Pathological hypersensitivity of the immune system to mold spores is recognized as one of the most dangerous allergic reactions. Since it is impossible to completely eliminate contact with the allergen, since it is present in the house and on the street. The disease develops separately or in combination with allergies to dust, pollen or food.
We offer you to learn all the features of the course of the disease, the causes of development and become familiar with effective treatment methods.
Epidemiology of the disease
Allergy is a disease associated with a pathological reaction of the immune system. The immune system reacts to proteins that enter the body from the outside. When the “stranger” is noticed by the cells of the defense system, work begins to eliminate it and remove it from the body.
Due to the fact that this mechanism operates, viral and infectious diseases can be avoided. But it happens that the immune system makes a mistake and sees a threat in safe proteins, including food ones. Allergies have unpleasant manifestations and consequences.
Fortunately, not all people develop the disease. For a disease to occur and make itself felt, several reasons must coincide.
The most common provoking factors:
- heredity;
- immaturity and weakness of organ systems;
- hormonal changes;
- acute viral or infectious disease;
- severe psychological or physical stress;
- one-time consumption of too much irritant;
- environmental problems.
Symptoms
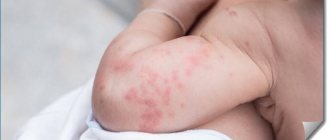
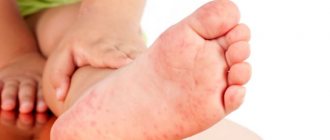
The symptoms of this disease are varied. This may be a rash on the child’s skin in the form of atopic dermatitis.
They appear in the form of a rash, redness of the skin in the form of spots or diaper rash in the folds of the skin. This may cause watery eyes and a stuffy nose.
Quite often in such children, disorders associated with the digestive organs are noticed.
Typically, in children of the first year of life, the most common are dermal and gastrointestinal symptoms, which involve a combination of both intestinal and skin manifestations. It is not difficult to identify this disease. At the first symptoms, it is necessary to take a blood test or skin test to determine the allergen.
An allergy to milk in an infant, or more precisely lactose intolerance, is a categorical intolerance to dairy products, which occurs due to the complete absence or reduced activity of the enzyme that breaks down milk sugar - lactose. In other words, it is the inability to digest it.
In order to avoid the occurrence of this disease and its unpleasant consequences, it is necessary to completely exclude products containing lactose from the diet.
What reasons can cause
Everyone knows the benefits of cheese. This is gourmet food, a real storehouse of nutrients. Plus, there is little that can compete with this off-the-shelf product in terms of versatility. Cheese is a snack, an appetizer, an independent dish, a component of hot recipes, and a dessert.
However, cheese can be quite a strong allergen. The immune reaction affects not only adults, but also children. In children, irritation manifests itself many times more strongly.
Cheese becomes an irritant product for several reasons. Some of them are dictated by the specific composition and preparation of the product, and some are caused by the human factor.

What causes an allergy to cheese:
- intolerance to milk and milk proteins (especially casein) and sugars (lactose);
- reaction to specific cheese bacteria and enzymes, molds;
- improper storage of cheese;
- using chemical reagents for fermentation instead of natural enzymes - this speeds up and reduces the cost of the production process, but negatively affects the quality of the product;
- intolerance not to the cheese itself, but to additional ingredients present in the product (this could be spices and herbs, nuts).
Important! The range of cheeses is wide. There are hard and soft cheeses, brine and curd cheeses, young and aged, ripening cheeses. Some types contain mold; white and blue ones are most often used in cooking. And although someone can treat themselves to a delicacy, it is not safe for allergy sufferers to eat such cheeses; they are the most dangerous. Mold continues to release spores into the air; they enter the respiratory tract and interfere with healthy gas exchange. Roquefort, brie, dor blue and similar varieties are a forbidden pleasure.
Symptoms and treatment of cheese allergy
Individual intolerance to various foods is a fairly common problem that people of all ages have to face. So, quite often children and adults are allergic to cheese.
Cheese intolerance
Various types of cheeses are quite healthy food products. They contain many vitamins and minerals, especially calcium.
Experienced pediatricians recommend introducing children to cheeses closer to the age of one, when the child’s body can already process such products without harm to health.
But even adults remain at risk of developing allergic reactions to such foods.
An allergy to cheese in a child most often occurs not to the food product itself, but to its components of dairy origin. In particular, a child’s body may show signs of intolerance to lactose, which is present in excess in such foods.
This reaction is explained by insufficient maturity of the digestive tract or certain individual characteristics and disorders.
Various chemical compounds present in cheese, which are often used in production for the purpose of economy, can act as an allergen for children and adults.
To reduce the risk of allergic reactions, you need to give children only high-quality cheeses with a low fat content. It is also better for adults not to take risks and try products of dubious quality.
Symptoms in children
Symptoms of a cheese allergy in children depend on which particular component of the product has become an allergen. In particular, with incomplete absorption of lactose, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract come to the fore:
- Flatulence (bloating).
- Pain and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Loose stools (not necessarily frequent).
- Constipation.
- Restlessness, moodiness and crying.
If additional components of the cheese, for example, various chemical additives, become an allergen, skin reactions will most likely develop:
- Your baby's skin may become dry and flaky.
- Various types of rashes may appear - small papules, blisters and even large merging spots, etc.
- The skin may itch and burn. Not all children can complain of such symptoms, so parents can pay attention to the baby’s anxiety and the appearance of scratching on the body.
Allergies can only occur to certain types of cheese. In particular, many children have a negative reaction to products made from cow's milk, but easily tolerate cheese made from goat or soy milk.
Symptoms in adults
Allergic reactions to cheese in adults can be very diverse. Possible occurrence:
- Skin reactions, represented by a variety of rashes, swelling, itching.
- Allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, cough.
- Disturbances in the digestive tract, for example, discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting.
- Local reactions, represented by swelling and pimples in the oral cavity.
- Atypical symptoms, represented by tachycardia, severe weakness, decreased blood pressure, increased temperature.
Allergies to cheese products in adults are not so common. Allergens can be accurately identified by performing various allergy tests under the supervision of a qualified allergist.
Allergy to blue cheese
Allergic intolerance to blue cheese should be considered completely separate from allergy to cheese in principle.
