Composition and release form
Appearance of the drug
The composition of the products is characterized by a high content of natural ingredients. The components differ depending on the form of release of the drug.
| Release form | Compound |
| Pills | Vitamin E, red kopeck root, zinc oxide, silicon oxide, calcium stearate. |
| Cream | Methyl nicotinate, methyl salicylate, glucosamine, glycerin, petrolatum, water, silicone oil, emulsion wax. |
| Gel | Methyl nicotinate, glucosamine, methyl salicylate, fatty alcohol, emulsion wax, glycerin, tea tree essential oil, water, castor oil, triethanolamine. |
The action of the main components is aimed at improving erectile function. Each component has its own properties that improve the quality of intimate life.
- Methyl nicotinate. It is a derivative of vitamin E. It has a local irritating and vasodilating effect. Due to this, improved blood circulation and a rush of blood to the penis are achieved. When used, a warming effect is felt. In addition, it helps remove excess fluid and toxins.
- Glucosamine. Promotes the production of your own collagen, improves skin tone and moisturizes it. Glucosamine also slows down the aging process of the skin.
- Methyl salicylate. Increases capillary permeability and accelerates blood circulation.
Nootropic drugs that improve nutrition and blood circulation
Stress, vascular spasms, blood clots, infectious diseases, osteochondrosis, and other pathologies lead to poor circulation.
Destabilization of the blood supply disrupts brain function, which is dangerous for all vital processes of the body. In pharmaceuticals, there is a special group of neurometabolic stimulants that improve brain function - nootropics. Medicines stimulate metabolism in nerve tissue, increase the brain’s ability to withstand a lack of oxygen, concentrate attention, and help increase intelligence and memory. Below is a list of nootropics:
- Microhydrin;
- Glutamic acid;
- Cerebrolysin;
- Actovegin;
- Pantogam;
- Phenotropil;
- Glycine;
- Cortexin;
- Piracetam.
Indications and results from use
Erectosil is recommended for use in the following cases:
- Inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
- Decreased potency and libido.
- Fast ejaculation.
- Problems with erection or its complete absence.
- Pathological processes in the bladder that contribute to impaired urination and stagnation of urine.
- Slow blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
In the presence of pathological processes, a combination of oral tablets with a product for external use is recommended. If there are problems with potency, in most cases a local drug is sufficient.
The products are allowed to be used as prophylaxis after the main treatment. This will help avoid problems with erectile function.
As a result of using medications, many men note the achievement of a quick and stable effect. The quality of intimacy and its duration improves, and the use of tablets has a positive effect on the general condition of the patient.
Side effects
the most common adverse events were fatigue, dry mouth and headache. Other side effects that have been reported very rarely during post-marketing experience are listed below. General violations:
hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylaxis, angioedema, shortness of breath, itching, rash, urticaria).
From the digestive system:
abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, diarrhea, increased levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, hepatitis.
From the nervous system:
dizziness, drowsiness, insomnia, psychomotor hyperactivity, convulsions, hallucinations.
From the cardiovascular system:
tachycardia, palpitations.
From the musculoskeletal system:
myalgia.
Contraindications
Erectosil has virtually no contraindications and rarely causes side effects. The only contraindications for taking tablets are individual intolerance and hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Erectosil cream and gel have a number of the following contraindications:
- Violation of the integrity and any damage to the skin on the penis.
- Allergic reactions to any component included in the composition.
- Partner's pregnancy, as well as the period of breastfeeding.
- The presence of any skin diseases in the penis area.
Also, the use of topical medications is not recommended when engaging in oral sex. If the product gets into the oral cavity, rinse immediately.
It is not advisable to use together with a condom. Since in this case the desired effect will not be achieved. For protection, it is worth choosing other methods; Erectosil does not have a contraceptive effect. The drug does not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, its use is permitted only with a regular partner.
