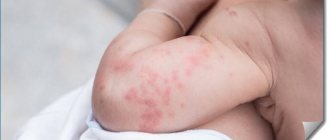
Allergy to mint is quite common and requires timely provision of the necessary assistance, since there is a high probability of developing various complications.
An allergic reaction can occur in patients of any age. In a child, the first symptoms of an allergy appear as a food reaction with pronounced diathesis. Infants have a high probability of allergens entering the body with breast milk, since mint is often recommended to be used as a lactation product.
Cause of illness
People use mint as a dietary supplement. For example, it is added to tea, ice cream, and meat products. It enhances the taste of the dish and gives it an aromatic aroma.

The cause of the pathology is quickly clarified, since the immune response develops instantly. This is mediated by the following mechanisms of action:
- mint penetrates the digestive tract, from where the immune system recognizes the antigen;
- immune cells begin to be actively released, among which eosinophils and basophils are common, responsible for the allergic reaction;
- leukocytes produce inflammatory mediators, which cause pain, swelling, redness, and exudate;
- if inflammation forms in the gastrointestinal tract, dyspeptic disorders appear, among which nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are especially prominent;
- if contact with a pathogenic agent was on the skin or mucous membranes, rashes, itching and other local reactions occur;
- In some patients, the contact of antigen and leukocytes most harms the respiratory tract, which is manifested by bronchospasm and attacks of suffocation.
If contact with the allergen is completely eliminated, the symptoms quickly disappear. But treatment may be required to make the patient feel better.
When people first encounter the plant, not all of them know whether they may be allergic to mint. If their body is prone to hypersensitivity, such a reaction is possible. Moreover, it manifests itself both locally and systemically. The type of hypersensitivity does not depend on the volume of the herbal product with which the person came into contact. Everything is related to the degree of immune response.
Some patients may have cross or mixed hypersensitivity. For example, if you develop an allergy to lemon balm and mint. Any of these components causes a response, a deterioration in well-being. To understand what causes cross-allergy to mint, diagnosis is required using laboratory tests (see “Allergy tests needed to make an accurate diagnosis”).
Allergies to mint in children may occur during breastfeeding. The mother consumes a product whose antigens penetrate into the milk, causing dyspeptic and skin reactions in the baby (see in more detail “Allergy to breast milk in a child”).
How to treat
If a connection has been identified between the use of cream, mascara or lipstick and allergies, you need to take all measures to relieve the symptoms of the disease:
As a preventive measure, you should always first buy samples of decorative cosmetics and check the reaction to them on a small area of the skin, and also avoid products with animal and plant ingredients.
medicala.ru
Although menthol has long been used as a treatment for various health conditions, research shows that there are some side effects associated with the use of this substance.
Menthol is an organic compound that is either naturally produced or synthesized from mint. It is characterized by a waxy, elastic crystalline structure and has the property of melting at slightly above room temperature. Medically known as methyl salicylate, menthol is widely known for its cooling effect and also has the ability to heal various diseases. Therefore, the medicinal properties of menthol are used in many herbal medicines and also in many products such as creams, ointments, sprays, lotions, etc.
Benefits of menthol
Menthol is widely used to treat muscle and joint pain or pain arising from arthritis, rheumatism, sprains, etc. Menthol mainly stimulates the cold receptors in the skin and has a cooling effect when inhaled or applied to the skin. This substance serves as a counter-irritant, causing superficial irritation of the skin in order to reduce inflammation in deeper layers. This property of menthol first has a cooling and then a warming effect on the skin. Consequently, such various sensations that occur on the skin distract the patient’s attention from pain in the muscles, joints and tendons, which to some extent helps to alleviate the discomfort and general condition of the person. However, menthol does not change the temperature of the skin, but simply gives the sensation of a change in temperature. In addition, it is also used to relieve sore throat and cough during colds, flu or allergies. But like two sides of the same coin, menthol also has some side effects.