After all, mold is a fairly strong allergen, so the body can react very violently to its consumption in the form of a delicacy.
In particular, pediatricians strongly do not recommend treating children with blue cheese. After all, even at school age there is a risk of developing:
- Runny nose and cough.
- Skin rashes.
- Palpable itching.
- Various digestive disorders.
- Quincke's edema (with this condition there is a sharp swelling of the mucous membranes of the larynx, which can lead to suffocation and even death).
The risk of developing allergic symptoms and other negative consequences increases if a child or adult has a history of:
- Intolerance to antibiotics, especially penicillin.
- Allergies of various types.
- Lactose intolerance.
- Dysbacteriosis.
Some doctors warn that in children, blue cheese can provoke disturbances in the liver, which are accompanied by disruptions in the functioning of the lymphatic and nervous systems.
Even adults are advised not to get carried away with such products and not to eat more than 50 grams. mold cheese at a time. In addition, it is important to consider that in many of our stores these products do not meet quality standards.
What to do?
If a child or adult develops individual intolerance to cheese, you should:
- Seek medical help. The younger the patient and the more severe the symptoms, the sooner you need to consult a doctor. Any breathing problems and rapidly progressing symptoms are a reason to call an ambulance.
- Stick to a diet. It is advisable to exclude all allergenic foods from the diet, even if they were previously tolerated normally (the diet is especially important for young children). Indeed, against the background of increased sensitization, the body can react negatively even to already familiar food. Of course, you can’t eat cheese again. The diet must be followed until allergy symptoms disappear completely.
- Use medications after consultation with your doctor. In particular, topical application of antihistamines (for skin allergies), for example, Fenistil gel, may be necessary. Also, children are often prescribed such medications in the form of drops or syrup, while adults are usually prescribed tablets. Complex treatment of individual intolerance includes taking sorbents to quickly remove allergens from the body.
Typically, the described treatment measures are sufficient to eliminate the manifestations of an allergic reaction in a child or adult. In the future, parents need to be especially careful when introducing new foods into their baby’s diet.
Cheese in baby food
To avoid a serious cheese allergy, it is necessary to introduce children to new foods correctly:
- Do not give cheese to children under 10 months, or better yet, up to a year.
- Purchase only high-quality products suitable for children.
- For the first time, give the baby only a small piece of cheese (a little more than a pea) and monitor whether there is a reaction to such an innovation throughout the day.
- Increase the volume of product consumed gradually, also carefully monitoring the child’s condition.
- If any negative changes occur, stop introducing cheese into the baby’s diet. Repeated attempts to introduce a child to such a product can only be made after a couple of months.
Consciousness and common sense of parents helps to avoid serious consequences of cheese allergies in children. If any unwanted reactions occur, it is better to stop consuming such a product.
Symptoms in adults and children
Allergies manifest themselves in different ways, it all depends on the individual patient and the characteristics of the body. For some people, the reaction takes a day or two. If you are particularly sensitive, your immune system will alert you to the problem with lightning speed; just a few minutes are enough.
You need to know the symptoms and be able to identify them. Knowing the “enemy” by sight in an emergency situation has saved more than one life. The most striking external manifestations of cheese allergy are divided into several groups.
Eating disorders
Mild manifestations of allergies are not life-threatening, but cause significant discomfort. Nausea, intestinal cramps, flatulence, severe heartburn, problems with bowel movements (frequent loose stools or constipation) occur.
In children, allergies cause watery stool with bubbles and traces of mucus. The baby spits up food more often than usual. Much more dangerous are severe diarrhea, profuse vomiting, inflammation of the intestines and pain in the stomach due to internal edema.
Respiratory system disorders
Respiratory problems occur due to the allergen entering the body. These symptoms are especially common if you are allergic to mold cheese. You don’t even have to ingest it – just inhale the aroma and absorb the spores.
Symptoms of a false cold occur: sneezing and rhinitis, pain when swallowing, cough and hoarse voice, tingling of the larynx, swelling of the palate and tongue. Allergic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract is more difficult to tolerate. The consequences are severe: swelling of the larynx and bronchi, barking cough, oxygen starvation, suffocation up to fainting, and without medical intervention - even death.
Dermatitis
There are also dermatological irritations. The skin becomes inflamed in those areas that are the most thin and vulnerable: the face and head, limbs, groin, armpits. In children, inflammation also occurs in the area of physiological folds. In principle, skin allergies are a common story in children.
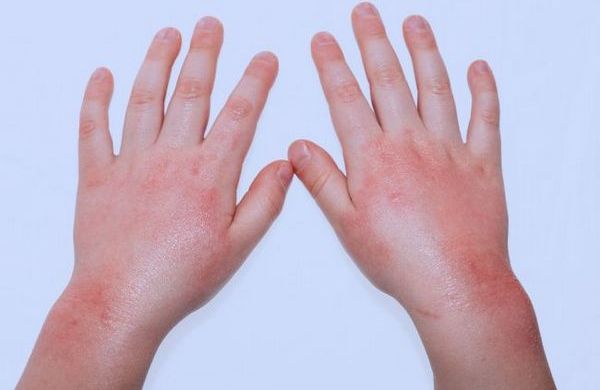
Allergies make themselves felt not only by red spots, but also by the formation of itchy crusts and small blisters. The temperature may rise due to inflammation. If you scratch your skin, you can easily get an infection.
Nervous system problems
Allergy sufferers suffer from apathy, poor sleep, and irritability. If the disease occurs with acute attacks, panic occurs. In infants, their sleep patterns are disrupted and increased excitability or moodiness occurs.
Tissue swelling
A common manifestation of food allergies is tissue swelling. Edema can affect any organ system. The most dangerous manifestation is cerebral edema. First, against the background of lethargy, vomiting occurs. The muscles in the back of the head become very tense, and the allergy sufferer suffers from cramps throughout the body. This symptom occurs rarely, but if ignored, it can claim life.
