Among scientists, doctors and nutritionists, the question is often discussed: how real is the harm of milk for the body of an adult. On the one hand, the drink is rich in vitamins, micro- and macroelements necessary for the body. On the other hand, there are ardent opponents of its use, whose arguments deserve attention. To determine whether drinking milk is beneficial for adult men and women, or whether it is worth avoiding it completely, it is necessary to consider factors confirming the value and danger of the product.
Is milk good for an adult?
For children and teenagers, milk is one of the staple foods. It is fully digestible and contains all the necessary substances for full development. Active components have a beneficial effect on the body even in adulthood:
- calcium strengthens bones and teeth;
- immunoglobulins help cope with infections and colds;
- amino acids support the nervous system, normalize sleep;
- Proteins are essential for increasing muscle mass.
However, the effect of cow's milk on the adult body is not so clear.
Is drinking milk healthy for adult men?
The microelements, vitamins, beta-carotene, folic acid, calcium, zinc and sodium contained in the product improve erectile function in men. The drink must be fresh. The goods reach stores after heat treatment, which destroys the beneficial enzymes that are present in fresh milk.
In the course of research, scientists have found that the chance of developing testicular and prostate cancer with systematic consumption of dairy products increases. The disease is a consequence of one of two factors:
- Changes in insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), a hormone involved in the regulation of the division of normal and abnormal cells under the influence of casein protein. This leads to a number of reactions that negatively affect health, including prostate and testicular health.
- Adding estrogen to animal feed. This allows you to maintain high milk yields for a long time after the cow calving. Once in the male body, female steroid hormones will provoke increased production of testosterone, which negatively affects the health of men.
The raw product contains estrogens and progesterone, even without their introduction into the animal’s body from the outside. This is caused by calving. After childbirth, hormone levels gradually decrease.
Abuse of dairy products containing estrogen increases the risk of developing gynecomastia in men over 30 years of age - benign enlargement of the mammary glands with hypertrophy of glandular and fatty tissue. The abundance of hormones in the product promotes early puberty. At an older age, a man’s stomach does not digest fatty milk well, which can lead to diarrhea.
Can adult women drink milk?
There are several reasons why women should not drink milk.
With frequent consumption of the drink, there is a risk of developing cancer of the ovaries, uterus, and mammary glands. The reasons are identical to the development of malignant processes in men - the content of hormones and casein.
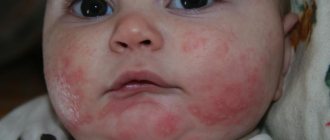
A number of studies show that milk is harmful to the skin and contributes to the appearance of eczema, rashes, and dullness.
The high calorie content of cow's milk leads to the appearance of extra pounds and fat deposits.
In the absence of contraindications, dairy products are beneficial for pregnant women. They normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, strengthen the immune system of the expectant mother, participate in the formation of muscle tissue, the nervous and skeletal systems, and maintain a sufficient amount of oxygen for the child.
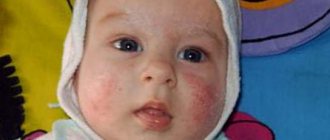
It is not recommended to consume cow's milk while breastfeeding, and it should not be given to infants. The presence of mucus in the product leads to its accumulation in the respiratory tract, which is manifested by bronchitis, tonsillitis, allergies in children and pneumonia in adults.
Specifics of the disease
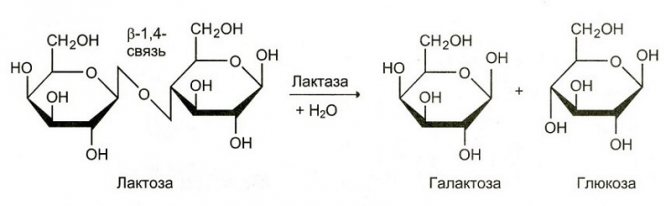
The fact is that an enzyme such as lactase is responsible for the absorption of lactose. It takes part in the hydrolysis of the disaccharide of this carbohydrate, therefore it constantly affects the digestion of milk and dairy products.

Lactose, previously insufficiently broken down in the body, reaches the large intestine and begins to cause unpleasant pain. It is noteworthy that some people suffering from this type of disease are not able to process dairy products at all, so they do not even touch them. Other patients can gradually digest lactose products, so they periodically consume milk and any of its varieties in small doses.
Lactose intolerance is more common in adults than in children. It is noteworthy that it affects mainly Americans, Asians and Africans. Europeans in general suffer from this disease very, very rarely.
What are the causes of lactose intolerance?
Milk intolerance
Lactose (milk sugar) intolerance is called hypolactasia. This is associated with a complete or partial cessation of the production of lactase, which is necessary for the breakdown of milk sugar into two simple sugars - glucose and galactose.
