Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about Loratadine and alcohol. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Compatibility of Loratadine and alcohol
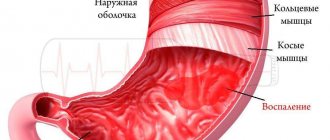
Both substances cause side effects. Taking into account the double load, the risk of their occurrence increases. The effect of treatment wears off. The drug increases the negative effects of drinking alcohol and worsens the alcoholic hangover syndrome.
Doctors insist that such a combination is undesirable. Use simultaneously with alcohol-based medications is prohibited.
Alcohol in excess causes:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Muscle pain.
- Headache.
- Liver failure.
- Failure of the exocrine gland.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
- Neurological abnormalities, mental disorders.
- Disturbances of water-salt balance.
- Visual and auditory hallucinations.
- Insomnia and nightmares.
- Fecal incontinence and voluntary urination.
A heavy dose of alcohol can cause the death of the patient.
Overdose
An overdose of Loratadine significantly increases the incidence of anticholinergic symptoms. In addition, there is evidence of drowsiness, tachycardia, and headache. In this case, symptomatic treatment is indicated for the required period of time. Sometimes, in case of an overdose of this drug, gastric lavage, as well as taking any sorbent, may be necessary. It is important to consider that Loratadine is not excreted by hemodialysis. However, the effectiveness of peritoneal dialysis is unknown for this drug.
The most dangerous combinations and consequences
The combination of alcohol and chemical-based drugs can lead to serious disorders in the body, and in some cases to fatal consequences.
List of medications and their side effects in combination with alcohol:
| Name of group, drug | Negative results of interaction |
| Neuroleptics (tranquilizers, anticonvulsants, hypnotics) | Severe intoxication, up to cerebral coma |
| CNS stimulants (Theophedrine, Ephedrine, Caffeine) | Rapid increase in blood pressure, hypertensive crisis |
| Antihypertensives (Captofrin, Enalapril, Enap-N), diuretics (Indapamide, Furosemide) | Sudden drop in pressure, collapse |
| Analgesics, anti-inflammatory | Increased toxic substances in the blood, general poisoning of the body |
| Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) | Acute gastritis, perforation of gastric ulcer and 12-PC |
| Paracetamol | Toxic liver damage |
| Hypoglycemic (Glibenclamide, Glipizide, Metformin, Phenformin), insulin | A sharp decrease in blood sugar levels, hypoglycemic coma |
The compatibility of Loratadine and alcohol can cause negative reactions from the organ system. The drug in a course form is prohibited from being used together with alcoholic beverages. If the tablets are used to treat allergic reactions, a mixture with alcohol will lead to unpredictable consequences.
- Compatibility of Loratadine and alcohol
- Brief characteristics of the drug
- Use of the drug for alcoholism
- Using the drug for a hangover
- Consequences of drinking alcohol
- When can you take the drug, after how long
- When can you drink alcohol?
- Loratadine and beer
- Organs affected by the toxin
- State of the nervous system under the influence of alcohol and drugs
- Rules for taking medications and alcohol
- Medicines, alcohol and chronic diseases
- The most dangerous combinations and consequences
- Reviews
Are you having any problem? Need more information? Type in the form and press Enter!
The drug is available in tablet form. Packs of 10 and 20 pieces. The volume of the active substance is 10 milligrams.
Drug interactions
In the case of simultaneous use of Loratadine and alcohol, according to studies, the effects of the drug are not particularly enhanced.
When using inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2D6, the level of the active substance of the drug increases. This may cause an increase in the incidence of various adverse reactions.
After simultaneous administration of Loratadine and Ketoconazole, Erythromycin, Cimetidine, the level of the first drug in the blood increases. But this is not accompanied by significant changes.
It should be borne in mind that studies of the interaction of Loratadine with other drugs were conducted exclusively with the participation of adult patients, so these conclusions do not apply to children.
Side effects of this medication
The chance of side effects from using Loratadine is very small. It can be said that placebo side effects are just as likely to occur.
