The skin in the intimate area is characterized by high sensitivity. Any negative impact can affect her condition. Therefore, allergies to the labia are not so rare. Usually this condition does not threaten a woman’s health, and with proper skin care, it goes away on its own. The main task in this case is the correct determination of the state. Is it really an allergy or is the reason something else? Symptoms such as redness of the skin, small rash, itching, irritation may be signs of:
- venereal disease;
- skin disease;
- parasitic activity;
- fungal infection, etc.
It is also very important to establish in time whether the reaction of the skin of the labia is local, or whether it is part of the signs of a general allergic process. A local reaction is harmless and does not require serious medicinal measures, while a general allergy affecting the entire body, on the contrary, poses a threat to human health and, in some cases, life.
Indications for the use of ointments in the intimate area
The causes of discomfort may be insufficient hygiene, hormonal changes, allergies to internal and external irritants, fungal infections, herpes virus, sexually transmitted diseases, parasites, taking antibiotics, injuries, pathologies of internal organs, neoplasms. Moreover, different factors may manifest themselves in the same way, but require individual therapy. It is necessary to visit a doctor to prescribe medications for itching in intimate places in women and men if additional symptoms are pronounced:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- burning during urination and during sexual intercourse;
- heavy discharge;
- sour or rotten smell from the genitals;
- the appearance of pimples, blisters, red spots in the perineum.
Concerns should also arise if it just itches in the groin without other side symptoms. This may be caused by the following factors:
- disruption of the endocrine and circulatory system;
- liver diseases;
- tumor formation.
The doctor will not just prescribe ointments for itching in the intimate area, but will also conduct a full examination to identify the main cause of the discomfort.
To relieve inflammation and allergies
Itching and burning in intimate places is not uncommon in women, men, children and adolescents. The discomfort can be barely noticeable and painful, pass quickly or drag on. But in any case, you need to get rid of unpleasant sensations by first establishing the cause. If this is a reaction to sweat, waste, or uncomfortable underwear, the problem is easy to solve, and for diseases of various etiologies, you cannot do without ointments and creams for itching in the intimate area. There are no general recommendations, and the doctor prescribes the drug based on the diagnostic results.
Why do genital allergies appear in children?
Children under one year of age are often susceptible to genital allergies. As the child matures, the symptoms may become localized and their manifestations may be weakened for a long time or disappear altogether. There are factors that cause this disease in children:
- Helminthiases;
- Low quality hygiene products;
- The presence of a fungal infection (candidiasis) in a breastfeeding woman;
- Baby food that a child receives instead of mother's milk or infant formula;
- Clothing, diapers that come into direct contact with the child;
- Medicines;
- Mother's breast milk containing an allergen for the baby;
- Heredity.
Treatment of the causes of rashes
Treatment is medicinal, carried out by a gynecologist - this is the specialist you should visit first - or by a dermatovenerologist. Therapy for identified pathology involves a systematic approach, i.e. both local and general means are used in the process.
For the entire period of treatment, you must completely abstain from sex.
The treatment regimen is based on the following principles:
- in case of an allergic reaction, drugs from a series of antihistamines are used, for example, Fenistil, Diazolin;
- fungal infection is destroyed with the help of antifungal agents (Nystatin, Clotrimazole);
- Acyclovir is used to treat genital herpes;
- if hormonal disorders are detected, hormonal levels are normalized; most often, Utrozhestan and Duphaston are used to normalize the cycle;
- If a streptococcal infection is detected, streptocide is prescribed.
If the rash on the labia majora is inflammatory in nature, then treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. The scheme is developed based on the diagnosed disease and the current clinical picture.
In addition to the appointment, the following are prescribed:
- complexes of vitamins and microminerals that strengthen the immune system;
- sedatives - tincture of motherwort, valerian, etc.;
- creams and ointments with a healing effect - Solcoseryl, Radevit, Bepanten.
If the internal surfaces of the vagina are affected, i.e. when pimples have formed inside the vagina or near the entrance, the woman will be recommended to sanitize with oak, chamomile decoction or soda solution.
Analyzes
If a pustular rash is detected on the labia or vaginal mucosa, a smear of its contents is taken. This is necessary to diagnose the infectious agent.
