To relieve allergenic manifestations, you can use the drugs Loratadine or Desloratadine. They have the same medicinal activity. However, these medications also have a number of differences, which you should definitely familiarize yourself with when choosing the most suitable remedy.
To relieve allergenic manifestations, you can use the drugs Loratadine or Desloratadine.
Composition and release form

The drug has the ability to block histamine H1 receptors. These receptors are responsible for the occurrence of allergy symptoms. They are located in smooth muscles, in the central nervous system and in blood vessels. Loratadine is quite effective in helping to cope with allergic rashes on the skin of the body, as well as severe itching.
| pharmachologic effect | antiallergic, antihistamine, antipruritic, antiexudative. |
| Active substance | Loratadine. One tablet contains 0.01 g. |
After reception:
- The manifestation of itching, the formation of exudate and other allergic reactions are reduced.
- A pronounced antispasmodic effect is observed in relation to smooth muscle fibers.
- The development of edema is prevented, and the possibility of penetration of chemicals through the single-layer capillary tissue is reduced.
The antiallergic, antipruritic and antiexudative effects of Loratadine appear within 30–60 minutes after use, and the maximum effect of the drug is observed after 4–12 hours and persists for 24–48 hours.
| Release form | |
| Syrup | The syrup has a specific smell and taste of apricot or cherry. In appearance, the syrup is transparent, colorless or light yellow. Ingredients: citric acid powder, cherry (apricot) flavor, 1, 2-propanediol, refined sugar, glycerol, sodium benzoate, purified water. |
| Pills | Loratadine in tablets: almost white or white, round, flat-cylindrical in shape, with a chamfer and a dividing line (10 pieces in a blister pack, 1, 2 or 3 packs in a cardboard box. |
| Effervescent tablets | Effervescent tablets are white or yellowish, round in shape, each containing 10 mg of loratadine. |
Depending on the form of release, various auxiliary components are added to the active substance; they do not affect the therapeutic effect.
Analogs
There is a third generation of antihistamines (analogues).
These include:
- Desloratadine Teva;
- Levocetirizine;

