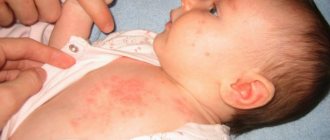
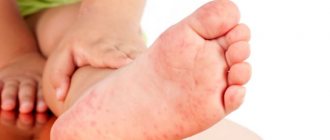
In approximately 3% of cases, children are allergic to gluten. Mostly, the first alarming signs can be observed before the age of one year, and in such a situation, parents should reconsider the diet. If a child is allergic to gluten, unpleasant symptoms are observed that are important to eliminate quickly. It is highly recommended to consult a medical specialist to make an accurate diagnosis and take the right measures. In the future, the patient will have to adhere to a gluten-free diet so as not to provoke pathological attacks. Additionally, it is worth understanding the specifics of a child’s bread allergy.
How to recognize?
Symptoms of a gluten allergy in a child are expressed as follows:
- bloating;
- insufficient weight gain;
- slow growth;
- unstable and frequent stools (feces have the consistency of porridge with a characteristic unpleasant odor, with a greasy sheen).
In addition, secondary symptoms may appear, such as irritability, fatigue, flaking of the skin and dermatitis, a tendency to bone fractures, gum problems and caries, and bulging of the abdomen.
Manifestations of allergies in infants
Infants require increased attention, because up to one year of age, children are given their first complementary foods or milk powder is used instead of breast milk.
The substance is found in cereal crops, such as:
- wheat;
- oats;
- barley;
- rye.
When gluten first enters a child's gastrointestinal tract, an immediate reaction is triggered. A few minutes after eating, characteristic signs of an allergic reaction may appear:
- hyperemia of the skin in the flexure areas of the joints;
- itching;
- increased breathing.
On a note! Infants who feed exclusively on mother's milk do not develop an allergy to gluten.
The substance is not found in breast milk.
Gluten intolerance in children
Increasingly, we are faced with a problem when children are on a gluten-free diet.
Because when consuming foods that contain gluten, a child may experience skin rashes, disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, anemia and even exhaustion.
Are all these symptoms related to gluten?
Gluten is a complex protein. It is found in wheat, rye, oat and barley grains.
The causes of celiac disease are not precisely established, but it is believed that gluten intolerance in children occurs for genetic reasons.
With this disease, damage to the villi in the small intestine occurs, so the substances necessary for nutrition (minerals, vitamins and many other necessary compounds) are disrupted.
Approximately every hundred Europeans suffer from gluten intolerance.
Most often, signs of celiac disease appear in a child at six months or a year, and their appearance is usually associated with the introduction of complementary foods.
But there are cases when the disease is not observed in childhood and is detected in an adult.
Infants who feed exclusively on mother's milk do not have gluten intolerance, because this substance is not found in milk.
Breastfeeding your baby while introducing gluten-containing foods (bread, cereal) into complementary foods reduces the risk of gluten intolerance.
Doctors recommend introducing gluten-containing products in small quantities into the children's menu after breastfeeding.
What happens with celiac disease
The occurrence of celiac disease is explained by the fact that gliadin, a component of the gluten molecule, comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the small intestine and provokes an immune system response in which it begins to attack the intestinal mucosa.
With this autoimmune reaction, the mucous membranes become inflamed and destroyed.
The inflammatory process lasts throughout the entire time of contact with gluten-containing products.
If we remember how much we consume wheat and other gluten flour in its different types, it becomes clear that the small intestine is provoked every day.
Even microdoses of gluten (0.1 gram: a few bread crumbs) can trigger an outbreak of inflammation in children with celiac disease.
Symptoms of gluten intolerance
How does gluten intolerance manifest in children? There are no universal symptoms, but classical doctors call the clinical picture that can be observed in young children:
- Loose stools.
- Abdominal pain, flatulence.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Skin rash.
- Pallor.
- Anemia.
- Lethargy, drowsiness, which can be replaced by irritability and aggressiveness.
Poor weight gain or weight loss by a child, or stunted growth are also signs of gluten intolerance in children.
Very often, parents mistake the symptoms of celiac disease for manifestations of other diseases and do not rush to see a specialist.
But in the absence of proper treatment (gluten-free diet), gluten intolerance leads to irreversible changes in the body.
Therefore, if parents notice such symptoms that are difficult to explain, show the child to a specialist, in case it is celiac disease.
To date, up to three hundred symptoms of celiac disease have been described in children and adults. This is a very complex and insidious disease that can hide under the guise of other diseases and atypical symptoms.
In the body, gluten intolerance begins to lack a variety of nutritional compounds, which can lead to disruptions in the functioning of any system or internal organ.
This is why celiac disease has so many symptoms: the symptoms often resemble signs of diseases of a variety of internal organs.

Diagnosis and treatment
How to determine gluten intolerance in a child? If celiac disease is suspected, the doctor will prescribe the necessary diagnostic measures to confirm or refute the suspicion.
An analysis for gluten intolerance in children, the result of which indicates celiac disease, must also be confirmed by a biopsy, when cells are taken from the small intestine for analysis, as well as a histological examination of the small intestine.
A gluten-free diet for life is the main and only treatment for celiac disease.
If the disease is detected on time, usually the child’s condition returns to normal when the diet is followed. The child’s intestines are completely restored in about six months and no longer cause any concern.
The disappearance of pathological symptoms finally and completely confirms the diagnosis.
If treatment began late, changes could occur in the child’s body, which doctors will treat while on a gluten-free diet.
Many experts agree that gluten intolerance is not a disease, but rather a lifestyle issue.
Against the background of a special diet, a person is absolutely healthy, because in the absence of exposure to gluten, there is no inflammatory process in his small intestine.