Triplixam®
All precautions associated with taking individual components of the drug should be taken into account when using their fixed combination as part of the drug Triplixam®.
Amlodipine
Chronic heart failure
Patients with chronic heart failure should be treated with caution.
When using amlodipine in patients with chronic heart failure of functional class III and IV according to the NYHA classification, pulmonary edema may develop. Slow calcium channel blockers, including amlodipine, should be used with caution in patients with chronic heart failure due to a possible increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events and mortality.
In patients with severe chronic heart failure (NYHA functional class IV), treatment should begin with lower doses and under close medical supervision.
Patients with arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease should not stop taking beta-blockers: an ACE inhibitor should be used in conjunction with beta-blockers.
Hypertensive crisis
The effectiveness and safety of amlodipine in hypertensive crisis has not been established.
Indapamide
Hepatic encephalopathy
In the presence of liver dysfunction, taking thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics can lead to the development of hepatic encephalopathy. In this case, you should immediately stop taking the diuretic.
Photosensitivity
Cases of photosensitivity reactions have been reported while taking thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics (see section "Side effects"). If a photosensitivity reaction develops while taking the drug, treatment should be discontinued. If it is necessary to continue diuretic therapy, it is recommended to protect the skin from exposure to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet rays.
Content of calcium ions in blood plasma
Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics can reduce the excretion of calcium ions by the kidneys and lead to a slight and temporary increase in the content of calcium ions in the blood plasma. Severe hypercalcemia may be a consequence of previously undiagnosed hyperparathyroidism. In such cases, you should stop taking diuretics and conduct a study of the function of the parathyroid glands (see section “Side effects”).
Uric acid
In patients with elevated concentrations of uric acid in the blood plasma, the frequency of gout attacks may increase during therapy.
Perindopril
Potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, potassium-containing table salt substitutes and food supplements
The simultaneous administration of perindopril and potassium-sparing diuretics, as well as potassium preparations, potassium-containing table salt substitutes and food additives is not recommended (see section “Interaction with other drugs”). Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
There is evidence of an increased risk of arterial hypotension, hyperkalemia and renal dysfunction (including acute renal failure) when ACE inhibitors are used simultaneously with ARB II or aliskiren. Therefore, double blockade of the RAAS as a result of combining an ACE inhibitor with ARA II or aliskiren is not recommended (see sections “Interaction with other drugs” and “Pharmacodynamics”). If a double blockade is necessary, it should be performed under the strict supervision of a specialist with regular monitoring of renal function, plasma electrolyte levels and blood pressure.
Concomitant use of ACE inhibitors with angiotensin II receptor antagonists is contraindicated in patients with diabetic nephropathy and is not recommended in other patients.
Neutropenia/agranulocytosis/thrombocytopenia/anemia
There are reports of the development of neutropenia/agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia and anemia while taking ACE inhibitors. In patients with normal renal function and in the absence of other aggravating factors, neutropenia rarely develops. Perindopril should be used with extreme caution in patients with systemic connective tissue diseases, while taking immunosuppressants, allopurinol or procainamide, or their combination, especially in patients with impaired renal function.
Some of these patients developed severe infections, in some cases resistant to intensive antibiotic therapy. When prescribing perindopril to such patients, it is recommended to periodically monitor white blood cells in the blood, and patients should report to the doctor any signs of infectious diseases (for example, sore throat, fever) (see section "Side effects").
Renovascular hypertension
In patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or arterial stenosis of a single functioning kidney during therapy with ACE inhibitors, the risk of developing arterial hypotension and renal failure increases (see section “Contraindications”). The use of diuretics may be an additional risk factor. Deterioration of renal function can be observed with even a slight change in serum creatinine concentration, even in patients with unilateral renal artery stenosis.
Hypersensitivity/angioedema
When taking ACE inhibitors, including perindopril, in rare cases, the development of angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx may occur. This can happen at any time during therapy. If symptoms appear, the drug should be stopped immediately and the patient should be observed until signs of edema completely disappear. If the swelling affects only the face and lips, it usually resolves on its own, although antihistamines may be used to treat symptoms.
