Fish is a product for everyone. Some prefer river fish, others prefer sea fish, while others cannot stand this product at all. And still others are allergic to fish.
If you still like this product, you should know about some specific points. We will talk about the allergenicity of this product.
We will also get acquainted with the dangerous proteins that make up fish:
- parvalbumin;
- aldolase and anolase;
- scombrotoxin.
If you are wondering whether fish causes allergies, this article will definitely be useful to you.
We'll look at what a fish allergy looks like. This will help you quickly recognize the problem and take action. It would also be a good idea to talk about the diagnosis and treatment of allergies if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Can there be an allergy to fish and why does it appear?
- The cause of allergy to fish is a specific protein contained in its muscles - parvalbumin. This substance belongs to the category of strong allergens and is not destroyed during heat or salt processing of fish products. Provided the immune system is functioning normally, parvalbumin does not cause any unpleasant symptoms, but for people prone to food allergies, it can cause a lot of problems.
- Also, the causes of allergies to river and sea fish include an atypical reaction to the products of their vital activity - excrement and special mucus covering the scales. If they are not carefully removed and get into food or onto the skin of your hands unprotected by gloves, an allergy may develop.
- An allergic reaction may occur in response to the chemicals that the fish was treated with during cooking. Recently, more and more manufacturers of smoked products do not use the classical technology of cold or hot smoking. Instead, so-called liquid smoke is used - a chemical substance containing purified condensate particles obtained from the smoke of certain types of wood.
- Manufacturers claim that fish smoked with liquid smoke is safer and less likely to cause allergies than traditionally smoked fish. However, some nutritionists and doctors tend to think differently: liquid smoke can cause severe allergic reactions. In this case, there is no allergy to fish protein, but an atypical reaction to liquid smoke does occur.
- Another reason that can provoke the appearance and development of fish allergy in an adult or a child is the use of dyes, flavor enhancers and preservatives in finished products. This is especially true for salmon: some manufacturers artificially improve the color of their products by adding dyes to them - this can cause an allergy to red fish. Therefore, before purchasing, carefully study the composition of the fish dish.
Allergen f3 – cod, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-639] Allergen f3 – cod, IgE (ImmunoCAP) 970 rub.
Quantitative determination in the blood of specific antibodies, class E immunoglobulins, which appear in the presence of an allergic reaction to cod.
Synonyms Russian
Specific immunoglobulin class E for cod.
English synonyms
ImmunoCAP f3 (Allergen, Food, Codfish); Specific immunoglobulin E to the code, Spec. IgE to the code (serum).
Research method
Solid phase immunofluorescence (ImmunoCAP).
Units
kUA/l (kilounit of allergen per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous or capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
An allergen is a substance that causes an allergic reaction. In atopic diseases, allergens stimulate the formation of IgE class antibodies and are factors in the development of clinical symptoms of allergic diseases.
The detection of specific immunoglobulins E in the blood for a specific allergen confirms its role in the development of type I allergic reaction (reaginic), and therefore allows us to determine the possible “culprit” of the allergic disease and prescribe appropriate therapeutic and preventive measures.
Food allergy is a reaction caused by food intake, which is based on immune mechanisms. It can often be confused with food intolerance associated with other reasons (features of food preparation, product composition, metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal diseases).
Food allergens can be of animal or plant origin. They differ from each other in solubility, enzymatic and temperature stability.
Some food allergens may lose their allergenic properties during cooking and canning, while others, on the contrary, become more allergenic.
Clinical manifestations of food allergies include acute urticaria, angioedema, attacks of bronchial asthma, anaphylactic shock, exacerbation of atopic dermatitis and, less commonly, allergic rhinitis.
Fish proteins are strong allergens, most of which are heat stable and are not destroyed during cooking. At the same time, sea fish are more allergenic than river fish. Sensitization to fish is detected in 10-40% of allergy sufferers.
Cod is one of the most important commercial fish. Fish oil is made from its liver.
Allergy to cod is the result of one of the most powerful food irritants - fish protein. Cod proteins make up almost 19% of the fish's body and contain significant amounts of three essential amino acids: lysine, methionine and tryptophan. They are included in the so-called allergen M (Gad c 1).
The reason for the body's sensitive reaction is not always the consumption of cod dishes. In some cases, allergies are caused by a substrate with low molecular density - it could even be the smell of cod or fish oil.
Systemic reactions have been described that occurred not only after eating cod, but also when inhaling steam or smoke during cooking, as well as when the fish comes into contact with human skin.
Cod allergens that enter food not only in the form of a finished product, but also in cooking fat and oil, can cause an anaphylactic reaction with a high risk of death.