Side effects of menthol
Like all other medications, menthol also has some side effects. And, while some are mild, others can cause immediate medical attention.
Cream or lotion
Menthol cream is generally used by people who suffer from constant muscle aches and pain due to arthritis or any other disease. However, some of them experience serious allergic reactions such as skin rashes, itching, redness and irritation in the area where the cream is applied. Other rare but serious side effects when using menthol creams include difficulty breathing, chest tightness, swelling of the mouth, lips, face, etc.
Ointment
Just like menthol cream, the ointment is used to reduce soreness and inflammation in muscles and joints. However, common side effects associated with the use of ointments include allergic skin reactions such as rash, itching and hives. Other negative effects of menthol ointment include difficulty breathing, chest tightness, swelling of the face, mouth, tongue and lips.
Spray
Menthol nasal spray is used to provide temporary relief from a stuffy nose, cough, and sore throat due to colds, allergies, sinusitis, or other respiratory infections. Despite the beneficial effects, many patients experience adverse reactions after using the nasal spray. Such reactions include breathing problems, difficulty swallowing, chest tightness, nasal irritation, redness and irritation at the application site.
The natural menthol extracted from peppermint also sometimes causes side effects that are common when using this plant. However, negative reactions to menthol are not widespread, and most people experience no or minor side effects. Moreover, some of the listed side effects are mainly due to improper use or method of application. Therefore, make sure that you carefully study the instructions attached to the menthol preparation, and do not rush to use the product until you carefully study the method of use and dosage. But despite taking all safety precautions, if you notice any of these side effects, stop using this drug and consult your doctor immediately.
www.yod.ru
Symptoms in adults and children
Based on the symptoms, your doctor can tell if mint is causing an allergy. They manifest themselves in varying degrees and can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient. How does an allergy to local mint manifest itself:
- discomfort - itching, pain, burning;
- swelling of the skin or mucous membranes;
- severe redness;
- rash in the form of small blisters containing clear serous fluid (no pus);
- nasal discharge accompanied by frequent sneezing;
- the epidermis peels and cracks, areas of hemorrhage may be detected, especially with prolonged scratching with nails.
If the antigen acts on the affected area for a long time, minor allergic reactions can develop into serious dermatitis and erythema. The symptoms that appear will remain the same, but will significantly increase their impact.
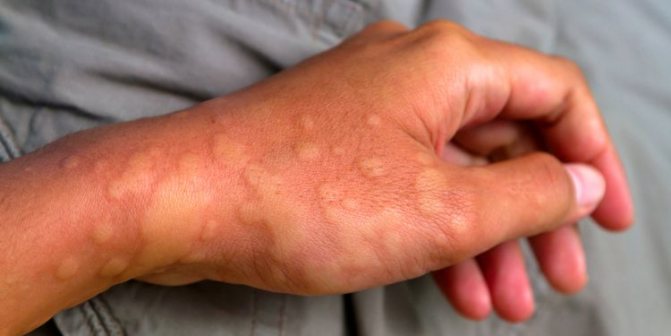
Manifestations of allergies in an adult - blisters on the skin
If the immune response is overdeveloped, systemic type deviations may occur. Each pathology has its own symptoms of mint allergy:
- anaphylactic shock - blood pressure drops sharply, blood vessels collapse, the patient faints, and there is a strong load on the cardiovascular system;
- urticaria - extensive red spots throughout the body that swell excessively and itch (see “What does urticaria look like in a child: causes, main symptoms and emergency care for sudden development of the disease” and “Causes of urticaria in adults, treatment and preventive measures“ );
- bronchospasm - narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, causing an attack of suffocation;
- Quincke's edema is swelling of the larynx, due to which a person cannot breathe, which causes rapid death in the absence of first aid (see “What to do if Quincke's edema suddenly develops in a child or adult?”).
