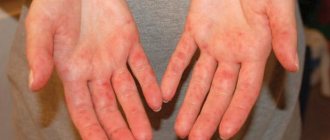
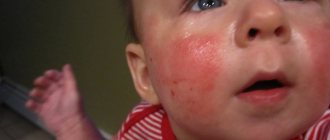
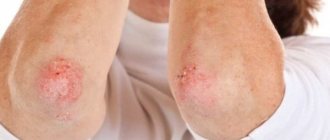
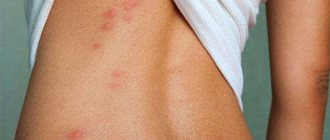
How is lichen different from dermatitis?
It is difficult to distinguish lichen from dermatitis on your own. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis after examining the test results. The difficulty is that the diseases are easy to confuse due to the symptoms: red, inflamed lesions and itching. In addition, do not forget that dermatitis and lichen are diverse, and each has a characteristic feature that can be distinguished by a specialist.
Treatment of deprivation in humans
At the appointment, the dermatologist first examines the clinical manifestations. Then he performs an inspection under a diagnostic device called a Wood's lamp.
Trichopetia is not visible under Wood's lamp, but Microsporia luminesces with an emerald glow. The next stage is laboratory diagnostics.
Hairs are either taken from the affected areas, or skin flakes are scraped from the lesions and the presence of spores or fungal mycelium is determined. Using this analysis, the type of mushroom is determined.
Dermatitis and pityriasis rosea
Dermatitis is usually called a group of skin diseases that appear due to the influence of a physical, biological or chemical factor. In other words, it is the skin's reaction to an irritant. Even a burn or callus is one of the manifestations of dermatitis. The group of diseases includes seborrheic, atopic (neurodermatitis), allergic dermatitis, and the list is far from complete. Symptoms occur in 2 directions - acute and chronic.
Ringworm is also a group of skin diseases that have different etiologies. Among the varieties, people most often suffer from pink and scaly ones. Tinea rosacea (Giber's disease) is a type of skin disease characterized by the appearance of pink spots. Unlike dermatitis, the nature of the occurrence of lichen is unknown. One of the reasons is weak immunity, since the disease often develops against the background of a cold.
Only a dermatologist can distinguish dermatitis from lichen after conducting appropriate skin scraping tests. It is also necessary to visit an allergist's office.
Common features
There are similarities in the symptoms of pityriasis rosea and atopic dermatitis. For reference: atopic dermatitis is a type of skin disease characterized by inflammatory skin lesions under the influence of an allergen. The disease is typical for children. Based on external symptoms, AD is confused with pityriasis rosea due to the following signs:
- skin redness;
- rash that bothers you with itching;
- inflamed areas that begin to peel off over time.
The development of diseases depends on the quality of the body's immune defense, and can become recurrent, especially during the spring-autumn period, when the immune system is weak and susceptible to colds. It is worth noting that atopic dermatitis and pityriasis rosea can resolve on their own without requiring treatment: in children by the age of 2 years, the symptoms of AD begin to decline and gradually disappear; in pityriasis versicolor, the onset period is up to 6 weeks.
Distinctive signs of lichen and dermatitis
Despite the general symptoms, the presence of a particular skin disease can be determined using the following factors:
Clinical variants of dermatitis
Manifestations of the disease can vary greatly from patient to patient, depending on the severity of seborrheic dermatitis. When only the scalp is affected, many struggle with ordinary dandruff and, in the case of using antifungal agents, solve the problem. However, it is not always possible to determine the etiology of the disease by external signs.
There are several forms of dermatitis, namely:
- eczematid is an uncomplicated form of the disease, characterized by mild hyperemia and minor itching;
- perinasal erythema is a “female” form of the disease, the symptom of which is yellow scales that form on the wings of the nose and in the area of the nasolabial fold;
- dermatitis of the auditory canal - a severe form of dermatitis, in which an erythematous rash occurs in the external auditory canal and behind the ears;
- dermatitis of the scalp is a type of dermatological disease in which a large number of yellowish scales stick together in the hair;
- Lichen asbestos is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by the formation of scabs on the scalp, which contribute to the development of alopecia.
The disease and its variety are not always easy to identify, so based on its external manifestations, the disease can easily be confused with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor or candidiasis.