Dishes in which fish were previously stored or processed may also be unsafe for sensitized patients.
Allergies to fish proteins are observed quite often. If you are sensitized to cod allergens, cross-reactions may develop when consuming carp, perch, eel and tilapia. However, some patients may be sensitized to cod but not sensitive to other fish.
There was no cross-reaction between cod and tuna.
The purpose of this study is to determine cod-specific IgE using the ImmunoCAP method. ImmunoCAP is characterized by high accuracy and specificity: even very low concentrations of IgE antibodies are detected in a small amount of blood.
The study is revolutionary and is based on the immunofluorescence method, which allows it to increase sensitivity several times compared to other tests.
The World Health Organization and the World Allergy Organization recognize ImmunoCAP diagnosis as the “gold standard”, as it has proven its accuracy and consistency in independent studies.
In the Russian Federation, until now, the technique has not become widespread, although throughout the world up to 80% of tests for specific class E immunoglobulins are performed using ImmunoCAP.
Thus, identifying specific IgE using this technique takes allergy diagnostics to a qualitatively new level.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of sensitization to cod in patients with allergic diseases (food allergies, acute and chronic urticaria, angioedema, atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis).
- To assess the risk of developing allergic reactions to cod.
When is the study scheduled?
- If you have the following symptoms indicating an allergic nature when eating cod: redness and itching of the skin, rash, angioedema, laryngeal edema, cough and bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
- With polyvalent sensitization.
- If the results of skin testing and provocative tests are questionable.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Indicator value, kUA/l | Class | IgE antibodies |
| 0 – 0,35 | 0 | Absent |
| 0,351 – 0,69 | 1 | Short |
| 0,70 – 3,49 | 2 | Average |
| 3,5 – 17,49 | 3 | High |
| 17,5 – 49,99 | 4 | Very tall |
| 50,0 – 100,0 | 5 | Intensely high |
| More than 100.0 | 6 | Extremely high |
Reasons for increased levels of specific IgE:
- the presence of allergic reactions to cod;
- food allergies, exacerbation of atopic diseases caused by sensitization to cod allergens.
Reasons for decreased levels of specific IgE
With repeated research (over time), the level of specific IgE may decrease for the following reasons:
- limiting or eliminating contact with the allergen;
- carrying out drug treatment.
Important Notes
- Performing this study is safe for the patient compared to skin tests (in vivo), since it eliminates the patient’s contact with the allergen.
- Taking antihistamines and age characteristics do not affect the quality and accuracy of the study.
- Cross reactions are allergic reactions to components of the same structure present in different allergens. To avoid unnecessary tests that are unnecessary for the patient and to individually select possible cross-reacting allergens, consultation with an allergist is necessary.
Also recommended
Who orders the study?
Allergist, pediatrician, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, therapist, general practitioner.
Literature
- Van Do T, Elsayed S, Florvaag E, Hordvik I, Endresen C. Allergy to fish parvalbumins: studies on the cross-reactivity of allergens from 9 commonly consumed fish. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;116(6):1314-20.
- Das Dores S, Chopin C, Villaume C, Fleurence J, Gueant JL. A new oligomeric parvalbumin allergen of Atlantic cod (Gad mI) encoded by a gene distinct from that of Gad cI. Allergy 2002;57 Suppl 72:79-83.
- Ma Y, Griesmeier U, Susani M, Radauer C, Briza P, Erler A, Bublin M, Alessandri S, Himly M, Vàzquez-Cortés S, Rincon de Arellano IR, Vassilopoulou E, Saxoni-Papageorgiou P, Knulst AC, Fernández- Rivas M, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Breiteneder H. Comparison of natural and recombinant forms of the major fish allergen parvalbumin from cod and carp. Mol Nutr Food Res 2008;52(S2):S196-S207.
- Hansen TK, Bindslev Jensen C, Skov PS, Poulsen LK. Codfish allergy in adults: IgE cross-reactivity among fish species. Ann Allergy 1997;78(2):187-94.
Source: https://helix.ru/kb/item/21-639
Fish allergy: symptoms
The first signs of an allergic reaction to fish and seafood usually appear within an hour after eating these dishes.
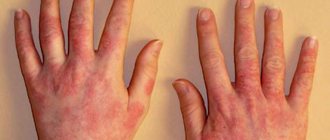
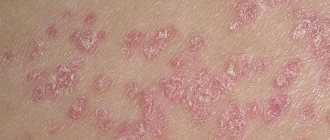
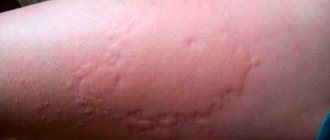
- Dry rashes are observed on the skin, accompanied by severe itching, redness and swelling. If no action is taken to promptly treat a fish allergy, a dry rash may give way to a weeping one, which can lead to infection.
