Gluten allergies can occur after eating foods that contain prolamines, which are proteins naturally found in wheat, rye and barley. The symptoms of a gluten allergy are similar to those of celiac disease, however, they are two different diseases. The modern market offers consumers many gluten-free products, but it should be understood that the currently fashionable “gluten-free food” is not as healthy as it seems. A gluten-free diet should be used by people diagnosed with a gluten allergy and only after consultation with a doctor or nutritionist.
Avoidance of gluten-containing foods
What is gluten?
This is a type of protein found in wheat, barley and rye grains. It gives these grains structure and flexibility. Without gluten, foods like bread and pasta will simply fall apart or become tough with a hard texture, losing their flexibility and chewiness.
Understanding that gluten is found in wheat can help you identify some of the most common sources of gluten, which include:
- Most breads and pastas (unless labeled gluten-free)
- Traditional dough and croutons
- Crackers
- Flour cakes
- Many more (highlighted in the table below)
Symptoms
Textbooks distinguish three clinical forms of celiac disease. In fact, its manifestations are much more diverse: the symptoms of celiac disease are disguised as various diseases of the digestive system, hypovitaminosis, dermatological pathologies and many others. That is why the diagnosis of celiac disease is given to a limited number of patients, while the rest are endlessly treated for its manifestations.
On the other hand, there are many clinical cases when all the manifestations of one of the forms of celiac disease are present, even a blood test indicates this. But a biopsy of the small intestine does not confirm the doctors' assumptions.
In 1991, celiac disease was presented in the form of an iceberg: at the top there is a small number of confirmed variants that occur with clear clinical signs. Underwater there is a huge number of those same undiagnosed, “masked” cases. And at the base of the iceberg are people who have a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, but the disease develops only when exposed to provoking factors (stress, decreased immunity, eating a large amount of foods with gluten, and so on).
The earlier and in larger quantities gluten is introduced into food (for example, semolina porridge, beloved by all grandmothers), the faster celiac disease occurs and the more severe it is.
We recommend reading: Peanut poisoning: symptoms and signs, first aid and treatment✅
What is gluten intolerance?
Gluten intolerance is a set of unpleasant symptoms that you experience after eating gluten.
The most severe form is an autoimmune disease called celiac disease, a digestive disorder caused by damage to the villi of the small intestine by certain foods containing certain proteins: gluten. It makes it difficult for your gut to absorb nutrients and is estimated to affect almost 1% of the population and around 1 in 141 residents, although many cases go undiagnosed.
Unlike celiac disease, gluten intolerance does not cause long-term damage to the intestinal lining, but is more commonly diagnosed. In addition, it may cause symptoms that are not limited to indigestion.
Common symptoms of gluten intolerance may include:
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Excessive bloating
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Unexplained mood changes
- Lack of ability to think clearly
Folk recipes
Celiac disease is a serious disease that cannot be completely cured. But regular monitoring of the patient’s condition is possible using a special diet of approved foods. Traditional medicines can reduce the acute form of the disease and improve the patient's condition, alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
It is best to use this treatment in conjunction with drug therapy. Folk medicines are safe for health, since they contain only plant components that do not have an irritating effect on damaged mucous membranes. They restore tissues and supply the body with vitamins and minerals.
These remedies include herbal medicinal collection, the preparation of which requires herbal plants:
- galega officinalis - 1 tbsp;
- Medunika and Zamanikha - 2 tbsp each;
- heather, meadowsweet and cudweed - 3 tbsp each;
- speedwell, bedstraw and lyubka - 4 tbsp each.
The ingredients are crushed and mixed, and a medicinal decoction is prepared from the prepared powder:
- 5 tbsp. l. pour 1 liter of water into the mixture, boil and cook for a quarter of an hour over low heat.
- Cool the solution and strain it through cheesecloth.
- Take 60 ml 6 times a day.
Another effective remedy is a decoction of sage and wormwood. The dried material is mixed in the ratio: 1 part wormwood and 3 parts sage. Steam 1 tbsp in a glass of boiling water. l. collection, leave for 1 hour, strain. Take ¼ tbsp. 4 times a day. Tea is prepared from dried flowers of calendula and chamomile, which has strong antiseptic properties. You need to drink it regularly 2-3 times a day.