Considering the human respiratory system, we can also name some side effects from using Loratadine:
- Dryness and bleeding from the nose;
- Dry cough;
- Painful sensations in the chest area;
- The occurrence of bronchitis;
- Infectious infection of the upper respiratory ducts.
If we consider the nervous system, the most likely cause may be a headache, about 12%. Less likely to occur are drowsiness and fatigue. Even less common are dizziness, insomnia, mild amnesia, impaired attention, depression and more.
Regarding the gastrointestinal tract, the following side effects occur:
- Increased appetite;
- Flatulence;
- Toothache;
- Vomit;
- Dry mouth;
- Diarrhea;
- Gastritis;
- Disturbed taste buds.
Cases of hepatitis, jaundice and death of liver tissue are quite rare.
You can look at the wide variety of consequences from using this drug from many angles. The most basic of all the others include painful sensations when urinating, hypertension, swelling of the urinary system, back pain, cramps, dry skin, increased sweating, thirst, change in the color of urine, skin rashes, urticaria and dermatitis.
Adverse reactions
In studies that included not only adults, but also adolescents, adverse reactions were recorded in 2% of patients. They had indications for taking Loratadine at a dose of 10 mg per day. The most common adverse reactions were: drowsiness, headache, increased appetite, insomnia. At the same time, in studies of children aged 2–12 years, the following side effects were most often noted: headache, nervousness, and increased fatigue.
Very rarely (<1/10,000) adverse reactions were recorded according to the classes of organ systems, a list of which in order of decreasing manifestations is given below.
- Immune system – anaphylaxis, angioedema.
- Nervous system – convulsions and dizziness.
- Heart – tachycardia, palpitation.
- Hepatobiliary system – changes in the liver and its functions, including pathological ones.
- Gastrointestinal tract - nausea, gastritis, dry mouth.
- Skin – rash, alopecia.
- The general condition is increased fatigue.
Interaction of Loratadine with the human body
As mentioned above, Loratadine can be called an anti-allergic drug. A component such as histamine is responsible for the manifestation of allergic reactions in the body. Therefore, the action of this medicine is aimed specifically at this component in the human body.
This drug begins to act approximately 2-3 hours after its use. Its most powerful effect on the body appears after 9-10 hours and ends after 24 hours.
The inability to directly affect the nervous system is that the components of this medicine cannot pass the blood-brain barrier.
The greatest absorption of this medicine into the body occurs in the gastrointestinal tract. Because Loratadine begins to act approximately 2-3 hours after its use, at the same time its maximum concentration in human blood is reached.
Eating food does not greatly affect the absorption of this drug, however, the time when its concentration in the blood becomes maximum is extended by about an hour. Based on this, we can say that it would be better to consume it before meals. Metabolism of Loratadiine occurs in the liver and therefore an additional load appears on it, although very insignificant.
The active substances of this medication can end up in the child’s body, for example, transmitted from the mother through breastfeeding the baby. In cases where the patient has abnormalities in liver function or there may be a risk of liver failure, then the dose taken is reduced exactly by half.
We recommend reading: How to choose a name for your child
What will be the mechanism of action on the body if you take Loratadine and drink alcohol?
Loratadine is a second generation anti-allergy drug. Its components affect human receptors, blocking them, which, in turn, significantly reduces allergic irritation.
Loratadine is a long-acting anti-allergy drug. Its effect can be active for 24 hours. It is the absence of any effect of this drug on the central nervous system that distinguishes it from similar first-generation medications.
Another positive point, no less significant, is the lack of dependence on this drug.
Mode of application
Loratadine is recommended to be taken before or after meals to avoid possible dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, stomach pain), with ½ glass of water. If it is impossible to swallow the tablet whole, chew it.
Take Loratadine for adults and children over 12 years of age - 1 tablet or 10 ml of syrup once a day . Children from 2 to 12 years old - in a dosage of 5 ml once a day. If the child weighs more than 30 kg, an adult dosage is indicated - 1 tablet or 10 ml of syrup per day.