- Erius (syrup, tablets);
- Lordestin (tablets).
The patient needs to remember that if the doctor has prescribed a certain drug, then it is not advisable to replace it with analogues, since each drug has its own negative manifestations.
What does Loratadine help with?
The drug creates a long-term therapeutic effect, exhibiting antipruritic and antiexudative properties. Loratadine is good for allergies, relieves spasms and swelling.
The drug helps with the following diseases and symptoms:
- Allergic rhinitis (seasonal and year-round),
- conjunctivitis,
- hay fever,
- urticaria (including chronic idiopathic),
- angioedema,
- itchy dermatosis,
- pseudo-allergic reactions caused by the release of histamine,
- allergic reactions to insect bites.
pharmachologic effect
Belonging to the long-acting histamine H1 receptor blockers, desloratadine is the primary active metabolite of loratadine. By inhibiting the release of histamine and leukotriene C4 from mast cells, the active substance of the drug prevents the occurrence and effectively alleviates the course of allergic reactions. The drug has antiallergic, antipruritic and antiexudative effects. By reducing the level of capillary permeability, desloratadine also prevents tissue swelling and relieves spasm of smooth muscles. At the same time, it has virtually no sedative effect, without changing the speed of psychomotor reactions (when taken at a dose of 7.5 mg). As comparative studies of desloratadine and loratadine have shown, the drugs do not have clinically significant qualitative or quantitative differences in toxicity.
Instructions for use
Loratadine is often included in the list of prescribed drugs when allergic reactions are detected. The effect of the drug on the body is complex. Reduces the level of histamine in the blood, reducing the manifestation of allergy symptoms. Loratadine can be taken as regular tablets, effervescent tablets, or syrup.
Instructions:
- Taken orally before meals. Adult patients and children over 12 years of age are prescribed one tablet (10 mg) or 2 tsp. syrup per day. The duration of the course is usually 10-15 days.
- Children from 2 to 12 years old with body weight less than 30 kg - 5 mg 1 time / day.
In some cases, the duration of therapy for adults and children with Loratadine is determined individually and can take from 1 to 28 days.
After taking the tablet/syrup, the active substance is detected in the blood within 15-20 minutes. The effect appears within 1-3 hours, reaching a maximum 8-12 hours after taking the syrup/tablet, and lasts for another 12-16 hours. The total duration of action is 24 hours.
While taking loratadine, as with any other antihistamine, it is highly recommended to completely avoid or reduce alcohol consumption to a minimum. In this case, the likelihood of various side effects occurring will be extremely low, and the therapeutic effect of the medication will be as high as possible.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Pharmacokinetics
The main antihistamines for relieving allergic symptoms include H1-histamine receptor blockers. To date, this list has been replenished with drugs of 2 streams, represented by metabolites.
In addition to Desloratadine, these include: Levocetirizine, Fexofenadine. The maximum concentration of the antihistamine is reached three hours after the start of use. The presence of the active substance is observed after 30 minutes. The drug binds proteins in plasma by 85-87%.
When using a dosage in adult patients (from 5 to 20 mg over 24 hours) for two weeks, it does not accumulate in the body and is not able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Desloratadine, Fexofenadine and Levocytirizine undergo active metabolic processes in the patient's body. The drug is excreted in the form of glucuronide compounds within 24 hours.
Contraindications
- The simultaneous use of Loratadine with Erythromycin (Ketoconazole) requires a dosage reduction.
- Loratadine requires careful use with medical supervision in case of renal and hepatic diseases.
- Severe liver pathologies do not allow the use of Loratadine.
- The drug is discontinued if, after taking it, an individual intolerance to its components is revealed.
- For children under 2 years of age, the dosage is prescribed by a pediatrician in the form of syrup.
- Loratadine is not prescribed to women during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
General information about the drug
The tablets are packaged in a cardboard box, with instructions and blisters containing the medicinal substance. Each tablet is white or almost white, round and biconvex in shape, the internal contents may be white or creamy pink. On the outside it is covered with a film shell. Blisters can contain different numbers of tablets, from 7 to 30 pieces. One package can contain up to 3 blisters.
The syrup is packaged in cardboard packaging, which contains a bottle with the contents and instructions for use. The bottle is dark to prevent direct sunlight. The syrup itself is a clear liquid with a raspberry color and odor. The volume of the bottle is 60 ml.
special instructions
The instructions for Loratadine indicate that if liver function is impaired, the initial dose of the drug is reduced to 5 mg per day due to the risk of impaired clearance of the active substance of the drug.
When using loratadine, the development of seizures cannot be completely excluded, especially in predisposed patients. Patients with impaired renal or liver function require dosage adjustment.
The use of the drug must be discontinued at least 8 days before the skin allergy test.
Loratadine in some cases may cause dose-dependent sedation.
When is it prescribed and are there any contraindications?
Desloratadine has a fairly narrow range of applications, which includes:
- hay fever;
- acute and chronic urticaria;
- allergic rhinitis of chronic, seasonal or single course.
Before prescribing the drug, the doctor is obliged to clarify with the patient the presence of diseases that are a contraindication to the use of Desloratadine. If they are present, the drug is contraindicated for use, as the risk of complications increases significantly. Contraindications include:
- The presence of hypersensitivity, as well as intolerance to the constituent component or an allergic reaction to it.
- Pregnancy. The drug is especially dangerous in the first and third trimester.
- Lactation.
- The patient's age is up to 12 years when using the tablet form, under 6 months for syrup.
- The presence of lactase, glucose-galactose deficiency.
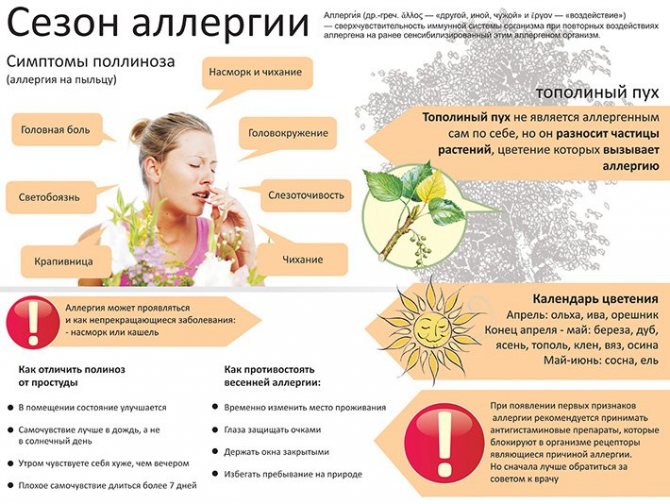
Side effects for the body
The most common cause of side effects is excessive sensitivity to the ingredients. They disappear quickly after stopping treatment. Their appearance is associated with a reaction to drug metabolism products that penetrate the body’s tissues.
Possible side effects from taking Loratadine:
- Cardiovascular system: rarely – tachycardia;
- Nervous system: rarely – headache, increased fatigue, in children – excitability;
- Digestive system: rarely - nausea, dry mouth, gastritis, vomiting; in some cases - functional liver disorders;
- Allergic reactions: rarely - skin rash; in isolated cases - anaphylactic reactions;
- Dermatological reactions: in some cases - alopecia.
Although loratadine is an anti-allergy medication, increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug may cause or worsen existing allergic diseases.
How it affects the body
Desloratadine, due to its selective blocking effect on peripheral histamine receptors, can have an antihistamine effect. As a result, the signs of an allergic reaction and the inflammatory process associated with it are eliminated.
It is able to inhibit the production of cytokines that exhibit anti-inflammatory activity, reduce the release of eosinophils to the site of inflammation, and influence the receptors and muscle elements of the vascular unit in order to prevent the development of tissue edema. Blocks the production of secretion by cells that produce it on the surface of the mucous membranes.

