Allergic diseases of the oral cavity
Allergic diseases of the oral cavity, especially in children, have become a serious problem quite recently.
This is associated with the emergence of a huge arsenal of synthesized pharmaceuticals, which are strong allergens and cause sensitivity of the body, especially under the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions. Allergic diseases of the oral cavity.
especially among children, became a serious problem quite recently. This is associated with the emergence of a huge arsenal of synthesized pharmaceuticals, which are strong allergens and cause sensitivity of the body, especially under the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions.
These diseases are classified as pharmaceutical allergies; they spread to the oral cavity and can be combined with other lesions of the body. The most common prerequisites are medications (penicillin, tetracycline, streptomycin), sulfonamide drugs, analgesics, novocaine, iodine, bromides, etc.
The rate of development and severity of the allergic reaction depends on the method of administration of the pharmaceutical product.
Often in pediatric dental practice, applications of painkillers and other pharmaceuticals are used. They most often cause sensitization. Frequent use and the highest dose of the product are also of great importance for the development of allergies.
The danger of pharmaceutical allergies is that they mix all types of allergic reactions. This happens for several reasons. Firstly, as a result, the personal reactivity of the child’s body, as well as the presence of general somatic pathology.
In addition, the nature of the pharmaceutical allergen and the method of its administration are important.
Relieving pain and clearing defects
Since stomatitis of allergic origin occurs with severe pain, complex treatment necessarily includes an anesthetic drug: Dentinox, Kamistad, Lidocaine Asept, Dentol, 5% novocaine or anesthesin. To relieve pain, you can prepare a special mixture, the recipes for which we reviewed in the article “Composition of mash for stomatitis.”
Vinylin or Shostakovsky balm
To cleanse defects in the oral mucosa from pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products, antiseptic rinses, baths or wipes with 0.05% chlorhexidine, a solution of furacilin, soda or potassium permanganate, or a decoction of chamomile or sage are carried out.
Allergic stomatitis
Allergic stomatitis is an inflammatory change in the oral mucosa caused by the development of immunopathological reactions (hypersensitivity, hyperergy).
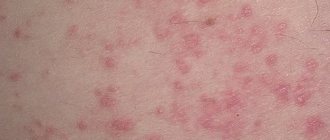
Manifestations of allergic stomatitis include swelling, hyperemia, bleeding, ulcers and erosions of the mucous membrane, burning in the mouth, pain when eating, hypersalivation, and from time to time deterioration of the general condition. Examination of a patient with allergic stomatitis includes collecting an allergic history, identifying the causes of an allergic reaction, examining the oral cavity, conducting provocative and elimination tests, skin tests, saliva examination, etc.
Medicinal and food types
The medicinal appearance appears during or after the use of local and internal medications. With the development of this form, symptoms appear such as irritation on the skin, difficulty breathing, and in some cases, suffocation, runny nose, and smoothing of the mucous membrane of the tongue. A lot of large eczemas appear in the mouth, and the general condition worsens sharply.
The food form of allergic stomatitis can occur when consuming any food or drink. It is often caused by citrus fruits, seafood, bee products, vegetables, berries or red fruits, nuts, milk, products containing dyes, preservatives and other harmful additives. The symptoms of this type completely depend on the individual characteristics of the organism.
Allergies in and around the mouth: signs, symptoms and treatment
One of the problems that a person faces throughout his life is allergic reactions.
These can be allergic reactions of an immediate or delayed type - this classification is given due to the time of development of symptoms.
In addition to those forms of manifestations of allergic reactions that affect the entire body as a whole, such as, for example, anaphylactic shock, one of the more severe and unsafe reactions for human life, there are also local manifestations of allergies that can occur on the skin of the face, the whole body, mucous membranes the lining of the oral cavity and so on.
Allergic reactions in and around the mouth are quite common and are a serious cause for concern.
First, you should understand the fact that allergy itself is an inadequate response of the body to an irritant that is adequate in its own strength.
It develops against the background of preparatory sensitization - an increase in the sensitivity of the whole organism as a whole.
It is in these conditions that sometimes an ordinary irritant, be it plant pollen, pet hair, food products, pharmaceutical substances and almost everything else, is transformed into a stumbling block and causes such a violent surge of reactions from the body, significantly worsening the quality of life of patients suffering from this problem .
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Drops for teething in children list
What to do if the allergy does not go away?