Additionally, the following studies may be required:
- general blood and urine analysis - allows you to determine the presence of foci of inflammation in the body;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - necessary to exclude various types of neoplasms;
- a biopsy of the affected tissue is performed to determine the nature of the changes.
A rash in the intimate area has bothered every woman at least once. Rashes on the genitals can cause not only mild discomfort, but also serious pain, for example, with genital herpes. That is why, if uncharacteristic pimples appear, you should consult a gynecologist.
How and with what to treat
If allergy symptoms occur for the first time, you should immediately take measures to reduce inflammation and itching:
- Take a shower or take a local cool bath. For greater effect, you can use chamomile decoction.
- Avoid soap and other detergents and use exclusively intimate hygiene gel. In this case, allergies to pads, symptoms of skin irritation and swelling will quickly disappear.
- If there are skin manifestations such as urticaria, you must take antihistamines: Zyrtec, Aleron, Suprastin - 1 tablet per day until the manifestations disappear. The general course of treatment usually takes 3-10 days.
- When a rash and dermatitis appear, redness and itchy areas are lubricated with anti-allergy products: Fenistil gel or Bepanten ointment. The latter has not only an analgesic and antipruritic effect, but also treats minor abrasions and abrasions. You can treat the skin with salicylic or boric alcohol.
Traditional medicine in such cases recommends drinking a nettle decoction (1 tablespoon of herb per glass of water) and supplementing it with calendula infusion. You need to wear only natural underwear and take a shower every day, which will help quickly remove the symptoms of the disease. These recommendations are especially good if you are allergic to panty liners - the symptoms are very unpleasant and can be completely eliminated.
First aid measures for a severe allergic reaction are as follows: immediately remove the pad, wash the genital area with cool, clean water without soap, take antihistamines and bronchodilators and call an ambulance (if difficulty breathing or severe swelling occurs).
In this case, a blood test will help clarify the diagnosis - an allergy is indicated by a sharp increase in the number of eosinophils and the detection of specific antibodies in the blood.
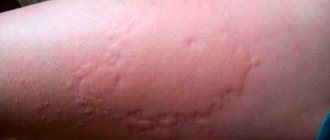
Types of rashes
There are different types of rashes. Pimples are certain elements that appear suddenly, usually after the end of the incubation period.
Types of rash on the genitals:
- blisters - do not last long and go away on their own;
- pustules - formations with purulent contents of green or yellow color, indicating an advanced stage of the disease;
- bubbles with liquid - can be located either in groups or individually, after opening (without lack of treatment) they transform into painful ulcers;
- chancre – characterized by a red tint, has a hard edge and an ulcerative bottom;
- erythema - reddened and swollen areas raised above the skin;
- condylomas - genital warts of a flesh-colored or brown color, can grow in the shape of a cock's comb, and are prone to fusion;
- nodules - the rash lies in the dermal layer at different depths and is characterized by a dense structure;
- plaques are flat formations that rise above the surface of the skin.
We recommend reading: Is it possible for a nursing mother to go to the bathhouse and take a steam bath?
These are the most common elements that form on the surface of the female genital organs.
Treatment is medicinal, carried out by a gynecologist - this is the specialist you should visit first - or by a dermatovenerologist. Therapy for identified pathology involves a systematic approach, i.e. both local and general means are used in the process.
Why does itching occur without discharge?
In the intimate area, itching can appear on the mucous membranes or on the skin. The main mechanism for the occurrence of itching is the active production of inflammatory mediators - histamine, prostaglandins, arachidonic acid and others. The list of reasons that provoke the active production of mediators is quite wide. This includes both local reactions and systemic diseases that affect the condition of the mucosa. In addition to inflammatory mediators, the feeling of itching can be triggered by changes in the structure of the skin or mucous membranes (for example, due to insufficient hydration or lubrication production). Itching and dryness are often observed due to hormonal imbalance. The main category of patients is women over 45 years of age. A well-known example of itching due to hormonal changes is abdominal itching during pregnancy. At the same time, the skin stretches, becomes drier and itches. Similar processes can occur in the genitals.
If itching occurs, a woman should definitely consult a doctor. Often such a symptom indicates the presence of inflammatory and infectious processes, so treatment should not be delayed. If the causes are less dangerous, for example physiological changes or local hypersensitivity, the doctor will help to quickly eliminate them and prevent re-exacerbation.
