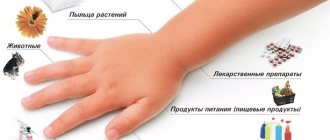
Rhinosinusitis in children is an inflammatory disease that affects the paranasal appendages and the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. Otolaryngologists associate its development with a bacterial infection, which is associated with ARVI. Doctors call factors predisposing to the appearance of sinusitis:
- narrow nasal passages;
- childhood infectious diseases (measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever);
- foreign body stuck in the sinuses;
- chronic diseases that suppress the immune system;
- allergies that precede respiratory diseases and occur in parallel with them (in this case, doctors diagnose allergic rhinosinusitis);
- anatomical features of the structure of the nose that create obstacles to the free outflow of pus (deviated nasal septum);
- dental procedures, the failure of which led to infection of the nasal cavity.
Reasons and forms
Ventilation of the paranasal sinuses occurs through special channels. As the disease develops, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which blocks these channels, making them sealed cavities, which promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in an environment favorable to them and the accumulation of purulent exudate.
Diseases are classified according to the following forms:
- Seasonal. The cause of which is allergens from pollen of flowering plants.
- Chronic. Develops as a result of hypersensitivity to household allergens.
- Mixed. Including allergic and infectious components.
The main causes of occurrence are considered to be:
- abnormal development of the nasal cavity,
- viral infections,
- mucosal injuries,
- severe hypothermia,
- pathology to allergens,
- weak immunity,
- polyps,
- teeth with caries.
Main classification of the disease
Allergic sinusitis differs in severity, frequency and clinical signs. If the symptoms differ slightly, then the nature of the pathology and frequency have a significant difference.
According to the severity, sinusitis of allergic origin is:
mild – discomfort occurs without complicating the patient’s usual life activities;- medium – symptoms become aggressive;
- severe – aggravation of the pathological process with disruption of work activity.
According to the period of development of the disease:
- year-round allergies;
- seasonal allergies;
- occasional allergies;
- occupational allergy.
Inflammation, regardless of intensity, can be either acute or chronic.
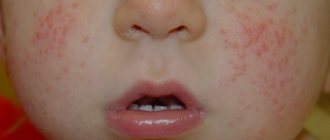
Symptoms of allergic rhinosinusitis
The characteristic symptoms of this type of rhinosinusitis are similar to the classic signs of a respiratory disease.
- sensation of itching and burning in the nasal cavity,
- difficulty breathing associated with swelling of the nasal pharynx,
- muconasal secretion,
- sneeze,
- rhinolalia,
- stuffy ears,
- vasodilatation of the sclera, causing lacrimation,
- paroxysmal dry cough.
In addition to the characteristic symptoms, there are certain systemic signs:
- asthenia,
- painful condition,
- hypersomnia,
- vertigo (dizziness) and headache, especially at the end of the day,
- elevated temperature.
Since the inflammatory process in most cases involves paired formations located on the sides of the vertical plate of the ethmoid bone and the cavity of the upper jaw, palpation of the lesion causes noticeable pain.
Diagnostics
The accuracy of the diagnosis is established by analyzing the medical history, the manifestation of clinical symptoms, the causes, and the allergic reaction that occurs.
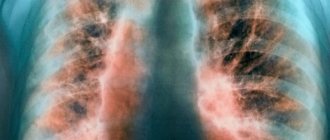
A diagnostic examination of the nasal cavities is prescribed: there is noticeable blueness of the mucous membrane, swelling of the turbinates and copious mucous discharge. An x-ray shows thickening of the paranasal sinuses and a decrease in their airiness.
A blood test is performed to check for the presence of eosinophilia. Radioimmunoassay studies reveal the concentration of IgE in mucus and blood serum. Differential diagnostic studies are aimed primarily at excluding an infectious nature.
Treatment of allergic rhinosinusitis
The main task in treatment is to eliminate the causes that provoked the development of allergic-type rhinosinusitis. In itself, treatment of the year-round form does not cause any particular difficulties. Contact with the allergen that caused the inflammation is identified and stopped.
Patients with the seasonal form of the disease experience certain problems with treatment. They are recommended to use antihistamine drops at least 10 days before the expected onset of the allergy, which significantly facilitates the course of the disease and reduces the likelihood of developing any complications.