You suffer from sneezing, coughing, itching, rashes and redness of the skin, and maybe your allergies are even more serious. And isolating the allergen is unpleasant or completely impossible.
In addition, allergies lead to diseases such as asthma, urticaria, and dermatitis. And for some reason the recommended medications are not effective in your case and do not combat the cause in any way...
We recommend reading in our blogs the story of Anna Kuznetsova, how she got rid of allergies when doctors gave her a hard time. Read the article >>
Author: Torsunova Tatyana
What to do if your eyes are itchy and swollen.
Main symptoms and methods of treating the disease.
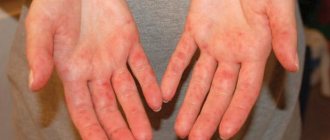
How does the disease manifest itself on the skin of the hands?
What should you do if you have allergic rashes on your face?
Comments, feedback and discussions
Finogenova Angelina: “In 2 weeks I completely cured my allergies and got a fluffy cat without expensive drugs and procedures. It was simple enough. » More>>
Our readers recommend
For the prevention and treatment of allergic diseases, our readers advise using the “ Alergyx ” product. Unlike other products, Alergyx shows lasting and stable results. Already on the 5th day of use, allergy symptoms decrease, and after 1 course it goes away completely. The product can be used both for prevention and for relieving acute manifestations.
The human body is a delicate instrument that reacts sharply to everything alien to it. Of course, this directly affects your well-being in the form of allergic reactions. But if allergies to dog hair and animal pollen are common and do not raise questions in terms of treatment, then allergies in the mouth are a fairly new phenomenon in the field of health.
Allergy on lips
Inflammation of the lips is called cheilitis. Cheilitis can be both infectious and allergic in nature, so cheilitis should not be classified as an independent disease, it is just a symptom. With allergic cheilitis, swelling, ulcers, rashes, blisters, and peeling of the lips can be observed. As a rule, inflammatory processes are accompanied by itching.
The treatment method for allergic cheilitis differs from the treatment methods for cheilitis of infectious origin. First of all, you should avoid contact with the allergen, if, of course, it is identified. In many cases, elimination of the allergen alone can cope with the situation. If this method does not help, then it is recommended to use antihistamines or anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
YKKHMKHVEYAYU YYUPRKHMYU X YAHLORNLSH YUKKEPTSKHVEYAYNTSN YAREOOEMKH
ON YARNLYURKHRYU BSHPYUFEMMNYARKH BNYAOYUKHREKEMNI PEYUYZHHH PUGKHVYUCHR YURYUPYUKEMN, YURYUPYUKEMSHI-TSELNPYUTSKHVEYAYKHI, ASKKEGMSHI, SCHPNGHBMSHI X ЪGBEMMN-YARNLYURKH R MEIPNRHVEYAYHI.
yYURYUPYUKEMSHI YARNLYURHR ЪБКЪРЯЪ MYUHANKEE TNPLNI KETSINI YARNLYURHRYU. anNKEMSHE FUKSCHRYA MU GSD, YASUNYARE KH FFEMKHE BN PRS. yPNLE RNTS MYUACCHDUERYA ANKE MEGMYUVHREKEMYU BN BPEL OPHELYU OKHYKH. oPH NOPEDEKERYA NYALNRPPE TSHOEPELKH NREY YAKHGHYARNI NANKNVYKH.
TsELNPYUTSKHVEYAYKHI-yYURYUPYUKEMN YARNLYURHR – OPH ShchRNL YARNLYURKHRE MU TsHOEPELKHH TNME NAPYUGSCHRYA TSELPYUTSKHVEYAYKHE RNVIYKH.
ASKKEGMSHI UYUPYUREPKHGSERYA – YARNLYURHR ONEBKEMHEL OSGSHPAINB MU NREVMNI YAKKHGHYARNI schPNGKHBMSHI.
NANKNVYE YARNLYURHR – ЪБКЪРЯЪ YAKEDYARBHEL ASKKEGMNTSN ONYAKE. YARNLYURHRYU BYAIPSHRKH OSGSHPEI TNPLHPSCHRYA ONBEPUMNYARMSHE ANKEMSHE. SHPNGHKH FUKSCHRYA MU ANKH, YNRNPSH SYAKHKHBYUCHRYA BN OPHELYU BPEL OKHYKH. ONYAREOOEMMN NAYEE YANYARNMHE JUDGER ANKEMNTSN.