Similar diseases
Psoriasis is a non-infectious skin lesion that affects only 5% of the world's population. Despite this, it is often confused with other dermatological diagnoses, because they all have similar symptoms and causes, but are treated completely differently.
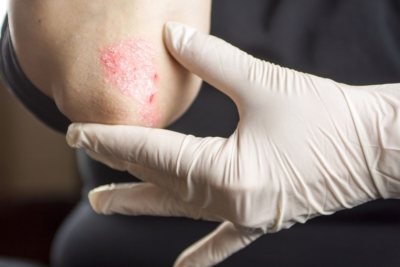
Can be confused with psoriasis:
- lichen;
- eczema;
- fungal infections;
- dermatitis;
- secondary syphilis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- skin cancer;
- seborrhea.
How is it different from other skin diseases?
With eczema, as with psoriasis, lesions appear on the elbows, knees, legs, and scalp more often than on other parts of the body. The affected area also itches, becomes inflamed, and the person experiences a burning sensation.
Distinctive signs of eczema:
- after peeling off the scales, bright red spots remain;
- weeping rashes;
- there are no clear boundaries of foci of inflammation;
- peeling occupy a smaller area;
- Mostly soft tissues are affected (inner bends of elbows, knees).
For dermatitis
In dermatitis, the skin flakes on the inflamed areas are yellow, while psoriasis is characterized by whitish or gray rashes.
Dermatitis does not cause discomfort: a person detects the disease only by characteristic external signs. There is usually no weakness, performance is maintained. However, the rash may be accompanied by suppuration and swelling.
From seborrheic
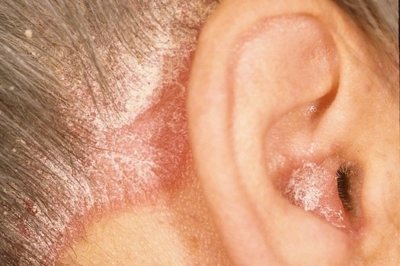
With seborrheic dermatitis, plaques never form, but yellowish, dense crusts with a shiny, oily surface often appear. Their structure can only be felt, because they are not visible externally.
The main difference is the location of the lesion. Seborrheic dermatitis is localized on the face, behind the ears, and on the neck, but does not spread to the body.
From atopic
Atopic dermatitis affects areas with thin skin:
In this case, the foci of inflammation are bright red, but when pressed they turn pale, while with psoriasis the rashes are pink.
A distinctive feature is damage to the feet . Atopic dermatitis is often found on the feet, which never occurs with psoriatic skin lesions.
For allergies
With allergies, the patient is bothered by constant severe itching, while the surface of the rash does not differ from healthy skin to the touch. With psoriasis, the spots flake and the skin around them becomes dry.
Allergic rashes do not have clear contours, they can be small or large, but they almost never turn into plaques, blisters, or purulent formations, because a person reacts to allergies in a timely manner due to severe itching.
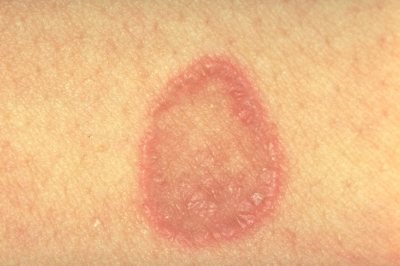
Ringworm affects the mucous membranes, genitals, armpits , and appears in the form of spots of different colors (from red to dark blue).
The scales and crusts that cover the spots peel off easily when damaged, revealing skin that is similar in color to healthy skin. With psoriasis, the detachment of scales is accompanied by the formation of a film and the release of a small amount of blood.
For neurodermatitis
Psoriasis and neurodermatitis are very similar and even doctors cannot always differentiate them without research.
The main sign that can help a dermatologist not make a mistake with the diagnosis is the severe discomfort that the patient complains about. With neurodermatitis, the patient is bothered by severe itching even with small spots, but scratching does not provide relief.
Interestingly, neurodermatitis can occur as a complication of psoriasis.
Types of lichen in cats
There are two forms of the disease depending on the fungus that is the causative agent: trichophytosis and microsporia. They proceed in different ways. The incubation period for trichophytosis ranges from one to six weeks. Lesions appear on the head and neck. Very rarely the paws and tail are affected. What does ringworm look like in cats with trichophytosis:
- Infected areas of the skin turn red and bald, and plaque appears on them.