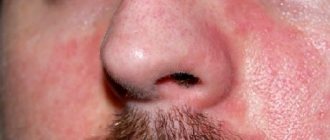
- The mucous membranes react with a tingling sensation and the appearance of swelling in the area of the lips and eyelids, which can cause the development of Quincke's edema. Watery eyes, allergic rhinitis, and sneezing may also occur.
- If a person prone to allergies inhales the vapors that rise into the air while cooking fish, he may develop a severe, dry cough, which can lead to difficulty breathing and an attack of suffocation.
Diagnostics
Only a general practitioner or allergist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe medications. The specialist will collect anamnesis, examine the patient, and prescribe general urine and blood tests.
An allergist conducts skin tests for allergen reactions - applying a solution with red caviar antigens to the skin and monitoring the reaction. Sometimes a special product is prepared and injected under the skin.
Does she react to the allergen with itching, burning and redness? Allergy confirmed. By the way, some modern clinics, equipped with the latest equipment, conduct a blood test for the content of immunoglobulin E. This allows you to find out about many unpleasant diseases before they develop in full force.
Allergy to fish in a child
The tendency to be allergic to fish can be inherited. If one parent has an unusual reaction to this product, it will most likely be passed on to the child.
Since fish and seafood are strong allergens, the mother should refrain from them while breastfeeding (the same applies to the gestation period). It is advisable to produce the first fish feeding no earlier than 8-8.5 months. At first, it is advisable to give your baby pureed boiled fish of low-fat varieties (ideally river fish, as it is less likely to cause allergies) in small quantities, supplementing it with vegetable puree.
If a child has at least one of the food allergy symptoms described above, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician and an allergist as soon as possible.
What can replace fish?
Seafood is rich in microelements and vitamins (phosphorus, zinc, calcium, iron, polyunsaturated fatty acids). Of these, they are well absorbed, but if you have allergies, you should not sacrifice your health.
You can replace seafood:
- walnuts;
- sesame;
- flax seeds;
- egg yolk;
- peanut butter;
- pumpkin seeds;
- Brussels sprouts;
- soy.
To avoid allergens entering the body, you should carefully monitor your food.
It is important to pay attention to the likelihood of allergies in boys. Whether someone with an intolerance to this product is accepted into the army depends on the symptoms and the presence of marks in the outpatient card. Fish intolerance gives the right to count on category B.
Fish allergy: symptoms in adults
In adulthood, the symptoms of fish allergy described above can be supplemented by asthma attacks if the person has asthma. This is especially true for the cooking process, when fish vapors rise into the air. We also must not forget that some building materials and adhesives contain flour obtained from fish bones: inhaling their fumes can also negatively affect your well-being.
Statistically, women are more susceptible to fish allergies compared to men. Cross-reactions to this product are also believed to occur more frequently in adults than in children.
Prevention measures
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from allergies: it is impossible to predict the body’s reaction to a particular product.
However, you can reduce the risk of its occurrence by following the recommendations:
- give preference to white, lean varieties of fish;
- Fish complementary foods are introduced to infants gradually upon reaching a certain age;
- give preference to wild specimens caught in clean waters;
- do not eat fish infected with parasites;
- Avoid canned food and preserves, as raw materials of inadequate quality may be used in their production.
If your immediate family has an allergy, the risk of developing it in the younger generation increases.
Fish that causes allergies
Most often, an unusual response from the immune system is observed in the case of eating sea fatty fish: it can be tuna, all representatives of the salmon family, eel, sea bass. Allergies can be caused not only by fish, but also by other seafood: squid, lobsters, shrimp, crabs, oysters, scallops, and so on. It is believed that among seafood, shrimp are especially dangerous for allergy sufferers: they contain two types of heat-resistant allergens (one is in the meat, the second is in the chitinous covering). River inhabitants can also cause allergies (especially catfish), but this happens less frequently.
Fish allergy treatment
For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to completely eliminate fish products from consumption. Please note: if other members of your family do not suffer from a similar reaction and you are preparing fish dishes only for them, always use gloves and wash dishes thoroughly after preparing food.
In order to quickly remove substances to which you are intolerant from the body as quickly as possible, you need to take a course of enterosorbents - activated carbon, enterosgel. To treat skin manifestations, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory ointments and creams are used, and hormonal drugs are used to combat swelling of the mucous membranes and larynx.
What to do?
People who experience such an allergic reaction should avoid various fish flavors, caviar, and herring oil. Any seafood, especially shrimp, should be excluded from the diet.
