The medicine "Maltofer" is a drug used for iron deficiency and normalizes its level. The composition of the drug includes iron (III) complex polymaltose hydroxide. Due to its similarity to natural compounds, it actively enters the blood from the intestines and then accumulates in the liver. The substance accumulates in the bone marrow, causing hemoglobin levels to rise. The drug is available in the form of syrup, chewable tablets or solution. If a more severe form of iron deficiency anemia occurs, the drug is recommended to be used intramuscularly. Children are usually prescribed drops or syrup, and adults are prescribed Maltofer tablets or solution, about which you can hear only positive reviews from doctors.
Use of the drug during pregnancy
No studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug on pregnant women. Therefore, it is prescribed in situations where the benefit to maternal therapy is higher than the potential risk to the fetus. However, the drug "Maltofer" during pregnancy is prescribed by a doctor in cases where a decrease in iron levels is observed. A deficiency of this substance is normal during pregnancy. This is especially noticeable in the last months of pregnancy. There are no negative reviews about the drug "Maltofer", but during pregnancy it must be taken with caution and under the strict supervision of a doctor. If the drug is prescribed to nursing women, they should remember that in small quantities it passes through breast milk into the baby's body. There is no data on the negative effects of the medication on the child.
The drug "Maltofer": drops for children
Maltofer drops are prescribed if necessary, starting from newborn age. The drug can also be used in premature infants. The medication "Maltofer" can cause abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea or constipation in a child. Other allergic reactions are also possible. Parenteral use of the drug in children may adversely affect the course of the infectious process. The bulk of reviews about the drug "Maltofer" sound positive. Many people actually note an increase in hemoglobin levels and an improvement in the child’s well-being. Although some young patients experience adverse reactions indicated by the manufacturer to the drug "Maltofer" for children. Reviews about them are extremely rare and talk about an allergic reaction in the form of diarrhea. Other concerned parents note the high cost of the medicine and the not very pleasant smell. In general, reviews of the drug "Maltofer" are positive. The drug in question is very popular.
Contraindications to the use of the drug
The drug is not prescribed in cases of impaired iron excretion, hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis, hemolytic or megaloblastic anemia, or hypersensitivity to the drug. Patients with diabetes mellitus should use the medication with caution. Due to the combination with chloramphenicol, the drug "Maltofer" can provoke a mutual deterioration of the therapeutic effects of chloramphenicol and folic acid. The medication must not be combined with other iron-containing medications. In cases of folic acid deficiency, the use of the drug may cause an increase in the metabolism of phenytoin in the blood serum.
Side effects
The medicine "Maltofer" is well tolerated by patients. In some cases, indigestion, vomiting, nausea or pain in the epigastric region may occur. An increased iron content in the drug may cause darkening of the stool due to the inability of the active substance of the drug to be absorbed. This process has no clinical significance. In patients with renal and liver failure, as well as people with allergies, the drug must be administered with extreme caution. In patients with cardiovascular diseases, it can cause side effects and aggravate the course of the underlying disease. Patients at high risk of developing anaphylactic and allergic reactions include patients with low iron-binding capacity or folic acid deficiency, as well as patients with bronchial asthma. The drug is unlikely to affect the ability to drive a vehicle or operate machinery. Cases of drug overdose have not been described to date: no signs of excess iron intake into the body, no symptoms of intoxication.
Causes of allergies
Individual intolerance to nickel or iron, manifested in the form of a rash, may have a genetic origin. A weakened immune system can also provoke an allergic reaction if a high dose of allergens has already accumulated in the body.
A person’s age does not in any way affect the likelihood of developing allergies, but living in large industrial cities is a risk factor.
The source of allergens can be food, clothing, accessories, jewelry, cosmetics, household items, dental crowns, braces.
Prophylactic use of the drug "Maltofer"
It is possible to use the drug to prevent iron and folic acid deficiency. In such cases, the drug "Maltofer" is prescribed 1 tablet once a day. To prevent anemia - 40 drops once a day. For iron deficiency anemia, nursing women and children over 12 years old – 20 drops per day. Babies under one year old and children under 12 years old – 10 drops once a day. Prophylactic use should last at least 30 days and no more than two months.
Maltofer is a drug prescribed to pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children for the treatment and prevention of iron deficiency anemia. This substance contains ferric iron , which is quickly absorbed in the body and is the closest thing to the natural component of iron contained in the human body.
When taking any medications, including Maltofer, a child may develop an allergy due to immunity to the active substance or its components.
Causes of an allergic reaction to Maltofer
Maltofer, like all other drugs, is made through the interaction of proteins and glycoproteins. These components can cause allergies in a child.
An allergic reaction in children and pregnant women may be associated with a person’s increased sensitivity to iron.
When purchasing Maltofer, be sure to check the expiration date, because the inattention and negligent attitude of the pharmacist can also cause a negative response to drug therapy. And also, pay attention to where and how it is necessary to store the medicinal substance - this property will help not only preserve the value of the medicinal product, but also save the body from the ingress of toxic substances formed when the substance is stored at the wrong temperature.
Only a doctor can find out the exact cause of the body’s allergic response to Maltofer, because each person’s body is individual.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to Maltofer
An allergic reaction to the drug can be delayed or immediate. In the first case, symptoms will appear immediately after Maltofer is absorbed into the blood, in the other, the allergy occurs after a few hours or days.