- The appearance of small spots with sharp outlines and tubercles is noticeable. As the disease progresses, they grow.
- The cat constantly scratches the lesions of lichen.
- The affected areas are covered with scales and crusts.
Microsporia, as a rule, is hidden and asymptomatic. Only sometimes, upon careful examination, do the owners discover that the cat has broken hairs here and there, and the areas around them are covered with scales. The fungus affects the head, limbs, and tail. The disease makes itself felt at moments when the animal’s immunity drops significantly, or due to deteriorating living conditions. Then microsporia takes one of the atypical forms:
- Dermatophytosis. With this type of lichen, constant severe itching is observed, hair begins to fall out intensively, but lesions do not appear. The skin becomes covered with dandruff and wounds. Possible inflammation of the nasal bridge.
- Ringworm. Lumpy skin lesion with clear outlines.
- Pustular dermatitis. A regular or purulent rash appears. The wool does not shed, there are no scales.
Differences from parapsoriasis
Parapsoriasis is a chronic skin lesion in which signs of several diseases are present:
Parapsoriasis and psoriasis have similar clinical manifestations and unclear etiology, but a significant distinguishing feature is visible symptoms of vascular lesions, i.e. deterioration of capillary permeability.
With parapsoriasis, the face and scalp are often affected, while the elbows and knees usually remain intact.
Almost all skin diseases have similar symptoms, so it is very important to make a timely diagnosis and begin treatment so that the disease does not become chronic. Only a doctor can do this for sure after conducting a series of studies, so if a skin rash and itching appears, you should immediately go to a dermatologist.
Diagnostic methods to help identify and differentiate the disease
When characteristic rashes appear on the skin, a person may have suspicions of both pityriasis rosea and psoriasis. In this case, you cannot do without visiting a doctor.
To make a correct diagnosis, a dermatologist conducts a visual examination of the patient’s skin. He carefully examines the patient's skin using dermatoscopy. If in doubt, the doctor may prescribe additional tests.
Typically, if Gibert's disease is suspected, diagnosis involves a detailed study of clinical data and characteristics of the disease:
- the appearance of rashes is preceded by viral diseases of the digestive and respiratory systems;
- a maternal plaque appears on the body, the diameter of which is 3 cm or more;
- a few days after the formation of a large spot, small rashes appear;
- small pink plaques flake and itch;
- The rash is usually localized on the trunk and limbs;
- in most cases, the disease goes away within 3 to 6 weeks.
When making a final diagnosis, the atypical form, in which the maternal plaque does not appear, is taken into account. Psoriasis is easy to diagnose. The skin with this disease has a characteristic appearance. There are no disease-specific diagnostic procedures.
With progressive psoriasis, various abnormalities may be detected in a blood test. They confirm the presence of inflammatory, autoimmune and other pathological processes.
Spots on the skin: how to distinguish ringworm from allergies
Ringworm is a fairly common lesion of the epidermis. The disease is caused by a fungal or viral infection. If spots on the skin similar to lichen appear, it is important to promptly consult a dermatologist to accurately identify the cause of the rash. Such spots may indicate manifestations of various diseases, ranging from an allergic reaction to a fungal infection of the epidermis. Ringworm is often accompanied by a decrease in immunity, which can cause the development of infectious skin diseases.
Can't deal with fungus?
Herpes on the lips is a common virus; more than 90% of the population is infected with it. The disease begins with itching, one or more blisters appear, as soon as a person catches a cold or freezes.
It is better to start treatment as soon as you see the first signs. Before the blisters appear, “experienced” patients already feel the first signs - itching, tingling or burning in the area where the ulcer appears. If you start treatment right away, you will be able to stop it!
Nail fungus, like all other fungal diseases, is contagious. The disease can occur even in those who lead a healthy lifestyle.
At the first symptoms of nail fungus, you should immediately begin treatment. If the disease starts, the nail peels off, changes color, shape, crumbles and noticeably thickens.
We recommend reading: Poisoning during pregnancy - what to do, treatment of food poisoning
Ringworm or another disease?
Ringworm is a whole group of dermal lesions that can be caused by various reasons.
Depending on the type, the disease can present with a number of different symptoms. Most often, people begin to think about lichen when they discover a spot, nodular rash, or discoloration of a small area of skin, which is accompanied by peeling and itching.
It should be remembered that some types of disease can be contagious, so it is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor to accurately diagnose the cause of the rash.