Gluten-free diet
A child with celiac disease should not eat any foods or products made from gluten grains.
Also excluded are sausages, semi-finished products, sweets, canned foods, various sauces and seasonings, milk (whole), yoghurts, and curd cheeses.
The basis of the diet is:
- Fish (low-fat).
- Meat (chicken, beef, rabbit).
- Seafood.
- Porridges made from corn, buckwheat, millet, rice.
- Potato.
- Legumes.
- Eggs.
- Soy products.
- Cottage cheese.
- Dairy products that do not contain starch, stabilizers, or dyes.
- Vegetables, fruits, herbs, dried fruits.
- Butter and vegetable oil (preferably olive).
Celiac disease and wheat protein allergy
Allergy to wheat proteins and gluten intolerance in a child are different diseases.
There are special elimination tests (when contact with the irritant is excluded) that help to accurately establish the diagnosis. Diagnosis is very important because children with celiac disease are on a gluten-free diet their entire lives.
And if you are allergic to wheat, the doctor will prescribe a hypoallergenic diet, if followed, the child can “outgrow” this allergy, which never happens when a child has celiac disease.
When following a gluten-free diet, the child lives a normal life, develops well, and does not lag behind his peers in any way.
Meeting dietary requirements is not so difficult, because today you can find gluten-free products in stores: flour and bread, cookies and pasta.
There is a sign on the packages: a crossed out ear of wheat. In addition, there are more gluten-free products than gluten ones, and the diet is not difficult to organize.
Treatment options
If the development of an allergy to gluten is suspected, the pediatrician prescribes skin tests, after evaluating the results of which further treatment tactics and a dietary menu are selected.
The basis of therapy is restriction of the daily diet. Dietary restrictions will help you accurately determine the root cause of the pathology.
The second, no less important part of treatment is taking medications. Pediatricians mainly prescribe enterosorbents and antihistamines. In addition, creams and ointments are used to relieve inflammation, as well as drugs to normalize intestinal functionality. This approach will help the child’s body work harmoniously and quickly cope with the problem.
What products does it contain?
The second name of the substance is gluten. It is found in 75% of foods consumed every day, even by infants.
An increased amount of gluten is present in bread and flour products, cereals, semolina, bran and pasta.
There is also a separate group of products where gluten is presented in hidden form - sweets, ice cream, sauces, crab meat by-products, snacks. Here gluten is used as an additional component.
List of products that should be removed from the menu
If you are allergic to gluten, you should completely remove the following products from the menu:
- gluten-containing cereal porridges;
- products made from rye or wheat flour;
- semolina porridge;
- yoghurts with all kinds of additives and fillers;
- ready-made semi-finished products, offal, sausages and smoked meats;
- pickles;
- sauces;
- canned food;
- kvass;
- cocoa.
In addition, you need to refrain from salty foods, dishes with hot spices, and whole milk.
On a note! Today, it is much easier for parents of children suffering from allergies or intolerances to monitor their child’s nutrition, because gluten-free products can be purchased in supermarkets.
Don’t think that you will have to forget about this food forever. If your baby has an allergy and not celiac disease, it will go away over time. After the problem subsides, the child can be transferred to a nutritious diet.
Gluten and gluten-containing products
Gluten is a protein of plant origin.
It is found in the seeds of some cereal plants such as oats, rye, barley and wheat. The second name for gluten is gluten. It is included in about 80% of human daily food products, including products for infants. The obvious presence of gluten can be found in bread, bakery products, porridges from the above-mentioned cereals, baked goods, semolina, pasta, and bran. Products with hidden gluten content include deli products, candies, ice cream, sauces, mayonnaise, dressings, chips, crab sticks and other products to which gluten is added as an auxiliary ingredient.
What can you eat if you are allergic to gluten?
The diet allows you to eat quite varied.
The child's menu can include:
- porridges and soups made from rice, corn and buckwheat;
- legumes;
- baked goods and other products made from soy, rice and corn flour;
- soy;
- lean meats and fish, seafood;
- skim cheese;
- vegetables and fruits in any form;
- vegetable oil (preferably olive).
They can be given to children without any fear both during the recovery period and during periods of exacerbation.
Principles of a gluten-free diet:
- Food products containing wheat, barley, rye, and oats are completely excluded from the child’s diet. Bread, pasta, cereals made from semolina, oatmeal, wheat, and canned baby food containing these grains are not allowed
- Pay attention to the presence of “hidden” gluten in products. In Russia, not all products indicate the presence of gluten, since there are no such indications in the current legislation;
- the carbohydrate component of the diet is replaced with buckwheat, rice, corn, vegetables;
- meat, dairy products, chicken eggs, vegetables and fruits are not limited in the diet;
- despite the large number of prohibited foods, the baby’s diet should be as balanced as possible in terms of energy value in order to prevent weight loss;
- Indigestible dishes that stimulate gastric secretion - rich broths, spices, concentrated juices - should be excluded from the diet;
- All products are steamed, pureed or chopped.
Tips and tricks
To protect an infant from developing allergies, parents should not rush to introduce complementary foods. It is best to include adult food in the baby’s menu no earlier than 6 months, and also try to prolong breastfeeding as much as possible. The first complementary food should be in the form of gluten-free cereals or vegetable purees from one component.
Pediatricians recommend that when introducing complementary foods, mothers keep a diary in which to record new foods and reactions to their use.
Newborns who are supplemented with formula milk or who are completely bottle-fed require special attention. Formulas contain gluten, so it is important to choose breast milk substitutes with care. To prevent the development of allergies or intolerance to gluten, it is better to give preference to gluten-free mixtures