If allergies occur, you should take an antihistamine. It is also recommended to empty the stomach and drink any sorbent that will help quickly remove the allergen from the body. If symptoms of a severe allergic reaction occur, for example, swelling of the larynx, asthmatic attack, the patient needs urgent hospitalization.
It is important to remember that not all types of fish are allergens. Having undergone a comprehensive examination by an allergist and having accurately identified which variety causes a negative reaction, you can adjust your diet so as not to completely give up this product. Quite often, patients with allergies to sea fish tolerate river fish well.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the product for children and adults has been proven by a clinical study. The products are also suitable for daily skin care for children with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
La-Cri cosmetics, according to research results, are recommended by the Russian Union of Pediatricians.
Allergic reaction to red caviar
Red caviar is a delicacy that takes pride of place on the holiday table. It is obtained from salmon fish - salmon, pink salmon, trout, chum salmon.
It has an exquisite taste, but this is not the only advantage - thanks to the presence of proteins, fatty acids and vitamins, consumption of caviar helps prevent circulatory disorders and helps strengthen the immune system.
However, even such a product, along with its benefits, can pose a health threat.
Allergy to caviar, which develops in children and adults, is manifested by dysfunction of the digestive and respiratory systems, leads to the appearance of a rash on the skin, and changes in the mucous membranes.
Diet
This is a change in diet so that contact with an allergenic product is completely excluded (elimination diet). It is worth considering not only the ingestion of caviar, but also the contact of the skin with it - for example, when cutting fish or making sandwiches.
Sometimes the development of allergic sensitivity even requires a change in professional activity if it is related to seafood processing. In addition to avoiding red caviar, it is important to identify and eliminate cross-allergens.
A food diary and special studies in the laboratory and allergology office will help with this.
It is necessary to adhere to not only an elimination diet, but also a hypoallergenic diet - that is, remove citrus fruits, peanuts, honey, mushrooms and other foods with a high level of allergenic potential from the diet.
Consumer Reviews
Margoscha (irecommend.ru)
“At the beginning of January, my neurodermatitis sharply worsened and my face became covered with peeling. It was not a very beautiful sight, and it gave me terrible moral and physical discomfort. I had to urgently go to the pharmacy because my favorite Bioderma had run out. At that time, there was nothing suitable for me from Bioderma, the pharmacist offered to buy a new product - La-Cri intensive cream for dry and sensitive skin, suitable for both adults and children. I bought the cream, the price is 269 rubles for a 50 ml package.
I have been using La-Cri intensive cream for more than two weeks. At the pharmacy, the pharmacist immediately warned that one of the customers had a severe allergy to this cream, and advised first applying a small amount of the product to a small area of skin.
My skin took the La-Cri cream calmly, there were no negative effects. The cream really removes peeling well, or rather, makes the peeling not noticeable, since there is a layer of non-absorbable fatty product on the skin.
I use La Cree intensive cream more like a mask, that is, I apply it in a thick layer to the skin of the face and leave it for half an hour, then remove the excess cream. The skin of the face is nourished with oils and noticeably softens.
La Cree is not suitable as a base for makeup; the face will be shiny and the foundation will not apply well. I use the cream in the evening a couple of hours before bed. I like the effect."
Ephemeral_Liberty (irecommend.ru)
“...What did I get?
The cream softens rough skin well and hides peeling perfectly. I wouldn’t call the result cumulative; it lasts as long as I don’t stop using the cream.
It doesn’t remove the redness, but it does tone down the redness, and that’s it.
The cream is not omnipotent and cannot get rid of dermatitis - the cause of its appearance must be sought in the body itself. He will not disappoint those who do not expect too much from him.
The composition is not bad. The manufacturer positions the cream as natural, but I could argue with this statement. However, I see no reason to criticize the composition of a really good cream. In this case, its components are the last thing I care about; the result is more important.
It contains a lot of oils and extracts; allergy sufferers should be careful. The cream does not contain dyes, fragrances or hormones.”
Sources:
- Yukhtina N.V., Modern ideas about atopic dermatitis in children https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-predstavleniya-ob-atopicheskom-dermatite-u-detey
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/metody-otsenki-stepeni-tyazhesti-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey-rannego -vozrasta
- G.V. Molokova, E.V. Bukina, Diaper dermatitis in children with sensitive skin, Journal of Dermatology and Allergology, 2019 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/pelenochnyy-dermatit-u-detey-s-chuvstvitelnoy-kozhey
- N.L. Rybkina, Modern approaches to newborn skin care: pediatrician tactics, Journal of Modern Clinical Medicine, 2014 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-podhody-k-uhodu-za-kozhey-novorozhdennogo-taktika-pediatra