These signs of a mint allergy can develop in a child or an adult. But in childhood they are less pronounced and gradually reach their peak during puberty if timely treatment is not carried out. For example, a minor skin rash can worsen to the point of bronchial asthma.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to mint are as follows:
- the sinuses swell, which is accompanied by increased mucus secretion;
- there is hyperemia of the skin, accompanied by profuse rashes and unbearable itching;
- During auscultation, wheezing in the chest and difficulty breathing may be heard;
- the patient's voice may be hoarse, and an attack of suffocation may develop;
- redness in the eyelid area and increased lacrimation;
- Often there are symptoms reminiscent of food intoxication with diarrhea, cramping pain in the stomach, uncontrollable vomiting and attacks of nausea;
- in addition, hyperthermia and hypertension are possible, accompanied by increased weakness and lethargy of the patient.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of the condition, it is important to contact an allergist in a timely manner. He will prescribe a wide range of tests to identify the damaging factor.
- General inspection. The doctor examines the patient, determining the quality of the skin and mucous membranes, eye sclera. If the patient has a skin reaction, it will be immediately noticeable.
- Anamnesis collection. The patient explains when the first reactions began, how much they increased or decreased during this time. He tells whether there are people in his family who suffer from immune hypersensitivity. The patient must remember all the foods, plants, and other substances to which he is allergic.
- General blood analysis. This is a non-specific test. It can only tell whether there is an inflammatory reaction in the human body. This is evidenced by an increase in leukocytes and ESR. Other parameters will remain stable.
- General urine analysis. If the allergic reaction is in the acute phase, a large number of leukocytes will be detected in the urine.
- Blood test for the main allergens (see “Blood test on a panel of allergens: types, indications for the study, preparation and interpretation of the results”). It is not the substances themselves that are released, but memory immunoglobulins, which remain in the human blood upon initial contact with the allergen. This way you can recognize the main types of allergies. For example, cow's milk protein, plants, animal hair. But many other factors will remain unclear.
- Allergy skin test (see “Skin tests for diagnosing allergies”). This is the most specific method. A series of antigens are applied to the patient's wrist. If swelling, inflammation, or redness forms on any of them, this indicates a negative reaction of the immune system in relation to its composition. It is also possible to recognize specific plant species. For example, an allergy to mint oil, an allergy to peppermint are detected.
The data obtained is sufficient to diagnose the patient. Additionally, he will be able to understand which substances may cause a cross-reaction. Not every person knows whether there is an allergy to mint. It is these tests that determine the predisposition of his immunity to a particular allergen.
When should you not use medications containing mint?
All the medicinal properties of mint have a downside - contraindications, so the remedy cannot be used for all people.
- Mint makes heart contractions rarer, but stronger - which means mint tea or other medications are contraindicated for bradycardia.
- Peppermint contains menthol and other active substances that increase the secretion of gastric juice, so it should not be used for gastritis with high acidity.
- Saponins, which are part of mint, enhance bronchial secretion and dilute secretions, but at the same time irritate the gastric mucosa, so the plant is not used for hypersecretion of the stomach.
- The use of peppermint lowers blood pressure, so contraindications apply to people with hypotension.
- Tea with mint and decoctions of the plant are used for dry, unproductive coughs, but these drugs are contraindicated in children under 5 years of age, and in infants, menthol can generally cause depression of the respiratory center.
- The use of mint herb as a mild choleretic agent is contraindicated for those who have been diagnosed with cholelithiasis with large stones.
- The herb gives a fairly pronounced sedative effect, it will help well with neurasthenia, but with asthenia, the use of peppermint is contraindicated for use, it can increase lethargy and worsen the condition.
Separately, it should be noted that the medicinal properties and contraindications of mint should be especially taken into account when treating asthma with the help of this plant. Bronchial asthma is often associated with allergies, therefore, although peppermint has the ability to dilate the bronchi, a history of allergies may be a contraindication for its use.