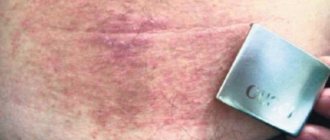
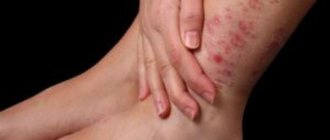
The main reason to suspect something is wrong is the appearance of a pinpoint rash on the skin. It can appear only in certain areas, but throughout the body. The child becomes weak, refuses to eat, and is capricious.
A delayed allergic reaction to Maltofer may manifest itself:
- Attacks of suffocation.
- Decreased appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- The appearance of attacks of heaviness, abdominal pain.
If Maltofer was administered intramuscularly, the allergy manifests itself in the form of discomfort, swelling and hardening at the injection site, headache, and hot flashes.
If an immediate type allergy develops, the person taking the drug may experience anaphylactic shock - this is a strong reaction of the body to the administered drug, in which the child loses consciousness, becomes pale, the heartbeat increases sharply, and blood pressure drops.
Quincke's edema is another very scary response of the body to the introduction of an allergen into the blood. In this case, it becomes difficult for a person to breathe, the area of the neck becomes swollen, and swelling of the vocal cords and larynx occurs.
Allergy to metals: causes and symptoms
Metal allergy is a rare type of hypersensitivity of the body to cobalt, chromium, copper, molybdenum, mercury, including nickel and iron, as well as alloys of valuable metals containing, for example, nickel. About 10% of people on the planet suffer from this type of allergic reaction. The exception is usually noble gold, platinum, and silver without impurities.
Residents of large industrial centers are more likely to encounter this problem, and the allergen can accumulate in the body for decades. You can wear earrings, rings, watches made of nickel, a belt with a metal buckle for a long time, and come into contact with iron elements of accessories and interiors without experiencing discomfort.
But usually an allergy to iron, as well as to other metals, makes itself felt within a few days after interaction with the body of the corresponding jewelry, objects or food containing nickel (low-quality chocolate, fish).
Its symptoms can be diagnosed independently.
Symptoms
Allergies to nickel and iron can manifest as contact dermatitis.
Penetrating through the epidermis, metal microparticles (ions) change the chemical structure of the protein cells of the affected organism, and they begin to be perceived as foreign, harmful.
Skin rash, itching, irritation and other symptoms are a protective immunological reaction of the body.
Symptoms of possible allergies are as follows:
- swelling of the earlobes;
- red spots like burns, rash on the skin;
- peeling of the skin, formation of dry crusts;
- irritation, itching, sometimes unbearable, in places where the metal comes into contact with the body (often the face, arms, legs, décolleté, navel area);
- formation of blisters with clear liquid.
The patient's temperature also rises. When nickel is consumed in food, it may:
- bloated stomach
- make you feel sick
- headache appears
- ulcers appear on the gums and in the mouth against the background of poor health in general.
But these signs may also indicate other diseases, so before self-medicating, consult an allergist or dermatologist.
Causes of allergies
Individual intolerance to nickel or iron, manifested in the form of a rash, may have a genetic origin. A weakened immune system can also provoke an allergic reaction if a high dose of allergens has already accumulated in the body.
A person’s age does not in any way affect the likelihood of developing allergies, but living in large industrial cities is a risk factor.
The source of allergens can be food, clothing, accessories, jewelry, cosmetics, household items, dental crowns, braces.
Treatment of allergies to nickel, iron
For metal allergies, treatment should begin with the elimination of all possible allergens. Allergy treatment is usually symptomatic, aimed at reducing painful reactions and relieving irritation.
Drug treatment consists of taking desensitizing, antihistamines, corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory ointments, creams (Polcortolon, Pdvantan), which must be applied in a very thin layer according to the prescription. Local treatment is carried out for no more than 7 days.
To remove toxins and metal salts from the body, dietary supplements with natural herbs (“Fitosorbovit-plus”) are effective and should be taken for 2-3 weeks. The homeopathic drug "Lymphomyosot" also helps the body fight allergies, and it is harmless even for children.
The treatment program is selected individually by the allergist.
What to do if you are allergic to Maltofer?
If any manifestation of intolerance to the drug occurs, you must immediately stop taking Maltofer and consult a doctor for further advice on treatment and prevention of complications.
When seeking medical help with allergy symptoms, the doctor should take tests to detect hypersensitivity to the drug. This will allow us to identify the cause and component that caused the occurrence of the pathological process.
The principle of treating delayed-type allergies is to influence the symptoms of the pathology:
- To treat the rash, ointments are prescribed that reduce the inflammatory effect and also promote wound healing.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- If a response occurs from the gastrointestinal tract, diet therapy and a course of medications that reduce pain are prescribed.
If an allergen is identified to one of the components of the medicine, the doctor prescribes a form of the medicine that does not contain the allergen.
The use of any drug, even for prophylaxis, must be prescribed and dosed directly by the attending physician. This will help not only to avoid overdose and side effects, but also to reduce the risk of a pathological response of the body to taking medications.
Can Maltofer be an allergy?