There are several types of disease:
- girdling type;
- lichen planus;
- pityriasis or color type of disease;
- trichophytosis or microsporia;
- Zhiber's disease or pityriasis rosea.
If the spots that appear on the body look like lichen and do not itch, the following diseases of the epidermis may be a possible cause of the rash:
Ringworm can also be confused with manifestations of an allergic reaction on the skin. Hyperpigmentation is often mistaken for a fungal infection.
Discoid eczema: typical elements
Discoid eczema causes the formation of oval spots with redness in the center or changes in pigmentation, discoloration of the skin. It causes patients to develop red or brown spots on the skin that are shaped like a coin or an oval. These spots may appear on the arms, legs, or torso. They can be present as single, separate formations or can combine to form large fields. The resulting lesions can range in size from 2-3 to 10 cm. Other symptoms of discoid eczema may include:
- dry skin;
- burning and itching that worsens at night;
- wet spots, crusts.
If the elements become eroded and wet, they are susceptible to bacterial infection. When eczema is complicated by a secondary infection, redness, swelling, an unpleasant odor from the skin, and fever may occur. According to the National Eczema Association, this lesion most often affects men, usually between the ages of 55 and 65. When women suffer from this type of eczema, they usually notice it between the ages of 13 and 25.
How to recognize lichen?
Manifestations of fungal or viral infection of the epidermis depend on the type of pathogen.
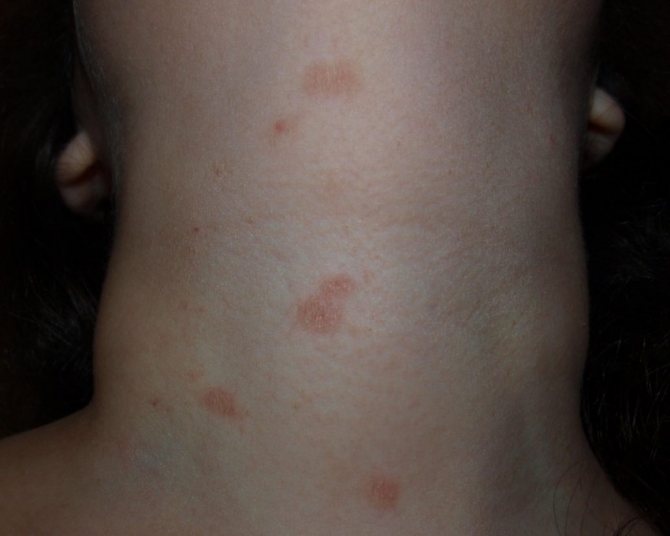
The following symptoms are characteristic of pityriasis rosea:
- round pink spots with a flaky center;
- discomfort in the affected area;
- severe itching.
Allergic pityriasis rosea is characterized by a clear border around the lesions. The spots can be localized on any part of the body.
Shingles is a viral disease. Only adult patients over 40 years of age are susceptible to it; in childhood, this disease manifests itself as chickenpox. Shingles is characterized by the formation of rash blisters, mainly on the torso. The blisters itch and the skin around them swells. The disease is characterized by damage to the nervous system, so often severe pain is felt in the area of the rash, as with neuralgia.
Tinea versicolor is characterized by the formation of small spots of light brown or dark brown color. This disease is often mistaken for a pigmentation disorder. Over time, small spots merge into large lesions of a darker color. With this disease, there is no itching, but the affected epidermis is dry and flaky.
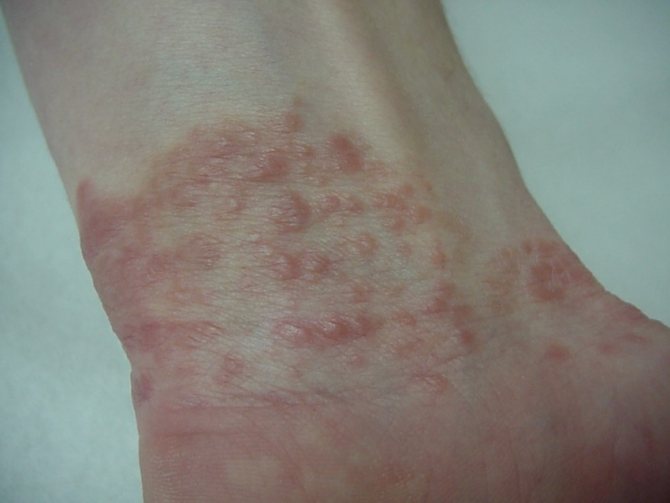
Lichen planus is characterized by the formation of a dense nodular rash, predominantly red or bluish in color. As the name implies, the rash does not protrude above the surface of the skin, however, when palpated, you can notice a denser structure of the epidermis in the affected area. A characteristic feature of the disease is the glossy surface of the skin in the affected area. Over time, the nodules merge into large plaques. The disease is characterized by severe itching, but there is no dryness or flaking.