ъGBEMMN-MEIPNRKHVEYAYKHI YARNLYURHR – YAYULYU TNPLYu RЪFEKYU YUKKEPTSKHVEYAYNTSN YARNLYURKHRYU. oPH ShchRNL YARNLYURKHRYU BKhDE YPNLE TsKHOEPELHH X ShPNGKHH YAKHGKHYARNI MUAKCHDUERYA, NANKNVYKH ONEBKEMKHE NVYUTsNB MEIPNGYU. YAKCHMNNRDEKEMKHE KHLTNSGKSH, ONBSHEMN SBEKKHVEMSH, RELOEPYURSPYU REKYU BSHYANYU, FUKSCHRYA ANKEMSHE MU ANKH BN BPEL OPHELYU OKHYKH. DPSTSHE X nRLEVYUCHRYA OPHGMYYH KHMRNYAHYUZHHH.
OPH YUKKEPTSKHVEYAYNL BSGBYUMMNL, YARNLYURKHRE GSAMSH OPNREGNL, MUACCHDYUERYA ONYARNMMNE FFEMKH VSBYARBN B NAKYUARKH YAKHGKHYARNI NANKNVYKH OPNREGMNTSN BYAKEDYARBKHE, KNFYU VETSN ANKEMSHE NRYUGSHBUCHRYA ONKEGNBUREYA khMNTSDU. OPNREGYULH LNFER ONЪBKЪREYA FFEMKHE ЪGSHYU, TsSA KH YEYE. aNKEMSHE FUKSCHRYA MU YASUNYARE BN PRS. NYALNRPE oPH NAMYUPSFKHBUERYA BNYAOYUKEMMYU YAKHGHYARYU NANKNVYU.
Diagnosis of allergic stomatitis
An examination of a patient with allergic stomatitis is carried out by a dentist with the involvement, if necessary, of related specialists: an allergist-immunologist, a dermatologist, a rheumatologist, an endocrinologist, a gastroenterologist, etc.
In this case, the collection and analysis of an allergy history and identification of a potential allergen is of fundamental importance.
During a visual assessment of the oral cavity, the doctor notes the moisture content of the mucous membrane, its color, the presence and nature of defects, and the type of saliva. During the dental examination, attention is paid to the presence of dentures, fillings, and orthodontic devices in the oral cavity; their composition and terms of wearing, changes in the color of iron prostheses, etc.
Chemical-spectral analysis of saliva and determination of pH make it possible to make a benign and quantitative assessment of the content of microelements and evaluate the chemical processes occurring.
Additional studies for allergic stomatitis may include a biochemical analysis of saliva with determination of enzyme activity, determination of pain sensitivity of the mucous membrane, hygienic assessment of dentures, scraping from the mucosa for Candida albicans, etc.
An allergic examination involves an exposure test (temporary removal of the prosthesis with assessment of the reaction), a provocative test (returning the prosthesis to its place with assessment of the reaction), skin allergy tests, and an immunogram study.
Differential diagnosis of allergic stomatitis should be carried out with hypovitaminosis B and C, herpetic stomatitis, candidiasis, mucosal lesions due to leukemia, AIDS.
Where to go if suspicious symptoms appear
If any of the above symptoms occur, you should immediately contact your dentist. The following will help establish a diagnosis, select treatment, and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists: for adults - a therapist, for children - a pediatrician. The doctor will ask you in detail when the first signs appeared and whether this has happened before. Ask about previous illnesses. Examine the oral cavity.
Tavegil
For research you will have to submit: saliva, smears and scrapings from damaged tissues of the oral mucosa, stool, urine and blood tests. If you have dental structures, you need to take a sample from them for analysis. It is mandatory to take tests to identify allergies and undergo an immunogram - measuring the main indicators of the body's defense system.
Such thoroughness in research is necessary for accurate diagnosis. In addition, allergic stomatitis must be distinguished from hypovitaminosis, fungal infection, herpetic stomatitis, AIDS, blood cancer and other diseases with similar symptoms.
Classification of allergic stomatitis
Depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations, catarrhal, catarrhal-hemorrhagic, bullous, erosive, and ulcerative-necrotic allergic stomatitis are distinguished. From the point of view of etiology and pathogenesis, allergic stomatitis includes medication, contact (including dentures), toxic-allergic, autoimmune dermatostomatitis, chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis and other forms.
