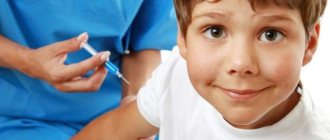
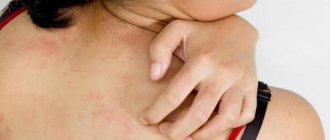
How to diagnose an allergy to ultracaine? Main symptoms
Each of us dreams of a beautiful and even smile, so it is important to constantly monitor the health of your teeth and undergo the necessary dental examination from time to time.
At the moment, dental treatment is completely painless and is carried out under local anesthesia. Most often, the honey product Ultracain is used for these purposes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
Ultracaine injection may cause allergies
In order to identify the allergen, you need to undergo an ELISA test. Nowadays, modern equipment and effective techniques make it possible to identify possible allergies with the highest accuracy after a routine blood test.
The main symptoms of an allergy to ultracaine:
- allergic rhinitis
- swelling of the mucous membranes
- anaphylactic shock
- itchy skin
- hives
- inflammation of the area where the drug was injected
It is important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms and get tested for allergies (determine the level of specific IgE antibodies).
Ultracaine is a modern remedy for local anesthesia.
It is widely used in dentistry due to its rapid anesthetic effect, with the introduction of a small amount, and the duration of the action. The product is well accepted by tissues, but has certain side effects and contraindications.
- Why is it used?
- Instructions
- Prices
- FAQ
- Reviews of ultracaine in dentistry
Allergen c68 – articaine/ultracaine, IgE
[21-604] Allergen c68 – articaine/ultracaine, IgE
950 rub.
Articaine (ultracaine) is a local anesthetic of the amide type of a series of thiophenes.
Allergy to this drug is rare and can manifest itself in the form of skin rash, itching around the injection site, rhinitis, and in severe cases, angioedema and anaphylactic shock.
Determination of specific immunoglobulin E for a given allergen in increased quantities indicates the presence of sensitization of the body to it.
A drug allergy is a specific reaction of the immune system to drugs.
Drug allergies can occur as a complication during the treatment of the underlying disease or as a result of prolonged contact with medications (by doctors, healthcare workers, pharmacists).
The main reasons for the development of allergies to drugs are hereditary factors, the presence of other types of allergies, long-term use of drugs, simultaneous use of a large number of different drugs, overdose (in this case we are talking about a pseudo-allergic reaction).
An allergic reaction can be provoked by any medications, but the most common allergens are antibiotics, local anesthetics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. This type of allergy is characterized by the following symptoms: redness of the skin, itching, various types of skin rashes, year-round conjunctivitis.
Allergic reactions to medications develop from a few seconds to several hours and can cause an attack of bronchial asthma, urticaria, Quincke's edema, allergic rhinitis or anaphylactic shock. If you have an allergy to a certain medicine, it should be taken into account that it can also occur when using medicines with a similar composition.
The study is carried out only for type 1 allergic reactions. A negative test result cannot guarantee that you will not have another type of allergic reaction.
Synonyms Russian
Specific immunoglobulins of class E to articaine (ultracaine).
English synonyms
Allergen c68 – Articaine/Ultracaine; IgE.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Units
IU/ml (international unit per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Articaine is the international name for an amide-type local anesthetic, widely distributed under the following trade names: Ultracaine, Ultracaine D-S, Ultracaine D-S forte, Alfacain, Ubistezin, Primacaine.
The drug is used for infiltration and conduction anesthesia, most often in dental practice.
The anesthetic enters the nerve fiber cells, where it blocks the entry of sodium ions, thereby temporarily stopping the conduction of the nerve impulse.
Articaine is a local anesthetic with a fairly strong anesthetic effect; the effect occurs almost immediately after administration and lasts up to several hours.
One of the side effects of using articaine is the development of an allergic reaction in sensitized individuals, which occurs quite rarely, but can lead to serious consequences. The reaction develops as an immediate type of hypersensitivity - within a few minutes or hours.
As a rule, a mild form of allergy occurs with the appearance of hyperemia or urticaria, itching at the injection site, and allergic dermatitis. In more severe cases, allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis, and bronchial asthma develop.
The most severe manifestations are angioedema (Quincke's edema) and anaphylactic shock, involving the vital cardiovascular and respiratory systems in the process, which requires urgent medical intervention.
What is the research used for?
- Diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to articaine/ultracaine;
- differential diagnosis of the causes of allergic reactions in children and adults during the use of local anesthetics.
When is the study scheduled?
- When planning local anesthesia with articaine/ultracaine in patients with suspected allergies to local anesthetics;
- when examining children and adults with urticaria, itching, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, angioedema, anaphylactic shock after the use of local anesthetics.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0.00 – 0.35 IU/ml.
Reasons for the positive result:
- immediate hypersensitivity to articaine/ultracaine.
Reasons for negative results:
- lack of IgE sensitization to this allergen;
- long-term restriction or exclusion of contact with the allergen.
- successful implementation of ASIT.
Important Notes
- The absence of sensitization to an allergen does not exclude the presence of allergies to other sources of allergens. In some cases, further allergy testing may be required to clarify sensitization to other possible allergens.
- Performing this study is safe for the patient compared to skin tests (in vivo), since it eliminates the patient’s contact with the allergen. Taking antihistamines and age characteristics do not affect the quality and accuracy of the study.
Also recommended
Who orders the study?
Allergist-immunologist, pediatrician, therapist, surgeon, dentist, general practitioner.
Literature
- Harboe T, Guttormsen AB, Aarebrot S, Dybendal T, Irgens A, Florvaag E. Suspected allergy to local anaesthetics: follow-up in 135 cases. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. May 2010; 54(5):536-42.
- Ren LJ, Song XY, Sun JS, Sun XQ. Analysis of adverse reaction induced by articaine hydrochloride and epinephrine tartrate injection in 75 cases. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 9; 53(2):107-110.
- De Pasquale TMA, Buonomo A, Pucci S. Delayed-type allergy to articaine with cross-reactivity to other local anesthetics from the amide group. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Jan – Feb; 6(1):305-306.
- Speer W.B. Local anesthetics. J Am Dent Assoc. 2013 Jan; 144(1):17.
Source: https://helix.ru/kb/item/21-604
Allergic reactions possible with local anesthesia
In order to prevent the occurrence of allergies to the product, you must first undergo a special examination and ELISA test.
With the help of modern equipment and special techniques, it is possible to identify hazards in advance and prevent various allergic reactions.
In rare cases, anaphylactic shock may occur; in this case, it is virtually impossible to help the patient without experts.
It is important to note the fact that during the initial use of Ultracain there cannot be an allergy to it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:tv.youtube.com
Reactions may occur with the following applications.
Ultracaine - what is it?
Ultracaine is a drug for local anesthesia, used primarily in dentistry. It has a superficial and antispasmodic effect. It is used when simple tooth extraction is necessary, when restoring crowns and cleaning the oral cavity. Sometimes the drug is used in obstetrics and traumatology.
Like any drug, Ultracaine has contraindications and side effects, so its independent use is unacceptable. The dosage is prescribed by a specialist based on the needs and general condition of the human body. The following side effects are worth highlighting:
- Muscle tremors;
- vomiting and nausea;
- breathing problems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- allergic reactions.
Allergy to Ultracaine is rare, but before using the drug you should definitely determine whether there is intolerance. Remember that Ultracaine is a rather serious drug and an allergy to it can be life-threatening.
Treatment of allergies to ultracaine
When symptoms occur, it is extremely important to establish the cause of their occurrence, since not always the symptoms may specifically indicate an allergic reaction. In case of an overdose or a toxic reaction, the symptoms may be the same.
If a specific allergy to Ultracaine is diagnosed, then popular antihistamines are used for treatment - Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil. They can be prescribed for minor manifestations of allergies. After getting rid of symptoms, the patient is recommended to undergo a full examination, and other anesthetic medications are most often prescribed.
If particularly strong reactions are observed, then the use of Ultracaine during treatment should be completely excluded, and the patient is prescribed other drugs for anesthesia.
Date of publication: 12/17/2016 The main food product is milk.
This product is especially important for children and young […]
Date of publication: 08/04/2016 Seasonal allergies are now becoming more common. Its symptoms reduce a person’s quality of life, so [...]
Causes of appearance Usefulness of vitamin C Symptoms of pathology Diagnostics Healing Ascorbic acid or vitamin C is […]
Reactions of intolerance to local anesthetics, including ultracaine, can be explained not only by allergies, but also by a toxic reaction or overdose of the product.
Having identified the main cause, making sure that it is an allergy, you can build a plan for further action.