Trichophytosis or microsporia are the names of ringworm, depending on the type of causative agent of the disease. The disease is caused by fungi. The danger of the disease is that this type of lichen is very contagious. Fungal infection affects not only the epidermis, but also the hair and nail plates. The disease is characterized by the formation of round or oval spots, which may not differ in color from healthy skin, or acquire a pinkish tint. The boundaries between the affected and healthy epidermis are always clearly visible. The skin in the affected area may itch and peel; the disease is characterized by the formation of large scales. Small blisters or nodules may appear at the border between the affected and healthy skin. The epidermis in the affected area swells, hair follicles weaken and hairs break off.
Are there any differences in treatment?

During the appearance of secondary rashes, you should wear loose-fitting clothing. This will avoid friction, which can cause an irritated form of pityriasis rosea. To treat the disease, zinc liniment is used, which is applied to the entire surface of the body . The procedure must be performed twice a day.
In the first 7 days of progression of the disease, it is forbidden to shower. This is because water can spread the rash over the entire surface of the skin. For severe itching, antihistamines are prescribed.
Allergy or ringworm?
A tendency to allergic skin reactions occurs in approximately every fourth person. However, this reaction is often mistaken for lichen. The following reminder will teach you how to distinguish ringworm from allergies.
- The edges of the area affected by lichen are always clearly defined. With an allergic reaction, the rash is vague, without precise boundaries.
- An allergy occurs immediately after contact with an irritant, while lichen is provoked by a virus, bacterial or fungal infection.
- Some forms of lichen are characterized by the formation of dense scales of skin that are similar to seborrheic dermatitis. In case of allergies, separation of scales is not observed.
Skin irritation or allergies develop rapidly, several hours after contact with the irritant. An allergen can be anything - from food to household chemicals or medications. The development of lichen on the skin occurs gradually. With a fungal infection, the first symptoms appear 5-7 days after infection. First, a small spot forms on the skin, which gradually increases in size. Over time, itching and discomfort appear, and the center of the spot begins to peel off.
Other forms of lichen also develop slowly, with symptoms increasing gradually.
In some cases of irritation or allergies, a rash appears within minutes. Depending on the type of reaction, a vesicular or nodular rash forms. As a rule, the affected area does not have clear boundaries, and the skin around the blisters becomes inflamed, red and swollen. With atopic dermatitis, red spots appear on the skin.
If you notice a rash, redness or spots on the body, it is important to promptly consult a dermatologist for a diagnosis. It should be remembered that some dermatological diseases can be contagious and also contribute to the weakening of the body's immune defense.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis

Its main symptom is irritation and redness of the skin.
The appearance of red plaques on the skin with this disease is accompanied by severe itching, which can subside and then return again with a repeated reaction to the allergen.
Red spots due to allergies have vague boundaries and can occupy large areas on the human body.
How to distinguish lichen from allergies?
Allergy symptoms can easily be confused with symptoms of other diseases. Skin rashes at the beginning of any pathology are often similar in color, shape and location. But the symptoms of each of these diseases are not limited to skin rashes, that is, fundamental differences still exist. How to distinguish lichen from allergies is the topic of today’s article.

Video on the topic
How to distinguish psoriasis from lichen, neurodermatitis, eczema and dermatitis:
Before treating skin rashes, you need to determine what caused them. Psoriasis and pityriasis rosea are often confused due to similar symptoms. These are completely different diseases. If a rash appears, you should immediately contact a dermatologist, who will determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Pityriasis rosea can be cured. But it is impossible to completely get rid of psoriasis. Sometimes there is no relapse for a long time. In some cases, patients experience an exacerbation of the disease every year.
To prevent pathology from having unpleasant consequences, you need to take some preventive measures: avoid stress, eat right and get plenty of rest.