Angioedema, accompanied by swelling of the larynx, can be fatal. Swelling of the tongue, glottis or larynx can lead to airway obstruction, in which case intensive care should be given immediately. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately administer a solution of epinephrine (adrenaline) 1:1000 (0.3-0.5 ml) and/or ensure airway patency. The patient should be under medical supervision until symptoms disappear completely and permanently.
Patients of the Black race had a higher incidence of angioedema while taking ACE inhibitors compared to other races.
Patients with a history of angioedema not associated with taking ACE inhibitors may have an increased risk of developing it when taking the drug (see section "Contraindications"). There are reports of rare cases of the development of angioedema of the intestine during therapy with ACE inhibitors. In this case, patients experienced abdominal pain as an isolated symptom or in combination with nausea and vomiting, in some cases without previous angioedema of the face and with normal levels of C1-esterase. The diagnosis was made using abdominal computed tomography, ultrasound, or at the time of surgery. Symptoms resolved after discontinuation of ACE inhibitors. Therefore, in patients with abdominal pain receiving ACE inhibitors. When carrying out differential diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of developing angioedema of the intestine.
Combined use with the combination of valsartan + sacubitril
Due to the increased risk of developing angioedema (see section “Contraindications”), simultaneous use of perindopril with the combination of valsartan + sacubitril is contraindicated. The use of the combination of valsartan + sacubitril is possible no earlier than 36 hours after taking the last dose of perindopril. If therapy with the valsartan + sacubitril combination is discontinued, the use of perindopril should not be started earlier than 36 hours after taking the last dose of the valsartan + sacubitril combination (see sections “Contraindications” and “Interaction with other drugs”). When taking ACE inhibitors concomitantly with other enkephalinase inhibitors (for example, racecadotril), the risk of developing angioedema may be increased (see section "Interaction with other drugs"). In patients receiving perindopril, a careful risk/benefit assessment should be performed before prescribing enkephalinase inhibitors (eg racecadotril).
Concomitant use with mTOR inhibitors (for example, sirolimus, everolimus, temsirolimus)
Concomitant use of an ACE inhibitor and an mTOR inhibitor (eg, sirolimus, everolimus, temsirolimus) may be associated with an increased risk of angioedema (eg, swelling of the airways or tongue, with or without impairment of respiratory function) (see Interactions with Other Drugs section) ).
Anaphylactoid reactions during desensitization
There are isolated reports of the development of prolonged, life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions in patients receiving ACE inhibitors during desensitizing therapy with hymenoptera venom (bees, wasps). ACE inhibitors should be used with caution in patients with a history of allergies or a tendency to allergic reactions undergoing desensitization procedures, and the use of an ACE inhibitor should be avoided in patients receiving immunotherapy with hymenoptera venom. However, an anaphylactoid reaction can be avoided by temporarily discontinuing the ACE inhibitor at least 24 hours before the start of the desensitization procedure.
Anaphylactoid reactions during LDL apheresis
In rare cases, life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients receiving ACE inhibitors during LDL apheresis using dextran sulfate. To prevent an anaphylactoid reaction, ACE inhibitor therapy should be temporarily discontinued before each apheresis procedure.
Hemodialysis
Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported in patients receiving ACE inhibitors during hemodialysis using high-flux membranes (eg, AN69®). Therefore, it is advisable to use a different type of membrane or use an antihypertensive agent of a different pharmacotherapeutic group.
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Patients with primary hyperaldosteronism are usually not susceptible to antihypertensive drugs whose action is based on inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system. Therefore, the use of this drug in such patients is not recommended.