What causes gluten intolerance?
Unfortunately, there is no definitive answer as to why people develop gluten intolerance. Some studies suggest that consumption of certain short-chain carbohydrates (oligosaccharides, disaccharides and monosaccharides) may contribute to its development. If a person stops including them in their diet, the symptoms of gluten intolerance may subside.
Other researchers believe it is caused by a variety of other factors, including other components of wheat, although this has not yet been proven.
Many people who believe they are gluten intolerant may actually be experiencing a placebo effect. This is when a person expects a positive health outcome based on anticipation of the intervention. For example: If you think you're on a gluten-free diet, your symptoms may go away even if you've been consuming gluten all along.
In one recent study, 20 people were divided into two groups. Each was assigned to a gluten-free or gluten-free diet. The group whose foods did not contain protein reported more symptoms than those who ate gluten.
This means that being afraid of protein due to media reports or believing that you have gluten intolerance without a confirmed diagnosis may lead you to believe that you have symptoms even if there is no factual basis.
Diagnosis of the disease
To identify the disease, specialists conduct an immunological analysis to determine antibodies to tissue transglutaminase and gladin. As a rule, such analyzes are 95–97% reliable. In addition to this analysis, doctors perform an intestinal biopsy, which helps determine the accumulation of lymphocytes in the mucosa and villous atrophy on the surface of the intestine. Of the additional diagnostic techniques, the most commonly used are endoscopic examination of the intestine, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT, MRI and fluoroscopy of the intestine.
How to deal with celiac disease
Once it occurs, celiac disease remains for the rest of your life, which means you should adapt to this disease and make sure its unpleasant symptoms do not bother you.
The only effective way to combat this scourge is to completely eliminate gluten-containing foods from your diet. Statistics show that within a year after starting a gluten-free diet, 90% of all existing symptoms disappear, and the person feels completely healthy.
In addition to a gluten-free diet, it is important to take measures to restore intestinal activity, take enzyme preparations that improve digestion, vitamin complexes and calcium, folic acid salts and iron supplements. If the diet does not give a positive result, the patient is prescribed a 6-8 week course of anti-inflammatory therapy with hormonal drugs (Prednisolone).

What is the difference between gluten intolerance and wheat allergy?
Since wheat is one of the main sources, it can be easy to confuse the symptoms of gluten intolerance with those of a wheat allergy. However, there are also very distinct differences.
All allergic reactions affect the immune system. It reacts to anything it considers a foreign substance that must be removed from the body. Your immune system produces antibodies known as immunoglobulin, which can cause a variety of reactions, including the life-threatening condition anaphylaxis (anaphylactic shock).
Gluten intolerance is less severe than wheat allergy and does not affect the immune system. Additionally, a qualified allergist can diagnose the allergy using a skin prick or blood test, while a doctor can diagnose gluten intolerance based only on your symptoms and rule out other factors.
Because these 2 conditions may share symptoms, it is important to first rule out a wheat allergy before suspecting gluten intolerance.
Treatment
First of all, the patient will need to follow a strict diet, which absolutely excludes the consumption of products even with a minimal amount of gluten. The treatment plan is also supplemented with medications that reduce the severity or completely eliminate allergy symptoms.

To quickly relieve allergy symptoms, antihistamines are prescribed - Tavegil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine. As soon as the acute period of the disease passes, more gentle drugs are prescribed - Erius, Ziratek or Telfast. In severe clinical cases, Prednisolone may be used.
To reduce the severity of skin symptoms, use ointments and gels that do not contain hormones:
- Fenistil gel;
- Solcoseryl;
- Gistan et al.
To normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, enzymes and probiotics are additionally prescribed.
How is gluten intolerance diagnosed?
As mentioned in the previous section, there are no specific laboratories or biomarkers to officially diagnose gluten intolerance. It can only be diagnosed subjectively from your words.
The diagnostic process usually includes:
1 Rule out wheat allergy and celiac disease, which may include blood tests and/or skin pricks, and an endoscopy procedure if necessary (for celiac disease only).
