma has 4 degrees of severity:
- intermittent. Symptoms of pathology progression appear no more often than once every 7 days. Attacks at night develop 2 times a month;
- persistent. Symptoms of the disease appear more than once every 7 days. A person’s daily activity, as well as his sleep, are disrupted because of this;
- average degree. It is characterized by daily manifestations of symptoms. Physical activity during the day and proper sleep are disrupted. At this stage, it is recommended to use salbutamol to prevent the disease from progressing to the next stage;
- severe degree. Symptoms are observed constantly. Choking develops 4 times a day. Attacks also often occur at night. During this time, a person cannot move normally.
The most dangerous is the progression of status asthmaticus. The attacks become more frequent and longer lasting. Traditional treatment is ineffective. Due to the fact that it is not possible to take a full breath, the patient may even lose consciousness. If emergency assistance is not provided immediately, death is possible.
Other types
One of the most important parameters taken into account when adjusting therapeutic methods is the body’s response to the treatment. Based on this, there are the following types of bronchial asthma:
- Controlled. FEV or PEF is normal, exacerbations are not observed. Changes for the better are recorded even in patients with moderate and severe severity.
- Partially controlled. Respiratory functions are reduced to 80%. Attacks occur more than twice a week, with at least one exacerbation every year.
- Uncontrollable. Here, the effectiveness of therapy is practically absent, which gives rise to a detailed study of the reasons for this reaction of the body.
Bronchial asthma, like many other chronic diseases, has two phases: exacerbation and remission (if there are no attacks for more than 2 years, it is called persistent). The possible presence of complications is also taken into account - respectively, complicated or uncomplicated forms.
Based on the above classifications, a clearly structured diagnosis is made. For example: bronchial asthma, mixed form, moderate severity, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis. This formulation greatly facilitates understanding of the etiology and course of the disease.
Treatment of the disease
Depending on what symptoms of the disease stand out, the allergist (immunologist, homeopathic doctor) can distinguish 4 stages of the disease, which determine the conduct of drug therapy.
1. Intermittent allergic asthma. In this form of the disease, asthmatic attacks are quite rare. During the day - no more than once every 7 days. During sleep - no more than twice a month. The attacks are very rapid and do not affect the physical condition of the patient.
2. Mild persistent. The disease worsens more than 1 time in 7 days (no more than 1 time during the day). At night, an attack can occur no less than 2 times within 1 month. In this case, the patient experiences insomnia and increased fatigue.
3. Persistent asthma (moderate). A daytime attack of the disease can be repeated every day, and at night - more than once a week. This is accompanied by a violation of the physical condition.
4. Persistent (severe). Night and daytime suffocation due to allergies recurs almost daily. The patient's activity after attacks of the disease is sharply reduced.
Allergic asthma is strictly prohibited from being treated at home. The therapeutic regimen is prescribed by the attending physician. He makes a decision taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the type of allergen. One of the main methods is allergen-specific immunotherapy.
Hyposensitization
Asthma is treated as follows: a diluted allergen is injected under the patient’s skin. As a result of multiple injections, the risk of negative symptoms is reduced. This phenomenon is called specific hyposensitization. The doctor must make adjustments to the diet and drinking regime. Diet is an essential part of the therapeutic complex.
Status asthmaticus is the most severe form of the disease, in which medications do not have the desired effect. While in this state, the patient may suffocate. The disease leads to dizziness and loss of consciousness. The result of such an attack may be disability.
To cure asthma, a complex of therapeutic measures is used. It includes a course of medication, physiotherapeutic procedures, breathing exercises and alternative medicine methods. At the first stage, the allergen is eliminated. On the second stage, manipulations are carried out, the purpose of which is to increase and strengthen the patient’s immune system. Thanks to combination therapy, the body produces blocking antibodies.
Humidity in living quarters for asthmatics should be no more than 50%. For this purpose, special humidifiers are often used. In addition, to achieve recovery, at home you need to:
- remove thick curtains and carpets;
- keep windows and doors closed during the flowering period;
- use air conditioners with filters that can be replaced.
Taking medications
Salbutamol
- Terbutaline, Salbutamol, Fenoterol - relieve suffocation;
- Tailed, Intal - stop the inflammatory process;
- Oxis, Pulmicort, Serevent - eliminate clinical symptoms.