Pregnancy
Taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy is contraindicated. If continued therapy with ACE inhibitors is necessary, patients should switch to other types of antihypertensive therapy with an established safety profile when taken during pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs, ACE inhibitors should be stopped immediately and, if necessary, alternative antihypertensive therapy should be started (see sections “Contraindications” and “Use during pregnancy and lactation”).
Cough
During therapy with an ACE inhibitor, a dry cough may occur. The cough persists for a long time while taking drugs of this group and disappears after their discontinuation. If a patient develops a dry cough, one should be aware of the possible iatrogenic nature of this symptom. If the physician believes that ACE inhibitor therapy is necessary for the patient, continuing the drug may be considered.
Mitral stenosis/aortic stenosis/hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy ACE inhibitors should be prescribed with caution to patients with left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
Ethnic differences
Perindopril, like other ACE inhibitors. obviously has a less pronounced hypotensive effect in patients of the Negroid race compared to representatives of other races. This difference may be due to the fact that black patients with arterial hypertension are more likely to have low renin activity.
Surgery/General anesthesia
The use of ACE inhibitors in patients undergoing surgery under general anesthesia can lead to a significant decrease in blood pressure, especially when using general anesthetic agents that have an antihypertensive effect.
It is recommended, if possible, to stop taking long-acting ACE inhibitors, including perindopril, one day before surgery.
Patients with renovascular hypertension
The treatment method for renovascular hypertension is revascularization. However, the use of ACE inhibitors has a beneficial effect in patients both awaiting surgery and in cases where surgery is not possible.
When using the drug Triplixam® in patients with existing or suspected renal artery stenosis, treatment should begin in a hospital setting with low doses with constant monitoring of the condition of the kidneys and potassium levels in the blood, since such patients may develop functional renal failure, which disappears with cessation of therapy.
Atherosclerosis
The risk of arterial hypotension exists in all patients, however, special care should be taken when using the drug in patients with coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular insufficiency. In such patients, treatment should begin with low doses of the drug.
Perindopril/Indapamide
Lithium preparations
The simultaneous use of a combination of perindopril and indapamide with lithium preparations is not recommended (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
Arterial hypotension and water-electrolyte imbalance
The presence of initial hyponatremia is associated with the risk of sudden development of arterial hypotension (especially in patients with renal artery stenosis). Therefore, clinical signs of dehydration and decreased plasma electrolytes, such as after diarrhea or vomiting, should be systematically assessed. Such patients require regular monitoring of blood plasma electrolyte levels.
In case of severe arterial hypotension, intravenous administration of 0.9% sodium chloride solution may be required.
Transient arterial hypotension is not a contraindication for continued therapy. After restoration of blood volume and blood pressure, therapy can be resumed using low doses of the combination, or the components of the drug can be used as monotherapy.
Hyponatremia at the initial stage may not be accompanied by clinical symptoms, so regular laboratory monitoring is necessary. More frequent monitoring of sodium ion levels is indicated for elderly patients and patients with liver cirrhosis (see sections “Side effects” and “Overdose”).
Therapy with any diuretic drugs can cause hyponatremia, sometimes with very serious consequences.
Hyponatremia with hypovolemia can cause dehydration and orthostatic hypotension. The simultaneous loss of chlorine ions can lead to secondary
compensatory metabolic alkalosis: the frequency and extent of this effect are insignificant.
Patients with diabetes mellitus
In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (risk of spontaneous increases in potassium ions), treatment should begin with lower doses and under close medical supervision.
When prescribing the drug to patients with diabetes mellitus receiving oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin, regular monitoring of plasma glucose concentrations is necessary during the first month of therapy. It is necessary to monitor blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus, especially in the presence of hypokalemia.