Nutritionists believe that lactase production decreases with age. Typically, dairy products included in the standard menu of an adult are perfectly absorbed by the human stomach, and milk intolerance is observed in older people. Hypolactasia is classified into:
- Primary. A sharp decrease in lactase production. Eating dairy products leads to discomfort. Often characteristic of African, Asian peoples, and southern Europeans.
- Secondary. The problem is caused by illness, injury, surgery.
Hypolactasia is a congenital disease.
Milk intolerance in adults, symptoms
Milk intolerance in adults is associated with a lack or complete absence of lactase. In such cases, unbroken milk sugar moves to the large intestine. The condition is characterized by the following manifestations:
- bloating, flatulence as a result of fermentation processes and excessive gas production;
- diarrhea;
- heartburn;
- nausea, vomiting;
- cramping pain.
Symptoms develop 0.5–1 hour after drinking milk.
Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed by eliminating dairy products from your diet for several weeks. If the corresponding signs disappear, then they speak of hypolactasia.
Treatment is a review of the diet. You can eat low-fat yoghurts, cheeses, and drink skim milk.
Diagnosis of the disease
In most cases, lactase deficiency is diagnosed by a doctor based on the symptoms expressed by the patient, which manifest themselves from consuming a certain amount of dairy products. But if there are doubts, the doctor may order a test to confirm the diagnosis. Currently, 7 types of tests are used to detect lactose intolerance.
| Hydrogen test | This analysis is considered one of the most accurate. Before the procedure, the patient must refrain from eating and drinking for several hours. Then, at the appointed time, drink a liquid containing lactose, after which you exhale air into a special device. The presence of hydrogen indicates lactose intolerance. |
| Lactose tolerance | The test is also carried out on an empty stomach. Before donating blood, you must drink lactose-containing liquid. Then, over a period of 2 hours, at intervals of 30 minutes, samples are taken to check the sugar level. The absence of an increase in sugar also indicates enzyme intolerance. |
| Stool acidity analysis | To conduct the study, stool analysis is used. If acid is detected in it, then this means that the body is able to digest lactose. |
| Load test | It is carried out after prolonged abstinence from food and liquid. The patient needs to drink one glass of milk. Then the body's reaction is observed for two hours. If enzyme intolerance is present, the patient will have corresponding symptoms. |
| Intestinal biopsy | It is one of the most accurate types of tests, but due to the peculiarities of its implementation and availability, it is rarely used to detect lactase deficiency. |
| Genetic typing | This type of test is used to detect the presence of a gene related to the production of lactase. |
| Gastrointestinal tract examination | It is carried out using an endoscope, which is inserted through the mouth. |
Most often, if there are problems with the digestibility of dairy products, many simply reduce its consumption to a minimum. Thereby protecting your body from the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms. But such measures are not rational. After all, dairy products contain a huge amount of useful substances that are of particular importance for the body.
Currently used treatment methods allow most people not only to remove the emerging symptoms of enzyme intolerance, but to be cured of this disease by restoring lactase activity.
At the moment, it is impossible to restore lactose production only if there are disturbances in lactase production due to a genetic reason. In this situation, there is definitely a complete exclusion of all types of shelf foods from the diet. But in order to obtain the important elements contained in them, the patient will need to periodically take complex multivitamins.
Can older people drink milk?
Japanese scientists have discovered that milk is dangerous for elderly people due to the content of harmful trans fats. The waste “vaccenic acid” interferes with the normal absorption of calcium. According to research by Swedish scientists, galactose weakens bones and causes a risk of hip fracture.
An excess of calcium and vitamin D negatively affects the mental activity of older people, which is expressed by blockage of blood vessels in the brain, obstructed cerebral circulation, multiple sclerosis and dementia.
Drinking milk after 50 years is not recommended due to the risk of developing atherosclerosis, since milk fat stimulates the formation of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels. Dairy products are replaced with fish, herbs, seafood, legumes, and sesame.

Why are dairy products not digested?
The main active substance in all dairy products, which causes problems with their digestibility, is lactose. And the main enzyme in the body that promotes its absorption is called lactase. From childhood, if there is no congenital intolerance to milk, all children equally normally digest dairy products. But, with age, the production of the lactase enzyme may decrease, so that it becomes insufficient for the absorption of milk, or lactase may cease to be produced by the body altogether.
Diseases associated with milk consumption
Many health problems are associated with milk consumption.
Allergic reactions
A milk allergy is an inappropriate reaction of the immune system to milk proteins. Manifests:
- abdominal pain, cramps, bloating, flatulence, constipation, vomiting, gastritis;
- dermatitis, rashes, urticaria, eczema;
- sneezing, runny nose, shortness of breath, bronchial asthma;
- Quincke's edema.
Severe allergic reactions are dangerous due to sudden changes in blood pressure, suffocation, and anaphylactic shock.
Content of dangerous microorganisms
From infected animals, dangerous microorganisms enter dairy products. The most well-known bacteria include salmonella, listeria, and colibacter. Modern hygienic requirements, including pasteurization and aging, do not exclude complete disinfection of the product.