Return to content
Drug treatment
The amount and type of medications are selected depending on the developing reaction. If it only forms locally, the following medications will help:
- ointments based on antihistamines (Fenistil);
- anti-allergy ointments containing hormonal drugs (Advantan);
- creams containing lidocaine, novocaine, benzocaine to eliminate pain;
- sorbents that bind and remove residual water from the digestive tract before the nutrients are absorbed into the systemic bloodstream (Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of creams (Diclofenac);
- oral antihistamines in tablets, suspensions, syrups, solutions (Zyrtec, Zodak, Suprastin, Claritin, Erius).
If the patient uses antihistamines orally and by injection, it is better to select the latest generation medicine. Their active components do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier into the brain, and therefore do not cause drowsiness.
If there is a systemic reaction, the treatment method for mint allergy changes:
- antihistamine injection;
- glucocorticosteroid in the form of an injection (Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone);
- if the pressure drops, the blood vessels dilate, administer Adrenaline subcutaneously;
- infusion therapy to eliminate the allergen from the systemic circulation.
If the patient wants to completely eliminate the hypersensitivity of the immune system to plants, you can use the method of gradual sensitization (see in more detail “The effectiveness of using allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) in the treatment of allergies in adults and children”). The doctor injects the patient with small doses of the antigen subcutaneously so that the immune system gets used to it. Then, upon contact with the plant itself, allergies will not develop. But this method is available only in the autumn-winter period, when his health is normal and allergies or other diseases do not occur.
If a systemic allergic reaction develops, therapy is carried out only by doctors. If a person nearby does not have knowledge of first aid, call an ambulance.
How is the plant useful?
Many people grow this plant in their dachas and even on window sills in flower pots, and use it as a food additive and to decorate dishes. However, it happens that when drinking mint tea, instead of the expected effect, your health worsens. Peppermint and other plant species common in our latitudes are not only spicy and aromatic herbs, but also have pronounced medicinal properties and contraindications that must be taken into account.
Peppermint, or mint, has found its place in medicine due to its medicinal qualities:
- improves the digestive process, eliminates nausea;
- used as a sedative, helps with insomnia;
- relieves spasms;
- eliminates inflammation;
- has a moderate choleretic, diaphoretic, diuretic effect.
Mint, the medicinal properties of which are determined by the content of active substances, can be used in the complex treatment of diseases associated with circulatory failure, diseases of the digestive system, nervous and depressive conditions, colds and gynecological disorders. Mint, the beneficial properties and contraindications of which have been quite well studied, is used to relieve symptoms of toxicosis in pregnant women, but in minimal doses and under the supervision of a doctor.

Return to content
Consequences of allergies
If allergies are not treated in time, the consequences can be disastrous. As for physical manifestations, this is, first of all, a weakening of the immune system, damage to organs and body systems, and an impact on the offspring. At the psychological level, allergies manifest themselves in increased fatigue, general weakness of the body, decreased level of performance, and much more.
Mint and its oil are very popular, and they can be found both in perfumery, cosmetics, and in herbal medicine, for example, mint leaves are added to tea, however, if a person has a weakened immune system, or has some hereditary diseases, then an allergic reaction to mint is provided.
Other restrictions
There is an opinion that mint is contraindicated for use by men.
It is believed that the plant inhibits the production of testosterone, which negatively affects sexual function. This statement is true when it comes to excessive and indiscriminate use of infusions and decoctions of the plant, as well as when a man has low blood pressure and pathologies of the genitourinary system.
A cup of mint tea is not contraindicated for men in a stressful situation or just to relax, provided that they do not suffer from excessive suspiciousness.
Pregnancy is a contraindication for the use of mint due to the fact that the plant promotes the production of estrogens. These hormones can trigger uterine contractions, which can lead to the onset of labor. At the same time, peppermint effectively relieves the symptoms of toxicosis, so in some cases it can be prescribed as a weak tea. Such a prescription can only be made by a specialist; self-medication in this case can cause irreparable harm.
herbaldoc.ru
Causes of cigarette allergies: tobacco or chemical components of cigarette smoke?