Source: psoriazonline.ru
What is lichen?
Ringworm is a skin infectious disease belonging to the group of dermatoses. The diagnosis of “lichen” simultaneously includes a whole list of skin pathologies that are of viral or fungal origin. At the same time, the mechanism of transmission of the infection still remains unknown, that is, not all people who are at risk for infection with this pathology become ill with lichen. But it has been established that predisposing factors to the development of the disease are a decrease in the protective forces of the immune system, stressful situations, hereditary predisposition, psycho-emotional and physical stress, hypothermia and frequent infectious diseases.
There are several forms of lichen:
- shearer;
- pityriasis;
- encircling;
- scaly;
- pink.
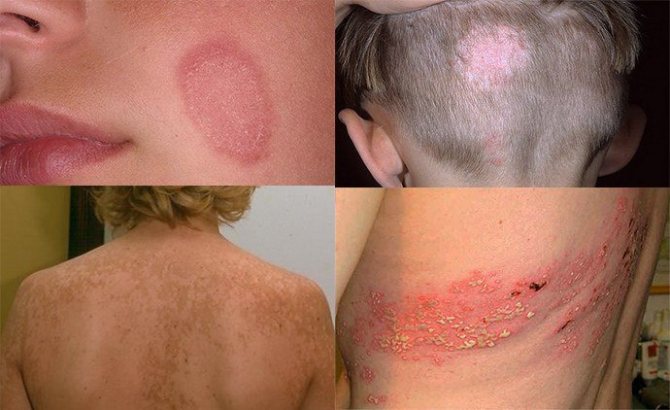
Since there are several types of lichen and the causative agents of the infection differ, it is important to determine the diagnosis on an individual basis and, depending on the nature of the disease (fungal or viral), select the appropriate effective treatment. Children are most often affected by shingles.
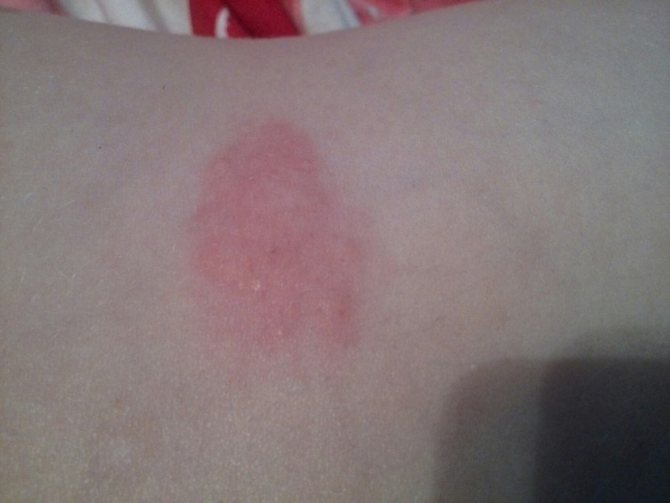
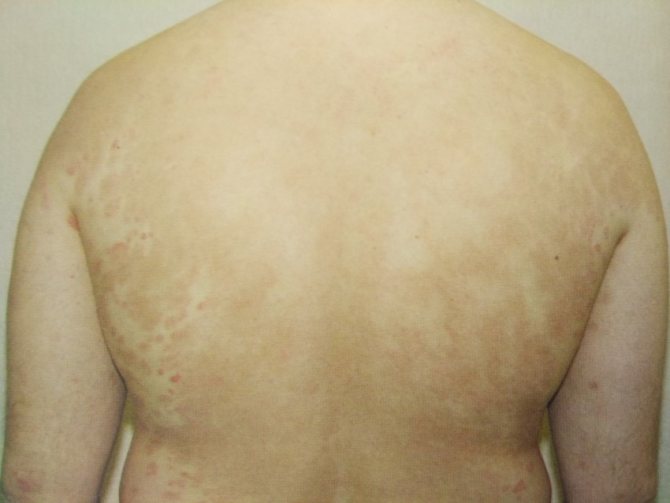
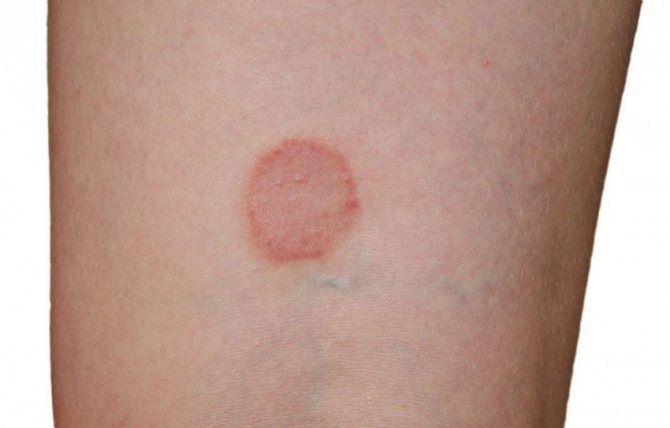
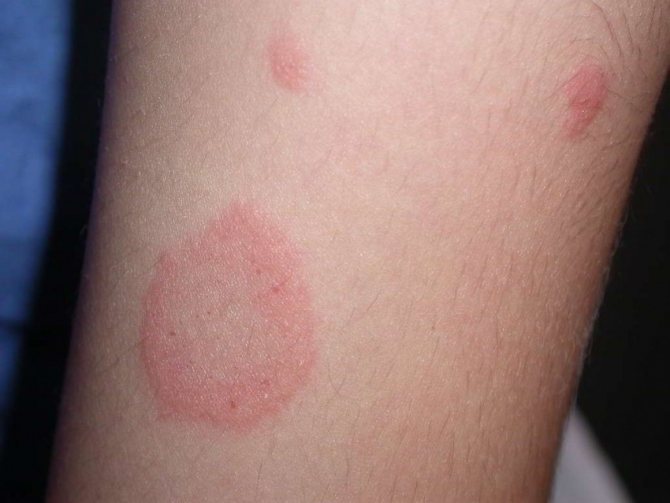
The rash with lichen looks like large spots that are pink in color, regular in shape and have strict boundaries. The rashes peel off and can change color. Foci of pathology usually appear in the abdomen, back, forearms and legs, less often in the genital area and on the scalp. Concomitant symptoms of lichen may be enlarged lymph nodes and hyperthermic syndrome. Ringworm can be cured quite easily and successfully; usually the course of treatment lasts no more than 2–3 weeks, provided that the disease has not progressed into an advanced process.
Atypical manifestations
Symptoms of lichen planus in the atypical type may vary based on the specific characteristics of the disease.
Atrophic
Failures in nutrition and replacement of skin-type tissues with connective tissue provoke sclerotic and atrophic deformities. This form has:
- primary character with independent development;