To treat allergies to ultracaine, traditional antihistamines are used, for example, Suprastin or Tavegil. After getting rid of the main allergy symptoms, you need to contact a specialist to select an alternative anesthetic medicine. In case of severe allergic reactions, of course, the future use of the product must be excluded.
It is also worth noting that if ultracaine has not been used previously, then an allergic reaction to it cannot occur. When taking the product for the first time, an allergy does not occur because the body is not yet “familiar” with these products, and therefore the immune system cannot give any “response”.
Allergies to anesthetics are treated according to the same usual regimens as other allergic reactions.
But since in most cases a similar pathology develops rapidly, the first aid in severe cases is provided by a dentist.
If changes appear on the skin and swelling, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin or Pipolfen should be administered intramuscularly.
If symptoms indicate the development of anaphylactic shock, 1 ml of Adrenaline should be urgently administered and, if necessary, connected to a ventilator.
In the future they act according to the situation.
If blood pressure drops, then it is necessary to put Prednisolone; if cardiac activity worsens, Cordiamine is used.
Usually these measures are enough to interrupt the allergic reaction and restore the functioning of all body systems. But if the symptoms do not stop, then the patient urgently needs to be hospitalized in a hospital - in the intensive care ward.
Fortunately, painful reactions to anesthetics occur very rarely, and their occurrence can be prevented by collecting an anamnesis and paying attention to the choice of dose and the drug itself for pain relief.
If rashes and skin itching on the body, as well as swelling on the face, persist even after visiting the dentist, you should take antihistamines for some time.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafety
This can be Claritin, Cetrin, Zyrtec, they are drunk for 5-7 days.
Enterosorbents - activated carbon, Polysorb - help speed up the removal of toxins from the body.
What to do if you have allergies
People from the so-called “risk group” need to treat visiting the dentist with more attention than anyone else. Be sure to note all symptoms of illness, if any, after visiting a doctor using painkillers. If necessary, do not hesitate and seek emergency medical help.
If you suspect this type of allergy, first of all you need to:
- Consult with an allergist-immunologist, who will determine your further actions based on the clinical picture.
- Undergo an allergy examination - take a blood test from a vein in a special laboratory, where it will determine the presence or absence of an allergic reaction to this medication.
- If the analysis is confirmed, then the use of this drug should be abandoned and when visiting a dentist, preference should be given to clinics with a high level of medical equipment, where it is possible to provide first aid to the patient.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about your allergy to ultracaine to replace anesthesia drugs.
- If it is not possible to visit a dental office with a high level of service, tooth extraction, etc. must be carried out in a hospital where there is the possibility of resuscitation measures.
- From a preventative point of view, check up with a dentist once every six months. In this case, dental treatment will be carried out in the early stages of caries development and without the need for anesthesia.
To summarize, I would like to add that if drug intolerance, which this allergy refers to, is still confirmed, do not despair and lose heart. If you follow certain measures and rules, you can achieve a fairly high quality of life and not experience discomfort when visiting the dental office.
- Cheap ointment for skin allergies
- What to give your dog if he has allergies
- Allergy to Nutrilon comfort - what to replace - Allergy and everything about it
- Homeopathy allergy drugs
Why is it used? ↑
Immunologists are sounding the ALARM! According to official data, a seemingly harmless allergy claims MILLIONS of lives every year. The reason for such terrible statistics is PARASITES swarming inside the body! People who are suffering are primarily at risk.
Ultracaine is one of the most effective anesthetics in dentistry, with a powerful effect and a minimum of side effects.
It is used for infiltration anesthesia during dental procedures that cause significant pain. The products are used to remove the dental nerve, during orthopedic manipulations and surgical interventions.
The pharmacodynamic effect of the product is 2 times greater than lidocaine and 6 times greater than novocaine. The toxic effect of ultracaine is 2 times lower than the toxicity of lidocaine.
The most important advantages are the highest ability to penetrate connective and bone tissue without disrupting the functioning of the heart, which makes it the first choice product for patients with cardiovascular pathologies.
Painkillers Sanofi aventis Ultracaine – review
I had no history of allergies in general, or to medications in particular.
4 days ago I went to a well-known, respected clinic for dental treatment, where I filled out the necessary forms about my health and allergies. When the doctor started injecting Ultracaine, I received a left hook in the nose and maxillary sinus area. In general, I’m quite patient, but then I closed my eyes. When the pain went away after a few seconds, I felt an instant numbness in half of my nose and the front of my face (no complaints about this – it froze wonderfully!).