Loratadine for adults, children over 12 years of age and weighing over 30 kg, suffering from severe liver pathologies, is prescribed in a standard dose every other day or daily, ½ tablet or 5 ml of syrup; for body weight up to 30 kg – 5 ml of syrup or ½ tablet every other day. The duration of treatment is determined by the severity of the disease and diagnosis. In mild cases, a single use is possible, in others - from 3 to 10 days. Long-term therapy over a year is allowed.
If the drug is used as a prophylactic agent, your doctor will give recommendations on how to take Loratadine.
Note! If the three-day course does not give a positive result, the drug is replaced with antihistamines with another active ingredient.
Sources:
Vidal : https://www.vidal.ru/drugs/loratadine__3595 GRLS : https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGu >
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Loratadine is a long-acting antihistamine that exhibits antiexudative and antipruritic effects on the body.
H1-histamine receptor blocker (long-acting). Suppresses the release of histamine and leukotriene C4 from mast cells. Prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions.
It has antiallergic, antipruritic, antiexudative effects. Reduces capillary permeability, prevents the development of tissue edema, and relieves spasms of smooth muscles.
Chemical name
| Loratadine tablets | Effervescent tablets (loratadine-hemofarm) | Syrup | |
| Main substance | Loratadine – 10 mg | Loratadine – 1 mg in 1 ml syrup | |
| Auxiliary components | Corn starch, magnesium stearate, talc, silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate | Sodium carbonate anhydrous, citric acid anhydrous, povidone, silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, macrogol 6000, polysorbate 80 | Glycerol, refined sugar, sodium benzoate, anhydrous citric acid, propylene glycol, cherry or Apricot 059 food flavoring, purified water |
| Physicochemical characteristics | Round, white or slightly yellowish flat-cylindrical tablets, biconvex, divided by a line on one side | Round tablets, light yellow or white | Transparent or light yellow, greenish-yellow syrup with a specific odor (cherry or apricot taste) |
| Package | 7 or 10 tablets in contour blisters made of foil and polyvinyl chloride. 1-3 blisters in a cardboard package | 10 tablets in contour blisters and cardboard packs | Bottles made of glass or plastic with a volume of 100 ml. The package contains a 5 ml measuring spoon. |
| Price | No. 30: 60-80 rub. | No. 30: 70-80 rub. | 100 ml: 120-200 rub. |
4-(8-Chloro-5,6-dihydro-11H-benzo-[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-ylidene)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester
| Name | The value of the Vyshkowski Index ® |
| Lomilan® | 0.0548 |
| Claritin® | 0.0534 |
| Clarotadine® | 0.0177 |
| Claridol | 0.0148 |
| Erolin® | 0.0133 |
| Clarisens® | 0.0099 |
| Loratadine | 0.009 |
| LauraHEXAL® | 0.0058 |
| Loratadin-Teva | 0.0021 |
| Loratadine-Hemofarm | 0.0014 |
| Loratadin-Akrikhin | 0.0013 |
| Loratadine Stada | 0.0009 |
| Loratadine 10-SL | 0.0006 |
| Clargotil® | 0.0005 |
| Vero-Loratadine | 0.0005 |
| Loratadine-Verte | 0.0003 |
| Clarifer® | 0.0003 |
| Tirlor® | 0.0003 |
| Lomilan® Solo | 0.0003 |
| Alerpriv® | 0.0002 |
| Clarendine | 0.0001 |
| Clallergin | 0.0001 |
| Loratadine-OBL | 0.0001 |
| Loratadine-Eco | |
| Loratavel | |
| Loratadine-VERTEX |
Analogues of Loratadine, price in pharmacies
If necessary, you can replace Loratadine with an analogue of the active substance - these are the following drugs:
When choosing analogs, it is important to understand that the instructions for use of Loratadine, price and reviews do not apply to drugs with similar effects. It is important to consult a doctor and not change the drug yourself.