If no changes are observed in vaginal discharge, it means that the mucous layer of the vagina is not affected. On the other hand, the discharge may be reduced in amount, which is also a diagnostic sign and indicates dryness and dysfunction of the mucous membrane.
Thus, the doctor’s task is to understand where exactly the itching is localized and what accompanying symptoms are observed with it. Based on these data, as well as laboratory tests, the exact cause can be identified and treatment can begin.
Do not forget about systemic diseases that manifest themselves as itching of the entire body, including the genitals - allergies, liver problems, parasite infection. The causes of itching are discussed in more detail below.
Prevention
Itching of the labia in women can be avoided by taking steps for perineal hygiene:
- Keep your genitals clean and dry.
- After bowel movements , wipe the area from front to back to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the vagina.
- Do not use special products (for example, vaginal sprays) that can disrupt the acid balance of the vagina.
- Do not use scented products (panty liners, soap).
- If the labia minora itch , use mild soap, prevent friction in the genital area by wearing natural cotton underwear and change it every day.
- Avoid unprotected sex.
- Be careful with toilet paper , as some brands contain chemicals and deodorants.
If a woman's groin itches after a course of antibiotics, she should regularly consume yoghurts rich in probiotics for several weeks.
Paying attention to intimate health is very important, but do not resort to self-medication, since any medications and traditional recipes must be used taking into account the patient’s medical history and his individual characteristics.
A visit to a qualified gynecologist will relieve both intimate itching and unplanned unpleasant consequences.
Itching during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a specific hormonal period in a woman’s life—the body is transformed in many ways. Itching in the intimate area is a common dermatological symptom during this period.
Also, intimate itching is a sign of dermatoses specific to pregnant women:
- pemphigoid gestation;
- polymorphic eruption of pregnancy;
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy;
- atopic dermatitis;
- itchy folliculitis.
During pregnancy, there is an increase in discharge, which causes irritation of the skin of the vulva and, accordingly, itching in the vaginal area. If the discharge is clear or white, odorless, then most likely it is caused by pregnancy hormones and there is no cause for concern.
One of the causes of irritation in the intimate area is detergents. But sometimes excess discharge signals an infection when the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina is disrupted.
Four types of infection pose a potential risk to pregnant women:
- bacterial vaginosis;
- thrush;
- group B streptococcal infection;
- trichomoniasis.
Seeing a doctor is necessary if redness and itching in the intimate area do not go away within a certain period, especially if ulcers appear on the skin of the vulva and vaginal discharge is abnormal.
We recommend reading: Nurofen overdose in a child: symptoms, consequences and first aid
Thrush
Vulvovaginal candidiasis, also called vaginal candidiasis or vaginal thrush, is caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast in the vagina and is characterized by a curdled discharge, itching of the labia and erythema.
They are usually present in the vagina in small quantities, but in certain situations they begin to actively develop.
Predisposing factors:
Under these conditions, the yeast begins to grow rapidly and, entering the vagina, causes itching in the intimate area.
Symptoms of vaginal thrush:
- painful condition and irritation of the vulva;
- itching in the groin;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse (superficial dyspareunia);
- burning when urinating;
- white coating on the small lips;
- whitish thick cheesy discharge without odor.
Symptoms worsen before the start of the menstrual cycle.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis can be sexually transmitted and has a high incidence rate. It seriously affects the quality of life of women, especially in chronic recurrent forms.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to wear underwear made from natural materials, avoid douching and not use aromatic hygiene products. Treatment is with antifungal medications (topical clotrimazole or oral medications such as fluconazole).
The cause of athlete's foot is the anthropophilic fungus Epidermophyton floccosum.
Pediculosis pubis
Tiny parasitic insects living in pubic hair cause severe itching of the genitals.
