What is pseudoallergy
Pseudoallergy is a pathological increased reactivity of the body to certain substances with the development of symptoms characteristic of ordinary allergies.
True pathology occurs due to the reaction of the immune system to a specific allergen. This is the so-called protective reaction of the body (the first immunological phase of the course). In false allergies (para-allergies), this stage is completely absent. Stage 2 - pathochemical process. Then stage 3 begins - manifestations of symptoms.
A pseudoallergic reaction differs from a true allergic reaction in the absence of the first phase of the immune response. The last two stages are the same for both allergies.
Symptoms
Pseudoallergic reactions are very similar to true ones. However, the symptoms of a false allergy directly depend on the amount of the provoking substance and are usually localized in one of the body systems.
May be observed:
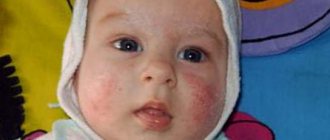
- hyperemia (redness) of the skin and mucous membranes;
- blisters, rash;
- itching, peeling of the skin;
- nasal congestion, runny nose;
- lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids;
- tissue swelling (small);
- disruptions in the functions of the digestive system (nausea, diarrhea, vomiting);
- headache.
Pseudoallergy in children most often manifests itself as a skin rash, diarrhea, and dysbacteriosis. The rash usually appears first on the face, then on the body. Headaches often begin, children become capricious and sleep poorly.
The difference between the symptoms of pseudoallergy and a real reaction:
- There is no too rapid onset of the disease.
- The symptoms are not so severe.
- There are almost no cases of asphyxia (suffocation) or a sharp decrease in pressure.
- There is no severe swelling.
- More often there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Headache occurs more often.
The difference between pseudoallergy and true allergy
- A common food allergy ( true allergy ) is manifested by the body's immune response and it occurs even if the body encounters a microscopically small dose of the allergen.
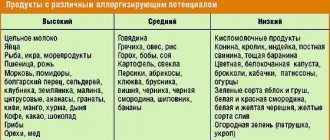
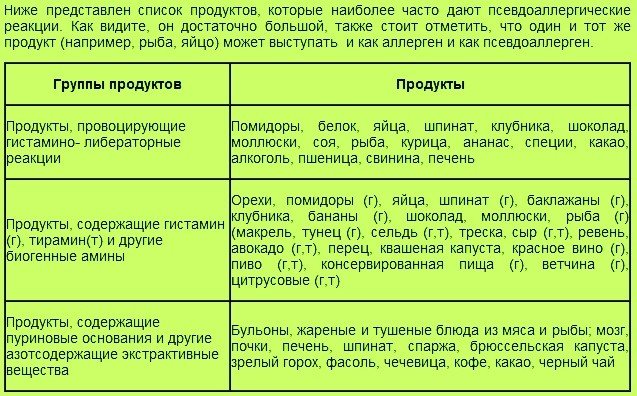
- Pseudo-allergy , also called false, does not always occur, it depends on the dose, the state of the immune system at the time of introduction (if the body is weakened after an illness, then the chance of encountering manifestations of pseudo-allergy is much greater). Pseudo-allergies also often occur with the concomitant intake of dyes, preservatives, emulsifiers, thickeners, sweeteners and other E-additives, which are now present in abundance in almost any food product.
The occurrence of food intolerance, also sometimes called pseudo-allergy, occurs under the influence of environmental pollution (air, water), frequent and abundant consumption of all kinds of medications and food additives, externally added in excess of household chemicals and cosmetics...
Symptoms of pseudo- and true allergies
Allergy and pseudoallergy in their manifestations , so sometimes it is difficult to differentiate them.
- Pseudoallergic reactions occur much more often in those predisposed to them due to dysbacteriosis and other diseases of the intestines and excretory organs (liver, kidneys);
- true allergies are characterized by a history of another type of allergy (hay fever, allergy to insect bites, etc.)
Treatment
Once the correct diagnosis is made, the doctor must determine what exactly caused the negative reaction. The patient (or his parents, when it comes to the baby) must remember what food he ate over the last 2-3 days, what medications he took, perhaps he was exposed to the Sun for too long, etc.
Diet
It will be necessary to exclude from the menu the food that caused the reaction. The ban on its use lasts at least three months. Then you can try eating a small portion of the product and see how the body reacts.
The diet is also optimized. Obviously harmful products (fast food, soda, canned food, smoked meats, etc.) are limited, as well as products with a high allergic index, which can act as a liberator. You need to eat more raw vegetables and fruits, dairy products, lean fish and meat, and greens. It is advisable to boil, steam, or grill food.
At the same time, therapy is carried out aimed at treating chronic gastrointestinal pathologies and treating dysbacteriosis. A specialist can recommend enzymes for better digestion of food and products that protect the mucous membranes from irritating factors.
Drug therapy
Treatment of pseudoallergy is practically no different from the therapy recommended for the true form of the disease. It is necessary to remove the consequences of histamine release (itching, rash, hyperemia), remove toxins and adjust the body to normal operation.