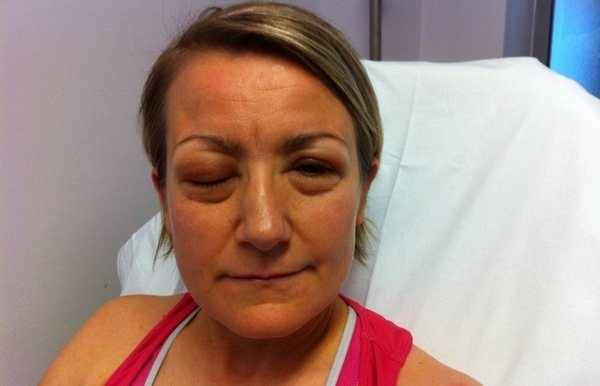
Allergy to cheese - can it happen in a child or an adult, symptoms, prevention, treatment
Allergies to cheese often occur after consuming milk-based cheeses. Children usually face the problem. The main allergenic substance in these products is lactose. This substance can cause a severe hypersensitivity reaction. In such cases, it is recommended to give preference to cheeses with plant ingredients.
Reasons for appearance
Food hypersensitivity is not that rare in people. It most often occurs on varieties made from cow's milk (not to be confused with lactose intolerance - these are different things). Why does this happen?
Cow's milk
The pathological reaction of the body is caused by proteins contained in the product. It develops in people who have a deficiency of digestive enzymes.
This happens as follows:
- milk proteins are not broken down in the stomach;
- enter the bloodstream in its original form;
- various external signs begin to appear.
Sheep cheese
casein, a protein that is the main allergen and predominates in cow's milk, is quite low in sheep products.
According to statistics, the immune system's reaction to sheep's cheese occurs much less frequently.
However, some people may have a congenital intolerance to several proteins contained in the milk of various artiodactyls.
Goat milk
This animal product does not contain the protein alpha-S1-casein.
This feature makes it neutral for 99% of people who are intolerant to cow's milk.
Eating pasteurized varieties of cheese products completely eliminates the occurrence of a pathological reaction of the immune system.
Symptoms of a cheese allergy
Intolerance to this dairy product is not much different from the typical manifestations of signs of sensitization to food. Symptoms of a cheese allergy will be quite pronounced.
Characteristic occurrence:
- asthma attacks (cough, shortness of breath);
- vomiting;
- diarrhea, stomach disorders;
- rash, itching, blisters on the skin;
- swelling on the body;
- vascular expansions.
At the first signs of hypersensitivity of the immune system to the product, its use should be stopped immediately.
For blue cheese
The strongest negative reaction of the body most often occurs when eating elite varieties containing penicillin.
Mold is a very strong allergen. It often causes the appearance of Quincke's edema, characterized by swelling of the mucous membranes of the larynx, face, feet, and hands.
In parallel with it, signs of urticaria are noticed: the upper layers of the skin are covered with itchy purple spots.
Laryngeal edema occurs as follows:
- it becomes difficult to breathe;
- increased anxiety appears;
- dry cough occurs;
- the voice takes on a hoarse tone;
- the skin of the face first turns blue and then becomes very pale;
- sometimes loss of consciousness occurs.
If Quincke's edema is not stopped in time, it can spread to the trachea, which is fraught with subsequent asphyxia. In the absence of medical care, the probability of death is quite high.
When edema spreads to internal organs, a person experiences:
- severe pain in the abdominal area;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- tingling in the mouth.
One of the most dangerous manifestations of the body’s negative reaction to blue cheese is swelling of the membranes of the brain.
Its main symptoms are:
- lethargy;
- increased tone of the neck muscles;
- the appearance of attacks of nausea;
- convulsions.
Fortunately, cerebral edema is extremely rare.
Why does it occur
The immune system reacts heavily to the penetration of certain substances in cheese into the body. But this is not a lactose allergy. Cheese intolerance is a completely different disorder. Symptoms occur under the influence of cheeses made from different types of milk:
- Cow's cheeses are dangerous due to their protein content. Their intolerance occurs when the body lacks food enzymes. Because of this, milk proteins do not break down in the digestive tract, and they enter the blood in this form. This leads to a deterioration in health.
- Sheep cheeses contain small amounts of casein. Therefore, they are less allergenic than other types. Some people do not accept several types of milk proteins at once. It is also important to remember that sheep's milk is much healthier than cow's milk.
- Goat cheeses. There are no complex proteins in cheese. Therefore, it is recommended for allergy sufferers. Cheese made from this milk is also very healthy.
Children prone to allergic reactions are recommended to drink goat's milk.
Features of allergies in children
In a baby, the body’s pathological reaction to cheese is expressed much more acutely than in an adult.
The resulting hypersensitivity is characterized by:
- severe attacks of suffocation;
- severe disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- terrible shortness of breath.
An allergy to cheese in a child is very dangerous because it can even cause anaphylactic shock.
It is expressed in the sequential and very rapid manifestation of the following symptoms:
- anxiety, worry, fear;
- jerking pain in the head;
- numbness of the face;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus;
- cold sweat;
- loss of consciousness. Rash on face
Is it possible to eat cheese during pregnancy?
While carrying a child, expectant mothers need to take very careful care of their health.
This is why doctors do not recommend that women during pregnancy consume soft cheeses, and especially varieties with mold:
Very often they contain food bacteria that can cause not only allergies, but also an infection - listeriosis.
When breastfeeding
During lactation, a woman should not overeat cheese, since intensive consumption may cause the baby to become sensitized to its components. However, a baby’s diet consists of those elements that come into his or her milk. Therefore, a product containing so many useful substances is not only possible for a nurse to consume, but also necessary.
It is important, when adding new food to the mother’s diet, to carefully monitor the reactions of the child’s body. If, after a woman eats cheese, her newborn develops any suspicious symptoms (rash, fever, vomiting, anxiety), the product should not be eaten. Also, you should not consume those varieties that can cause allergic reactions in the body.
Food allergies
A set of treatment measures
If after eating cheese (especially if this is your first acquaintance with the product) a person feels unwell, you should immediately consult an allergist. The degree of manifestation does not matter. Both mild rhinitis and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract require treatment equally. The first thing to do is to exclude cheese and other dairy products from your diet so as not to aggravate the condition.
Important! When adjusting your diet under the influence of allergies, you need to take into account that there are cross (related) types of diseases. In addition to cheese and all dairy products, you should avoid grains, seafood, citrus fruits, nuts, and eggs.