Price in Russian pharmacies: Loratadine 10 mg tablets, 10 pcs. – from 8 to 20 rubles, according to 792 pharmacies.
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at temperatures up to 25°C. Keep away from children. Shelf life – 3 years. Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies - without a prescription.
Instructions for use Loratadine, dosage
Regardless of the form, it is taken orally before meals.
According to the instructions, adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed 1 tablet of Loratadine (10 mg) or 2 tsp. syrup per day.
The duration of the course is usually 10-15 days. In some cases, the duration of therapy is determined individually and can take from 1 to 28 days.
Children aged 3-12 years are usually prescribed 1/2 tablet of Loratadine or one teaspoon of syrup per day.
For children whose body weight exceeds 30 kg, the drug is prescribed 1 tablet or 2 tsp. syrup per day.
The effectiveness and safety of use in children under 1 year of age have not been established.
- The presence of individual intolerance to the components of the medication.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Lack of lactase in the body.
- Individual lactose intolerance.
- The presence of malabsorption (galactose and glucose).
- Pregnancy period.
DRUG FORMS
• Syrup. • Suspension for oral administration. • Pills. • Effervescent tablets.
Possible adverse reactions
Loratadine very rarely causes side effects. Negative effects from it in terms of frequency of occurrence can be compared with side effects from placebo. But such undesirable manifestations, although extremely rare, are possible.
The human respiratory system can sometimes react with the following phenomena:
- dryness of the nasal mucosa;
- unproductive cough;
- painful sensations in the chest;
- damage to the bronchi and lungs.
The nervous system may respond:
- headache;
- drowsiness, fatigue;
- sleep disturbances, deterioration of memory and concentration.
From the gastrointestinal side, the following manifestations are possible:
- excessive dryness in the mouth;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- flatulence or diarrhea;
- gastritis.
The skin may exhibit the following negative reactions:
- severe dry skin;
- increased sweating;
- skin irritation, rash.
The genitourinary system reacts negatively with the following manifestations:
- pain when urinating;
- problems with the menstrual cycle;
- change in the color of urine excreted.
All these manifestations are possible only from taking the drug itself. All these manifestations are possible only from taking the drug itself. And drinking alcohol during treatment can seriously aggravate the situation.
Facts about combining alcohol and antihistamines
First of all, you also need to find out some points about alcoholic beverages:
- Alcohol reduces the effectiveness of the drug due to its effect on metabolism.
- Alcoholic drinks, especially beer and white wine, are the strongest provocateurs of allergic reactions.
- The load on the liver increases, especially if you take Loratadine and alcohol. This duet can provoke serious pathologies and lead to cirrhosis of the liver.
- The reaction to the brain and cardiovascular system doubles, thereby provoking irreversible processes.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract develop.
- The drug delays the elimination of alcoholic beverages from the body.
- One can observe a strong exacerbation of all previously declared pathologies.
You can see that the two drugs Loratadine and alcohol are absolutely incompatible and deadly.
Topic of the article: Is it possible to combine Loratadine with alcohol? — we understand the issue, trends for 2020.
Loratadine is a popular and effective remedy for suppressing allergy symptoms. The drug belongs to the second generation of antihistamines and is suitable for adults and children. Since allergies can be accompanied by very severe symptoms, this medicine is vital for many. Unfortunately, careless use can cause significant harm .You should handle the drug especially carefully when combined with alcohol.
- Alerpriv;
- Vero-Loratadine;
- Clallergin;
- Clargothyl;
- Claridol;
- Clarisens;
- Claritin;
- Clarifer;
- Clarotadine;
- Lomilan;
- Lomilan Solo;
- LauraHexal;
- Loratadine 10-SL;
- Loratadine-OBL;
- Loratadine-Verte;
- Loratadine-Teva;
- Loratadine-Hemofarm;
- Loratadin-Stada;
- Lotharen;
- Tirlor;
- Erolyn.