I didn’t like the feeling of being suddenly frozen, and besides, I began to lose reality. The doctor took a number of measures to bring me to my senses. I didn’t smell the ammonia right away, but I more or less came to my senses.
After that, the doctor started drilling, and I felt a severe toothache - the area near the ear and lower jaw remained sensitive, they treated the lower 7 (apparently, they didn’t hit the nerve very well). I had to add an anesthetic, but a different one. As a result, the tooth “fell asleep” and was cured.
An hour after the first injection, the frost began to subside, and I began to feel a tickling sensation in my nose (on the left, at one point).
Later the tickling got worse and I ended up sneezing constantly for 3 days! Unfortunately, with my chronic sinusitis, any sneezing, especially a long one, threatens to turn into acute sinusitis, which is probably what happened.
Within 4 days from the start of treatment, I had aches in the bones of the skull on the left side of my head, dizziness, pain when touched in the area of the left maxillary sinus, and, of course, a runny nose. On the fifth day I feel better. I can attribute these symptoms to an exacerbation of sinusitis, or a reaction to Ultracaine, or both.
Next time I will give up Ultracaine. Definitely! I hope that someone will read the reviews and draw conclusions, but I did not prepare in advance for taking this product, so I gained my own invaluable experience.
Advantages
Flaws
- Possible allergies
- There are side effects
panthagruheldoes not recommend Read all 21 reviews
Other reviews
Read all reviews 21
see also
- Painkillers Actavis Spazmalgon It’s so good that there is spasmalgon, it saves you from terrible pain! That's what I thought until I read the ingredients... be careful! This is good old baralgin!!! contains analgin, banned all over the world!! I want to share my impressions of a miracle analgesic that surprised me! After the birth of my child, I began to experience terrible headaches with cramps. In search of an ideal painkiller after citramon, pentalgin, nurofen, nise, etc., I turned my attention to Spazmalgon.
- Painkillers Tamipul / Tamipul A real treasure: a magic pill that will relieve pain in a matter of minutes or how to find an alternative to an expensive drug? Good afternoon I would like to write not just a review, but an indignant response, because... If it weren’t for the situation that happened to me today, this review might not have happened.
- Painkillers Sopharma Tempalgin Tempalgin review after several years of use. My opinion about it has radically changed, the side effects forced me to completely stop taking it and look for a replacement. Good afternoon to EVERYONE. I try to do without unnecessary medications, but I can’t stand the headache. I often have a headache; neither sleep nor other methods help me cope with it. The pain continues to increase until I take a painkiller.
- Painkillers Ranbaxy KETANOV That case when there is more harm than good. My experience of using Ketanov, SIDE effects. A useful LIFEHACK for those who often take painkillers. ANALOGUES I want to share my negative experience of using Ketanov tablets. This drug is familiar to many as an effective and potent pain reliever. For some time I abused it, but not because of a good life.
- Painkillers Pharmstandard ARTROZAN One end heals, but the other cripples! A very effective remedy, with unpleasant side effects! I already wrote about the joint problems that overtook me this summer in this review. And then I was prescribed Artrosan, Alflutop and Diclofenac. Now half a year has passed and the course of treatment needs to be repeated, so having extensive experience with the stim drug, I can write a high-quality review.
- Painkillers Zentiva Tramadol Helps with severe pain. Drug. Tramadol is an analgesic that belongs to the group of opioid drugs. It is a drug, so tramadol cannot be purchased without a prescription. I was injected with it in the hospital when NSAIDs did not help, for pain caused by a herniated disc.
- Antibacterial agent Sanofi aventis Sofradex 420 rub. for 5 ml. is it worth it? CRY OF THE SOUL for public and private doctors! When everything has already been tried for otitis media and ALL HOPES are only on SOFRADEX! I was already familiar with the treatment of childhood otitis - we always fought it comprehensively and after a couple of days there were no more symptoms. That is, when my youngest (2 years old) first fell ill with otitis media, I already knew roughly what and how to do.
- Sanofi aventis vasodilating agent Trental Trental ® 400 - with it I stopped crying for the first time in 1.5 years. One of the helpers in the fight against hair loss. This review is a pain, my review is a revelation. To be honest, I’m afraid to write so as not to jinx it, and it’s scary to scare people with disgusting photographs. But suddenly someone has a similar problem, or was prescribed this drug, but there are doubts “to take it or not to take it”...