Another drawback of the waste product of European cows is the presence of A1 beta-casein, an abnormal protein that is harmful to the body. It is involved in the formation of beta-casomorphin-7 (BCM 7), an opioid and oxidant.
BCM 7 (beta-casomorphine) increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, mental pathologies, stroke, Crohn's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Whether dairy products are healthy for an adult is a controversial issue that depends on the individual characteristics of the body. In some cases, you can drink them all your life and remain healthy, in others, the drink is contraindicated even in a small dosage.
After 40, it is recommended to drink milk no more than one glass daily, if you are confident in the quality and freshness of the product.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Lactose intolerance directly depends on a person's age. The older a person becomes, the less lactase enzyme is secreted in the digestive tract. This is caused by eating more varied foods that completely replace mother's milk. This pathology is extremely rare in infants.
Scientists have found that people of the Asian race are more prone to lactose intolerance. Most of the population suffers from this disease already at four years of age. But Europeans reach the same indicators already at the age of 25. Only Northern Europeans are almost free from lactose intolerance. A high level of the enzyme that breaks down lactose accompanies them throughout their lives.
The cause of intolerance can be various problems in the digestive system:
- intestinal infections;
- gastritis;
- intolerance to certain proteins (celiac disease);
- inflammatory diseases of the small intestine;
- surgical intervention in the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis and more.
All this injures the intestinal walls and interferes with the normal production of enzymes.
Even viral diseases and influenza have a traumatic effect on the intestinal mucosa, which can also cause pathology.
Allergic reactions can often be caused by a lack of lactase.
The cause, which is lifelong (it cannot be cured and eliminated), is a genetic predisposition. That is, one of the parents passed on to the child a mutated gene that regulates the production of lactase. In such a situation, the body simply does not know how to produce the enzyme. A person has to abstain from using milk and its derivatives for life.
Signs of lactose intolerance include the following symptoms:
- bowel disorders (diarrhea);
- feeling of nausea;
- sometimes gagging;
- unpleasant symptoms in the abdominal area (gurgling, rumbling, swelling);
- excessive gas (colic);
- distinct pain in the abdominal area.
Treatment of illness in adults
Often the treatment itself in adults manifests itself only in a complete and categorical refusal of milk and dairy products. Still, remember that lactose is not only found there. Products containing this carbohydrate are sausages and sausages, spices and fast food sets, baked goods and chocolate, chewing gum and vodka, as well as almost all fast food products.
If you're terrified by the list above, don't worry—there are plenty of dairy-free products out there! A diet for lactose intolerance includes the use of such useful ingredients as:
Vegetables, fruits, berries;
Coffee, tea, juices;
Rice, all grains, pasta and legumes;
Soy, nuts and eggs;
Homemade alcoholic drinks (homemade beer and wine).
However, do not rush to switch completely - listen to your body. Perhaps, depending on how you feel, you will be able to consume dairy products in small doses from time to time. It's also worth considering switching to cheeses, which are sold in some supermarkets.
Alarming symptoms in children
It should be remembered that lactose intolerance manifests itself differently in each individual. However, there are a number of main manifestations of this disease. In total, this is bloating and gas.
How to determine lactose intolerance in a baby? The symptoms can be very obvious and intense.
First of all, observe how your baby feels while breastfeeding. Does he reach for the breast on his own or refuses to eat, knowing that it will hurt?
Does he fall asleep sweetly after feeding or does he spit up milk and cry loudly?
In general, strong, sudden and repeated crying of a newborn often indicates that he is bothered by colic and abdominal pain. This may be due to lactose intolerance.
You should also pay attention to the baby's stool. Does it have a strong sour smell? Are the stools frequent and foamy, with a lot of mucus?
When examining a sick baby, bloating of the tummy is also revealed.
Treatment of the disease in infants
Treatment for lactose intolerance in children and adults may differ in many ways.
If the disease occurs in a newborn, then, first of all, it is necessary to monitor the nutrition of the nursing mother. With the permission of the pediatrician, she should use drugs with lactase - an enzyme for the proper digestion of lactose, which, when entering the child’s body with milk, will help him break down milk sugar.
To improve the structure of the intestinal microflora, you may need to use drugs such as Linex, Bifidumbacterin and others. Folk remedies can also help here, which should be used with extreme caution and discretion.
For example, with bloating and colic, a light decoction of chamomile and weak fennel tea can help, which are recommended to be given to the baby three times a day, one teaspoon or 50-70 ml, respectively.
Moreover, herbal decoctions of coriander, fennel, anise and chamomile will help improve the child’s digestion. This weak tea can be given three or four times a day, ten drops or less.
To eliminate symptoms, you can also use medications such as Smecta, Espumisan, Bobotik and others.
Often, it may be necessary to completely stop breastfeeding and transfer the child to artificial lactose-free feeding. This important step should be taken only after consultation with your doctor.
However, we discussed a set of methods for treating lactose intolerance in children. How to be an adult?