Drug therapy

Allergies are incompatible with self-medication. An unprofessional approach will lead to unpleasant consequences. After diagnosing and confirming the diagnosis, the doctor will select the plan of action that is acceptable for a particular patient. The fight against allergies is always complex and is carried out using certain groups of medications:
- Antihistamines are the required minimum, a medication base. These drugs normalize the level of histamine in the blood, which helps reduce swelling and heal inflammation. But medications have side effects, especially affecting the nervous system. You should not take such medications without consulting a doctor.
- Glucocorticosteroids are the main enemy of severe attacks. Hormone-based medications relax the muscles of the respiratory and digestive organs immediately after the first use. But hormones can act unpredictably, so they are prescribed only by a doctor according to an individual dosage regimen.
- Adsorbents are necessary to collect antigens in the gastrointestinal tract and stop the wave of reaction to a foreign substance. Regular activated carbon is the most effective remedy.
- Local symptomatic drugs provide external healing and elimination of external symptoms. These include nasal drops and sprays, creams and ointments for the skin, suspensions and aerosols for the throat.
- Sedatives are necessary if the patient is very agitated. Stress interferes with speedy recovery.
ethnoscience

You can also fight against allergies using traditional medicine, but with one condition: folk remedies are only a supplement to medications. If the auxiliary means are correctly selected, they will make the treatment more effective. Without consulting a specialist, you should not resort to amateur medicine.
Some recipes that really heal:
- Shilajit is a panacea for allergies. Its aqueous solution is taken orally in a glass three times a day, used for lotions, compresses and rubdowns.
- If the oral cavity is inflamed, rinse with calendula infusion or “sea” water (salt and iodine).
- Inhalations with essential oils of eucalyptus, pine, spruce, orange, and mint help with rhinitis.
- To relieve itching, take baths with nettle and chamomile. Such bathing is beneficial even for babies.
Cause and symptoms
There are several reasons why an allergy to dairy products may be detected. First of all, it is heredity. If one of the baby’s parents suffers from this disease, then the child has a predisposition to this disease.
An allergic reaction to breast milk may be caused by the fact that during pregnancy a woman consumed cow's milk and casein, which is part of it, could penetrate the placenta, and then into the bloodstream of the fetus.
If the mother eats foods that can cause an allergic reaction, the likelihood of the baby being sensitive to them increases significantly . Therefore, a woman who is breastfeeding a child should exclude seafood, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, honey, nuts and other equally dangerous foods from her diet.
As a rule, a list of permitted and non-recommended products is offered in the maternity hospital.
Prevention

Allergy is a disease that cannot be cured completely. Most often this is a genetic predisposition. You can only “put to sleep” the disease and take measures to prevent exacerbations from occurring.
To avoid relapses it is necessary:
- follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- strengthen the immune system through hardening and physical activity;
- Always have an antihistamine on hand in case it is not possible to check the composition of the dish for the presence of cheese.
Prevention of allergic reactions
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it, everyone knows this. Therefore, preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of a problem occurring. They are quite simple, but can save you from many problems.
First, you should follow a hypoallergenic diet. Do not consume foods that can provoke allergic symptoms. Secondly, if we are talking about an infant, adhere to the basic rules of complementary feeding.
Give all foods according to age, starting with small portions. If there are no manifestations of the problem, the amount of product is increased. Thirdly, it is necessary to take care of the immune system and consume vitamin and mineral complexes.
Following these simple rules will help, if not completely eliminate the risk of a problem, then it will significantly facilitate its occurrence.
allergiku.com
ALLERGY IN BABIES
What is a “three-week rash” and does it require treatment? What factors aggravate allergies? What is healthier for an allergy sufferer – breast or formula? How to create a diet for a nursing mother with an allergic baby? Probably, none of the mothers were spared by the cries of well-wishers “Diathesis!” at the sight of any red spot on a child’s cheek. But in some places the problem is resolved very quickly, while in some families it risks dragging on for years. It is from the point of view of the development of allergies that the first year of life is more important than any other. What should a mother consider if her baby is allergic?
Is this an allergy?
For many mothers, a phenomenon known as “baby mileage” provides a “false alarm.” The bottom line is that most babies develop rashes around three weeks of age - small red bumps on the face and sometimes the upper body. The reason is that the mother’s hormones received during pregnancy finally leave the child’s body, and from now on he must switch to “self-regulation”. While the child's body adapts to these changes in its own hormonal status, the baby is sprinkled. And after about three weeks (sometimes a little more or less), the rash disappears safely. Therefore, this phenomenon is sometimes also called the “three-week rash.”
Very often, such a picture is mistaken for a manifestation of diathesis and forces the mother to significantly limit her diet. There is no point in this: such rashes disappear by about a month and a half, in any case, whether the mother is on a diet or not. But what you really shouldn’t do is squeeze out milia pimples or try to remove them with cotton wool or gauze. In this case, an infection may occur and quickly spread throughout the face.
Manifestations of true allergies are not limited to such rashes. This includes redness and roughness of the skin, the appearance of dry areas, frequent green stools in the baby, anxiety, itchy skin, sometimes sneezing or coughing... Unfortunately, a child’s intolerance to certain factors can take a wide variety of forms.
Harmful factors
It is popularly believed that the main cause of allergies in a small child is what his mother eats. In fact, this is not true. According to the observations of natural feeding consultants, very often the manifestations of allergies are significantly reduced or disappear completely if parents take measures to improve the general climate in the apartment and carefully monitor what the baby comes into contact with. The most common causes of irritation to your baby's skin are:
children's cosmetics; fabric softeners - try to stop using them for a while, not only for children's clothes, but also for everything that the child comes into contact with, including the clothes of the adults nursing him; washing powders - use only baby detergents and, if possible, give the washing machine a couple of extra rinses; Sometimes babies react to perfumes and cosmetics used by their mother and immediate family.
We draw the attention of mothers of sensitive children to the website “Allergy and methods of its treatment” allergology.ru, it talks a lot about ways to improve the climate in the apartment, and also gives recommendations for adjusting the diet depending on the flowering time of urban plants.
Let's breastfeed!
Sometimes a mother very quickly realizes that the baby is reacting precisely to what she eats. Unfortunately, this often leads the mother to the idea that the best solution to the problem would be to switch the child to formula. Unfortunately, not very competent doctors can support this idea, saying that the child has an “allergy to breast milk.” In fact, an “allergy to breast milk” is impossible - the baby reacts not to mother’s milk, but to a foreign protein that penetrates there from the mother’s food.