Source: https://irecommend.ru/content/allergicheskaya-reaktsiya-3
Instructions ↑
Compound
Ultracaine (Articaine) belongs to the amide group products.
- Articaine hydrochloride - 40 mg;
- Epinephrine hydrochloride - 6 mcg.
(In the Ultracain DS forte solution, the amount of adrenaline is 12 mcg); - Sodium bisulfite - 0.5 mg;
- Sodium chloride - 1.0 mg;
- Water for injections - 1.7 ml.
The solution is transparent, does not contain foreign impurities and odor.
The high quality of glass and rubber parts of the capsule, the highest degree of purity of the product allow you to get rid of parabens and preservatives, which are most often the culprits of allergic reactions.
The ultracaine solution also lacks ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid - EDTA, which is included in some pharmaceutical preparations to bind heavy metal ions, when the quality of the glass is low and when the solution is not cleaned sufficiently.
Release forms
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
The drug is available in 2 forms.
In ampoules of 2 ml (100 ampoules per package) and in capsules (cartridges, carpules) of 1.7 ml - 100 ampoules per package.
The capsule is graduated in 0.3 ml increments, which is extremely convenient for the doctor when calculating the size of the administered drug.
Ultracaine is a local anesthetic. Used for conduction and infiltration anesthesia. It is a combined product of a local anesthetic and a vasoconstrictor component.
The drug has the highest degree of anesthesia, which allows you to obtain a suitable degree of anesthesia with the least amount of solution injected. The action consists of assisting with nerve sensors and blocking the conduction of impulses in nerve fibers.
The drug begins to act from the first minute after administration. The duration of the anesthetic effect lasts from 45 minutes to 4–5 hours. It is not contraindicated for pregnant women or during breastfeeding. It breaks down mostly in the kidneys and is excreted in the urine.
Indications
Ultracaine DS (adrenaline 1:200000) is used for conduction and infiltration anesthesia for:
- multiple or single tooth extraction;
- preparing the tooth for a crown;
- preparing the dental cavity for healing procedures;
- dental fillings and other routine dental interventions, including patients with severe concomitant pathologies.
DS forte (adrenaline 1:100000) is used for the most complex and painful interventions, including:
- operations on bones and mucous membranes;
- operations on the dental pulp (amputation, extirpation);
- removal of a broken tooth and teeth affected by apical periodontitis;
- resection of the apex of the tooth root;
- percutaneous osteosynthesis;
- cyst escision;
- pain relief for inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial area (ostemyelitis, periostitis).
Dosage
The dose of the product is set individually depending on the severity and duration of the intervention.
When removing teeth of the upper jaw, taking into account the absence of inflammation, infiltration anesthesia with ultracaine is performed in a dose of 1.7 ml for each tooth.
In some cases, the dose of the product must be increased to achieve complete pain relief. When removing a pair of teeth that are located nearby, one injection is traditionally enough.
When removing premolars of the lower jaw, an injection of 1.7 ml is also sufficient. In this case, there is no need to perform mandibular anesthesia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:www.googleadservices.compageadaclk
If a suitable analgesic effect is not achieved, repeated administration of 1-1.7 ml of solution is recommended. If pain relief is ineffective, a blockade of the lower jaw is indicated.
When preparing a cavity or preparing teeth for a crown, ultracaine solution is used as infiltration anesthesia in a dose of 0.5–1.7 ml for each tooth.
If during a dental procedure there is a need to cut and suturing the palate, 0.1 ml of solution is sufficient for a palatal depot injection.
When performing one dental procedure, the highest dose of articacaine for an adult is 7 mg/kg body weight.
A dose of the product up to 500 mg (12.5 ml of injection solution) is normally tolerated.
For children over 4 years of age, the dose of the product is selected individually depending on the patient’s weight and the severity of the manipulation, while the highest dose should not exceed 5 mg/kg body weight.
Side effects
Side effects can be divided into 2 types: those caused by epinephrine and the body’s reaction to local administration of ultracaine.
Most often, epinephrine in the product leads to headaches.
From time to time, palpitations, increased blood pressure, and arrhythmias are possible.
Complications from other body systems are rarely possible.
- Central nervous system. Respiratory dysfunction, including respiratory arrest, impaired consciousness, involuntary muscle contraction, up to the appearance of generalized convulsions.