The therapeutic regimen includes glucocorticoids and blockers that have a long-lasting effect. Antiallergic and hormonal agents are also used. In the treatment of allergic asthma, the medicine enters the respiratory tract through inhalation. The drugs used for this procedure are highly effective and have a minimal number of adverse reactions. Medicinal compositions are sold in the form of aerosols, sprays and tablets.
Ledum decoction
- wild rosemary;
- nettle;
- coltsfoot;
- Jerusalem artichoke.

A mixture of components such as hydrogen peroxide (35 drops) and water (100 mg) is also used. The folk remedy is taken 30 minutes before breakfast.
Form of physical effort
Many asthma patients notice an exacerbation after exercise. However, in many patients, physical effort is the main cause of the attack. If with normal obstruction suffocation begins at the moment of exertion, then in people with AVFN it follows 10 minutes after exertion.
Symptoms are moderate, lasting for 10-15 minutes, less often they can last up to an hour. According to research, the culprit of the pathology is irritation of the nerve endings, which provides innervation to the muscle tissue of the bronchi. Sometimes the reflex is caused by a temperature difference in the system, which occurs during intense inhalations. Attacks are rarely severe, but this does not eliminate the need for relief.
In addition to the traditional classification, there is a division according to the characteristics of the clinical picture:
- The allergic type is manifested by cough, lacrimation and redness of the eyes, rhinitis. After symptomatic therapy, the symptoms usually disappear and relief occurs.
- Severe asthma is typical for patients suffering after physical exertion. The cough begins suddenly, for no apparent reason.
- Nighttime manifestations are especially dangerous, as there is a risk of apnea; a person may suffocate in his sleep.
- The cough type is associated with an infectious lesion and is characterized by the presence of purulent sputum, intoxication and high fever.
In addition, the pathology is classified according to the severity of its manifestation:
- Stage 1 intermittent - attacks are short-lived, occur more than once a month, exacerbations are rare
- Stage 2 mild persistence – manifestations several times a week during the day and 2-3 times a month at night
- Stage 3 medium – daily attacks, insomnia, weakness, general malaise
- Stage 4 is severe - poorly controlled attacks, low patient activity, constant respiratory failure.
Also, asthma symptoms can be divided into periods:
Precursor
This is the pre-attack stage. It begins with sudden emotional swings - irritability gives way to apathy. The patient develops a runny nose, red eyes, and reacts to both habitual and atypical irritants. The skin becomes itchy, the person gets tired quickly and loses his appetite. Shortness of breath is accompanied by a nonproductive cough. The condition can last from several hours to 3-4 days.
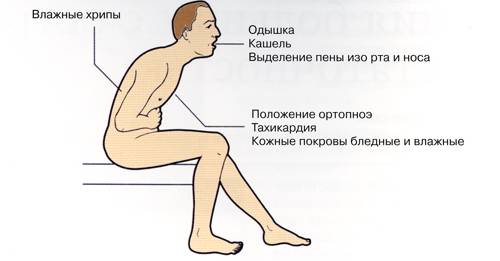
height
After asthma, there is a tightness in the chest, a feeling of lack of air. Exhalation is several times longer than inhalation. During breathing, wheezing and sometimes whistling sounds are heard. The patient's position is typical - the torso is tilted forward, the hands rest on a hard surface, the mouth is open. The nostrils are greatly dilated, the face is pale, with bluish spots. Cold sweat appears, the body is very tense. The muscles of the shoulders and peritoneum are involved in the breathing process.
The depression of the clavicular cavities and the lower part of the chest is clearly noticeable. The diaphragm moves in waves, the neck veins are swollen. When coughing, viscous sputum is produced. After evacuation of the secretion, the patient's condition improves. The attack can last several minutes, hours or even days.
This period ends with a reverse course, in which patients experience weakness, thirst and hunger. Difficulty in breathing persists.
Status
This is the most severe complication that can develop after a fever. It is not relieved by dilators, the mucous membrane swells, and bronchial patency is impaired. During a short inhalation, a much larger volume of air enters the lungs than a person can exhale. As a result, oxygen-filled tissues swell and the amount of carbon dioxide in the arteries increases. Due to constant spasm, muscles are overstrained. Regular heavy attempts to overcome resistance lead to deformation of the chest.