The doctor may prescribe:
- Antihistamines - Telfast, Aleron, Xyzal, Zyrtec, Erius, Loratadine, Cetrin, etc. Syrups and drops are usually prescribed to young children. Infants are prescribed drops for oral use - Fenistil, Zodak, Parlazin, Zyrtec. Tablets for children, taking into account the drug, are prescribed either from 6 or 12 years.
- Remedies for itching and urticaria - Soventol, Fenistil-gel, Beloderm, Psilo-balm, Lorinden, etc.
- Vasoconstrictor drugs that remove swelling of the mucous membranes - Naphthyzin, Irifrin, Vizin, Nazol, Metazon, etc.
- Drugs that reduce inflammation of the mucous membranes - Cromohexal, Allergokrom, Kronasol, etc.
- Sorbents that help quickly remove toxins from the body - Laktofiltrum, Polysorb, Carbosorb, Enterosgel, for small patients - Smecta.

Traditional methods
They must be combined with traditional therapy. Consultation with a specialist is advisable, since there is a risk that folk remedies can also cause allergies.
Recipes:
- Pour 200 g of large oat flakes into 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 8-10 hours. Strain and drink little by little all day. Course – 2-3 weeks.
- Mix 100 g of glycerin or olive oil with 1 tsp. dry sage powder. Apply once a day to areas of skin that are itchy and flaky.
- Baths and compresses with a decoction of string, yarrow, chamomile, and mint help relieve itching and rashes.
- 1 tsp Steam chamomile flowers with a glass of boiling water and strain. Drink a third of a glass three times a day before meals.
- 2 tbsp. strings and 1 tbsp. hop cones pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 40 minutes. Use as a lotion for itching.
Frequency of occurrence of pseudoallergy
According to scientific data, pseudoallergic reactions occur 8 times more often than true ones. There is also a dependence on age. If at a young age (20-25 years old, the immune system is more tense than ever) true allergies are more common, then in childhood (diathesis) and in the elderly pseudo-reactions are more common.
For children, they even invented an expression that they “outgrow” allergies with age. And by the age of 5-7 years, the manifestations of food allergies disappear. But the topic of childhood diathesis is quite extensive and we will devote time to it in another article.
Differential diagnostic signs of allergic and pseudoallergic reactions
As a rule, a pseudo-allergy occurs unexpectedly, but not instantly (if an allergy occurs within three hours after eating a food product, then in this case we are dealing with a true allergy, but if after eating a suspicious food more time has passed, from 4-5 hours to a day, then most likely we encountered a pseudo-allergy... Yes, what can I say, how many times have we overeaten crayfish or other seafood and the next day a rash, itching and other “delights” appear.
Additional differential diagnostic signs of allergic and pseudoallergic reactions can be seen below:
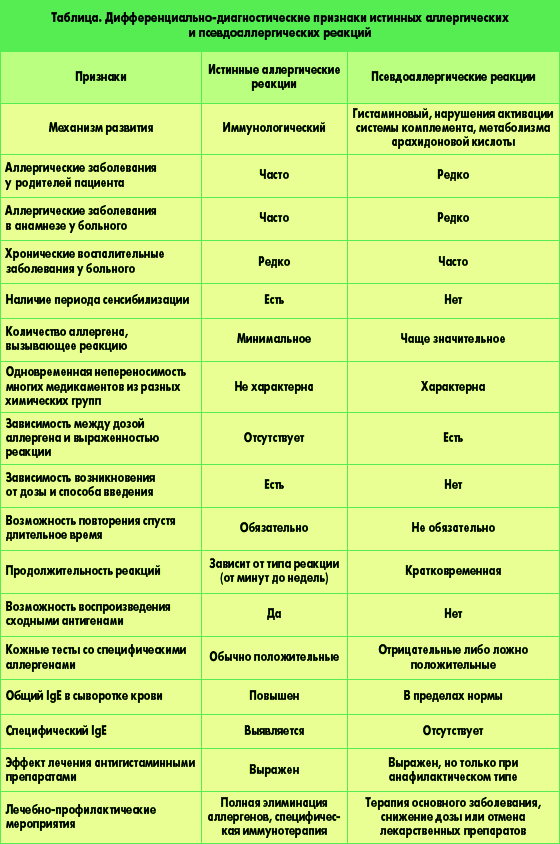
Cross allergy with true allergy
In patients with true allergic reactions, cross-allergy often occurs, that is, hypersensitivity to allergens that are similar in structure.
For example:
- If you are allergic to apples, you will also be intolerant to peaches, nuts, kiwi, potatoes, cherries.
- If you are allergic to oranges and other citrus fruits, most likely you will not tolerate honey, halva, or sunflower oil well.
- And if you are allergic to eggs, then in 4 out of 5 cases you will also be allergic to chicken or rabbit meat.
- Combined reactions are also often found with melon, banana, and beets.
