An allergy to antibiotics in a young child is determined by diagnostic results and signs that parents remember before starting therapy. Medicines cause many bad side reactions if the body is weakened and the immune system does not respond correctly to the action of the components. A child’s reaction to taking antibiotics manifests itself in the form of a skin rash, irritation of the eye mucosa, headache, and gastrointestinal disorders. The doctor prohibits the use of the medicine if the patient’s health worsens and prescribes safe drugs.
Quincke's edema as a reaction to antibiotics
Quincke's edema occurs for several reasons, but more often it appears as an allergy to food or medications, mainly in people who are allergic to other irritants. Children and young women are most susceptible to angioedema.
If you suspect angioedema, you should immediately call an ambulance or a doctor
Swelling of the deep layers of the skin and mucous epithelium may be a reaction to the treatment of infectious diseases and indicate that an allergy to antibiotics has occurred. Most people may experience a skin rash. With Quincke's edema, fluid accumulates in deep layers, and the surface of the skin does not change its color. It can appear on the hands, genitals, eyes and legs. There is no itching.
Symptoms may worsen over 1-2 days
If swelling affects the upper respiratory tract, life-threatening suffocation may occur. After stopping taking medications, swelling will disappear. But in severe cases, antihistamines and steroids are prescribed.
This is interesting: Signs of iron deficiency in the body
Note! In severe cases, Quincke's edema can affect internal organs, including the meninges and joints.
In this case, the manifestations of the disease can develop rapidly and require urgent medical intervention.
Reasons for the body's reaction
The main factor identified by scientists in light of this problem is a family predisposition to allergies. The reaction can be caused not only by frequent irrational use of drugs - for young children, a single dose is enough to cause characteristic symptoms.
Allergies in a child - what to do
The genetic nature of pseudoallergy has not been fully studied, although doctors largely blame the drugs themselves and their properties for the problem:
- how well they dissolve in water and fats;
- in what quantity they contain polysaccharides, proteins and their complex compounds;
- what is the degree of biological activity of the antibiotic.
Note! The physicochemical properties of drugs are determined by their composition. Therefore, your baby may be allergic to some medications, but not to others.
Often, previously tolerated drugs become allergens due to breakdown or oxidation, which is caused by long-term storage of drugs in inappropriate conditions (despite the fact that they are not expired).
Predisposing factors to allergies to antibiotics are:
- insufficiency of the functions of the excretory systems of a small organism;
- past infections;
- gastrointestinal problems.
The last factor has a special effect when drugs are administered orally. In this case, antibiotics pose a great danger to young children due to the development of dysbacteriosis and food allergies.
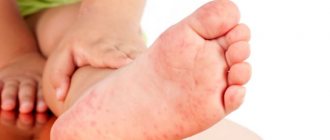
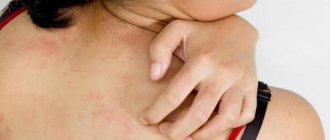
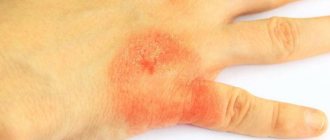
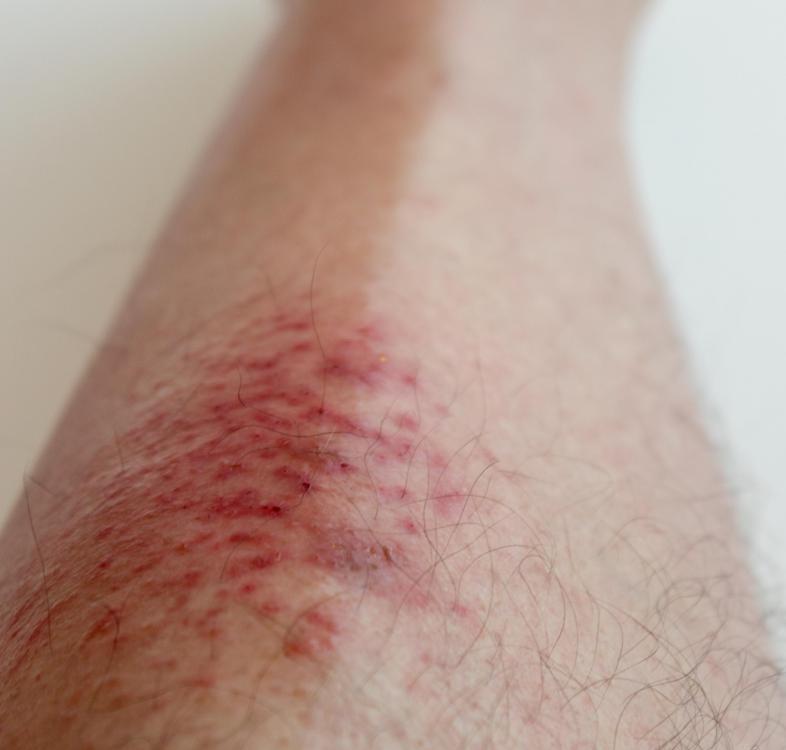
Skin rash after taking antibiotics
According to statistics, more than 20% of the population had the problem of rashes appearing on the body. Approximately 1-2% of patients experience such an allergy to antibiotics (skin rash). Treatment of this disease is aggravated in people suffering from such serious diseases as leukemia, HIV, monoculosis and cytomegalovirus infection.