The medicine "Maltofer" is a drug used for iron deficiency and normalizes its level. The composition of the drug includes iron (III) complex polymaltose hydroxide. Due to its similarity to natural compounds, it actively enters the blood from the intestines and then accumulates in the liver.
The substance accumulates in the bone marrow, causing hemoglobin levels to rise. The drug is available in the form of syrup, chewable tablets or solution. If a more severe form of iron deficiency anemia occurs, the drug is recommended to be used intramuscularly.
Children are usually prescribed drops or syrup, and adults are prescribed Maltofer tablets or solution, about which you can hear only positive reviews from doctors.
Reviews about the drug
Doctors often recommend the drug Maltofer. Patient reviews of the drug prove its effectiveness.
Some patients complain of nausea after taking this medication, but this does not affect its effectiveness. In some patients, nausea was caused by side effects.
There are also patients who noted that the drug did not provide the desired result. Most likely, this is due to its incorrect use.
Use of the drug during pregnancy
No studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug on pregnant women. Therefore, it is prescribed in situations where the benefit to maternal therapy is higher than the potential risk to the fetus.
However, the drug "Maltofer" during pregnancy is prescribed by a doctor in cases where a decrease in iron levels is observed. A deficiency of this substance is normal during pregnancy. This is especially noticeable in the last months of pregnancy.
There are no negative reviews about the drug "Maltofer", but during pregnancy it must be taken with caution and under the strict supervision of a doctor.
If the drug is prescribed to nursing women, they should remember that in small quantities it passes through breast milk into the baby's body. There is no data on the negative effects of the medication on the child.
The drug "Maltofer": drops for children
Maltofer drops are prescribed if necessary, starting from newborn age. The drug can also be used in premature infants. The medication "Maltofer" can cause abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea or constipation in a child. Other allergic reactions are also possible.
Parenteral use of the drug in children may adversely affect the course of the infectious process. The bulk of reviews about the drug "Maltofer" sound positive. Many people actually note an increase in hemoglobin levels and an improvement in the child’s well-being.
Although some young patients experience adverse reactions indicated by the manufacturer to the drug "Maltofer" for children. Reviews about them are extremely rare and talk about an allergic reaction in the form of diarrhea. Other concerned parents note the high cost of the medicine and the not very pleasant smell.
In general, reviews of the drug "Maltofer" are positive. The drug in question is very popular.
Contraindications to the use of the drug
The drug is not prescribed in cases of impaired iron excretion, hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis, hemolytic or megaloblastic anemia, or hypersensitivity to the drug. Patients with diabetes mellitus should use the medication with caution.
Due to the combination with chloramphenicol, the drug "Maltofer" can provoke a mutual deterioration of the therapeutic effects of chloramphenicol and folic acid. The medication must not be combined with other iron-containing medications.
In cases of folic acid deficiency, the use of the drug may cause an increase in the metabolism of phenytoin in the blood serum.
Prophylactic use of the drug "Maltofer"
It is possible to use the drug to prevent iron and folic acid deficiency. In such cases, the drug "Maltofer" is prescribed 1 tablet once a day. To prevent anemia - 40 drops once a day.
For iron deficiency anemia, nursing women and children over 12 years old – 20 drops per day. Babies under one year old and children under 12 years old – 10 drops once a day. Prophylactic use should last at least 30 days and no more than two months.
Allergy to Maltofer: causes, symptoms and what to do
Maltofer is a drug prescribed to pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children for the treatment and prevention of iron deficiency anemia. This substance contains ferric iron , which is quickly absorbed in the body and is the closest thing to the natural component of iron contained in the human body.
When taking any medications, including Maltofer, a child may develop an allergy due to immunity to the active substance or its components.
Causes of an allergic reaction to Maltofer
Maltofer, like all other drugs, is made through the interaction of proteins and glycoproteins. These components can cause allergies in a child.
An allergic reaction in children and pregnant women may be associated with a person’s increased sensitivity to iron.
When purchasing Maltofer, be sure to check the expiration date, because the inattention and negligent attitude of the pharmacist can also cause a negative response to drug therapy.
And also, pay attention to where and how it is necessary to store the medicinal substance - this property will help not only preserve the value of the medicinal product, but also save the body from the ingress of toxic substances formed when the substance is stored at the wrong temperature.
Only a doctor can find out the exact cause of the body’s allergic response to Maltofer, because each person’s body is individual.
What to do if you are allergic to Maltofer?
If any manifestation of intolerance to the drug occurs, you must immediately stop taking Maltofer and consult a doctor for further advice on treatment and prevention of complications.
When seeking medical help with allergy symptoms, the doctor should take tests to detect hypersensitivity to the drug. This will allow us to identify the cause and component that caused the occurrence of the pathological process.
The principle of treating delayed-type allergies is to influence the symptoms of the pathology:
- To treat the rash, ointments are prescribed that reduce the inflammatory effect and also promote wound healing.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- If a response occurs from the gastrointestinal tract, diet therapy and a course of medications that reduce pain are prescribed.
If an allergen is identified to one of the components of the medicine, the doctor prescribes a form of the medicine that does not contain the allergen.