What happens if an allergic child receives formula instead of breast milk? Conventional formula is made from cow's milk, which contains more than 20 substances known to be potential human allergens. Such a mixture for a child as the main food is the same as almost eight liters of cow's milk a day for an adult! And many, unfortunately, do not understand that cow or goat milk was originally intended for animals of a different biological species - to feed not a human baby, but large or small livestock. Therefore, often an allergy to the formula turns out to be even more pronounced than the reaction to mother’s milk. Parents who feed their baby formula try different brands until they find one that the baby doesn't respond to. For some, the solution is formulas based on goat's milk or soy products, but often the allergy does not make itself felt immediately, but only some time after the child is switched to formula...
In addition, formula feeding also has long-term consequences for an allergic child. The less children receive formula from animal milk or soy products, the less chance of developing allergies in the future. Thus, an allergy to cow's milk occurs up to seven times more often in older children if the child was “artificial.”
Mother's milk itself is the best prevention of allergies. A newborn baby's immune system is immature - nature expected that during the first period of life the child would receive nothing but mother's milk. Therefore, the production of its own immunoglobulins - protective antibodies - only begins at about 6 weeks of age. A child’s own immune system, at least somewhat functional, albeit still immature, is formed only by six months. Until this time, the baby receives protection from mother's milk. Milk and especially colostrum are very rich in living antibodies, which protect the child’s health from many harmful factors. The mixtures lack immune support. That is why the transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding does not solve the problem of allergies, but only aggravates it, leaving the baby without protection from foreign substances.
So, if a child clearly reacts to mother’s milk, it is better not to run for formula, but to change his diet for a while.
Mom's diet
If a child is very prone to allergies, a reaction to what the mother ate can occur literally within minutes. But still, in most cases it takes from 4 hours to a day. An unpleasant nuance: often allergens need to reach a certain level in the body before a reaction occurs. Therefore, situations may arise when, for example, a mother drinks a liter of milk every day for a month without any visible consequences, and then in just a couple of days the child develops severe neurodermatitis on previously clean skin. In such a case, the improvement will also not be immediate: it is at least five days from the moment the mother removed the allergen from her menu, and it may take two weeks before traces of the allergen disappear.
The most common allergen for young children is cow's milk protein. Therefore, a lot of problems are caused by the ingrained popular belief that supposedly tea with milk or just warm cow or goat milk increases lactation. In fact, this does not affect the amount of breast milk in any way; it’s just that any warm drink (even simple boiling water) increases the flow. That is, it is not the mother’s milk quantity that grows, but the strength and speed of its supply. At the same time, if a nursing mother drinks a total volume of more than a glass of milk per day, very often the baby soon develops indigestion: colic, abdominal pain, gas, foamy green stools. If the mother does not change anything in her diet, these symptoms are soon joined by skin rashes, which become more severe over time... That is why the first thing that natural feeding consultants advise to do with such symptoms is to remove all dairy products from your menu for a couple of weeks, excluding except hard cheese. In most cases, it solves the problem. If mom is afraid of a lack of calcium, then, in addition to dairy products, collards, spinach, broccoli, liver, almonds and Brazil nuts, and canned fish (eaten with the bones) are rich in calcium.
The second most common cause of problems is various chemical additives to food. Do not get carried away with food with all sorts of fillers, preservatives and dyes. Vitamin complexes, drug coatings, fluoride, iron, and some herbs also often provoke allergies.
The reaction to brightly colored vegetables and fruits is actually caused by the red pigment contained in the skin and pulp. Therefore, for example, if the mother of a child prone to allergies eats a couple of glasses of cherries, the child will almost certainly get sprinkled. As for the “red apples” that people like to scare people with in maternity hospitals, they are quite safe: nothing will happen from one apple, and you can eat more, just remove the bright peel.
Reactions to gluten, a protein found in a number of grains, are becoming increasingly common. Only buckwheat, corn and rice are gluten-free; accordingly, these porridges and breads made from these cereals are quite safe.
A mother of an allergic child should keep a food diary, where she writes down all the changes in her menu and the baby’s reaction to them. It's done something like this. There are foods with low allergic potential that can be introduced into your menu, preferably one at a time in the morning, so that you can observe the reaction. If the reaction is quick, write down the product itself and the date of the test, and next time try no earlier than in one and a half to two months. If a reaction appears but takes a few hours, try the product again in about a month. If there is no reaction, enter it into your menu. So, this group includes: hard cheese, horse meat, rabbit meat, lean lamb, millet, rice, buckwheat, corn, pearl barley, zucchini, cucumbers, green varieties of apples and pears, parsley, dill.
If you want something sweet - and, as a rule, a nursing mother wants it! – then “store-bought” sweets pose a danger primarily due to various chemical additives. Very rarely, children react to white marshmallows and pale yellow marmalade.
Products that you can try to introduce into your menu after 6 months of the child’s life and watch the reaction: fermented milk products, beef, chicken, peas, beans, potatoes, beets, peaches, apricots, bananas.
Products that should be limited until the allergic child is at least a year old - with a high allergic potential: eggs, fish, seafood, caviar, carrots, tomatoes, peppers, strawberries, raspberries, citrus fruits, kiwi, pineapple, pomegranates, mango, persimmon, melon, natural coffee and cocoa, chocolate, mushrooms, nuts, honey.
What to do next?
First of all, be patient. The body's initially immature defense systems almost always mature successfully if they are not overloaded. Therefore, with the right mother’s strategy, by the end of the first year of life, the baby will outgrow the symptoms of an allergy to at least what the mother has eaten.
If you can’t find the allergen on your own, try to get examined by an allergist and a pediatric gastroenterologist with allergy tests. Very often, an improvement in a child is observed after the mother personally applies for the prescription of enzymes that improve digestion. More complete digestion of food by the mother herself reduces the supply of potential allergens to the baby.
It is better not to force complementary feeding; for allergic children it is quite normal to start it a little later - the harm from direct exposure to allergenic factors outweighs the benefits. And before the child turns six months old, there is absolutely no need to give anything: the earlier the product was introduced into the diet and the more often it was consumed, the greater the likelihood that it will become an allergen in the future. While the baby is exclusively breastfed, he becomes familiar with the foods his mother eats through breast milk - contact with potential allergens is minimal, but adaptation gradually occurs.