- Organ of vision. Blindness, double vision, blurred vision. These side effects are temporary.
- Digestive system. Nausea, vomiting.
- The cardiovascular system. Fall in blood pressure, acute cardiovascular failure, tachycardia, bradycardia, shock.
Allergic reactions to the product are possible, which appear in the form of:
- skin itching;
- hives;
- erythema;
- swelling of the glottis, nasal mucosa, lips;
- conjunctivitis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyright
In severe cases, asphyxia and anaphylactic shock may occur.
In patients with bronchial asthma, signs of increased sensitivity are possible, which appear in the form of impaired consciousness, wheezing, vomiting, diarrhea, and an attack of bronchial asthma.
This is due to the presence of sodium bisulfite in the product.
Local reactions are observed if the technique for administering the product is not followed, or if the solution enters the vascular network. They appear as ischemic disorders, including tissue necrosis and paresis of the facial nerve.
Allergy to local anesthetics: myth or reality?
Quite often, patients with any manifestations of adverse reactions to the administration of local anesthetics are recommended by dentists or other doctors to exclude the use of all “cains”, as a result of which they prefer to prescribe a potentially more dangerous general anesthesia in the future.
Classification of anesthetics
Local anesthetic substances, depending on their chemical structure, are divided into two groups (Table 1): derivatives of benzoic acid esters (Ester-type) and others (Amide-type).
Table 1
Drugs used for local anesthesia
| Groups of local anesthetics | |
| Group I: Ester-type | Group II: Amide type |
| Procaine (procaine hydrochloride) Tetracaine (dicaine) Benzocaine (anesthesin) Butethamine Chloroprocaine Cyclomethicaine Proximetacaine Bencaine Oxetacaine | Lidocaine (xycaine, xylocaine, lignocaine) Trimecaine (mesocaine) Prilocaine (cytanest) Mepivacaine (carbocaine, scandonest, mepicatone) Bupivacaine (marcaine) Levobupivacaine Ropivacaine (naropine) Etidocaine (duranest) Articaine (ultracaine) Pyromecaine (bumecaine) Cinchocaine ( sovcaine) Dyclonine Pramocaine Ubistezin and others. |
In fact, most adverse reactions to local anesthetics are not associated with true allergic reactions, but with vegetative-vascular disorders, toxic and hysterical reactions, as well as side effects of additives included in some anesthetics.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5iqQgI8KGuc
The true incidence of allergic reactions to local anesthetics is unknown. They are described by some authors as rare events, and their incidence is less than 1% of all adverse reactions with local anesthetics.
Classification of complications associated with taking local anesthetics:
1) Toxic effects - convulsions, hypotension, respiratory arrest and circulatory collapse, drowsiness, muscle fasciculations, ventricular arrhythmias, fibrillations, etc. Toxic reactions are the most common.
Systemic toxic effects result from absorption or intravenous injection of local anesthetic into the systemic circulation. The cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity of local anesthetics are directly related to the plasma concentrations of these drugs.
The toxic threshold concentration may be exceeded as a result of accidental intravascular injection, overdose, or as a result of prolonged infusion of the drug.
2) Pseudoallergic reactions (PAR). They are more common in women from 40 to 80 years of age, especially with concomitant chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary system, kidneys and neuroendocrine system.
The clinical symptoms of PAR are varied and correspond to the clinic of true allergic reactions, although the mechanisms of development differ from the latter.
The most severe are: anaphylactoid shock , skin manifestations (toxicoderma, rashes, dermatitis), vegetative-vascular reactions.
3) Effect on the central nervous system (exciting or calming): nervousness, fear, euphoria, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, blurred vision or double vision, increased or decreased temperature, stupor, twitching, tremors, convulsions, loss of consciousness, depression and respiratory arrest. Manifestations of excitement may be short-lived or not occur at all, while the first manifestation of intoxication may be drowsiness, turning into unconsciousness, and respiratory arrest.
4) Effect on the cardiovascular system (usually depressant): bradycardia (decrease in heart rate), hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, which can lead to cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of depressed cardiovascular function may usually occur due to a vasovagal reaction, especially if the patient is in an upright position.
Less commonly, they may result from a direct effect of the drug.
5) Local reactions - swelling and inflammation at the injection site, the appearance of ischemic zones at the injection site (up to the development of tissue necrosis - in case of accidental intravascular injection); nerve damage (up to the development of paralysis) - occurs only when the injection technique is violated.