Taking into account the speed of development of symptoms, allergic reactions of immediate and delayed types are distinguished: in the first case, allergic stomatitis, as a rule, occurs in the form of angioedema. If a delayed allergic reaction occurs, symptoms of allergic stomatitis are most often detected a few days after exposure to the allergen.
According to the severity of symptoms, allergic stomatitis can be:
- catarrhal;
- erosive;
- erosive-ulcerative;
- ulcerative-necrotic.
Etiopathogenetic classification includes stomatitis:
- contact;
- autoimmune dermatostomatitis;
- medicinal;
- toxic-allergic;
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (CRAS, extreme manifestation - Setton's aphthosis).
Forms
Depending on the cause of the development of the pathology, allergic stomatitis is divided into several forms.
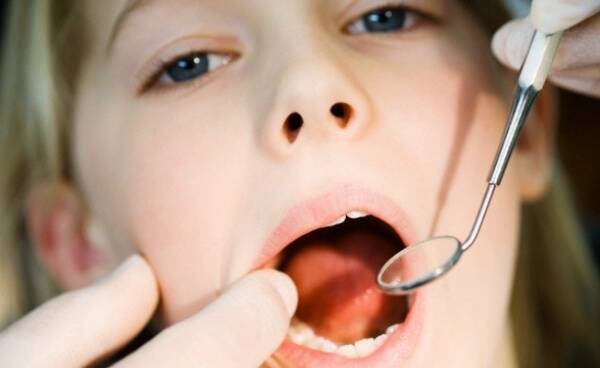
Medication
Drug-induced stomatitis occurs after the use of medications. Pathology develops in the same way both when the product is applied locally and when it is taken orally.
In different people with an allergen to one component, drug-induced stomatitis can manifest itself differently. Some will have only isolated rashes, while others may have them cover all mucous membranes and skin.
Stomatitis can begin either immediately after using the drug or after a few days. The body responds with the most protracted reaction to the use of sulfonamide group drugs and antibiotics.
In addition to rashes, this form of pathology manifests itself as follows:
- skin irritation occurs;
- breathing becomes difficult, even to the point of suffocation;
- sinusitis develops;
- the texture of the tongue changes. Its surface becomes smoothed;
- numerous small eczemas appear;
- often these phenomena are accompanied by headaches;
- The general condition worsens: the temperature rises, nausea and weakness appear.
As a rule, after using the drug, the intensity of symptoms decreases within a few hours. In case of severe intoxication, this period can last 1–2 days.
After relief of primary symptoms and removal of intoxication, treatment of ulcers affecting the mucous membrane begins.
Contact
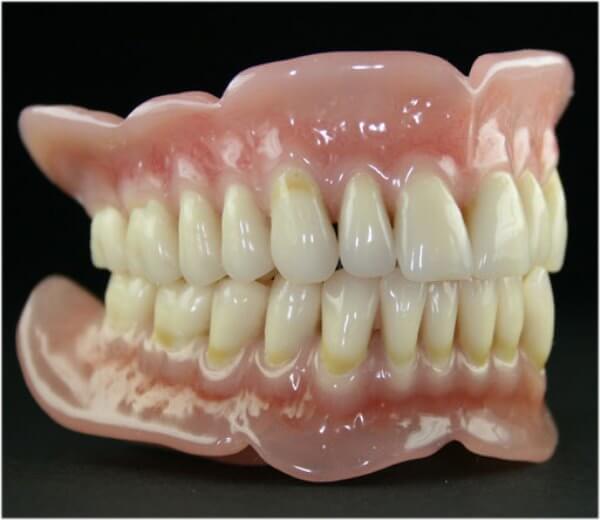
The main cause of the contact form of stomatitis is prolonged exposure to materials or drugs on the mucous membrane.
The irritant can be a prosthesis, a means for fixing it or for caring for the oral cavity. Unlike medication, it has a clear localization, developing only on the oral mucosa.
In addition to the symptoms common to all forms of allergic stomatitis, the following manifestations are characteristic of contact stomatitis:
- severe itching in the contact area;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes, which are painful when palpated;
- the lesions have diffuse outlines, but are located only in the area of contact with the allergen;
- with regular exposure to an irritating factor, vesicles or deep erosions form on the mucous membrane.
Toxic-allergic
This type of stomatitis occurs under prolonged and regular exposure to microorganisms that have a toxic effect, both locally and on the entire body.