Amlodipine/Perindopril
Liver failure
In rare cases, cholestatic jaundice occurs while taking ACE inhibitors. As this syndrome progresses, fulminant liver necrosis develops, sometimes with death. The mechanism of development of this syndrome is unclear. When jaundice or a significant increase in the activity of liver enzymes occurs in patients taking ACE inhibitors. you should stop taking the ACE inhibitor and consult a doctor (see section “Side effects”),
In patients with impaired liver function, T1/2 and AUC of amlodipine are increased. Amlodipine should be started with the lowest doses and precautions should be taken both at the beginning of treatment and when increasing the dose. In patients with severe hepatic impairment, the dose should be increased gradually, ensuring careful monitoring of the clinical condition.
Triplixam® has not been studied in patients with liver failure. Considering the effect of each component included in the drug separately, Triplixam® is contraindicated in patients with severe liver failure, and also requires special caution when prescribed to patients with moderate and mild liver failure.
Amlodipine/Indapamide/Perindopril
Renal dysfunction
The drug is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) (see section "Contraindications").
In patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), the use of Triplixam® in dosages containing 10 mg of perindopril and 2.5 mg of indapamide is contraindicated (i.e., dosage of Triplixam® 5 mg + 2.5 mg + 10 mg and 10 mg + 2.5 mg + 10 mg).
Some patients with arterial hypertension without previous obvious renal impairment may develop laboratory signs of functional renal failure during therapy. In this case, treatment with the drug should be stopped with the further possibility of resuming combination therapy using low doses of the drug, or using the components of the drug in monotherapy.
Such patients require regular monitoring of the content of potassium ions and creatinine in the blood serum - 2 weeks after the start of therapy and then every 2 months. Renal failure occurs more often in patients with severe chronic heart failure or underlying renal dysfunction, including renal artery stenosis.
Triplixam® is not recommended for patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery of a single functioning kidney.
There is a risk of arterial hypotension and/or renal failure (in the presence of chronic heart failure, dehydration and decreased electrolyte levels in the blood plasma, etc.): in some pathological conditions, significant activation of the RAAS may be observed, especially with severe hypovolemia and decreased electrolyte levels blood plasma (against the background of a salt-free diet or long-term use of diuretics), in patients with initially low blood pressure, renal artery stenosis (including bilateral), chronic heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver with edema and ascites.
Blockade of the RAAS by ACE inhibitors may be accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood pressure and/or an increase in the concentration of creatinine in the blood plasma, indicating the development of functional renal failure. These phenomena are more often observed when taking the first dose of the drug or during the first two weeks of therapy. Sometimes these conditions develop acutely and the time of their onset may vary. In such cases, it is recommended to resume therapy starting with lower doses, gradually increasing them. In patients with coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular diseases, a sharp decrease in blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident.
Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics are fully effective only in patients with normal or slightly impaired renal function (plasma creatinine concentration in adult patients below 25 mg/l or 220 µmol/l). In elderly patients, creatinine levels should be assessed taking into account age, body weight and gender.
At the beginning of treatment with diuretics, patients may experience a temporary decrease in glomerular filtration rate and an increase in the concentration of urea and creatinine in the blood plasma due to hypovolemia and hyponatremia. This transient functional renal failure is not dangerous for patients with unchanged renal function, but its severity may increase in patients with underlying renal failure. Patients with renal failure can take amlodipine in standard doses.
Changes in plasma concentrations of amlodipine do not correlate with the degree of renal dysfunction.
No special studies have been conducted on the use of Triplixam® in renal dysfunction. When using the drug Triplixam® in case of impaired renal function, the effects noted when taking individual components of the drug should be taken into account.
Content of potassium ions in blood plasma
Concomitant therapy with indapamide, perindopril and amlodipine does not prevent the development of hypokalemia, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus or renal failure. As with the use of other antihypertensive drugs in combination with a diuretic, regular monitoring of the content of potassium ions in the blood plasma is necessary.