The use of medications should be carried out strictly according to the recommendations of the attending physician.
The main treatment is carried out using local therapy methods, and if it is ineffective, drug treatment is prescribed, consisting of a specific combination of drugs.
- In mild cases, drops are prescribed to suppress the allergic reaction.
- A complex form requires the prescription of complex drugs containing hormones.
- A combination of antihistamine tablets and drops when the latter are ineffective.
- Drops for allergy-induced conjunctivitis.
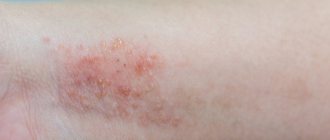
- Ointments, creams for skin rashes.
- Medicines that contain hormones or hormonoids are prescribed in rare cases.
When polyps form, they are removed.
People suffering from seasonal allergic rhinosinusitis should be aware that vasoconstrictor drops are not effective in treatment.
Firstly, they have a short course of use, which does not correspond to the duration of seasonal allergies.
Secondly, they do not eliminate the cause, but only relieve swelling a little.
Prolonged self-use of such medications can lead to atrophy of the nasal mucosa and will only worsen the situation. It is better to consult with an ENT specialist and choose a combined method that will give a positive result.
How to recognize allergic sinusitis and treat it?
Allergic sinusitis is one of the types of sinusitis or sinusitis (this is the second, more common name for the disease among people).
Sinusitis in general is an inflammatory process of the maxillary sinuses - the paranasal sinuses, located in the body of the maxillary bone. The frontal, paranasal and ethmoid sinuses are also affected. In other words, the entire area near the wings of the nose, above and below the eyes becomes inflamed.
Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases in the world. It affects men and women, adults and children equally. Residents of literally all countries get sick; neither epidemiologically dangerous nor epidemiologically clean regions with respect to sinusitis are identified.
Causes and nature of sinusitis
Most diagnoses of sinusitis are made against the background of a viral infection complicated by bacterial invasion.
Rhinitis (runny nose) caused by a viral disease, in the absence of treatment or with prolonged or inadequate treatment, creates conditions that are ideal in terms of humidity and temperature for the appearance and spread of pathogenic bacteria in the sinuses.
Sputum accumulates in the sinuses, in which microorganisms thrive - streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci and others. The immune system ceases to cope with the progressively growing number of harmful microbes and an inflammatory process begins, fraught with many complications.
Sometimes bacterial invasion does not occur and sinusitis develops against the background of only a viral disease. This happens when the pathogens are influenza viruses, adenovirus, and parainfluenza.
Less commonly, the cause of sinusitis is fungal infestation.
There have been cases where sinusitis developed against the background of multiple lesions and tooth decay, severe nosebleeds of various etiologies. Getting contaminated water into the nose or mouth when swimming in pools and open water also causes sinusitis.
Sometimes sinusitis is allergic in nature. It can develop against the background of allergic rhinitis, which is not compensated in time. It also happens that allergic sinusitis develops on its own, and not against the background of another disease of an allergic nature.
Symptoms of sinusitis
In the earliest stages, the patient experiences watery, mucous or mucous-watery discharge from the nasal passages. These discharges do not indicate that sinusitis is developing in the body, including allergic sinusitis, but it does indicate the development of rhinitis - inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
If rhinitis is not eliminated in time, the structure, color and density of the discharge changes.
Sinusitis should be suspected in the following cases:
- Rhinitis continues for more than a week and either there is no improvement in the condition or it worsens,
- The discharge becomes thick, acquires a yellow-green color, and is difficult to discharge from the nose,
- In addition to nasal congestion and runny nose, sore and sore throat, irritation, and cough are added, caused by the flow of thick mucus down the back wall of the throat,
- The patient experiences pain around the nose, around the eyes, and in the middle of the forehead. Inhaled air, accumulated thickened sputum, and pus press on the inflamed walls of the affected sinuses, which causes pain. The pain intensifies when tilting the head down, tensing the facial muscles, coughing and sneezing.
- My head hurts and I feel a little dizzy. This is explained by the fact that due to impaired nasal breathing, increasing oxygen starvation occurs in the body, including brain cells.