Finally, sometimes it happens that a strict diet objectively harms the health of the mother herself. In this case, it is worth considering the option in which the mother, while still on a diet, tries to strain milk for future use, and then take care of her own health. Lactation can be curtailed gradually, simply by pumping the breasts a little as they fill. The psychological difficulties of weaning for a child will play a lesser role if the mother has a desire to return to breastfeeding after some time - after all, children at the age of 8-10 months often feel much better, and at least they accept mother’s milk normally. Source: akev.ru, newsletter for mothers “Feed your baby with love”
Author: Irina Ryukhova
Video. allergic rash in newborns
www.baby.ru
Traditional methods of treating the disease
An allergy to cheese can also be treated with folk remedies, but before using them you should consult your doctor, because all this can have the opposite effect and complications. The following recipes can be used:
- tincture using celandine, which helps eliminate allergic attacks. To make it you will need a spoon of celandine and 400 ml of boiling water. The resulting liquid should be drunk two glasses a day 15 minutes before eating;
- mummy solution. Pour a small amount of the substance into warm water and take it for 20 days with warm milk. This composition allows you to relieve swelling of the larynx and eliminate allergy symptoms;
- activated carbon or other types of sorbents will remove cheese from the patient’s body and reduce allergic symptoms;
- Sage decoction also helps to get rid of allergic symptoms. To do this, you will need to steep 100 g of leaves in boiling water and consume the resulting liquid.
Allergy to cow protein during breastfeeding: features ~
Breastfeeding is considered the ideal nutrition for any newborn, because human breast milk contains all the substances necessary for a baby, and this has long been proven by science.
What if a child is allergic to cow protein?
Doctors recommend in this case to continue breastfeeding as long as possible . However, in this case, the mother has to follow a strict diet and not eat any foods that may contain cow protein, a potential allergen for the child.
What should a woman not do if her child is allergic to cow protein?
A woman's low-allergen and dairy-free diet during breastfeeding excludes a fairly large number of foods. Usually these are products containing cow's milk or traces of it, but doctors also advise abolishing the consumption of inherently harmful products.
Dairy products:
- Fresh unpasteurized milk, milk from the store in a tetra pack, powdered milk, any milk in any form.
- Sour cream.
- Cream of any fat content.
- Yogurt.
- Sour milk (kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk).
- Cottage cheese.
- Store-bought desserts (puddings, soufflés).
- Cheese. Any type of cheese from hard to soft.
- Oil. Butter is excluded, but you can try using ghee. It must first be melted at room temperature and only the yellow sediment should be consumed, and the white residue should be thrown away or cooked with it in dishes that the nursing mother will not eat.
Products containing traces of lactose:
Condensed milk, chocolate and candies, cocoa, ice cream, any baked goods with butter, including cookies, cake creams, cream soups and instant soups, sauces and seasonings.
Knownly harmful foods that should be excluded from the diet to adhere to a strict hypoallergenic diet: smoked meats, chips, different types of sausages, various dye-based delicacies (chupa chups, bright candies), foods that have a strong smell.
Fruits and vegetables of bright colors and especially red are also prohibited . The fact is that such products contain some irritating acids, which, passing through the intestines of a child with allergies, irritate him even more and provoke the development of allergies and their transition to a more severe form.
What fruits should a mother not eat if her baby is allergic to cow protein?
Pomegranate, mango, kiwi, persimmon, melon, red apples, any citrus fruits (orange, lemon, tangerine), berries.
What vegetables should a mother not eat if her baby is allergic to cow protein?
Carrots, bell peppers of any color, tomatoes, celery, beets.
Canned fruits and vegetables are also prohibited.
Doctors sometimes say that the mother should not eat if the child is allergic to cow protein, also the following:
- Sometimes it is worth excluding chicken eggs and chicken meat, since infants with an allergy to cow protein often have an allergy to chicken protein.
- Nuts are a highly allergenic product, so they should be excluded.
- Some doctors also advise excluding all types of fish.
- Semolina and dishes made from it.
- Semi-finished meat products and canned food.
- Sparkling water.
While following a low-allergen diet, mothers are concerned about several questions, two of which are:
- How to avoid reducing the amount of breast milk if there is no milk protein in the diet?
- How to give your child all the necessary nutrients if you follow a dairy-free diet?
As for the answer to the first question, doctors have recently been of the opinion that milk in a mother’s diet does not increase lactation at all, as everyone was sure ten years ago.
Previously, it was believed that cow's milk, and especially fresh, unrefined, straight from the cow, increases the amount of breast milk and improves its quality, saturating it with all the micro- and macroelements and substances beneficial to the child.
The latest research suggests that this is not entirely true and a woman’s consumption of cow’s milk during lactation does not in any way affect the quality and quantity of her breast milk.
As for the answer to the second question, there are several possible options:
- You can drink baked milk , not fresh. In baked milk, the protein composition changes slightly, making it less allergenic for the child.
- Introduce goat's milk . Indeed, depending on the degree of complexity of the allergy in a newborn, his body may not accept cow's milk protein, but be tolerant to goat's milk proteins. You can find out by doing tests for allergies to cow's and goat's milk or simply letting your baby try this product and monitoring the reaction.
Goat's milk is generally less allergenic, it contains trace amounts of casein and is rich in calcium. There is 13% more of it in goat milk than in cow milk, although you need to know that in general cow milk is richer in vitamins.
Read - what is the difference between goat's milk and cow's milk?
Replacing cow's milk with goat's milk is not suitable for all breastfed babies, but some mothers still noted a positive effect.
- Replenish the balance of vitamins and elements with the help of special vitamin complexes purchased at the pharmacy.
- Balance your dairy-free diet so that the substances found in cow's milk still enter your body.
What can a woman eat if her child is allergic to cow protein?
It would seem that with such a large list of “don’ts,” what remains?
And this remains:
Porridge with water from any cereal, except semolina.
Instead of butter, you can use vegetable .
Green vegetables : cucumbers, zucchini, onions, broccoli, cauliflower, but it is advisable to boil these vegetables before eating.