- secondary in nature, when the reverse process occurs in the development of papules.
The disease manifests itself in the form of keratinized cells covering the hair follicles on the bends of the limbs, which leads to follicular keratosis. If lichen occurs on the scalp, hair loss is possible.
Warty
Hypertrophic lichen can be identified by the presence of shiny papules. They are distinguished by a brown, purple or pink hue. They often join together, creating new plaques.
Externally, it can be confused with a wart covered with scales. There are rashes on the front side of the lower leg.
Erosive-ulcerative
This is a complex case with rashes on the oral or genital mucosa. The changes take the form of painful ulcers and erosions. They are distinguished by their roundness and irregular shape. The healing process is very slow and is accompanied by relapses.
Cystic
In the bullous form, large and small blistering formations occur. They spread widely throughout the body, accompanied by papules and plaques.
What is an allergy?
Currently, allergies are considered the most common disease on Earth. According to the World Health Organization, every fifth person on the planet suffers from one or another allergic disease.
Allergy is a kind of protective reaction of the body, its individual sensitivity to certain substances - environmental factors. Allergens can be food, dust, medicines and much more. Most people react to these factors completely calmly, but a certain group of people develop increased resistance to them.
Causes of lichen planus
The actual causes of the disease have not been fully studied. Various experts put forward several groups of factors that provoke lichen planus:
- Heredity
- Neurogenic causes - psycho-emotional stress, exposure to stressful situations, mental and nervous disorders, sleep problems.
- The action of viruses that are localized in skin cells begins to actively develop and act when immunity declines.
- Allergic manifestations in response to individual components in products, drugs - tetracyclines, streptomycin, sulfonamide substances, drugs with mercury, arsenic, gold, etc.
- Deviations in the functioning of the endocrine mechanism and metabolic processes.