2 You then follow a diet that temporarily eliminates gluten from your diet. The doctor evaluates your symptoms and then brings it back again to monitor your reaction. If he can make a clear connection between the protein and your symptoms, then a conclusion is made about intolerance.
However, it is very difficult to distinguish gluten intolerance from other digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome, so doctors may order further testing and monitoring.
Preparing and conducting analysis
To obtain the most reliable data from a study, you need to properly prepare for it, following a few simple rules.
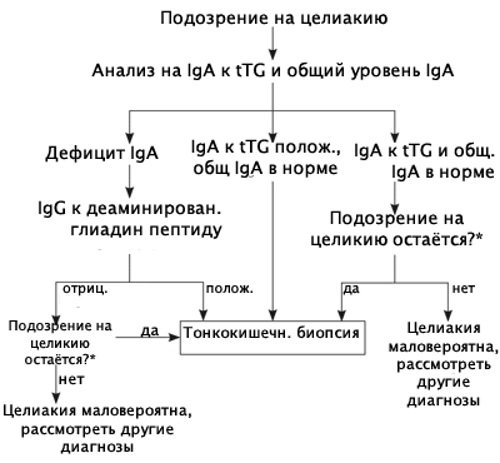
You should prepare for submitting biomaterial as follows:
- Blood sampling from a vein is carried out only on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 8 hours before visiting the laboratory. If the patient has been recommended a gluten-free diet, then 2 days before blood sampling it must be abandoned.
- It is forbidden to drink tea, juice or coffee before blood collection. You are allowed to drink no more than ½ tbsp. still water.
- The doctor must be notified about what medications the patient is taking. Perhaps the doctor will decide to stop taking some of them. If the patient cannot do without medications, the specialist will take this fact into account when interpreting the analysis.
Also, 2 days before the test, you should avoid any stress. Mental instability may not give an accurate result and it will be difficult to make a diagnosis.
How is gluten intolerance treated?
If your doctor determines that you have gluten intolerance, eliminating it is the best way to reduce discomfort. This can be difficult as it is found in so many different foods.
If with some products containing wheat, barley or rye, the obvious sources of this protein, everything is more or less clear, then what about other types? See the table below for information on foods containing gluten and for alternative substitutes.
| Products containing gluten | Gluten-free analogues |
| Couscous | Brown or white rice |
| Durum wheat | Rice or coconut flour |
| Coarse wheat flour | Almond flour |
| Kamut | Buckwheat |
| Semolina | Corn or potato products |
| Spelled | Amaranth grains (shiritsa) |
| Seitan | Tofu |
| Bulgur | Sorghum |
| Semi-finished meat products | Natural meat |
| Oats (oats themselves do not contain gluten, but they are often processed in a facility that produces gluten-containing grains and can be a source of cross-contamination) | Labeled Gluten Free Oats |
In addition, below is a table of other foods that may contain hidden gluten, as well as their gluten-free counterparts.
| Products with gluten as an ingredient | Gluten-free analogues |
| Barley malt and malt vinegar | Balsamic, red wine, apple cider or rice vinegar |
| Beer | Wine or spirits |
| Meat or vegetable broth | Certified gluten-free broth or bone broth |
| Brewer's yeast | Nutritional yeast |
| Some salad dressings | Dressing made with natural gluten-free ingredients such as olive oil |
| Many veggie burgers | Labeled gluten-free patties |
| Some seasonings and spice mixtures | Fresh herbs or homemade spice blends |
| Soba noodles | Bean or lentil noodles |
| Soy sauce | Tamari sauce |
| Sauces and gravies | Sauces made without wheat or cornstarch |
| Some medications and supplements | Certified gluten-free analogues |
| Other grain products such as crackers, cereals, muesli, baked goods, flour tortillas, croutons, energy bars, etc. | Grains such as rice, quinoa, corn tortillas, granola and energy bars made with gluten-free oats or nuts, nut or rice crackers, baked goods made with gluten-free flour, and certified gluten-free cereals |
Remember that the products, oh, do not mean gluten-free, as there are many other grains that contain it. Look for a special certified label that guarantees the composition of the product.
conclusions
Gluten intolerance is a complex condition that can easily be misdiagnosed. Talk to your doctor to rule out wheat allergies and celiac disease, and try eliminating foods with short-chain carbohydrates before diagnosing yourself. Also, make sure your symptoms are not caused by a placebo effect.