Circulatory system
Long-term intake of alcohol in combination with Loratadine leads to a decrease in the number of platelets and the formation of persistent thrombocytopenia. With standard administration of the drug, tissue swelling decreases, fluid exudation from the capillaries stops, and inflammation stops. But combined use with alcohol leads to the opposite effect - the release of leukocytes to the site of inflammation is inhibited, the body’s response to infection is absent, and immunosuppression occurs. As a result, a person’s risk of viral and bacterial infections increases.
We recommend reading: Common Kirkazon - medicinal properties, photos, application
How to take loratadine
Today we will talk: How to take loratadine
Loratadine is a popular 2nd generation antihistamine that does not have a sedative effect when used in therapeutic doses and does not have a negative effect on the cardiovascular system. After treatment, drug dependence does not develop.
It is a histamine H1 receptor blocker and is characterized by rapid and long-lasting action. Effective for various types of allergies, quickly relieves allergic reactions.
Loratadine is used for allergies in the treatment of adults and children and is available in three dosage forms.
Clinical and pharmacological group: antiallergic agent.
Composition, physical and chemical properties, price
All dosage forms are intended for oral use:
pharmachologic effect
It has antiallergic, antiexudative, antipruritic effects, reduces the permeability of capillary walls, relieves swelling and spasms of smooth muscles.
The drug has a selective blocking effect on peripheral histamine H1 receptors.
These receptors, located in smooth muscles, the central nervous system and blood vessels, are responsible for the development of allergic reactions and allergy symptoms: they are involved in the production of histamine. The drug, influencing these receptors, reduces the rate of histamine production.
This leads to the fact that allergic reactions do not develop, and allergy symptoms (swelling, itching, rash, redness of the skin, etc.) disappear.
Among the distinctive advantages of the drug, we note:
- lack of sedative effect. Treatment can be given if it is necessary to perform precise work, drive a car, while studying, etc.;
- there is no negative effect on the function of the cardiovascular (does not lead to prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG) and nervous systems (does not pass through the BBB);
- does not cause addiction after treatment;
- taken only once a day.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
It is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract: the active substance shows its effectiveness after 20-30 minutes. after oral administration of the drug (effervescent tablets - after 15 minutes). Binds to plasma proteins by 97%.
The maximum concentration of the active substance in the blood is observed 1.3 hours after use, and desloratadine (active metabolite) - after 2.5 hours. Equilibrium concentrations of loratadine and desloratadine in plasma are observed on the 5th day after administration.
Eating extends the period of reaching maximum blood concentration by approximately 1 hour. Blood concentrations are higher in elderly patients and in people with chronic renal failure or alcoholic liver damage. Hemodialysis does not affect the pharmacokinetics of the active substance and its active metabolite.
The peak of therapeutic effectiveness occurs 9-10 hours after administration. The drug acts within 24 hours. Metabolism of loratadine occurs in liver cells with the participation of cytochrome P450 3A4 and cytochrome P450 2D6.
The half-life is 8 hours (extended in elderly patients and in the presence of liver damage). Excreted through the kidneys, bile and large intestine.
special instructions
During treatment, the possibility of developing seizures cannot be 100% excluded, especially in patients with a predisposition.
Patients with kidney or liver dysfunction should receive an adjusted dose of the drug (most often the dose is reduced by 50%).
Dosage
All dosage forms should be taken at the same time of day, 5-10 minutes before meals.
Pills:
- Adults and children over 12 years of age (and weighing more than 30 kg): once a day, 10 mg (1 tablet);
- Loratadine for children 3-12 years old (and weighing up to 30 kg): once a day, 5 mg (half a tablet).
Effervescent tablets:
Before taking, the tablet is dissolved in 200 ml of clean water. Do not suck or chew the tablet!
- Adults and children over 12 years of age (and weighing more than 30 kg): once a day, 10 mg (1 dissolved tablet);
- Loratadine for children 2-12 years old (and weighing up to 30 kg): once a day, 5 mg (half a tablet dissolved in water).
Loratadine syrup:
Take in its pure form, with water if necessary.