The use of any drug, even for prophylaxis, must be prescribed and dosed directly by the attending physician. This will help not only to avoid overdose and side effects, but also to reduce the risk of a pathological response of the body to taking medications.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO BE ALLERGY TO IRON PREPARATIONS?
The use of iron supplements is often mandatory in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia. This allows you to normalize the blood picture and increase the hemoglobin content in red blood cells. Equally important is the saturation of the body’s internal depots with iron, which serves to prevent relapse of anemia.
But sometimes people refuse to continue taking iron-containing medications due to the appearance of a number of uncomfortable sensations. They often consider it an iron allergy. And the primary task for the attending physician is to determine the true cause of the appearance of such symptoms.
Urticaria from iron supplements – Allergic skin lesions
There is plenty of iron in nature; it is one of the most common elements on Earth. It is especially abundant in meat, various vegetables and fruits. Every day we get much more iron from food than the body needs. The trouble is that it is very poorly absorbed.
Of the total volume that we consume with food, no more than 1–2% is retained in the body. And about the same amount is lost every day. These indicators refer to a healthy person who is not familiar with the symptoms of anemia.
But any disturbance in the absorption of iron and an increase in its loss cause a deficiency, which is called iron deficiency anemia. What happens if an allergy develops?
Impaired absorption of iron occurs, in particular, in the intestinal form of food allergies. Malfunctions in the intestines prevent the body from properly absorbing iron.
With severe digestive disorders, the intestinal walls become more vulnerable, and sometimes the integrity of the vessels supplying the intestines with blood is disrupted.
Even with minor bleeding that occurs when the intestinal mucosa is damaged, iron loss increases significantly.
But iron is lost not only in the intestinal form of allergies. Skin allergic reactions also lead to increased loss of the vital element. This is due to the faster death of epithelial cells on skin affected by allergic rashes. Along with the desquamation of epidermal cells, the body also intensively loses iron.
Allergy to iron supplements
Iron supplements used to treat anemia in children and adults often cause allergic reactions. Most often, an allergy to iron supplements manifests itself as a rash and hives on the skin. Sometimes intestinal manifestations are also possible. Typically, treatment with iron supplements begins with small doses, gradually increasing the dosage if no adverse reactions are detected.
In addition to allergies, other undesirable reactions of the body to iron-containing medications are possible. Treatment of anemia in children requires special care. Self-medication can cause serious harm to a patient with anemia. If symptoms of anemia appear, you must be examined at a medical center and undergo a full course of treatment.
Sources used: medaboutme.ru
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC: Urticaria due to stress Urticaria and pigmentation
Allergy to metals: causes and symptoms
Metal allergy is a rare type of hypersensitivity of the body to cobalt, chromium, copper, molybdenum, mercury, including nickel and iron, as well as alloys of valuable metals containing, for example, nickel. About 10% of people on the planet suffer from this type of allergic reaction. The exception is usually noble gold, platinum, and silver without impurities.
Residents of large industrial centers are more likely to encounter this problem, and the allergen can accumulate in the body for decades. You can wear earrings, rings, watches made of nickel, a belt with a metal buckle for a long time, and come into contact with iron elements of accessories and interiors without experiencing discomfort.
But usually an allergy to iron, as well as to other metals, makes itself felt within a few days after interaction with the body of the corresponding jewelry, objects or food containing nickel (low-quality chocolate, fish).
Its symptoms can be diagnosed independently.
WHAT SYMPTOMS ARE USUALLY ATTRIBUTED TO ALLERGIES?
Some of the most common manifestations of individual intolerance to iron-containing drugs are:
feeling of heaviness and pain in the stomach;
- tendency to constipation or loose stools;
- increased gas formation in the intestines (flatulence), accompanied by a feeling of bloating and intestinal colic;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and even vomiting;
- metallic taste in mouth. With parenteral (intramuscular or intravenous) administration of iron preparations, hot flashes, headache, discomfort in the body, palpitations, and a slight decrease in blood pressure may occur. At the injection site, there is sometimes soreness, swelling, tissue hardening, or signs of inflammation of the venous wall.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of contact dermatitis and allergies to iron supplements are almost the same, as they are caused by the same allergen. Therefore, even knowing the signs of an iron allergy should not stop you from going to the doctor: without the intervention of a specialist, you may not only not alleviate your condition, but also worsen it.
Symptoms of an iron allergy:
- Skin rashes. Contact dermatitis is characterized by a rash, peeling of the skin, and crust formation in places where the allergen has been in contact with the skin for a long time. Allergies to metal preparations can manifest themselves in different ways. For example, an excessive reaction to nickel, which enters the body with food, manifests itself in the form of a rash in the genital area and anus;
- Wet eczema;
- Blisters filled with clear fluid;
- If you are allergic to metal objects surgically placed in the body, such as dental implants or metal rods that are inserted for severe bone fractures, inflammation will be noticeable in these areas, and the body will begin to reject these objects.
It is worth noting that many people confuse allergies to iron supplements and their side effects.
To better understand the problem, we list the signs of side effects to drugs that occur when taking or dosing medications incorrectly:
- Heaviness and pain in the stomach;
- Problems with stool;
- Bloating, colic, increased gas formation;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Decreased appetite;
- Metallic taste in the mouth.
