Lactose is a type of complex sugar. It is found in natural dairy products, which are digested by the human body using an enzyme called lactase. A small percentage of people have this enzyme. In this article we will look at what lactose allergy is, the symptoms and causes of its occurrence, and also introduce the reader to the main methods of treating this disease.
According to statistics, both children and adults suffer equally from this disease. In both cases, it is important to establish the presence of this disease as early as possible, and also to distinguish it from a milk allergy. Because these are completely different things. So, in the case of hypersensitivity to lactose, it is not necessary to completely exclude dairy products from the diet, but in case of an allergic reaction to milk, this is simply necessary.
What it is?
A milk allergy is the body’s reaction to milk protein; the immune system, against the background of various factors, accepts this substance as an allergen and begins to actively fight it.
In fact, there is no specific concept as a reaction to lactose or sugar, but it's all about the animal protein that is found in dairy products.
If the body is unable to digest this component fully, then side effects occur in the form of allergic reactions, rashes, redness, nausea and dizziness.
Forms of release of dietary supplements
Lactase for newborns varies.
Lactase in capsules
The most common option is that it is more convenient to select the dosage and store it . Of course, the capsule itself is not given to a newborn - he will choke and suffocate. The shell is opened, but pure powder cannot be given either. It is diluted in a teaspoon of expressed milk or formula, and given immediately before or during feeding.
Lactase enzyme in capsules from KAL
It is possible to prepare the mixture with enzymes in advance - half of the recommended dose is added to warm, fresh baby food (not hot). The liquid must be used within 4 hours. But this is not allowed with all dietary supplements - look for information in the instructions for use of the purchased lactase drug.
Lactase drops
This version of the dietary supplement is rare. This is “Baby Doc” from Stericon Pharma, for example. Drops are mainly prescribed for transient hypolactasia, but sometimes they are also given to full-term newborns.
This LFG cannot be taken in its pure form: according to the instructions, it is measured into a teaspoon of baby food and given to the baby before feeding.
How is it related to gluten?
Celiac disease is very similar to lactose intolerance; the clinical picture is sometimes the same, which complicates the possibility of a correct diagnosis.
Observed:
- increased gas formation;
- flatulence;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and diarrhea.
Lactose allergy is not an immune disease, but celiac disease is more severe and causes autoimmune damage.
When gluten enters the stomach, it irritates the mucous membrane and causes an inflammatory process.
To know exactly why a patient has allergy symptoms, you need to keep a food diary and write down everything that was eaten during the day.
Or take clinical tests and blood tests for the presence of antibodies.
Allergies in children and infants
Now let's look in more detail at how symptoms of lactose allergy manifest in children. Mild lactase intolerance is typical for all children over two years of age. This is a completely normal age-related change in the body. Since the need for milk is significantly reduced. It is quite logical to assume that with a decrease in the need for milk, there is also a decrease in the body’s production of the lactase enzyme. This leads to lactose intolerance.
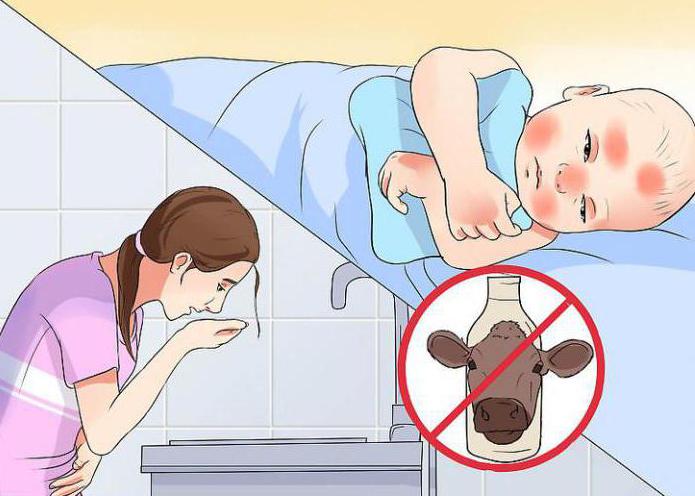
Since the child’s body is not yet strong enough, it is difficult for him to cope with any diseases, including various types of allergies. Parents should closely monitor the child's condition and, if necessary, seek medical help. It is especially dangerous to miss the symptoms of lactose allergy in infants. Since for a tiny organism to cope with the disease on its own is an impossible task. You can suspect lactose intolerance in a baby if the child does not stop vomiting and diarrhea after drinking breast milk. Some other signs should alert the mother:
- no or slight weight gain;
- stool disorder;
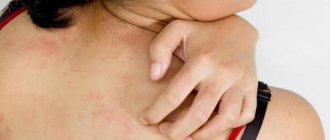
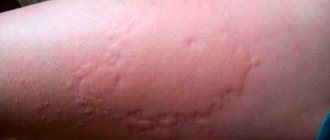
- various manifestations on the skin - rashes, redness, itching;
- refusal to breastfeed after 3-5 minutes of feeding;
- the child draws in his legs, cries and is capricious.
An allergy to lactose can occur not only during breastfeeding, but also when feeding a child artificial formulas that contain soy or cow protein. For infants diagnosed with lactose allergy, special lactose-free nutrition has been developed. It is important to detect the problem in a timely manner. And also switch to lactose-free formulas to avoid delays in the child’s development and other health problems.
Intolerance is especially common in premature babies, whose gastrointestinal tract is not mature enough to produce the lactase enzyme. Babies born prematurely should receive increased attention both from medical personnel and from parents, primarily mothers.
Why does it happen?
From a medical point of view, lactose allergy is a pathology of the enzyme systems of the digestive tract; intolerance can be either congenital or acquired.
- With a congenital defect, a mutation occurs in the gene that is responsible for the synthesis of the enzyme. In premature babies, this is a passing phenomenon; with age, the ability to digest lactose is restored;
- the acquired form develops against the background of a decrease in nominal activity, with a natural transition to a dairy-free diet, previous chronic intestinal infections, acute and chronic pancreatitis, etc.
An allergy to lactose occurs when an excess of animal protein enters the body; it can be caused by frequent consumption of sweets and fruits, which contain a lot of lactose.
Can it appear suddenly in an adult?
Lactose deficiency can occur due to:
weak immune system; in the presence of diseases of the digestive tract; when an infection enters the intestines; with an excess of foods high in animal protein.
In order to eliminate such a disorder, it is necessary to carry out medicinal treatment of existing diseases and reduce the amount of products containing lactose in the diet.
Consume more vitamins and minerals of natural origin.
The likelihood of secondary lactose deficiency is possible in adults with short bowel syndrome after surgery, encephalopathy, celiac disease, Crohn's disease.
Paying attention to your health should become a good habit. Take care of yourself, eat right and be in a great mood!
Lactose is rightfully ranked among the complex sugars contained in natural dairy products, which are digested under the influence of an enzyme (lactase). When the patient has low levels of these enzymes, an allergy to lactose occurs.