- Adults and children over 12 years of age, as well as children weighing more than 30 kg: 10 mg once daily;
- Children 2-12 years old and children weighing less than 30 kg: 5 mg once daily.
The duration of use of loratadine is determined individually, the average course: 7-14 days.
Many people are interested in, if loratadine is prescribed, how long can it be taken as a maximum? In some cases, the drug is prescribed for a period of up to 30 days.
Since it is not addictive, you can take the medicine for a long time to achieve the proper therapeutic effect. In any case, the duration of treatment is determined only by the doctor!
Overdose
Exceeding the therapeutic dose leads to the development of weakness, drowsiness, tachycardia, and migraine. If you accidentally or intentionally exceed the dose, you should rinse your stomach and take absorbent drugs (Polysorb, activated carbon). If necessary, more serious measures are taken in a medical facility.
Side effects
The most common cause of adverse reactions is hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary components of the drug. All side effects quickly disappear after discontinuation of treatment.
- On the part of the digestive system, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, gastritis, and flatulence are rarely observed. In some cases, liver function disorders are possible.
- From the side of the central nervous system, headache, insomnia, decreased concentration, dizziness, anxiety, nervousness, increased fatigue, excitability (more often in children) sometimes develop.
- On the part of the heart, in rare cases, tachycardia may be observed.
- From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, myalgia, back pain, calf muscle cramps.
- From the respiratory system: sneezing, nasal congestion, cough, laryngitis, shortness of breath.
- From the urinary organs: discomfort when urinating, vaginitis, change in urine color, menorrhagia.
- Allergic reactions: skin rash. In isolated cases, anaphylactic reactions have been observed.
- Skin reactions: alopecia (rare).
- Other reactions: blurred vision, fever, chills, ear pain.
Drug interactions
When co-administered with drugs that inhibit the isoenzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 or which are metabolized with the participation of these enzymes (including cimetidine, erythromycin, quinidine, ketoconazole, fluoxetine, fluconazole), the plasma concentration of loratadine and/or these drugs may change.
Inducers of microsomal oxidation (ethanol, barbiturates, phenytoin, rifampicin, zixorin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of loratadine.
Which is better: loratadine or suprastin
Suprastin is one of the most popular antiallergic drugs, which is widely known and probably found in every home medicine cabinet. Suprastin belongs to the first generation antihistamines, acts for a shorter period of time (up to 8 hours), and is taken several times a day.
The drug penetrates the blood-brain barrier and can cause the following adverse reactions: drowsiness, headache, decreased concentration, fatigue, dizziness, which imposes certain restrictions on its use.
However, which drug is better in each specific case, only the attending physician can say.
Analogs
Analogs of loratadine according to the active substance:
Especially for: Medical portal – https://pomedicine.ru
Source: https://pomedicine.ru/2164-kak-prinimat-loratadin.html
Facts about combining alcohol and antihistamines
First of all, you also need to find out some points about alcoholic beverages:
- Alcohol reduces the effectiveness of the drug due to its effect on metabolism.
- Alcoholic drinks, especially beer and white wine, are the strongest provocateurs of allergic reactions.
- The load on the liver increases, especially if you take Loratadine and alcohol. Such a duet can provoke serious pathologies and lead to cirrhosis of the liver.
- The reaction to the brain and cardiovascular system doubles, thereby provoking irreversible processes.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract develop.
- The drug delays the elimination of alcoholic beverages from the body.
- One can observe a strong exacerbation of all previously declared pathologies.
You can see that the two drugs Loratadine and alcohol are absolutely incompatible and deadly.
Characteristics and use of the drug
This drug is antihistamine, that is, it has an antiallergic effect. Loratadine acts as an assistant in preventing negative reactions of the body in the event of allergens. The product is very effective and has virtually no side effects.
The substance loratadine does not begin to act immediately, but only after several hours; this must be taken into account in patients with acute symptoms. The drug fights allergy symptoms gradually and remains in the body for 24 hours. This fact must be taken into account when planning your routine, and the diet, after all, Loratadine interacts with alcohol, causing negative consequences.