6) Side effects due to altered sensitivity to local anesthetics.
7) Idiosyncrasy (reduced sensitivity).
 True allergy - hyperemia and itching of the skin, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, Quincke's edema of varying severity (including swelling of the upper and/or lower lip and/or cheeks, cleft with difficulty swallowing, urticaria, difficulty breathing), anaphylactic shock .
True allergy - hyperemia and itching of the skin, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, Quincke's edema of varying severity (including swelling of the upper and/or lower lip and/or cheeks, cleft with difficulty swallowing, urticaria, difficulty breathing), anaphylactic shock .
Cross allergic reactions between anesthetics:
• Among group I local anesthetics, intragroup cross-allergic reactions are often observed. In this case, drugs from the second group are prescribed. Exceptions: lidocaine - novocaine; lidocaine - benzocaine.• Between drugs of group II with a similar structure (lidocaine, prilocaine and mepivacaine), they are also possible.
• Until recently, it was believed that in case of intolerance to group I , group II drugs could be used due to the absence of intergroup cross-reactions.
However, there are reports of the possibility of developing allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, to lidocaine (xicaine) with intolerance to novocaine, as well as to benzocaine (anesthesin) with intolerance to lidocaine.
It should be borne in mind that many side effects of local anesthetics, for example, swelling at the injection site, arterial hypotension, tachycardia, collapse, occur in both allergic and non-allergic reactions to these drugs. Allergic reactions when using local anesthetics often develop to the additives (bisulfite and parabenzoic acid, etc.) included in their composition.
Additives to anesthetics:
1) Vasoconstrictors - added to increase the effectiveness of local anesthesia, as well as to slow down the entry of anesthetics into the bloodstream.
Adrenaline is used most often.
A relatively safe dilution of adrenaline is a concentration of 1:200,000, which can only be achieved in capsule preparations.
Norepinephrine It is used less frequently as a vasoconstrictor. Norepinephrine, unlike adrenaline, is less dangerous in patients with cardiac pathology (coronary heart disease), but there is a higher risk of developing a hypertensive crisis with concomitant hypertension.
Used instead of adrenaline for thyrotoxicosis and diabetes. Contraindicated in glaucoma
Filipressin (octapressin) A synthetic drug that does not have a direct effect on the heart. The effect is associated with its direct effect on the smooth muscles of blood vessels.
Contraindicated during pregnancy, because may cause myometrial contractions.
Undesirable systemic effects of vasoconstrictors: • rise in blood pressure, • tachycardia, • heart rhythm disturbances, • angina attacks, • centralization of blood circulation,
• headache.
Risk group when using vasoconstrictors : patients with glaucoma, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus; patients taking drugs rauwolfine, thyroid hormones, tricyclic antidepressants, antidepressants - MAO inhibitors.
2) Preservatives
Parabens (methylparaben - methyl 4-hydroxybenzonate, ethylparaben) Parahydroxybenzoic acid esters (parabens), which have antibacterial and antifungal effects, are used as preservatives.
It must be remembered that parabens are included in various cosmetics, creams, toothpastes and can provoke contact dermatitis, so there is a real danger of an allergy to the local anesthetic drug.
Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is a metabolite of novocaine, has a similar structure to parabens, which can cause cross-allergic reactions. Many drugs (sulfonamides, oral antidiabetics, furosemide, etc.) are derivatives of PABA.
Therefore, it is not advisable to use drugs containing parabens if you have a drug allergy to the listed medications. The presence or absence of parabens in the local anesthetic drug is indicated by the manufacturer.
Parabens can cause sensitization of the body and anaphylactic shock.
3) Stabilizers Sulfites (sodium or potassium disulfite) are used as vasoconstrictor stabilizers.
Allergy to sulfites is most common in patients with bronchial asthma (frequency - about 5%), so you should be especially careful when treating such patients.
Sulfites cause edema, urticaria, bronchospasm through irritant receptors, nervous and vagal reflexes.