Potatoes, if pre-soaked overnight to release excess starch.
Pumpkin.
Meat : any, except chicken and beef, that is, you can eat rabbit, duck, turkey, pork. It is also acceptable to eat horse meat and venison. Still, doctors advise to cook the meat separately and not to use the broth from it.
Bread and pastries made from second grade flour. This flour retains more useful elements than finely ground first grade flour.
Green fruits and berries : apples, pears, gooseberries, white cherries and currants.
You can eat dried fruits.
You can also have fruit tea that is pre-brewed, not in bags.
How long should a diet be followed if an infant is allergic to cow's milk protein?
No matter how difficult it may be for a mother to be on a special diet, it must be done. Unfortunately, a diet of low-allergenic foods should be on a woman’s menu for at least 6 months. Yes, exactly six months is the period that experts call the minimum for an allergy to cow's milk protein to begin to subside in an infant.
It is worth switching to a normal diet from such a diet gradually, day by day, daily checking the condition of the child who is still breastfeeding.
There are several rules for “quitting a diet”:
- A new product is introduced every 3-4 days, rather than daily. A woman’s body needs time to accumulate the “allergens” of a new product in breast milk, and the baby’s body needs time to “accept” or “not accept” a potential allergen and react to it. For example, allergy symptoms (to cow protein, in particular) such as constipation and diarrhea do not appear immediately, but within a couple of days.
- To start trying a new product, or rather, to return the product to the mother’s diet, you need to start with tiny doses - half a teaspoon. Gradually the dose should be increased.
Where to begin?
First, you can try to return soups with meat broth , then try fruit drinks (juices, compotes), then oil returns.
Fermented milk products should be returned last , as they directly contain milk protein and there is a high probability of an allergic reaction.
What to do if, even though the mother follows a diet, the baby’s allergies do not go away?
After consultation with a pediatrician, the baby can be transferred from breastfeeding to artificial feeding. In this case, as a rule, mixtures with protein hydrolysis (casein or whey) are prescribed.
Remember : the mother herself should not decide to prescribe some kind of diet for herself if her child shows signs of allergies.
First, you need to consult a doctor, who may prescribe a test to detect an allergy to cow protein in an infant.
Secondly, in any case, only a doctor can create the right diet.
Now you know what a mother can and cannot eat if her newborn is allergic to cow protein.
Read:
Allergy to cow protein: what to feed your child
Allergy to cow protein in infants: signs, symptoms
Menu for a child with an allergy to cow protein
Source: //timosha-s.ru/zdorove-grudnichka/allergiya-na-korovij-belok/%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B3%D0%B8 %D1%8F-%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B9-%D0%B1%D0% B5%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BA-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8-%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B4%D0%BD%D0% BE%D0%BC/
Can cheese cause allergies in babies?
The body of a small child requires comprehensive care and guardianship on the part of parents, who are often frightened by the manifestation of various allergic reactions.
After introducing cottage cheese into a baby's diet, unforeseen complications may arise due to poor absorption of nutrients.
Parents' worries are absolutely justified - the child's immune system is capable of mistaking milk proteins for harmful substances and joining the fight against them.
However, you should not rush to conclusions and stuff your baby with allergy medications, causing him even more harm.
When and how to introduce it into the diet
Any pediatrician will confirm that cottage cheese is a very important product in an infant’s diet.
A growing body, as you know, requires a large amount of nutrients.
You can get them from various sources, but it is cottage cheese that contains animal proteins, calcium and phosphorus, which are so necessary to strengthen the baby’s bones and muscles.
Preparing the right diet will be the key to the successful development of a child.
Children's doctors recommend giving a baby cottage cheese little by little at 7-8 months of life, but do not overdo it - portions should be small but regular.
In rare cases (for example, with rickets, underweight), it is allowed to feed this dairy product from 4 months.
For a child to successfully digest cottage cheese, parents should carefully consider the following recommendations:
- the baby has reached six months of age;
- the child is able to sit independently;
- the baby watches with interest the adults eating and strives to take food from their plate;
- the baby's weight doubled after birth;
- The baby is in normal health and has not received any medications during the previous week.
Is this possible?
Rejection of dairy products by a child’s body is a fairly common phenomenon.
And although most often it manifests itself in poor absorption of milk itself, an allergy to cottage cheese in an infant can also occur.
This delicacy is incredibly useful for the baby, but the immune system can act at its own discretion.
It should be remembered that each body reacts individually to food: one child will digest cottage cheese well, while another will develop skin rashes and vomiting.
What exactly gives the reaction?
A study of the composition of cottage cheese showed the presence in this product of:
- animal protein;
- vitamins;
- calcium;
- phosphorus.
Analyzing the effects of food components on the body, doctors came to the conclusion that an allergic reaction can rarely be caused by micro- and macroelements.
This factor cannot be completely excluded, but protein rejection still occurs more often.
Products of animal and plant origin have an individual chain of amino acids, which the body of any person strives to break down and obtain the necessary components for life.
However, there are cases when the immune system perceives them as a foreign body and danger, and therefore seeks to destroy it.
It is not the natural digestion of protein that occurs, but its neutralization using protective reactions.
When breastfeeding, the baby's body gets used to a certain set of nutritional elements.
The influx of cottage cheese can be regarded as an attack from the outside, which is primarily due to the high concentration of foreign protein in the delicacy.
Food allergies
How does an allergy to cottage cheese manifest in a baby?
Allergies in each child can have a different character and manifest themselves individually.
A common symptom is a skin rash that can cover both local areas and the entire body.
In addition, infants often have a gag reflex, which is caused by a sharp rejection of unfamiliar food.
In young children, an allergy to cottage cheese has the following symptoms:
- lips and skin around the mouth swell;
- the oral cavity is characterized by high dryness;
- the skin all over the body swells from excess fluid, becomes covered with a rash, and sometimes with pustules;
- frequent vomiting;
- The baby's belly may swell;
- indigestion causes diarrhea. The appearance of a rash after homemade cottage cheese
Review of children's product manufacturers
The baby food market is quite diverse, and parents have the opportunity to choose the most suitable product.
Children, as you know, are often capricious, not eating all the food offered.
However, there are now so many manufacturers that feeding a child delicious cottage cheese will not be difficult.