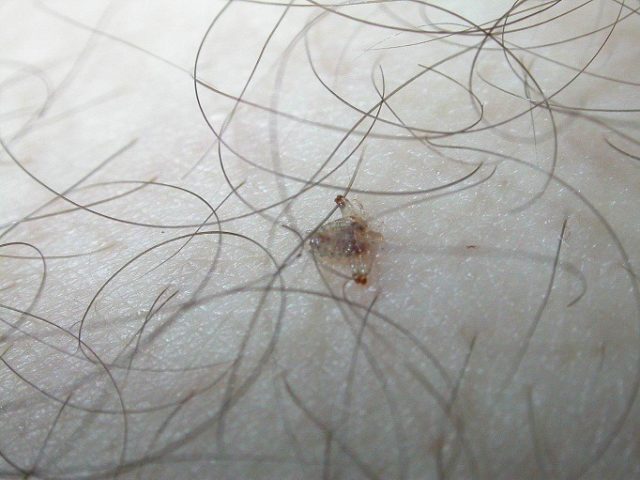
It occurs as a result of hypersensitivity to the saliva of pubic lice, which feed on blood, and becomes stronger for two or more weeks after the parasites enter, especially at night, when the lice are especially active.
Sometimes a characteristic macula (gray-blue or spotted) appears in an intimate place, which persists for several days.
Pediculosis pubis, the main symptom of which is vaginal itching, requires treatment with insecticidal ointments, creams, lotions or shampoos that kill parasites and their eggs, which can be done at home.
If infected scratches appear on the skin in an intimate area as a result of scratching, qualified medical assistance is needed.
The most common way to contract lice pubis is through sexual intercourse. But you can acquire pubic lice by using bedding, towels or clothing of an infested person.
Psoriasis
An inflammatory, autoimmune condition, psoriasis affects the skin anywhere on the body, including the intimate area. Psoriatic lesions on the vulva are more common in girls than in adult women.
Psoriasis affects the outer lining of the vagina, usually sparing the mucous membranes and causing itching in the groin area. There is no difference in clinical presentation between adults and children. These are clearly demarcated red plaques in the vulvar and perianal area.
In the folds, the skin cracks and looks sick. Tight clothing, the use of rough toilet paper or sanitary products, and anything that causes friction, including sexual intercourse, aggravate the symptoms - the discomfort that accompanies psoriasis, burning and itching of the labia
Doctors can make a diagnosis just by looking at the lesions, but in some cases additional testing is ordered to rule out bacterial or fungal infections.
Prevention
Itching of the labia in women can be avoided by taking steps for perineal hygiene:
- Keep your genitals clean and dry.
- After bowel movements , wipe the area from front to back to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the vagina.
- Do not use special products (for example, vaginal sprays) that can disrupt the acid balance of the vagina.
- Do not use scented products (panty liners, soap).
- If the labia minora itch , use mild soap, prevent friction in the genital area by wearing natural cotton underwear and change it every day.
- Avoid unprotected sex.
- Be careful with toilet paper , as some brands contain chemicals and deodorants.
If a woman's groin itches after a course of antibiotics, she should regularly consume yoghurts rich in probiotics for several weeks.
Paying attention to intimate health is very important, but do not resort to self-medication, since any medications and traditional recipes must be used taking into account the patient’s medical history and his individual characteristics.
A visit to a qualified gynecologist will relieve both intimate itching and unplanned unpleasant consequences.
Diagnostics
In clinical dermatology, determining genital allergies is often not difficult due to the severity of symptoms. The main diagnostic measures are aimed not so much at clarifying the type of pathology, but at finding out its causes and excluding other skin or sexually transmitted diseases. Accurate identification of the allergen allows you to give the patient the right recommendations to prevent relapses of allergies in the future. The following diagnostic procedures are prescribed:
- Questioning and inspection. The specialist examines the patient’s genital area, assesses the condition of the skin, the prevalence and severity of disorders. If necessary, a gynecologist is consulted. Through a survey, the duration of manifestations, the presence of itching and pain are determined, and the possible connection of symptoms with the use of cosmetics and food intake is clarified.
- Laboratory tests. It is mandatory to carry out serological tests for the presence of antibodies to the causative agents of the main STDs - gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, which can be disguised as allergic manifestations. Specific IgE is determined by enzyme immunoassay.
- Allergy tests. Based on anamnesis data, the range of possible allergens is narrowed, then accurate identification is carried out using skin allergy tests (prick test). The body's reaction to antigens of latex, seminal fluid, and some medications is most often studied.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with sexually transmitted pathologies and some systemic skin diseases (eczema, seborrhea). With the development of urethritis, taking into account the data of a general urine test and urethral smear, its non-infectious nature is confirmed. The presence of candidiasis (the head of the penis in men and the vagina in women), in which mixed inflammation of an infectious-allergic nature is often observed, is excluded.