You can take Desloratadine for allergies at any time. Its action is not associated with food intake, since food does not affect the absorption and manifestation of the properties of the drug. The drug is absorbed quite quickly and can be detected in the blood within 30 minutes after administration. There, Desloratadine binds to plasma proteins (the percentage of binding can reach almost 90%). The maximum concentration when taking the drug in an average therapeutic dosage appears after 3 hours.
Metabolism occurs in liver cells. Excretion occurs through the urinary and digestive systems. The half-life is approximately 24 hours.
The drug is not able to penetrate the organs of the central nervous system. The pharmacokinetics of the syrup is similar to that of the tablet.
Interaction with other drugs
This drug should be combined with other medications and antibiotics only after the doctor’s recommendations, since sometimes the effect of one or all of the drugs taken is weakened if they are metabolized by the same enzyme system.
The instructions state that:
- erythromycin, cimetidine, ketoconazole increase the concentration of loratadine in the blood plasma without causing clinical manifestations or affecting the ECG.
- Inducers of microsomal oxidation (phenytoin, ethanol (alcohol), barbiturates, zixorin, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) reduce the effectiveness of loratadine.
"Erius"
The drug belongs to the group of antihistamines. Blocks the production of histamine H1 receptors. The medicine contains desloratadine. Available in the form of blue tablets or syrup. The drug prevents the development and eliminates the symptoms of an allergic reaction. Does not have sedative effects and does not affect the functioning of the nervous system. Used to treat symptoms of allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Pregnancy and lactation are considered contraindications to treatment. You should also not take the pills if you are under 12 years of age. The medication is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the medication.

The drug "Erius" is prescribed with caution for pathologies of the kidneys and liver. In most cases, take one tablet per day. Syrup for adults is dosed at 10 ml per dose. Depending on age, young children are given 2.5 ml to 5 ml of medication per day. The medication has the same indicators as Desloratadine. Instructions for use, price, analogues of the medicine - every allergy sufferer should know all this.
What can be replaced
Among the analogues of Desloratadine, the following drugs can be distinguished:
- Erius . A medicine that also contains desloratadine. It has a small number of side effects and does not affect the nervous system. The average cost can be 500-600 rubles.
- Blogger-3 . Product produced in Croatia. It has a similar composition and concentration of the main active ingredient, but at the same time it shows its effect much earlier. This is achieved through the form of administration; in Blogir-3 it is sublingual, that is, placed under the tongue. The price averages about 300 rubles.
Possible adverse reactions and overdose
It should be noted that side effects when taking Desloratadine occur quite rarely. This is usually due to the development of hypersensitivity or incorrect dosage regimen.
The most common negative reactions of the body to taking the drug are:
- The occurrence of rashes, urticaria, and Quincke's edema.
- The appearance of periodic or constant headaches, dizziness, insomnia, seizures and hallucinations.
- Feeling of increased fatigue.
- Disruption of the cardiovascular system, which is expressed by tachycardia or arrhythmias.
- The appearance of dry mouth, spasmodic abdominal pain, diarrhea. In some cases, the patient may experience the development of pain in the liver area, and laboratory tests may reveal an increase in bilirubin.
- Development of myalgia.
In the photo you can see a more detailed list of side effects.

Symptoms of overdose when taking Desloratadine occur extremely rarely. Even when the average therapeutic dose was exceeded by 2-3 times, no pathological reactions occurred. They can appear with multiple increases in dosage, extremely low body weight, or the presence of diseases of the organs in which metabolism and excretion of the main active substance occurs.
In case of an overdose, symptoms appear that are characteristic of side effects. If such a clinical picture appears, you should immediately seek medical help and stop taking Desloratadine. To improve the condition, only symptomatic therapy can be used. Infusion therapy and plasmapheresis do not give the desired effect.