Although store shelves are full of baby food, parents usually give preference to well-known companies:
- "Subject";
- "Agusha";
- "Yagotynskoe for children."
Each of these companies supplies curds made using the ultrafiltration method of cow's milk.
The technology is quite complex and is characterized by dehydration of the feedstock and the use of additional components, for example calcium chloride.
Children's curds come both without and with fillers, but they are all environmentally friendly.
The baby may like absolutely any product, and parents do not have to worry about the safety of the child’s health.
However, an allergy to cottage cheese can occur in an infant even with high-quality nutrition.
In rare cases, rejection by the body is associated with the manufacturer, although this option cannot be ruled out either.
Violation of technology, storage and transportation conditions can damage the goods.
But still, allergies more often manifest themselves due to the large amount of protein in cottage cheese, so this problem must be solved, first of all.
Is home cooking the solution?
Many parents do not trust suppliers of fermented milk products to take care of their child’s health and prepare food for the baby themselves.
Although this is painstaking and responsible work, the child receives only natural treats.
There are a lot of time-tested recipes that you can use to make tasty and tender cottage cheese.
The baby will like some of them and not others, but you can always make the product using a new method, pampering your child and promoting the growth and strengthening of his musculoskeletal system.
Kefir cottage cheese
The usefulness of kefir is due to the presence of both protein and lactic acid bacteria, which have a positive effect on digestive processes in the human body.
But it is also possible to make very tasty cottage cheese for children from this product.
You won’t have to perform any particularly difficult actions for this, but it is important to strictly follow the technology:
- fill the pan with the required volume of kefir;
- turn the heat to medium and make sure that the contents do not boil, but only heat up;
- after a few minutes, curd will begin to form on the surface;
- collect the cottage cheese and strain with gauze, removing excess moisture;
- You can give it to your baby right away.
Cottage cheese with calcium chloride
Calcium is one of the most important macronutrients involved in the process of muscle contraction.
In addition, it strengthens bone tissue and activates certain enzymes in the body.
Its deficiency can significantly slow down a child’s development and even lead to some diseases.
To prepare cottage cheese from milk using calcium, you need to follow simple steps:
- pour the required amount of milk into the pan and bring to a boil;
- for 1 liter of milk add 2-3 tablespoons of 10% calcium chloride solution;
- after a few minutes the curd mass will begin to separate;
- Cool the contents of the pan and strain with gauze;
- You can add any fruit puree and feed the baby.
Cooking cottage cheese in a slow cooker
If you have a household appliance such as a multicooker, the process of making cottage cheese can be significantly simplified:
- pour a liter of kefir into a special bowl;
- program a temperature of 80 °C and a time of 45 minutes;
- after turning on, you do not need to change anything in the settings;
- after the time has passed, take out the resulting cottage cheese;
- cool and strain with gauze;
- squeeze well to remove excess liquid;
- You can feed immediately.
What to replace
An allergy to cottage cheese in an infant often occurs after consuming a product made from cow's milk.
Although not every baby exhibits a food rejection reaction, if this happens, then it is worth trying to replace the raw materials.
One option would be to use goat milk, which is rich in calcium, potassium, phosphorus, vitamins and albumin.
This product is easily digestible by children and very rarely causes complications.
Making delicious and nutritious cottage cheese is not difficult:
- Goat milk should be stored in a warm place for 2 days;
- after souring, pour it into a saucepan and put on low heat;
- you need to heat to 60 ° C, stirring constantly;
- if a solid substance appears, extinguish the fire immediately;
- strain through a colander and squeeze lightly;
- cool, allow excess whey to drain;
- Goat milk cottage cheese is ready to eat.
How to prevent
The gradual introduction of fermented milk products into his diet, which must be done in small portions and not very often, will help to effectively prevent the development of a violent reaction in a baby.
Experts also advise alternating cottage cheese with kefir and yogurt.
If the child’s body reacts too sharply, then you should consult a doctor for advice.
Treatment
The sudden onset of allergies in a child can greatly frighten parents.
In such cases, you should immediately call a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications if they are really needed.
However, cottage cheese is too important a product for babies, so a gradual normalization of the reaction will only be beneficial.
A sequence of several simple steps will eventually relieve your baby of an allergy to this product:
- after symptoms appear, stop taking cottage cheese for a month, which will clear the memory of the immune system;
- after a month, start feeding in small doses - one teaspoon once a day;
- over time, gradually increase the frequency and quantity of the product;
- in a few months there will be no trace of the allergic reaction.
Diagnostics
Timely detection of an allergy to cottage cheese in a baby will help avoid a lot of undesirable consequences.
Pediatricians recommend taking advantage of the child's sleep time and applying a little cottage cheese to the back of his hand, lightly bandaging his hand.
If an infant has an allergy to cottage cheese, it will manifest itself as redness of the skin within an hour.
The baby’s body’s rejection of this product also becomes obvious after general symptoms. But there is one drawback to this: allergies can also occur to other substances.
Therefore, visiting a doctor will make it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the correct course of treatment.
Source: //allergic.lesovir-c.com/mozhet-li-syr-vyzyvat-allergiju-u-grudnichka/
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure, cheese should be consumed with great caution, especially for children. If you suspect that you are allergic to this product, you should first eat a small amount of cheese and only if there is no reaction, use it constantly. It is worth eating cheese made from plant-based components, without the use of lactose and casein. If necessary, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo a course of immunotherapy, which will not only get rid of the symptoms, but also the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
A person can go to a medical institution to determine the presence or absence of an allergy, or they can conduct testing at home. The laboratory takes appropriate samples and performs test tests. The procedures are prescribed by an allergist and, based on the results obtained, a treatment is drawn up. For home testing, it is enough for a person to try a small amount of cheese to see if symptoms of the disease appear. If by the evening a rash appears on the patient’s skin and the patient begins to have diarrhea, then we can safely talk about an allergic reaction. However, even if it was possible to identify the cause of the allergy, it will not be possible to avoid visiting a doctor. This will be necessary in order to identify the type of allergen and determine what other products can cause a similar reaction in a person. Most often, a blood test is taken from a vein for diagnosis. This allows you to determine the patient's immunoglobulin level. A reaction is also observed after a microscopic amount of allergen is placed under the patient’s skin. If the disease occurs, then a corresponding reaction will appear.