We repeat once again that the above symptoms have nothing to do with the appearance of allergies.
ALLERGIES OR SIDE EFFECTS
In fact, all these symptoms are not signs of allergies. They refer to the side effects of iron-containing products. Their appearance does not pose a threat to life, although it causes obvious discomfort to a person. Even severe side effects do not require stopping treatment, but only dosage adjustment or changing the iron-containing drug.
A true allergy to iron during antianemic therapy is a fairly serious condition. Most often it manifests itself in the form of skin rashes, itching, and small papular (pimply) rash. It is also possible to develop urticaria, Quincke's edema, fever and anaphylactic shock. It is imperative to inform your doctor about any such manifestations.
HOW AND WHY AN ALLERGY TO IRON APPEARS
Allergies can be caused by hypersensitivity to both the main active ingredient (2- or 3-valent iron compound) and to the auxiliary components of the drug. For example, many antianemic drugs contain ascorbic acid, cyanocobalamin, or other compounds that are intended to further improve hematopoiesis or absorption of salt (ionic) iron preparations.
Unfortunately, there are no characteristic signs that can reliably determine the true cause of an allergic reaction. The symptoms that arise are the body’s universal response to the introduction of any allergen. They are determined not by the structure or origin of incoming substances, but by the type of pathological immune response that forms. So, a papular rash is a sign of a delayed type reaction. And urticaria and anaphylaxis appear with immediate-type hypersensitivity.
The appearance of signs of allergy to iron preparations is a reason to discontinue the drug used. Carrying out a differential diagnosis between allergies and side effects is the basis for determining further treatment tactics.
Urticaria as a manifestation of drug allergy
Allergy to drugs in the form of urticaria (urticaria) is the most common pathological reaction of the immune system to medications and herbs.
Its symptoms are often confused with symptoms of a food allergy or a nervous rash.
Drug-induced urticaria is considered a harmless allergic manifestation, but it should be taken into account so as not to provoke more serious complications.
Reasons for appearance
An allergic reaction after taking medications or herbs can be caused not only by the patient’s immediate high sensitivity to the components of the drug. In addition to individual intolerance to the components of the drug, urticaria occurs in the following conditions:
- Genetically determined slow metabolism of medications. The concentration of the active substance in the blood may remain high, provoking an allergic reaction .
- One-time intravenous administration of large doses of drugs.
- Overdose of medications.
- The use of several medications that are prohibited to be combined due to their chemical composition.
- Concomitant use of certain medications and alcohol.
- Excess dosage or unreasonable intake of multivitamins (mainly A and C).
- Disorders of the kidneys and liver that slow down the removal of drugs from the body.
The presence of other allergies and viral infections are risk factors for drug-induced urticaria. However, even with this prerequisite, it is impossible to accurately predict the appearance of characteristic blisters after administration. In many ways, the likelihood of an allergic reaction is determined by the group of drugs taken.
What drugs often cause an allergic reaction?
Drug-induced hives can be caused by any chemical with varying degrees of likelihood.
The highest risk of an immune response is observed when taking the following groups of antibiotics:
- penicillin (Amoxiclav);
- cephalosporin (Ceftriaxone, Cephalexin);
- tetracycline (Doxycycline, Vibramycin);
- sulfonamide (Albucid, Ftalazol);
- aminoglycosides (Gentamicin, Neomycin);
- fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Norfloxacin);
- Levomycetin.
In addition to antibacterial drugs, the following types of drugs can also cause drug-induced urticaria:
- opiates (codeine, morphine);
- NSAIDs (Indomethacin, Aspirin);
- analgesics (Tempalgin);
- barbiturates (Phenobarbital);
- antidepressants (Cipralex);
- statins (Lipitor);
- alkaloids (papaverine, atropine), herbal medicines;
- blood substitutes (dextran);
- a preparation for binding iron (desferam);
- protamine sulfate (a medicine that neutralizes the effect of heparin);
- anesthetics (lidocaine, novocaine);
- iodine-containing preparations (Lugol's solution);
- vitamins A, C, group B.
Symptoms of urticaria may appear after the administration of certain vaccines (Pentaxim, DTP, Priorix, BCG, etc.).
As a rule, a once-induced reaction persists in the future. This is due to the mechanism of interaction of the allergen with specific proteins (immunoglobulins E).
Even medications that have been used previously successfully without side effects can cause an allergic reaction in the form of hives. Not only patients are at risk, but also healthcare workers who often come into contact with various drugs.
Features of the course of medicinal urticaria
Drug-induced urticaria can develop not only by an immunological mechanism. If you are sensitive to the components of the drug, the first entry of an allergen into the body is accompanied by the production of antibodies, which accumulate and attach to special mast cells and basophils.
They store active substances - in particular, histamine and heparin, which are released into the blood upon contact with the medication. This causes the blood vessels to dilate and increase their permeability to blood components, which leads to swelling and blistering.
There is also a non-immune mechanism for the release of histamine.
It is realized due to the ability of some drugs (for example, Indomethacin, Aspirin, etc.) to act on mast cells directly, without the participation of immunoglobulins.
The symptoms of non-allergic drug-induced urticaria do not differ from the manifestations of allergies externally, but have a number of diagnostic signs and relatively simple ways to solve the problem. One of them is to administer medications slowly.