Statistics indicate that the disease is equally common among both adults and children. It is important to distinguish an allergic reaction to milk from a negative reaction to lactose. Hypersensitivity to lactose does not require exclusion from calcium-rich dairy products, unlike milk allergy.
What products does it contain?
A huge amount of lactose is found in milk powder, whey, whole milk and other fermented milk products.
Also available:
- in sausages, soup sets;
- in salad dressings;
- in bakery products;
- nut butter;
- ice cream;
- in breadcrumbs;
- baking and confectionery products;
- ham in molds;
- in flavor enhancers;
- in chocolate bars;
- in puddings;
- in mashed potatoes.
And in various medications that are prescribed to normalize the activity of the gastric tract (No-spa, Lopedium, Motilium, Gastal, Enap, birth control pills).
Who needs a gluten and lactose free diet!
The number of search queries on the topic of gluten-free and lactose-free products on the Internet is growing every year. You just have to look a little more closely, and you will certainly find people around you carefully studying the menu for gluten content in dishes or invariably buying coffee with plant-based milk. For example, there are countless types of milk existing today: rice, almond, cedar, sesame, hemp, coconut, soy, pumpkin, poppy. These drinks, of course, are conventionally called milk (the only thing they have in common with cow’s milk is the name), the composition of these products is completely different, and the motivation for their choice can be both a vegan lifestyle and raw food diet, and the desire to avoid the unpleasant sensations that arise after drinking cow’s milk , or even lactose intolerance (how real it is is another question).

I wonder why there are so many difficulties associated with a product that we have all grown accustomed to considering as extremely useful since childhood. It turns out that casein is to blame for everything: an adult simply does not have enough enzymes (namely, renin) to break it down, so the presence of casein in milk negates all the benefits of calcium that enters the body with the same milk (casein is a strong oxidizing agent, and To achieve acid-base balance, the body neutralizes increased acidity in the stomach with calcium).

Roughly the same thing happens with the absorption of lactose, another milk component. Once in the stomach, it is broken down into glucose and galactose - and the adult body again cannot cope with the latter. As a result, galactose is not excreted, but is deposited in tissues, which can lead to the most unpleasant consequences - from cellulite and various forms of arthritis to decreased muscle tone and even cataracts.