The composition of some modern local anesthetics:
• lidocaine (xylocaine) in carpules – contains lidocaine, methylparaben, sodium chloride; • xylostesin F-forte in carpules – contains lidocaine, norepinephrine hydrochloride, anhydrous carbonic sulfite, carbonic chloride; • xylocaine MPF – sterile pyrogen-free solution without methylparaben (in carpules); • xylocaine in vials – contains methylparaben; • xylocaine MPF with epinephrine – sterile pyrogen-free solution contains xylocaine, epinephrine, sodium metabisulfite, citric acid; • mepivacaine (mepidont, mevirin, mepivastezin, scan-dicaine, scandonest) – without the addition of vasoconstrictors, sulfites, parabens; • ultracaine in carpules – contains articaine, adrenaline (0.006), sodium disulfite, methylparaben; • ultracaine Dc forte – contains articaine, adrenaline (0.012) and sodium disulfite; • septanest – contains sulfites, EDTA, does not include parabens; • ubistezin , ubistezin forte (based on articaine, do not contain parabens, but contain sulfites as a preservative).
Diagnosis (G. Lawlor Jr. et al., 2000):
1. If you suspect an allergy to local anesthetics, try not to use them. However, it is often impossible to avoid these drugs, since their replacement with general anesthetics increases the risk of complications.
In addition, some of the local anesthetics (lidocaine, procainamide) are prescribed for arrhythmias, and they cannot always be replaced with other drugs.
In all cases, it is necessary to compare the risk of complications that can result from using the drug with the negative consequences of abandoning it.
2. If previous reactions (both allergic and non-allergic) were severe, it is necessary to completely abandon local anesthetics.
3. Based on anamnesis, it is difficult to assess the risk of allergic reactions, therefore, if in the past the use of local anesthetics was accompanied by reactions, skin and provocative tests are performed.
4. The patient should be explained for what purpose skin and provocative tests are carried out, warned about possible complications and obtained written consent from him for the study.
5. Although the reliability of skin testing with local anesthetics has not been fully established, it is recommended to start with the selection of a safe local anesthetic agent.
6. The local anesthetic used for skin and provocative tests should not cause cross-reactions with the drug that previously caused the allergy. If the drug that caused the allergic reaction is unknown, a local anesthetic from group II is selected for testing.
7. To avoid false negative results, preparations used for skin testing should not contain vasoconstrictors.
For provocative tests and treatment, it is better to use drugs that contain vasoconstrictors, since they enhance pain relief and limit the systemic effect of local anesthetics, and allergic reactions to these drugs or to sulfites added to them for stabilization rarely occur.
8. Local anesthetic preparations used for skin and provocative tests should not contain parahydroxybenzoic acid esters (preservatives), since it often causes allergic reactions.
9. In case of negative puncture and intradermal tests, a provocative test is performed with a local anesthetic. Provocative tests are carried out under the supervision of an allergist with experience in treating severe allergic reactions.
10. If a provocative test with a local anesthetic is negative, the risk of side effects of the drug is minimal.
References:
1. Zaikov, S.V. The problem of drug allergies in anesthesiology / S.V. Zaikov, E.N. Dmitrieva // Rational pharmacotherapy. – 2009. – No. 3.
2. Lawlor Jr., G. Clinical immunology and allergology / G. Lawlor Jr., T. Fisher, D. Adelman: trans. from English, M., “Practice”, 2000 – 850 p.
3. Murzich, A.V. Drug allergy / A.V. Murzich, M.A. Golubev, A.D. Kruchinin // South Russian Medical Journal. – 1999. – No. 2-3.
4. Fesenko, V.S. Intoxication with local anesthetics: old danger, modern myths, new drugs and the “silver bullet” / V.S. Fesenko // Clinical issues. – 2008. – 4(17).
5. Allergy to local anaesthetics in dentistry. Myth or reality? / Por JCBaluga a et al. // Allergologia et Immunopathologia. – 2001. – Vol.30.
6. Eggleston, ST Understanding allergic reactions to local anesthetics / ST Eggleston, LW Lush // Ann. Pharmacother. – 1996. – V.30, No. 7-8. – R.851-857.
7. Main principles of pathogenesis, diagnostics and prevention of drug allergy caused by local anesthetics / BV Machavariani et al. // Georgian Med. News – 2009. – V.168. – R.67-72.
8. Por D El-Qutob Allergic reaction caused by articaine / Por D El-Qutob a et al. // Immunopathology. – 2002. – Vol.33.
9. Speca SJ Allergic reactions to local anesthetic formulations / SJ Speca, SG Boynes, MA Cuddy // Dent. Clin. North. Am. – 2010. – V.54, No. 4. – R.655-664.
Source: https://krsk.sibnovosti.ru/health/124998-allergiya-k-mestnym-anestetikam-mif-ili-realnost