Development speed
According to the speed of manifestation, drug-induced urticaria can be:
- instantaneous (the allergy appears after a few minutes);
- fast (1-2 hours pass from taking the medicine to the first symptoms);
- prolonged (may appear 1-2 weeks after the drug enters the body).
Cure time
As a rule, manifestations of drug-induced urticaria disappear several hours (up to 1-2 days) after the start of antihistamine therapy and the end of taking the drug to which the patient is allergic.
Symptoms of the disease
Drug-induced urticaria in most cases occurs in an acute form and its duration does not exceed 6 weeks. The main signs of the disease include:
- sudden severe itching;
- hyperemia (redness) of the skin;
- rash in the form of characteristic blisters.
Redness, swelling and rash associated with drug-induced urticaria can be seen in the photo below: these symptoms can appear in specific areas of the body or throughout the entire skin.
The skin most susceptible to rashes is on the bends of the limbs, face, neck, and abdomen. In rare cases, the rash covers the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, eyelids and genitals. If there are blisters in the mouth, swelling of the larynx occurs, making swallowing and breathing difficult.
A rash that covers the entire skin, as in the photo below, is more common in children. Otherwise, in young patients, urticaria is more severe than in adults: the rash is accompanied by weakness and fever.
In addition to rashes and itching, the disease can manifest itself:
- headaches;
- increased temperature;
- bronchospasm;
- difficulty breathing;
- itching on mucous membranes;
- runny nose;
- secretion of tears;
- impaired functioning of the kidneys and cardiovascular system.
Drug-induced urticaria, unlike other subtypes of the disease, is often accompanied by atypical symptoms: aching joints, the appearance of blood in the stool and cutting pain in the abdomen.
Diagnostics
An important diagnostic measure is taking an anamnesis. The allergist is obliged to find out a detailed treatment regimen and clarify the presence of a hereditary tendency to allergic reactions. In addition, the following are carried out:
- General urine and blood tests.
- Immunological tests (immunoglobulin E level, enzyme immunoassay, Shelley test, sublingual test, etc.).
General blood and urine tests help confirm the absence of infections that could cause hives. An increase in eosinophils in the blood indicates an allergic reaction .
In some cases, the level of immunoglobulins, as well as eosinophils, may be within normal limits. Then specific tests are used to determine pseudo-allergy. As a rule, it is distinguished by the dependence of the reaction on the amount of the provoking substance and the absence of constant exacerbations with repeated contacts.
Treatment of urticaria
Treatment of urticaria caused by medications begins with identifying and stopping the allergen. You can speed up the healing process with the help of enemas and enterosorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb). A diet that excludes alcohol, fatty foods and common food allergens (chocolate, nuts, eggs, red vegetables and fruits) is recommended.
Medications
Patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetirizine, Loratadine). They block histamine receptors and gradually stop the symptoms of urticaria.
- Antipruritic ointments (Akriderm, Fenistil). These drugs alleviate the patient's condition and reduce the chance of infection of damaged skin.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone). Prescribed for complications and generalized urticaria.
- Miramistin solution for washing rashes on the mucous membrane.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine is unable to help with the main cause of drug-induced urticaria, but can relieve symptoms and have an antiseptic effect on the skin. Baths with the following herbs have a calming effect:
- Chamomile. Pour 1-4 tablespoons of dried flowers into 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave in a water bath for 15 minutes and leave for another half hour.
- In succession. Pour 50 g of dry herb into 0.5 liters of hot water, cover with a lid and heat in a water bath for 20-25 minutes. Let it brew for an hour. Infusion and heating can be replaced by cooking for a quarter of an hour over low heat.
- Oak bark. Pour 80-100 g of raw material into 0.5 liters of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes.
Strained infusions can be added to a bath of warm water.
The intake of herbal decoctions internally is agreed with the attending physician . It is possible to use tinctures of valerian and hawthorn (dissolve 15 drops in a glass of water, drink before bedtime), calamus powder (0.5 teaspoon at night, washed down with water), yarrow decoction (1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, drink 3 times a day) and other remedies.
Prevention of urticaria
To prevent drug allergies in the form of urticaria, you must:
- Promptly inform your doctor about medications to which an immune reaction has occurred in the past.
- Avoid self-medication, especially with antibiotics.
- Do not prescribe additional vitamin complexes without consulting your doctor.
It is not recommended to introduce new foods (especially potential allergens) into the children's diet for 1-2 days before and after vaccinations. Before vaccination, patients of any age should be carefully examined for hereditary predisposition to allergies, infections and helminthic infestations .
Source: https://kozhainfo.com/dermatit/krapivnitsa-kak-allergiya-na-lekarstva.html
WHAT TO DO IF ALLERGY
The main rule if any unwanted symptoms occur during treatment is to consult a doctor as soon as possible. What to do next and how to treat an allergy to iron should only be decided by a specialist. If there are obvious signs of an allergic reaction, you should stop taking the drug, and it is advisable to see a doctor before the external symptoms of intolerance disappear. This is especially important if you suspect an allergy to iron during pregnancy. Only a specialist will be able to reliably distinguish allergic skin manifestations from symptoms of liver failure, gestosis and dermatological diseases.