If you have a gluten intolerance, eliminating it from your diet has become much easier in recent years thanks to advances in food science. However, it should not be avoided unless your doctor determines that it is necessary and beneficial for your body.
List of dangerous products
It is present in many products as a thickener. Parents need to pay special attention to this. Read the ingredients of sweets, sauces, yoghurts, mixtures, even tablets. In medicines, gluten is used to create coatings.

The following should be removed from the menu of children with cereal gluten intolerance:
- dishes based on rye, wheat, barley - soups, porridges;
- all products made from wheat flour and with its addition;
- semolina;
- whole milk;
- meat by-products – sausages, frankfurters;
- ketchups, mayonnaise, sauces;
- fatty, salty, smoked foods;
- drinks with gases and yeast (kvass, sweet soda);
- canned food
Now the trip to the store for parents will be longer. Study the composition of the products. If gluten is not listed or the product is labeled “Gluten Free,” purchase it with confidence. For people with celiac disease, shopping centers create special departments where they sell only gluten-free products. This helps mothers establish nutritious and safe nutrition for their children.
At the age of up to 6 months, and some up to 8–10 months, children are not yet ready to meet vegetable protein and react negatively to its introduction to the menu.
Development mechanism
The mechanism of development of celiac disease is that gluten, entering the gastrointestinal tract, literally sticks food together, stagnates and irritates the mucous surface due to the lack of an enzyme capable of breaking it down. As a result of the production of decay toxins, the body perceives the protein as foreign and activates the immune system, producing antibodies that destroy the inner surface of the intestine - the villi.
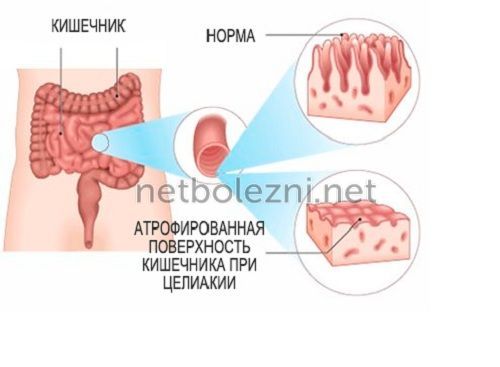
Because of this, metabolic processes are disrupted
- the ability to absorb nutrients is lost, which is the main sign of the disease.
In medical practice, a violation of the absorption process of nutrients is called malabsorption, which leads to serious disorders associated with the loss of vitamins.
Cases of gluten intolerance have increased since the mid-20th century. This is explained by the development of modern genetic technologies and hybridization of cereal crops.
One of the important enzymes
, which is secreted by the intestinal walls, is lactase. Due to its absence, intestinal villi lose the ability to “capture” and process casein and lactose molecules, which contributes to the development of intolerance to milk proteins and carbohydrates. In these cases, patients can safely consume cheeses and yogurts - in these products, lactose and casein are already broken down.

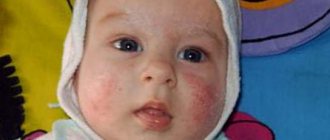
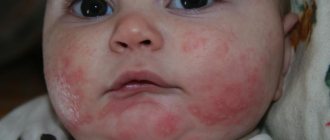
What are the symptoms of celiac disease in adults?
- Weight loss
- Prolonged causeless diarrhea
- Prolonged bloating
- General weakness and decreased performance
- Loose stools that do not change for a long time – more than 1 week
- A sharp decrease in weight gain due to adequate feeding
- Increased gas formation, flatulence
- Loss of body weight due to adequate feeding
- Increased fatigue and unstable mood of the child.
- If the symptoms described above are observed for more than a week, then there is reason to suspect that the child has an intolerance to foods containing gluten.