Hyperkalemia may develop in some patients during treatment with ACE inhibitors, including perindopril. Risk factors for hyperkalemia include renal failure, deterioration of renal function, advanced age (> 70 years), diabetes mellitus, certain concomitant conditions (dehydration, acute cardiac decompensation, metabolic acidosis), concomitant use of potassium-sparing diuretics (such as spironolactone, eplerenone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium preparations or potassium-containing substitutes for table salt, as well as the use of other drugs that increase the content of potassium ions in the blood plasma (for example, heparin, co-trimoxazole, i.e. the combination of trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole). The use of potassium supplements/preparations, potassium-sparing diuretics, and potassium-containing table salt substitutes can lead to a significant increase in potassium levels in the blood, especially in patients with reduced renal function. Hyperkalemia can lead to serious, sometimes fatal, heart rhythm disturbances. If combined use of the above drugs is necessary, treatment should be carried out with caution, against the background of regular monitoring of the content of potassium ions in the blood serum (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
Therapy with thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics is associated with a risk of hypokalemia. Hypokalemia (less than 3.4 mmol/L) should be avoided in the following high-risk patients: elderly and/or malnourished patients (even if not receiving concomitant drug therapy), patients with cirrhosis with edema and ascites, patients with coronary heart disease, chronic heart failure. Hypokalemia in these patients increases the toxic effect of cardiac glycosides and increases the risk of developing arrhythmia.
The risk group also includes patients with a prolonged QT interval, and it does not matter whether this increase is caused by congenital causes or the effect of drugs.
Hypokalemia, like bradycardia, contributes to the development of severe cardiac arrhythmias, in particular polymorphic ventricular tachycardia of the “pirouette” type, which can be fatal. In all the cases described above, regular monitoring of the content of potassium ions in the blood plasma is necessary. The first measurement of potassium ion content should be carried out within the first week from the start of therapy.
If hypokalemia is detected, appropriate treatment should be prescribed.
Elderly patients
Before starting to take the drug, it is necessary to assess the functional activity of the kidneys and the content of potassium ions in the blood plasma. At the beginning of therapy, the dose of the drug is selected taking into account the degree of reduction in blood pressure, especially in the case of a decrease in circulating blood volume (CBV) and loss of electrolytes. Such measures help to avoid a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
In elderly patients, increasing the dose should be done with caution (see sections “Dosage and Administration” and “Pharmacokinetics”).
Excipients
Sodium level
The sodium content in the drug Triplixam® is insignificant, as it is less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per tablet.
Instructions for use
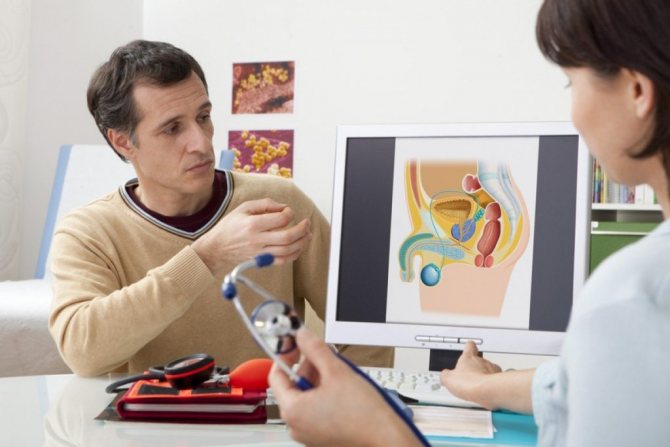
Before using the drug, it is better to first consult with your doctor.
The method of use of the drug depends on its form. The use of external agents is permitted without prior medical consultation, but before starting to take pills, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Pills
Erectil tablets should be taken in the amount of 1 piece 25-30 minutes before sexual intercourse. They do not react with alcoholic drinks, so combining them is not prohibited. It is not recommended to increase the dosage on your own; you should consult your doctor before doing so.
As a rule, tablets do not cause side effects. But if they occur, a dosage reduction or complete discontinuation of the drug is required.
Tablets are also used for therapeutic purposes. To do this, you need to take them daily after eating food. They are used as an additional remedy to the main treatment. Only a doctor can select a treatment regimen, since it is individual for each patient and depends on the type of pathology.