Experts believe that this is dictated by nature itself, because once upon a time our ancestors consumed milk only in infancy. “People sometimes have no idea that they cannot tolerate one or another component of milk, because the clinical manifestations can be erased: a single malaise, weakness, bloating and increased flatulence - it is difficult to analyze these processes yourself and understand what they are connected with, - says Ksenia Selezneva, gastroenterologist at the Atlas clinic. “And then specialists come to the rescue and prescribe the necessary examinations, including tests for food intolerance to milk sugar - lactose, or milk protein - casein.”

If the results of such tests are positive, one can draw conclusions about the dangers of cow’s milk for a particular person and think about finding a replacement. For supporters of animal products, goat and sheep milk may be a good option: intolerance to them is much less common. Well, for everyone else - all the types of plant milk mentioned above. With gluten it's more complicated. If lactose intolerance is observed in approximately every fifth person in Russia (and in China in general in 90% of the population), then celiac disease (“flour disease”) is a rather rare guest in our ranks. “Gluten is a protein found primarily in grain products. Celiac disease is the most severe form of intolerance, when a person is advised to exclude all gluten-containing products from the diet for life. If he breaks his diet even a little, it will be difficult not to notice: celiac disease immediately manifests itself with severe abdominal pain and bloating, weight loss, weakness, diarrhea and other unpleasant consequences. But as soon as you switch to a gluten-free diet, improvements come almost instantly,” notes Sergei Vyalov, gastroenterologist at the French Clinic.

Celiac disease is congenital - you don't wake up one day with an acquired gluten intolerance. The patient has increased permeability of the intestinal walls and an inadequate response of the immune system to gluten. All this manifests itself in infancy - almost immediately after the introduction of complementary foods and cereal porridges. It is better to understand the diagnosis as early as possible - pathologies with celiac disease can be very severe: progressive atrophy of the intestinal mucosa, delayed physical and mental development, type 1 diabetes, osteoporosis, iron deficiency anemia, dystrophy.
As with lactose intolerance, only see a doctor for a diagnosis and appropriate diets. “If gluten intolerance is suspected, a biopsy is performed during gastroscopy and the tissue is examined under a microscope to identify certain indicators of the disease, for example, the height of the intestinal villi - with celiac disease it is much lower. There are also laboratory tests that determine specific blood markers. It makes sense to take a test for food intolerance, to see how the immune system reacts to gluten and products containing it. And even then, if gluten intolerance or even celiac disease is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a diet and, if necessary, therapy,” adds Ksenia Selezneva.

A self-prescribed gluten-free diet is absolutely useless for a healthy person. Moreover, it can be harmful, because excluding grains from the diet creates a deficiency of fiber, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the body. Fortunately, there are many times fewer real victims of celiac disease than those who buy themselves a gluten-free bun simply under the influence of fashion. And, by the way, it is precisely on food trends that manufacturers manage to earn good money: gluten-free products in supermarkets cost an order of magnitude more than regular ones, and this no longer surprises anyone. Meanwhile, the market does not stand still, and in the wake of the popularity of gluten-free diets, a new trend has begun to actively develop - gluten-free cosmetics. However, experts are unable to explain what the point is: the fact that gluten can be absorbed into the skin and thus cause harm has not been scientifically proven.
Each of us is responsible for himself and his own diet, and there is nothing wrong with following fashionable food trends, wanting to try out all kinds of diets, and even without any particular reason for a while limiting the consumption of lacto- and gluten-containing products. in general, no. The main thing is that all this does not turn into orthorexia, when the desire for healthy and proper nutrition becomes an obsession and leads to really serious consequences.
Source
I like 2
Related Posts
leave a comment
Symptoms of lactose allergy
The body's reaction to milk proteins is as follows:
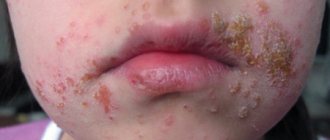
- a rash, redness, inflammation, swelling, and incessant itching occurs in various parts of the body;
- the clinical picture is accompanied by problems with stool, bloating, flatulence;
- symptoms of gastritis, stomach pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting may be observed;
- A runny nose, increased mucus production, sneezing, and shortness of breath appear.
In severe cases, the patient’s condition passes a critical point, and the following is observed:
- severe swelling of the larynx;
- sudden changes in pressure;
- suffocation;
- it all ends in anaphylactic shock.
Only urgent resuscitation measures can save a person’s life.
Causes of lactose intolerance