Medicines and materials used to solve dental problems: fillings, aseptics, etc. can act as provoking factors.
Stomatitis of this form can affect the inner surface of the lips, gums, tongue and palate.
Pathology is identified by the following signs:
- the oral mucosa swells greatly and acquires a pronounced red tint;
- itching and soreness of soft tissues appears;
- the back of the tongue becomes smoothed, the rest of the surface is covered with a white or brown coating;
- single rashes appear, which burst, grow and merge with each other;
- saliva production increases.
Autoimmune dermatostomatitis
This pathology combines autoimmune damage to the skin and oral mucosa.
The reasons for the development of this type of disease are:
- lichen planus;
- rheumatic diseases;
- pemphigus and similar diseases;
- psoriasis.
The pathology is most often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- numerous rashes that are wavy in nature. As a rule, they are localized not only on the mucous membrane, but throughout the body;
- the tissue of the vesicles is characterized by severe thinning and laxity;
- increased production of saliva is noted;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- eating is accompanied by severe pain;
- the resulting erosions have a glossy pink surface;
- As the disease progresses, erosions grow and merge with other lesions.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
Therapeutic measures for allergic stomatitis will depend on the prerequisites that led to the development of the disease.
The fundamental principle of therapy for allergic diseases is to avoid contact with the allergen: following a diet, stopping a pharmaceutical product, refusing to wear dentures, changing mouthwash or toothpaste, etc.
We suggest you read: How to deal with gum disease
Drug therapy for allergic stomatitis traditionally involves the prescription of antihistamines (loratadine, dimethindene maleate, chloropyramine, etc.), vitamins B, C, PP, and folic acid. Local treatment of the oral mucosa is done with antiseptics, pain-relieving products, enzymes, corticosteroid products, healing agents (sea buckthorn oil, etc.).
Patients who have allergic stomatitis as a complication of dental treatment will need to consult a dentist-therapist, orthopedic dentist, or orthodontist; changing fillings or crowns, replacing braces, denture bases, etc.
The mechanism of development and prerequisites for an allergic reaction
Allergic stomatitis occurs in response to re-entry of an antigen into the body. When an allergen is first introduced, T lymphocytes
T lymphocytes under a microscope
transmit information about its structure to B lymphocytes, which become plasma cells and begin to produce antibodies to a foreign protein compound.
This process is called sensitization of the body.
When the antigen protein enters the bloodstream for the second time, it binds to immunoglobulins and triggers the release of inflammatory mediators.
This is how a hypersensitivity reaction occurs. Depending on the speed of symptoms, hypersensitivity is classified as immediate or delayed hypersensitivity.
In the first case, the main prerequisite for the occurrence of symptoms is the massive release of histamine from basophilic leukocytes. In the second - indirect reactions, in which a foreign protein “labeled” with antibodies interacts with cells, and they are lysed (destroyed) by cellular immune agents that recognize the antigen.
When an allergy manifests itself in the oral cavity, it is often necessary for a foreign agent to be repeatedly introduced into the body and “tease” the immune system, prompting it to produce more and more immunoglobulins.
As a result, so many of them accumulate that if a small amount of antigen gets in, a violent allergic reaction can occur.
Substances that can stimulate allergies in the oral cavity can be:
- antigens of microorganisms living in the oral cavity, this is especially important if there is a carious lesion or periodontitis (foci of acquired infection);
- intolerance to pharmaceuticals, which occurs with prolonged use;
- contact allergic reactions to denture structures (most often, so-called “prosthetic” contact allergic stomatitis).
The reaction itself goes through three main stages:
- Immunological.
A foreign substance is introduced into the body, where the process of secreting a specific protein against which antibodies can be produced occurs - antigen presentation. Then a cascade of reactions is launched aimed at sensitizing the body. When this substance enters the body again, it is conjugated with immunoglobulins. - Pathochemical. The antigen-antibody complex provokes the release of various mediators of the inflammatory response.
- Pathophysiological. The effect that occurs due to the release of inflammatory chemical agents ultimately leads to symptoms.
In the photo, allergic prosthetic stomatitis
Causes of allergic stomatitis
The occurrence of allergic stomatitis can be associated with the penetration of an allergen into the body or specific contact with the oral mucosa.
In the first case, allergic stomatitis will serve as a manifestation of a systemic reaction (to pollen, medications, mold, food, etc.); in the second - a local reaction to irritating causes specifically in contact with the mucous membrane (toothpaste, dentures, pharmaceutical lozenges, mouth rinses, etc.).