Before determining the best way to treat lichen planus, it is advisable to consider the following factors in the development of the disease:
- infectious diseases such as hepatitis;
- metabolic disruptions in the body;
- bilinary cirrhosis of the liver of a primary nature;
- malfunctions of the digestive system that become chronic.
be careful
People suffering from psoriasis often make one big mistake:
The patient is trying to eliminate the external signs of the disease, but eliminating the external manifestations of psoriasis does not solve the problem from the inside.
Roughly speaking, even if it is possible to remove the signs of psoriasis from the outside and put the skin in order, inside the body the disease continues to devour the autoimmune system, which provokes severe diseases, many of which are fatal. Particularly scary is the fact that psoriasis can provoke cancerous tumors.
The only remedy that is currently available for self-use by patients with psoriasis is the special product “PsoriControl”, which is available at a discounted price. Read the details in the official source.
How to distinguish lichen from psoriasis
Many people are interested in the question of how to distinguish lichen from psoriasis, because some types of lichen are contagious and require urgent treatment.
Psoriasis is a type of lichen, the so-called scaly lichen. How to recognize two diseases? Let's figure out how psoriasis differs from pink and red lichen.
These types are quite common, but doctors have no difficulty making a diagnosis.
Lichen erythematosus (LP), distinctive features
This disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process on the surface of the skin. What is the difference between psoriasis and lichen red? Many factors.
- The main difference between LLP and other types of skin diseases is the location. Most often the mucous membrane (oral cavity, genitals), as well as the elbow and knee bends, and armpits are affected.
- LP can occur on the thighs in the inguinal folds, less commonly on the shoulders. Scaly psoriasis and lichen planus have similar symptoms.
- In both cases, the sores have scales and shiny skin underneath, but in the case of LLP, the sore has a pronounced red-crimson color, sometimes with a dark bluish or purple tint. The plaques are very itchy and itchy.
Both of these diseases are not transmitted through the air, through direct contact, sexual intercourse, and so on.
It is impossible to become infected with them from a patient. The reasons why psoriasis and lichen planus appear are identical:
- Malfunctions in the immune system.
- Hereditary factor.
- Neurological pathologies, stress.
- Intoxication (ecology, drugs, hazardous industries).
- Injuries.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver.
LLP begins with a red rash. You can understand what disease the patient has: lichen ruber or scaly psoriasis by doing a blood test. With LP, there is a decrease in the number of T cells in the blood and their activity.
- There is a decrease in T-hellers and an increase in the coefficient of T-suppressors.
- In doubtful cases, in order to distinguish lichen ruber from scaly psoriasis, histology is prescribed.
- In the case of LP, this study will reveal a mononuclear infiltrate with disruption of the basal line of keratinocytes.
Pityriasis rosea or psoriasis
Unlike pityriasis ruber and psoriasis, pityriasis rosea is transmitted by direct contact. It is known that it can appear after a viral infection.
Many scientists classify it as a fungal or infectious disease. All doctors and scientists agree on one thing: the disease can only develop if the immune system is weakened.
But how to distinguish pityriasis rosea from psoriasis and limit dangerous communication?
- The onset of the disease itself occurs in different ways. The appearance of pityriasis rosea is accompanied by an increase in temperature and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Then one or more pink spots appear with folds and bumps in the middle, which then begin to peel off.
- Near these initial spots, constantly increasing in size, several new, smaller ones appear.
Pityriasis rosea differs from scaly psoriasis in the speed of development.
It is directly related to the state of the immune system, but the spread of pityriasis rosea occurs more rapidly.
In addition, a psychological factor is added. Knowing that his disease is contagious, a person begins to get nervous and feel even more discomfort, thereby accelerating the development of the disease.
Types of lichen in people by manifestations
How to determine the main types of lichen in humans? It is not always possible to visually identify the type of pathology, but its very presence is quite realistic. Some of the most famous species can be recognized with the naked eye. These include multi-colored and ringworm, eczema, psoriasis.
How to identify signs of lichen in a person? The first signs appear as areas of red color, often with itching, flaking and limitation of healthy skin. These lesions rise slightly above the skin. There may also be papules. Further, the process progresses, and symptoms of the disease appear.
How to determine the symptoms of lichen in a person? The affected skin will have distinct ridges around it and is often red or blistered. Often such bubbles burst, become crusty, and begin to actively peel off. A lot of scales appear around. The general condition is rarely disturbed.