- A mild toothache is felt. The lower wall of the maxillary sinuses is so thin that accumulated phlegm and pus can flow to the roots of the teeth, causing local inflammation there.
- The temperature rises and remains at approximately 38 degrees.
Allergic sinusitis has the same symptoms and the same treatments as other types of sinusitis.
Treatment of sinusitis
Only an otolaryngologist can competently treat allergic sinusitis and its other types.
He will make a diagnosis based on an examination of the patient and the results of laboratory tests and prescribe the following drugs: antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal to eliminate the infection, antihistamines to extinguish the allergic reaction, decongestants to relieve swelling, vasoconstrictors to reduce secretion, painkillers to relieve pain.
Advanced conditions require surgical treatment, for example, puncture to remove thick mucus from the sinuses.
You should seek medical help in the treatment of allergic sinusitis in the following cases:
- When a runny nose does not stop within a week,
- There was a deterioration in health after the first three days of the disease,
- The temperature remains stable and does not drop,
- Visual and/or hearing impairments have been noted,
- Concerned about severe headaches that cannot be stopped or subside,
- There was a history of sinusitis of any etiology,
- Allergic sinusitis is accompanied by swelling of the nasopharynx, severe difficulty breathing, an allergic rash on the face and neck, and swelling of the face.
If left untreated, sinusitis leads to inflammation of the optic nerve, which can lead to loss of vision, inflammation of the meninges (meningitis), and osteomyelitis (purulent damage to the bones of the skull).
Treatment in adults is easier than in children.
- Firstly, the range of antibacterial agents approved for use by children, especially in the first years of life, is limited.
- Secondly, children do not know how to clear mucus from their nose by blowing their nose, and toileting their nose performed by adults does not guarantee complete cleansing.
- Thirdly, the condition of children deteriorates faster and most often it is difficult to help them at home.
Prevention of sinusitis
Allergic sinusitis is difficult to prevent if allergic reactions have not occurred before.
If a person knows his tendency to immunopathological reactions, he should limit contact with allergens, adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and regularly perform nasal toilets.
In case of allergic rhinitis, it is necessary to prevent the accumulation of mucus in the nasal passages and use anti-allergic drops.
To prevent a runny nose from turning into sinusitis, you need to thin the mucus in the nose. To do this, you need to drink plenty of fluids and regularly irrigate the nasal cavity with seawater sprays.
Facilitate the condition of inhalation with saline solution. The use of herbs and essential oils for unknown causes of allergies is prohibited due to possible complications.
It is necessary to stop smoking at least for a while while you have a runny nose. Smoking irritates the mucous membrane, causing additional mucus secretion. In addition, substances in tobacco smoke are strong allergens and toxins.
It is important not to drink alcohol due to its ability to cause swelling. Against the background of sinusitis, swelling can be very dangerous.
Following the rules of personal hygiene will help prevent infection from entering the sinuses: washing your hands before washing and touching your face, rinsing the nasal passages, using only clean individual handkerchiefs.
Allergic sinusitis
Source: https://allergiu.ru/bolezni/allergicheskij-sinusit.html
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in adults
To avoid the transition of an acute inflammatory process to a chronic one, treatment must begin with the appearance of the first symptoms. An advanced form of the disease, especially with reduced protective functions of the body, can stimulate the development of very serious complications, such as meningitis and sepsis.
Antibacterial therapy
Often the etiology of the development of the disease is pathogenic microflora. Therapy in this case is based on the use of antibiotics, which are selected after a sensitivity test.
But basically, the doctor uses an experimental method using broad-spectrum drugs that help get rid of many types of pathogens.
- Antibiotics of the penicillin group.
- Group of cephalosporins.
- Group of macrolides.
Local therapy
- Vasoconstrictor drops and sprays.
- Expectorants.
- Substances that can have a regulatory effect on the immune system.
Procedures
Procedural measures are considered an effective addition to antibacterial and local therapy.
Such as:
- Rinsing the nose helps relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, localize congestion and improve the secretion of nasal mucus.
- Inhalations.
- Ultrasound waves.
- Physiotherapy.
- Folk remedies.