The contents of cigarettes are tobacco, which, like tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, henbane and nightshade itself, belongs to the nightshade family (Solanum). Of the three tobacco alkaloids - anabasine, ornicotine and nicotine - the most famous is nicotine, part of the molecule of which is similar to the important neurotransmitter of the human central nervous system, acetylcholine. It is precisely a drop of this alkaloid that should, in theory, kill a horse... For humans, nicotine is a potent neuro- and cardiotoxin (that is, poison), and for the plant itself it is just a protection against harmful insects.
How allergies to cigarettes are related to the chemical composition of the raw materials for their production, scientists are still finding out to this day. Until recently, there was an opinion that an allergy to cigarettes does not have an immune component and, in fact, is a typical allergic reaction to an external irritant. That is, immune cells (antibodies) do not react to tobacco, and only flavorings added by manufacturers to tobacco products (for example, menthol) can cause an allergy to cigarettes. In extreme cases, allergies are provoked by the remains of insecticides used to treat tobacco plantations. Or cigarette paper, which is impregnated with ammonium nitrate (ammonium nitrate) to speed up combustion. In addition, no one knows what “secondary tobacco” contains - that is, tobacco dust and waste from tobacco production, which is used to stuff cheap smokes...
During the drying and fermentation process, the chemical composition of tobacco leaves is approximately the following: nicotine (0.2-4.6%), carbohydrates (1.6-23%), organic di- and tricarboxylic acids (9-16%), proteins (6.4-13%), polyphenods and phenolic glycosides (1.2-7.5%), pectins (10-14%), phenolic glycosides (2-6%), essential oils (up to 1.5%) , resins (2.5-5%).
It is the protein content that is the biochemical basis for the appearance of a real allergy to cigarettes (as to pollen or animal dander).
As for cigarette smoke, as a result of pyrolysis (thermal decomposition of organic substances) during smoking, over 4 thousand chemical compounds are formed, of which about 200 are poisonous, 14 are narcotic and 44 are carcinogenic. The gas phase of cigarette smoke contains: nitrogen and its oxides, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide), acetaldehyde, methane, hydrogen cyanide (hydrogen cyanide), nitric acid, acetone, ammonia, methanol, specific nitrosamines (acrolein, benzene and benzopyrene ), nitrobenzene, carboxylic acids, phenols, cresols, naphthols, naphthalene. Among the 76 metals found in cigarette smoke are nickel, cadmium, arsenic, mercury, lead, strontium, cesium and polonium - in the form of radioactive isotopes.
So what are the causes of cigarette allergies? Studies of skin tests with an experimental tobacco allergen have shown that antigens from both tobacco itself and cigarette smoke are capable of stimulating the body’s immune response (that is, activating T-lymphocytes). They can also increase irritation in those who are generally prone to allergies.
ilive.com.ua
Electronic cigarette for allergy sufferers
Switching an allergic person from regular cigarettes to an electronic equivalent will most likely not solve the problem, and in some cases will even worsen it.
Electronic cigars contain substances that are dangerous to patients, such as:
- propylene glycol;
- nicotine (some brands);
- glycerol;
- lead;
- bismuth;
- arsenic;
- cadmium;
- benzene;
- anabasine;
- hydrogen cyanide;
- nitrogen dioxide;
- formaldehyde;
- ammonia;
- flavorings, etc.
Although an allergy to electronic cigarettes is rare, it can make itself felt at any time, especially in a person prone to such reactions.
Symptoms of the disease:
- nausea;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- hoarseness of voice;
- dyspnea;
- rhinitis;
- cough;
- conjunctivitis;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- sneezing, etc.
In particularly severe cases, skin rashes may appear, as well as Quincke's edema and even anaphylaxis.