The development of contact allergic stomatitis is most often associated with increased sensitivity to materials used in dentistry: products for topical anesthesia, iron fillings, braces, orthodontic plates, crowns, acrylic or iron dentures.
In acrylic dentures, allergic factors, as a rule, are residual monomers, and in rare cases, dyes. When using iron dentures, an allergy to alloys containing chromium, nickel, gold, palladium, platinum, etc. may develop. In addition, caries, acquired tonsillitis, as well as tiny pathogenic organisms accumulating in the denture bed play a certain role in the pathogenesis of allergic stomatitis. and their waste products that irritate the mucous membrane.
Contact allergic stomatitis is more often observed in patients suffering from acquired gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis, dysbacteriosis, helminthiasis, etc.), endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, menopausal disorders, etc.).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Tooth bleeding under a filling - Dentistry
This is explained by the fact that organic and multifunctional disorders in these diseases change the body’s reactivity and cause sensitization to contact allergens.
The development of severe forms of stomatitis is facilitated by other allergic diseases: pharmaceutical disease, food allergies, rhinitis, urticaria, eczema, Quincke's edema, asthmatic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, etc.
Reasons for the development of the disease
A negative reaction develops after contact of the oral mucosa with various allergens. External agents are plant pollen and mold spores.
Allergic stomatitis often develops in the following cases:
- negative reaction to installed crowns, fillings, prostheses, especially those made from cheap, low-quality materials;
- in children - an acute response to certain types of food;
- irritation of oral tissues due to decreased immunity due to a course of treatment with sulfonamides or antibacterial drugs;
- advanced caries, bleeding gums, inflammatory processes accompanied by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- as a complication of Lyme disease, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemorrhagic diathesis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
According to the international classification of diseases, negative reactions in the oral cavity are included in a special section. Allergic stomatitis code according to ICD 10 - K12 “Stomatitis and other related lesions” and subsection K12.1 “Other forms of stomatitis”.
Learn about the use of bay leaves in folk medicine to treat allergic diseases.
Read about the first signs and symptoms of a gluten allergy in a child at this address.
Forecast and prevention of allergic stomatitis
Timely diagnosis of allergic stomatitis allows you to overcome the disease at an early stage; The treatment period for catarrhal and catarrhal-ulcerative stomatitis traditionally does not exceed 2 weeks.
In the most severe and advanced cases, long-term healing of allergic stomatitis may be required.
Preventive measures include good hygienic care of the oral cavity, timely treatment of caries and gum disease. You need constant preventive visits to the dentist to remove dental plaque, adjust dentures, and replace them in a timely manner. Of fundamental importance in the prevention of allergic stomatitis is a personal approach to the treatment and prosthetics of teeth, the use of hypoallergenic ones.
Symptoms of allergic stomatitis
Manifestations of allergic stomatitis depend on the form of the disease. Thus, catarrhal and catarrhal-hemorrhagic allergic stomatitis are characterized by xerostomia (dry mouth), burning, itching, impaired taste sensitivity (sour taste, iron taste), discomfort and pain when eating.
Bullous allergic stomatitis occurs with the formation in the oral cavity of vesicles of various diameters with transparent contents.
Traditionally, after opening the blisters, allergic stomatitis turns into an erosive form with the formation of erosions covered with fibrinous plaque on the mucous membrane. The occurrence of ulcers is accompanied by a sharp increase in local pain, especially manifested when talking and eating. When individual defects merge, vast erosive surfaces can form on the mucosa. There may be a deterioration in general health: loss of appetite, weakness, increase in body temperature.
The most severe in its manifestations is the ulcerative-necrotic form of allergic stomatitis. In this case, a sharp hyperemia of the mucous membrane is determined with multiple ulcers covered with a dirty-gray fibrinous coating and foci of necrosis.
Ulcerative-necrotizing allergic stomatitis occurs against a background of severe pain when eating, hypersalivation, high fever, headache, submandibular lymphadenitis.
General symptoms of allergic stomatitis may include multifunctional disorders of the nervous system: insomnia, irritability, cancerophobia, sensory lability.
How to treat
The duration and nature of therapy depends on the type of disease.
An integrated approach and compliance with hygiene requirements are important. Change your diet: it is imperative to avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes. Offer your baby warm, pureed, sticky foods. Sour and spicy foods are prohibited.