Operation
If the above treatment methods are ineffective, surgical intervention is prescribed to pump out purulent exudate from the sinuses and completely clean them. Usually, after it is performed, the patient’s well-being improves significantly.
Therapeutic and preventive measures
Therapeutic measures to eliminate allergic sinusitis in adults include the following steps:
- Relief of symptoms in the acute stage of the disease. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed antiallergic drugs such as suprastin or tavegil. Vasoconstrictor drugs in the form of sprays can also be used. However, the use of the latter requires the consent of a doctor.
- One of the most important conditions for getting rid of a disease such as allergic sinusitis in children and adults is to minimize direct contact with potential irritants. This may negatively affect the rehabilitation process. If possible, you should stop taking other medications for the period of therapy.
- Before treating sinusitis with antihistamines, you should consult your doctor. Taking them for an excessively long time can have a bad effect on the patient’s body.
- After the disease goes into remission and all symptoms are eliminated, work begins to detect the allergen. Samples are taken from the patient to find out what exactly caused the illness.
- The key factor in the fight against sinusitis of an allergic nature is the correction of the patient’s life position. For example, cigarette smoke or alcohol can be strong allergens for many people. Bad habits must be abandoned for the treatment to be successful.
- The final stage of recovery from illness is the use of preventive measures. A person needs to avoid crowded places, dress appropriately for the weather, undergo regular dental examinations, and sanitize the nasopharynx. It is possible that the pathology of the respiratory system will not be passed on to you from another person. And also quite often the root of the problem is untreated caries.
- Take daily walks in the fresh air, do breathing exercises, and learn yoga. It would be useful to master some kind of sport - swimming, running or cycling.
Rhinosinusitis: treatment in children
Almost every second child suffers from this disease. But parents, not knowing the symptoms, underestimate the risks of subsequent complications that their baby may encounter if they do not consult a doctor - an ENT specialist in time.
And the sooner treatment begins, the better it will be for the child. In children, the acute form of the disease very quickly develops into a chronic form, so you should not delay contacting a doctor. The best thing to do is to call him at home.
Usually medications are prescribed that restore normal mucus production. This frees up the sinuses and makes it easier for the child to breathe. Such drugs are Nazivin or Galazolin, which are recommended to be taken for no more than 7 days.
If you do not carry out timely therapy, you can get complications that are painful for the child, the cure of which will require radical measures. For example, puncture and pumping out pus from the maxillary sinus.
Also, drug therapy involves the use of systemic antibiotics, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs and agents that dilute sputum and promote its removal from the lungs.
Do not forget about supporting the baby’s body with immunostimulants. It is better to use decoctions of medicinal herbs for this.
Important! Do not self-medicate and endanger the child’s health. All health activities must be carried out strictly according to the doctor’s instructions and under his supervision.
Allergic (or eosinophilic) fungal rhinosinusitis
This type of allergic sinusitis is characterized by a fungal infection in the sinuses. Fungi are inhaled into the air, resulting in an allergic reaction, leading to the release of sticky mucus and clogging of the affected sinuses.
Very often a chronic form develops, which significantly affects the patient’s sense of smell. An advanced disease can lead to displacement of the eyeball and even loss of vision.
Endoscopy reveals multiple polyps in the nasal sinuses and a viscous, rubbery consistency ranging from yellow to brown. During surgery, allergic mucin is detected in all affected sinuses.
In the presence of large polyps, treatment is carried out surgically (endoscopy) in order to remove the substrate that promotes the growth of fungal mycelium.
Complications and consequences
Despite the fact that this disease is not particularly severe, the lack of drug treatment can result in the following complications for the patient:
- loss of smell without the prospect of restoring sensitivity to smells;
- the occurrence of foreign tumors in the cavity of the nasal canals (polyps, warts, adenoids and other benign tumors);
- transition of an allergic reaction to a more severe form, which no longer manifests itself only in the form of rhinosinusitis, but has all the signs of bronchial asthma;
- atrophic processes in the nasal mucosa, the appearance of erosion and ulcerative formations;
- decreased immune status, formation of a tendency to frequent colds, infectious and viral diseases.
These negative consequences are not fatal for any adult, but they significantly reduce the quality of life and force the patient to make plans taking into account existing complications.