At the first stage of development, the patient is conscious. The symptoms are typical of a normal attack, but the absence of sputum indicates that the situation is worsening. The second stage is manifested by decompensation and metabolic disorders. The patient's reactions are inhibited, speech is incoherent or absent, and the pulse is weak. With the third degree of development of the status, coma occurs. The patient is unconscious, cerebral and neurological disorders are increasing. Blood pressure drops sharply, and the risk of death is high. Sometimes pneumothorax occurs.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of the disease, you should follow some simple recommendations:
- change synthetic underwear to natural ones;
- carry out wet cleaning of the house daily;
- do not have pets;
- It is better to cover window openings with a frame with mesh or gauze to trap dust;
- balanced diet. It is necessary to completely exclude fast food and semi-finished products from the diet. Food must be natural and contain the required amount of vitamins and minerals.
The most dangerous stages
A mild asthma attack causes only minor inconvenience, and the patient retains the ability to speak without much difficulty, making it easy to explain the situation or request professional help. At the middle stage, it is no longer possible to speak in full sentences, and one should not count on spontaneous cessation of shortness of breath, but the patient can still formulate a request for help. If a person only “squeezes out” individual short words or says nothing at all between waves of coughing, then he is in one of the most dangerous stages:
- Heavy. It is characterized by a transition to a forced position, refusal to move, pronounced shortness of breath (up to 30 breaths per minute), and an almost complete inability to talk. At the same time, a state of panic develops, body temperature drops (not always), and the heart rate jumps sharply (up to 120 beats per minute). The auxiliary muscles unsuccessfully try to compensate for difficulty breathing, and bronchial spasm intensifies over time. Potent drugs in high doses (Dexamethasone, Eufillin, etc.) are immediately prescribed to prevent progression to the next stage.
- Asthmatic status. The most dangerous condition that develops as a result of prolonged severe suffocation. An asthma attack completely blocks the functions of the speech apparatus and any physical activity. Consciousness becomes confused, a transition into a coma is possible. Respiratory movements are compensatory and uneven. The pulse drops to 60 beats per minute or less, while the condition remains the same, the costal spaces sink. Treatment at this stage requires promptness and great precision, therefore, after providing first aid measures (intense relaxants, adrenaline to restore heart rate and muscle activity, others depending on the condition), the patient is sent to the intensive care unit.
The danger can be fraught with both habitual “allergenic” and so-called nocturnal asthma. Even a hint of a transition to a severe stage should be enough to call an ambulance, especially if the patient has not previously encountered difficulty breathing. After neutralizing the threat to life and health, preventive treatment is selected.
Preventive measures
Ventilation of premises
- regularly clean and ventilate living spaces;
- avoid contact with allergens;
- take medications with antihistamine properties in a timely manner;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- exercise;
- Healthy food;
- promptly treat infectious pathologies;
- undergo a medical examination annually.
People suffering from bronchial asthma should carry an inhaler with them.
There are a number of rules, the implementation of which significantly reduces the risk of developing an infectious-allergic form of bronchial asthma in humans:
- avoid contact with potential allergens (smoke, animal hair, dust, etc.);
- Healthy food;
- avoid nervous tension and stressful situations;
- treat colds in a timely manner;
- regularly ventilate the room, do wet cleaning;
- At the first symptoms, do not hesitate to contact a specialist.
If there is a genetic predisposition to bronchial asthma, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures that are aimed at reducing the impact of external and internal irritants.
It is also recommended to avoid severe hypothermia and observe good personal hygiene, this will help prevent the development of asthma.
Forecast
It should be noted that bronchial asthma that appears in a person in adulthood is quite difficult to treat, and the prognosis in this case is less favorable.
Currently, medicine cannot cure asthma completely. This disease is chronic and you can only increase the intervals between attacks to make life easier for the person suffering from this disease. Currently, effective treatment methods have been developed that can extend the time of remission even by several years. To do this, you need to consult a specialist in time, undergo a comprehensive examination and receive an effective treatment regimen.
Carefully monitor your health, listen to individual symptoms and analyze. At the first suspicion of illness, contact a medical facility. Remember, at an early stage, treatment is more effective, and there is much more hope for a full recovery.