How to distinguish true allergies from false ones
Author Inna Novikova
Updated: 06/04/2020 04:59 Published: 07/30/2019 12:00
Health » Health and prevention » Prevention
Allergy is a mysterious disease. It can be true and false. And it arises due to the body’s reaction to certain proteins and only to them. And it is not at all necessary, as many believe, that if an allergy appears to a certain product, then it will later appear to others.
0 shared
The chief physician of Moscow clinic No. 11, allergist, candidate of medical sciences Galina Kotova told the general director of Pravda.Ru Inna Novikova about this and much more .
Read the beginning of the interview: How and why allergies occur
— Galina Yuryevna, there is a strong opinion that an allergy can begin, for example, to strawberries, eggs, chocolate, anything, but if it begins, then it will then manifest itself to other allergens, their number will increase. Is this true or not?
- No, that's not true at all. It is not true. And if a person is allergic to a certain product, to a certain type of pollen, then it is not at all necessary that the spectrum of these causative allergens will expand. It may expand, but it may never expand.
All allergists do not like the term “polyvalent allergy” because it is in fact completely inappropriate and practically illiterate. There are no polyvalent allergies. There is an allergy to a certain protein - such, such and such. There may be one or two, or there may be ten or more. But it is not at all necessary that if there is one, then there will be many of them.
— I myself am probably a polyvalent patient, because in my youth I had an allergy and even angioedema (though against the backdrop of excitement, it was also spring), because I put on makeup... And then there were reactions to a variety of things - to tomato pasta, ascorbic acid, glucose with apple, which do not seem to be allergens. I know I'm allergic, but I still don't understand what.
- All this suggests that your mast cells are in a state of readiness to destabilize the membrane and release histamine. The powder is not a protein product. It does not contain protein. And you cannot have a true allergy...
— So washing powder is not an allergen?
- No. Washing powder is not allergenic. And shoe polish is not an allergen, and rosin, and hot air are not allergens. When they say: “I have an attack of suffocation if I approach the subway, the door opens and hot air blows on me”...
- And there are also allergies to cold, to the sun...
- Yes, such reactions also happen. And the same goes for the cold, the sun - this is not an allergy. This is insolation urticaria, for example, which occurs during sun exposure, cold urticaria, which occurs in response to the cold factor. During physical activity, there may be a release of biologically active substances into the blood and bronchospasm occurs. But this does not mean at all that a person is allergic to physical activity. This means that he is in a state of readiness for such a pseudo-allergic reaction.
- What to do with this condition?
- And this also needs to be treated. This needs to be examined and treated. If the examination does not immediately give any definite results, then this once again confirms that there is no true allergy. This means that it is necessary to treat those organs that can react with such a release of these biologically active substances. First of all, this is the gastrointestinal tract, of course. Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract greatly contribute to such conditions.
- It is believed that very often and primarily it is associated with the liver.
— With the liver, of course . Any chronic inflammatory diseases of the liver, pancreas, intestines (this could be polyps of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcers and erosion of the gastric mucosa) - all these conditions not only contribute to, but cause such things. Therefore, we always prescribe to patients, first of all, examinations of the gastrointestinal tract: ultrasound of the abdominal organs, gastroscopy without fail, colonoscopy, biochemical blood tests.
— Is allergy a hereditary disease or acquired in connection with some conditions, external and internal influences?
— In general, it is believed that allergies are a disease of young city dwellers. People living in the city, especially young people, are susceptible to allergies. At least, it is extremely rare to encounter situations where a true allergy arose in a middle-aged or older person, say, over 65 years old, and was first discovered. Perhaps there is some correlation with intellectual development.
— With intellectual development?
- Yes. A number of scientists claim that people with developed intelligence are more susceptible to allergic diseases than people with underdeveloped intelligence, so I congratulate you. As for heredity, if one of the parents has a true allergic disease, then there is a 50/50 chance that the child will inherit it.
- Then the disease occurs right at a very early age?
- It happens differently. Usually, allergic diseases do not occur at an early age, because the so-called immunological start and the real functioning of the immune system begin around the age of five. Until the age of five, children do not suffer from true allergic diseases or suffer extremely rarely. And children's exudative diathesis, which is regarded as an allergy, is in fact not an allergy at all.
It is extremely rare for true allergies to occur in young children. And this is all so-called digestive enzymopathy. This is an imperfection of the gastrointestinal tract, which underdigests certain foods, and what is not absorbed into the blood is what should be absorbed. As the gastrointestinal tract matures, these manifestations will subside. But this does not mean that they do not need to be treated. Diathesis also needs to be treated. You just don’t need to think that this is already an allergy, and the person is an allergy sufferer.
Read the rest of the interview:
How are allergies, pseudo-allergies treated and how are tests done?
Allergies and immunity - what do they have in common?
Allergy to allergy medications: what to do?
There is no need to be afraid of allergies - you either have them or you don’t.
Interviewed by Inna Novikova
Prepared for publication by Yuri Kondratyev