The most common cause of lactose intolerance is a congenital disease - alactasia. This is a hereditary disease in which a mutated gene interferes with the synthesis of lactase. Among residents of Asia, insufficiency of enzymes for the breakdown of milk proteins is much more common than on other continents.
In children, lowering lactose levels is a natural process that begins around age three as the need for milk decreases. How painless this process will be for a small organism depends on individual characteristics.
Typically, insufficient enzyme production occurs in children born prematurely. The problem should go away as the child gets older.
Oddly enough, the development of lactose intolerance is more common in adults than in infants. This can happen due to the occurrence of intestinal diseases. Surgery can also affect the production of essential enzymes. After the patient undergoes examination and treatment, the symptoms should disappear.
How to make a diagnosis?
The diagnosis of cow protein intolerance or milk allergy is made through a routine test; all foods that can cause an allergic reaction are excluded from the diet.
When following such a diet, the symptoms of disorders should disappear; such a provocative test helps to easily get rid of various food loads that provoke signs of sensitization.
Over time, after six months to a year, you can gradually switch to a normal diet, including milk and other products with animal protein in your diet.
If there are no violations, then lactose intolerance has completely disappeared.
This diagnostic method helps to initially determine the source of the allergy; in more severe forms of the disease, you should seek emergency qualified help.
When to see a doctor
An adult or child should seek help from a gastroenterologist, therapist or pediatrician if he or she has had diarrhea for 2 weeks. The child may appear unnaturally pale, be overly irritable, have trouble gaining weight, have a belly that is too large and protruding, or have feces that smell too bad.
It is imperative to consult a doctor before starting a gluten-free diet. Otherwise, the survey data will be inaccurate.
If celiac disease is diagnosed in one family member, then everyone needs to be tested, since this disease can affect everyone. Those who belong to a risk group, for example, a person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, should also take the test.
Before going to the doctor, you need to prepare:
- Eat only those foods that were previously included in your diet. Start dietary nutrition only if it is recommended by a specialist.
- It is imperative to write down the date the first symptoms appeared and describe what exactly appeared first and how events developed further.
- Write down all the key personal information, in which you must indicate whether there were stressful situations and what changes occurred in your life.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins and dietary supplements that the patient is currently taking.
- Make a list of questions that you will need to ask at your doctor’s appointment in order to fully assess the situation and understand what to do next.
How is it different from intolerance?
An allergy to lactose occurs due to the lack of breakdown of glucose and galactose; lactose is a sugar that, in its entirety, causes fermentation in the digestive tract.
This intolerance is the result of a lack of glucose enzymes.
An allergy to whole milk occurs due to problems with the immune system, because such disorders are often accompanied by respiratory symptoms, which cannot be said about lactose intolerance.
Find out if there could be an allergy due to nerves. Why is there an allergy to apples? Follow the link.
Symptoms of Enzyme Deficiency
If the baby has too little lactase, the parent will understand this by the following symptoms:
- the baby is restless, cries a lot and sleeps poorly;
- there are many lumps of undigested milk in his stool;
- The baby's stool is too frequent and liquid - like water, sometimes streaks of blood appear in it, foam, it has a sour smell;
- there are rashes and peeling on the skin;
- The baby lags behind in terms of development - grows poorly, gains weight slowly.