Continuation of antianemic therapy is possible even in the presence of individual intolerance. The doctor may recommend changing the drug by prescribing a drug from a different pharmaceutical group. For example, if you are allergic to an ionic (salt) iron compound, medications based on polymaltose complexes can be used.
It is important to know that the likelihood of an allergy to dietary supplements is much lower. However, before starting to take it, especially if you have a history of allergic reactions, you should consult your doctor.
To eliminate the lack of iron in the blood, doctors prescribe Maltofer - the instructions for use of the drug indicate its effect on the stomach and brain. The medication is available in several convenient formats and is prescribed to adults and children for special indications. You should carefully read the instructions for use of the medicine to cope with the disease.
Analogues and substitutes
Ferrum Lek is not the only iron-containing drug used in the treatment of anemic conditions and decreased hemoglobin. There are many analogues that differ in the composition and biological form of iron, as well as in cost and application features.
| A drug | Active substance | Manufacturer | How much does it cost (RUB) |
| Dextrafer | Iron oxide dextran complex | Health, FC, LLC, Ukraine | 1860 |
| Likferr 100 | Iron(III) Oxide Polyhydrate | Samrud Pharmaceuticals, India | 1500 |
| Maltofer | Iron (III) hydroxide polymaltose complex | Vifor (International) Inc., Switzerland | 505 |
| Sorbifer Durules | Iron (II) sulfate anhydrous, ascorbic acid | Egis, Pharmaceutical Plant, JSC, Hungary | 360 |
| Feroxide | Iron (III) hydroxide sucrose complex | Help S.A. for M. Biotek, Greece/UK | 1600 |
| Ferromed | Iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate | Med-interplast, Republic of Belarus | 440 |
| Ferropol | Iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate | Medana Pharma, Poland | 600 |
Since Ferrum Lek analogues contain trace elements in different forms, if you need to replace one drug with another, you should consult your doctor.
Iron supplement Maltofer
The pharmacological classification of drugs classifies the iron preparation Maltofer as antianemic. This means that the drug counteracts the lack of hemoglobin in the blood serum and replenishes iron deficiency. The active ingredient of the composition is iron hydroxide polymaltosate; the instructions indicate the amount of the component in terms of pure iron.
Composition and release form
Maltofer is available in five convenient formats for oral administration: chewable tablets, syrup, drops, solution and injections for intramuscular administration. Detailed composition of each medicine:
Concentration of iron hydroxide polymaltose, mg
Sucrose, methyl and propyl parahydroxybenzoate, ethanol, sorbitol solution, cream flavor, water, sodium hydroxide
75 or 150 ml in bottles with measuring cap
Water, sucrose, sodium methyl and propyl parahydroxybenzoate, sodium hydroxide, cream flavor
10 or 30 ml in bottles with a dispenser or polymer tubes
Dexrates, microcrystalline cellulose, macrogol, vanillin, cocoa powder, tal, sodium cyclamate, chocolate flavor
Brown with white splashes, round, flat, with a notch
10 or 30 pieces in blisters
Injection
50 or 100 per 1 ml
Sodium hydroxide, water, hydrochloric acid
2 ml in ampoules, 5 ampoules in a pack with instructions for use
Oral solution
Sodium propyl and methyl parahydroxybenzoate, sorbitol solution, water, cream flavor, sucrose, sodium hydroxide
10 pieces. 5 ml per package
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Ferric hydroxide contains the metal in the form of polymaltose hydroxide. Its structure is similar to the structure of the core protein ferritin, which is a physiological iron depot in the human body. Once inside, the substance is incorporated into hemoglobin and red blood cells, binds to transferrin, participates in the synthesis of hemoglobin in the bone marrow and liver for connection with ferritin, and in choline metabolism. Maximum absorption activity is observed in the duodenum and small intestine. The remains are excreted in the feces.
With intramuscular injections of a solution, iron polymaltosate hydroxide enters the bloodstream through the lymphatic system. Due to the slow release of iron, it is well tolerated. In the liver, the active drug enters the structure of hemoglobin, myoglobin, enzymes, and is used in the process of erythropoiesis. The substance reaches its maximum concentration within 24 hours.
Indications for use
The instructions for use of Maltofer highlight the following indications for use by patients:
- treatment of iron deficiency without anemia (latent deficiency), symptomatic iron deficiency anemia;
- increased need for iron (pregnancy, lactation, blood donation, intensive growth, vegetarianism, old age);
- Iron solution is used when it is impossible to take oral iron supplements or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Directions for use and dosage
Each package of the drug contains Maltofer instructions, which determine the method of use of the drugs and their dosage. Oral medications are taken during or after meals, the daily dose is divided into several doses or taken once. The dosage is indicated in the table:
Release form of the drug
Dose for anemia
Dosage for iron deficiency
Dose for the prevention of anemia
Teenagers over 12 years old
Adults, including nursing mothers
The course of Maltofer for adults and children depends on the degree of iron deficiency; it is indicated in the instructions for use:
- iron deficiency anemia – 3-5 months, then therapy lasts 1-2 at a reduced dose to replenish microelement reserves;
- anemia during pregnancy - until hemoglobin stabilizes, after which treatment should be continued at a minimum dose;
- prevention of iron deficiency without signs of anemia – 1-2 months.