Gel
Erectosil gel is intended for external use. It is applied immediately before sexual intercourse to the penis. The product is rubbed in with gentle, smooth movements from the root of the penis to its head. You must wait until it is completely absorbed.
The drug begins to act within 5-10 minutes after application, during which time you can begin sexual intercourse.
If the product is used for medicinal purposes, the frequency and number of applications is determined by the doctor.
Cream
The method of using Erectosil cream is no different from using the drug in gel form. The only difference is that the cream has a thicker and greasy consistency, so you will have to rub it in more thoroughly. The cream takes longer to be completely absorbed than the gel.
The warming effect of the cream is more pronounced than that of the gel. Therefore, it is most often used for therapeutic purposes. The cream is used as part of complex treatment and can be applied up to 2 times a day. It is worth considering that Erectosil is not suitable for the treatment of all urological diseases. Therefore, if its use is planned as a therapeutic drug, prior consultation is necessary. To improve erectile function and duration of sexual intercourse, no prior consultation is required.
The action begins on average after 15 minutes, when the product is completely absorbed into the skin.
Trexil Neo tablet. p/captivity coated 5 mg blister No. 10
10 tablets per blister; 1 blister per cardboard package.
Pharmacological properties
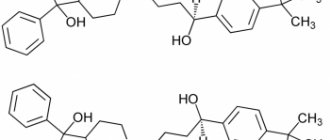
Desloratadine is a long-acting, non-sedating histamine antagonist with selective peripheral H1 receptor antagonist activity. After oral administration, desloratadine selectively blocks peripheral histamine H1 receptors to prevent this substance from entering the central nervous system. Desloratadine exhibits antiallergic properties.
Suppresses the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-13 from human mast cells/basophils, and also inhibits the expression of the adhesion molecule P-selectin on endothelial cells. Desloratadine does not penetrate the central nervous system. Desloratadine is determined in blood plasma 30 minutes after administration.
Cmax of desloratadine in blood plasma is achieved after 3 hours, T½ is on average 27 hours. The degree of accumulation of desloratadine corresponds to its T½ (≈27 hours) and the number of applications (1 time per day). The bioavailability of desloratadine is proportional to the dose in the range of 5–20 mg. Desloratadine is moderately (83–87%) bound to plasma proteins.
Desloratadine does not inhibit CYP3A4 in vivo, and in vitro studies have shown that this drug does not inhibit CYP2D6 and is neither a substrate nor an inhibitor of P-gp. Food does not affect the distribution of desloratadine.
Application
The drug is intended for oral administration. To relieve symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis (including intermittent and persistent) and cough, Trexil Neo should be taken internally, regardless of the intake. Adults and children over 12 years of age take 1 tablet (5 mg) 1 time per day.
Therapy of intermittent allergic rhinitis (presence of symptoms less than 4 days per day or less than 4 days) must be carried out in accordance with the history: take note after symptoms disappear and renew the diagnosis For repeated їх guilt.
In case of persistent allergic rhinitis (presence of symptoms for more than 4 days per week or more than 4 days), it is necessary to continue to wash throughout the entire period of contact with the allergen.
Interaction
Desloratadine, taken simultaneously with alcohol, does not potentiate the effects of alcohol, which may reduce productivity. With one-hour administration of erythromycin or ketoconazole, no clinically significant interactions were observed. Due to this, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of desloratadine did not interact with others It is impossible to turn it off completely using medicinal means.
Side effects
The most common unpleasant symptoms were fatigue, dry mouth and headache. Other unforeseen effects that were reported only rarely during the post-marketing period were overestimated. Body: hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylaxis, angioneurotic swelling, backbone, itching, sagging skin, urticaria).
On the side of the herbal tract: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, elevated bilirubin, hepatitis. On the side of the nervous system: confusion, drowsiness, insomnia, psychomotor hyperactivity, seizures, hallucinations. On the side of the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, heart failure.