If you notice these symptoms in your child, contact your doctor . He will prescribe a series of tests (CBC, skin prick test, hydrogen breath test or elimination diet for a nursing mother) that will show the level of enzyme production. If it is not enough, then perhaps the pediatrician will recommend switching to formula - breast milk contains the most lactose. In addition, there is artificial lactose-free baby food. If this option does not suit you, the baby will be prescribed lactase supplements.
Treatment
How to treat these disorders?
First of all, completely eliminate dairy products from the diet, and also reduce the amount of consumed products that contain animal protein in abundance.
Lactose allergy can be treated with antihistamines, which will promptly relieve symptoms of disorders immediately after consuming prohibited foods.
In severe cases, an injection of adrenaline will be needed.
Intolerance can be a temporary clinical condition in the presence of inflammatory bowel diseases, infection in the digestive tract, or parasites.
Such disorders must be eliminated with antibiotics.
Important! Strengthen the immune system using folk methods, increase the body’s resistance to various pathogens. Thus, it will be possible to reduce the risk of developing lactose allergy in both adults and children.
If there is a deficiency of enzymes that effectively break down lactose, you need to take:
- probiotics linex;
- bioform;
- bifistim;
- enterol, etc.
If the reaction is accompanied by intestinal disorders and sharp pain in the stomach and abdomen, myotropic antispasmodics are prescribed.
A significant achievement in the prevention and treatment of reactions to milk is the production of special hypoallergenic formulas, milk proteins are replaced with soy proteins, and are used for the preparation of pastes, creams and other food products.
The lack of calcium can be easily replaced with vitamin forms, eating natural vegetables and fruits.
Indications for the study
A test for gluten intolerance is prescribed in cases where other types of studies have not provided a complete picture of the disease. Celiac disease can masquerade as various pathologies, so they should definitely be excluded.
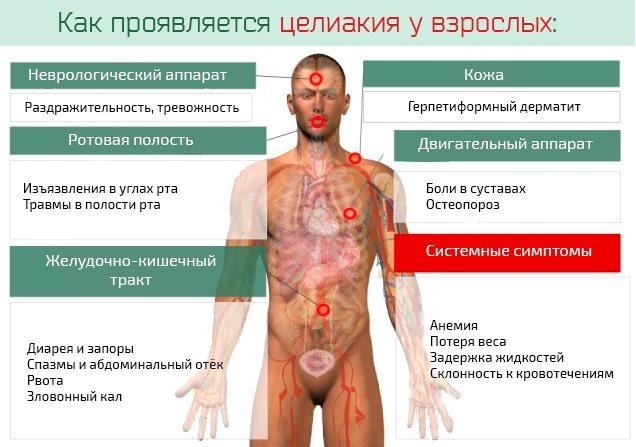
Celiac disease. Symptoms in adults
A gluten level test is prescribed if the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- signs of anemia;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- multiple caries;
- hemorrhage in the lower extremities and peritoneum;
- infertility;
- a constant feeling of thirst, which is difficult to quench;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- stomatitis;
- dermatitis;
- glossitis;
- anxiety, frequent mood swings;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- fast fatiguability;
- black shade cal.
Very often, gluten intolerance is diagnosed in children.
The following symptoms may indicate their illness:
- unnatural bloating;
- irritability;
- tearfulness;
- refusal of food;
- loose stools;
- stool contains fatty inclusions and has a persistent unpleasant odor.
If you experience such symptoms, you should definitely seek help from your family doctor or pediatrician.
Nutrition
Nutrition for allergies to gluten and lactose should correspond to the nature of the disease; cow's milk and its derivatives should be strictly excluded from the diet.
Eat in small portions so that the food is effectively absorbed by the body.
If you have allergic rashes, remove the allergenic product from the menu; eat steamed dishes.
Make compotes from dried fruits, bake with corn or rice flour.
Drink plenty of water up to 2 liters per day, preferably purified distilled water or unsweetened compotes.
Introduce fresh vegetables and fruits, walnuts, and soy products into your diet.
The menu should include foods rich in magnesium, iron, sodium, and fiber.
It is important to exclude fatty meats, goose, duck from the diet, stop eating sausages, smoked meats, canned food, giving preference to low-fat fish, hare, and turkey.
The diet should be balanced; if you have problems with the digestive system, follow a gentle diet, which will normalize metabolic processes and put the gastrointestinal tract in order.
Consequences of lactase deficiency
Not so long ago it was believed that milk intolerance was an age-related problem, that is, nothing needed to be done about it. On the one hand, there is some truth in the statement: many children react acutely to lactose up to 4-6 months, and then the production of the necessary enzyme is established. But it is a myth that you need to close your eyes to the problem.
This action will lead to the following consequences:
- developmental problems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- increased gas formation;
- chronic lactose intolerance (persists even in adults).
Therefore, if the doctor advises medications with the lactase enzyme, you should not refuse them.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of lactose deficiency, you need to follow simple preventive measures:
- eliminating contact with food allergens;
- take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, strengthen the immune system;
- beware of excessively salty and spicy foods;
- take milk boiled.
It’s also not worth giving up dairy products completely; these are sources of calcium in the body.
People with lactose intolerance should take such products in small doses, not as a separate dish, but while eating other foods.
Fresh milk can be replaced with kefir or yogurt.
Other products are also rich in calcium:
- fish;
- soy milk;
- almonds;
- broccoli and other green vegetables.
When the first signs of an allergy appear, immediately take basic steps to eliminate the allergen, seek qualified help, monitor the composition of your diet, and take medications if necessary.
Read how eggshells help with allergies in children. Is there an allergy to sperm? The answer is here.
What to do if you are allergic to sugar? Click go.
Regimen for newborns
An enzyme supplement is given with each feeding. The norms for its reception are as follows:
| Alactasia | Up to 1000 units every time |
| Transient failure | Strictly as prescribed by the pediatrician (it all depends on the degree of prematurity and the condition of the baby) |
| Secondary mild intolerance | From 300 to 700 units. |
| Secondary severe form of hypolactasia | Up to 1000 units |
Table 1. Scheme for taking enzyme supplements in capsules for infants.