Maltofer drops
According to the instructions, the drops are allowed to be combined with fruit or vegetable juices, soft drinks, infant formula, and dairy products. The products are slightly colored, which does not affect the taste of the food or the effectiveness of the drug. To accurately measure the dose, the bottle should be held vertically. If the liquid does not flow out immediately, lightly tap the bottom until it appears. Do not shake the container.
Injection
According to the instructions, the solution is administered intramuscularly. Before administration, doctors conduct a test - adults are administered from a quarter to half the dose (25-50 mg / 0.5-1 ml), children from four months - half the daily maximum. If no adverse reactions appear within 15 minutes, the remaining portion is administered. The approximate adult dosage is one ampoule daily. Maximum daily doses depend on body weight:
- up to 6 kg – ¼ ampoule;
- 5-10 kg – ½ piece;
- 10-45 kg – 1 ampoule;
- adults – 2 pcs.
The instructions for using the solution indicate the injection technique, because incorrect injection can cause pain and staining of the skin:
- the upper outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus muscle is used for insertion;
- the needle should have a narrow opening; for children, thin short needles are chosen;
- the needles are disinfected, the skin is moved about 2 cm to close the puncture channel;
- the needle is positioned vertically in relation to the skin;
- after the injection, the needle is slowly removed, and the area of skin near the injection site is pressed with your finger for five minutes;
- After administering the solution, patients are advised to move.
Oral solution
According to the instructions, the solution is taken orally during or after meals in a dose depending on the degree of iron deficiency. The duration of treatment for symptomatic iron deficiency is 3-5 months, plus after that therapy continues at a reduced dosage. For latent deficiency, the solution is taken for 1-2 months. Replenishment of iron deficiency is observed after 2-3 months from the start of treatment.
Maltofer tablets
According to the instructions, from the age of 12 years, chewable Maltosphere tablets are allowed to be taken orally. According to the instructions, they are chewed or swallowed whole. In the second option, do this during or after a meal, drinking a glass of clean boiled water at room temperature. The dosage of use depends on the severity of iron deficiency and should not exceed the daily maximum. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Maltofer syrup
According to the instructions, Maltofer syrup can be mixed with vegetable and fruit juices, soft drinks, infant formula or other foods. As a result of mixing, the food is colored, but does not change in taste. The effectiveness of the drug also does not suffer. To accurately measure the dose of syrup, use the measuring cap that comes with the bottle.
Dosage and features of administration
The dosage, duration and features of treatment depend on the severity of anemia and are determined by the doctor on an individual basis. For children, the drug is usually prescribed in the form of syrup, for adults - in the form of chewable tablets.
It is better to take oral medications (syrup, tablets) only during or after meals to avoid nausea and loss of appetite.
The course of treatment for iron deficiency anemia lasts on average from 1 to 5 months, and the medicine must be taken for several weeks after normalization of hemoglobin levels in the blood.
People with a tendency to iron deficiency are recommended to undergo preventive treatment with Ferrum Lek from time to time.
special instructions
When studying the instructions for use of Maltofer, you should pay attention to the special instructions section:
- if anemia occurs due to infectious diseases or malignant neoplasms, iron should be taken after eliminating the cause;
- the daily dose of syrup contains 0.008-0.1 g of ethanol;
- 1 ml of Maltofer drops contains 0.01 bread units (XE), a chewable tablet - 0.04 XE, 1 ml of syrup - 0.04 XE, patients with diabetes mellitus should know this;
- syrup and drops contain sucrose, which can harm teeth;
- during therapy with Maltofer, stool turns dark;
- it is unlikely that Maltofer can cause a slowdown in psychomotor reactions;
- if an allergy to the parenteral solution occurs, antihistamines are prescribed; if an anaphylactic reaction develops, epinephrine is administered;
- preparations containing iron are used with caution in patients with renal failure and liver diseases.
What is Ferrum Lek
Ferrum Lek is a preparation containing iron in special forms - hydroxide with dextran or polymaltosate hydroxide (depending on the form of release). These are substances that are closest to the biological compound of a microelement contained in the blood.
Thanks to this, it is well absorbed and assimilated by the body, quickly eliminates the deficiency of the microelement, its symptoms and prevents the consequences of pathology.
Most often, patients are prescribed iron in the form of tablets - injections are used when it is necessary to quickly increase the level of the microelement in the blood.
The product is available in the form of tablets, chewable or for oral administration, syrup, solution for intravenous or intramuscular administration in ampoules. The characteristics of absorption and action of drugs depend on the method of their administration (orally or through injections) - the concentration of the active substance reaches its peak within 3-7 days, the half-life is 3-4 days.
During pregnancy
The instructions for use of Maltofer state that to date there are no reports of adverse reactions when taking the drug during pregnancy. According to animal studies, the medication does not cause danger to the fetus and mother after the end of the first trimester. There is no information about the effect of the drug in the first trimester of pregnancy.
According to reviews, during breastfeeding the medicine is prescribed only after consultation with a doctor and assessment of the potential risk and expected benefit for the child and mother. The active component of the composition passes into breast milk, its amount has not been studied. Theoretically, the use of the drug by women who are breastfeeding will not cause negative reactions for the baby.