On the side of the bone-muscle system: myalgia.
Special instructions
Desloratadine does not enhance the effects of alcohol such as impaired psychomotor function and drowsiness. Patients should be advised to use Trexil Neo tablets as prescribed. Since food does not affect the bioavailability of the drug, desloratadine tablets can be taken without regard to meals.
Patients should be advised not to increase the dose or frequency of the drug as studies have not demonstrated an increase in effectiveness with increasing dose. And increasing the dose may cause drowsiness. The ability to influence reaction speed when driving a vehicle or operating machinery.
The effect of desloratadine on driving a car or working with complex technical devices has not been noted. However, patients should be informed that, on rare occasions, some patients experience drowsiness, which may affect their ability to drive and operate machinery. Use during pregnancy and lactation.
The safety of the drug during pregnancy has not been established. Therefore, the use of Trexil Neo tablets during pregnancy is not recommended. Desloratadine passes into breast milk; therefore, it is not recommended to use the drug during breastfeeding. Children. The effectiveness and safety of desloratadine tablets in children under 12 years of age have not been established.
Experience with the use of desloratadine tablets in adolescents aged 12–17 years is limited, so the drug should be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Price and analogues

The drug is an analogue in terms of indications and pharmacological action
The average cost of Erectosil tablets is 650 rubles. Cream and gel cost on average from 700 to 750 rubles.
The drug has no analogues in its composition. It is possible to select a remedy only with a similar therapeutic effect. These include:
- Viagra.
- Cialis.
- Formula for a man.
- Erexil.
Most similar products contain many chemical elements and are more expensive. In the absence of indications, it is not advisable to select a replacement for Erectosil. This may be required to treat certain diseases where a drug with a faster and stronger effect is needed.
Side effects
Sedation (more pronounced when used in high doses), dryness of the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose and throat, increased appetite and body weight, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, gastralgia, nausea, tachycardia, when used in high doses - drowsiness, various rhythm disturbances ( including ventricular arrhythmia of the “pirouette” type), palpitations, prolongation of the QT interval, collapse, cardiac arrest. Overdose. Symptoms: headache, nausea, confusion, prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG, ventricular dysrhythmia (including pirouette type), ventricular fibrillation, convulsions, collapse, cardiac arrest, death.
Treatment: gastric lavage, cardiac monitoring for 24 hours, symptomatic and supportive therapy.
Vasoactive drugs
These pharmacological agents contain substances necessary for the brain that restore the blood supply to affected tissues. Drugs restore the functions of the lost part of nerve cells
Neurons are able to regenerate, but very slowly, so it is important to start therapy as quickly as possible. In neurology, vasodilators are divided into several pharmaceutical groups of drugs:
- myotropic antispasmodics;
- agents that affect neuronal metabolism;
- angioprotectors;
- neurotransmitter substances;
- other means that improve the nutrition of neurons.
How to take Trexil tablets - instructions for adults and children
Trexyl, instructions for use for children:
| Age | How to use, description |
| 3-5 years | A suspension is prescribed. Take 15 mg at a time. A day – 2 doses. |
| 6-12 years | Prescribed for children, in the form of a suspension. Dosage – 30-60 mg per dose (selected depending on the child’s weight). A day – 2 doses. Dependence on weight – 2 mg per 1 kg of child’s weight. |
Adults, instructions for use:
| Mode of application | |
| Adults, children - after 12 years | Tablets – 1 tablet per 1 dose. Suspension – 10 ml. A day - 2 times. Or 120 mg – 1 time per day in the morning. |
| People with asthma | A dosage is prescribed, which can reach 540 mg per day in tablets or suspensions. |
It is not recommended to drive while taking it, as it may cause decreased attention.
Live healthy! One minute tip: allergy medications(05/04/2018)
Watch this video on YouTube