- type, form of pathology;
How to get rid of mouth ulcers forever and how to treat them, will ointment help? As a rule, treatment should be comprehensive, and it consists of three parts. It is necessary to neutralize the cause of the appearance of an ulcer on the cheek or a white ulcer in the mouth. Wounds need careful treatment, and the oral cavity needs general sanitation.
- Chamomile infusion. One teaspoon of chamomile flowers is steamed with a glass of boiling water. Strain the cooled infusion through cheesecloth and add a teaspoon of honey. Rinse your mouth four times a day after meals.
- Burdock root decoction. Grind burdock root to a volume of two tablespoons. Pour 400 ml of boiling water and cook for about forty minutes. Add a tablespoon of chicory. Let it brew for about an hour, strain and rinse twice a day after meals.
- Rinse with baking soda and salt. In 200 ml of warm water, mix well one teaspoon of soda (5 g) and two tablespoons of salt (it is better to take sea salt). Rinse twice a day.
- Milk-garlic ointment. Take three medium cloves of garlic, chop as much as possible, passing through a press. Pour a tablespoon of sour milk or yogurt into the resulting slurry. Treat the affected area with ointment up to three times a day.
- Aloe ointment. Finely chop the aloe stem and pour in one teaspoon of olive oil. Mix thoroughly and lubricate the sores twice a day.
- Carrot juice for mouth ulcers. Mix freshly squeezed carrot juice with warm water in equal parts. Rinse four times a day.
- Onion broth. Chop a medium onion and add ¼ cup of water, boil and cool to room temperature. To treat ulcers, you need to keep the resulting decoction in your mouth.
- A mixture of protein and honey. Take 1 tablespoon of honey, sunflower oil (preferably unrefined), an ampoule of novocaine and chicken protein, mix well. For treatment, keep the resulting mixture in your mouth for ten minutes up to eight times a day.
Traditional methods of treatment are more effective when used in parallel with traditional ones prescribed by a doctor. You should not self-medicate or self-diagnose if ulcers appear in your mouth. Incorrect treatment can lead to a delay in the recovery process and a worsening of the patient's condition.
Therapy for adult patients
The therapeutic tactics chosen by a specialist depend on the factor that causes the disease. At the same time, they adhere to the main principles of combating allergic phenomena:
- the effect of the allergen is eliminated;
- a diet with hypoallergenic products is formed;
- exclusion of medications is ensured;
- use of antihistamines and immunosuppressants.
Pain relief is carried out through the use of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and analgesics. They also help relieve inflammatory changes. To relieve pain, use:
- Camistad with lidocaine and chamomile extract for pain relief, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Hexoral Tabsom with chlorhexidine and benzocaine. The drug is produced in lozenges. Acts against pain and microbial activity.
- Lidocaine Asept, saturated with lidocaine and chlorhexidine. In addition to relieving pain, the drug removes the action of pathogenic bacteria.
- Instillagel contains the components of chlorhexidine and lidocaine. Helps get rid of fatotic and erosive disorders.
To eliminate allergic manifestations, antihistamine drugs are prescribed in addition to painkillers. The oral cavity is usually treated with proteolytic enzymes. These include Lysoamidase, Chymotrypsin, Trypsin.
Antiseptic mouth rinse is made with Chlorhexidine (0.02% for adults and 0.06% for children), a solution of 0.02% Furacilin, a solution of potassium permanganate in a weak concentration. Local antiseptics include Rotokan, Miramistin, Malavit.
To accelerate the restoration of the condition of the mucous membranes, it is necessary to use a dissolving oil type with vitamins A and E for treatment. Solcoseryl and Actovegin are used for effective action. Adults are prescribed Linetol ointment 5%.
Main therapeutic task
The main treatment for stomatitis of allergic origin depends on the factor that influenced its manifestation. That is, first of all you need to eliminate the antigen.
If the cause is medication, the previously prescribed therapy needs to be adjusted; if it is some product, the diet will have to be reconsidered. According to the same principle, everything that caused the allergy is changed - hygiene products for oral care, dentures, fillings and other dental structures, gel for fixing the prosthesis. If stomatitis of the allergic variety occurs against the background of the development of another disease, you need to urgently undergo treatment from an appropriate specialist.
Rupafin
To avoid additional irritation of damaged mucosal tissues, you need to go on a special diet. The basics of proper nutrition can be found in the article “What you can eat with stomatitis.”