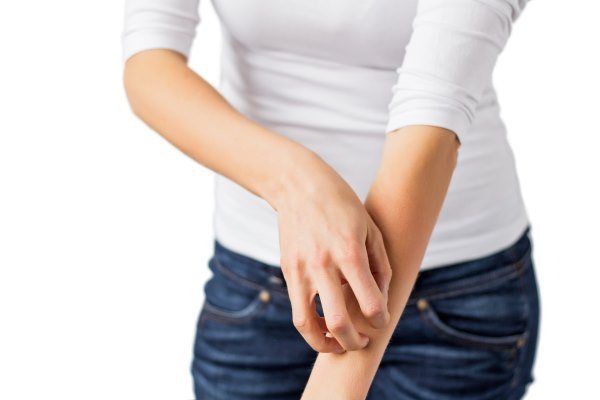

A rash is just one symptom of an allergy.
A rash is an allergic reaction with a change in the affected area of the skin. Not only the color but also the texture of the affected skin changes. The rash is localized to a specific area, but can spread throughout the body.
In addition to external signs, this manifestation of an allergy may be accompanied by other symptoms: itching, swelling, soreness or flaking of the skin . This causes not only an aesthetic problem, but also a general malaise.
Signs of ALLERGY to antibiotics may appear only after 3 weeks FROM THE DAY YOU START
The longer the course of antibiotic use, the greater the likelihood of an allergic reaction in the body, in particular such as a skin rash.
General manifestations
Common allergy symptoms following antibiotics include anaphylactic reaction, serum-like syndrome, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell syndrome, drug fever, and intoxication.
Anaphylactic shock is characteristic of a severe form of allergy. The reaction develops immediately after taking the medicine (maximum thirty minutes). The condition is manifested by increased blood pressure, difficulty breathing due to swelling of the larynx, itching and hyperthermia, the presence of a rash on the skin, and heart failure.
Serum sickness develops one to three weeks after taking an antibacterial drug. This syndrome is characterized by high body temperature, pain and aching in the joints, enlarged lymph nodes, and rashes. Urticaria and Quincke's edema occur. There is a dysfunction of the cardiovascular system: shortness of breath with slight exertion, chest pain, tachycardia, and general weakness. Complications of the disease include anaphylactic shock.
Allergies after antibiotics in an adult may be accompanied by drug fever. Typically, a complex of symptoms develops a week after the start of therapy and resolves within a maximum of two to three days after discontinuation of the drug. If you take the same antibiotic again, a fever may develop within a few hours. The main symptoms are a significant increase in body temperature, bradycardia, itching, and skin rashes.
Drug fever is characterized by an increase in the number of eosinophils and leukocytes in the blood (occurs in a fairly large number of diseases) with a decrease in platelets. The latter is complicated by problems with stopping bleeding and increased bleeding.
Lyell's syndrome is extremely rare. The condition is characterized by the formation of large bubbles filled with liquid on the skin. When they burst, huge wound surfaces are exposed, die, and infectious complications often develop. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is manifested by skin rashes, changes in mucous membranes, and high fever.
But allergies after antibiotics are not always so severe. Often the complication is limited only to local symptoms.
Photosensitivity: symptoms and manifestations
A small portion of the population experiences a disorder called photosensitivity, which is characterized by an allergy to ultraviolet radiation even after short exposure to sunlight. This effect can appear within a few seconds, and sometimes this period lasts up to 2-3 days.

Photosensitivity - allergy to sunlight
The disease is characterized by redness of the skin in the form of a sunburn . This condition is accompanied by pain and itching. With a stronger reaction of the body, pigmentation in the affected areas is disturbed, the skin thickens, swelling and blisters appear. In some people, this process can affect not only areas that were in direct contact with the sun's rays, but also those areas that were not exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
Photosensitivity is often observed in infants, in people with chronic diseases, or in those who have recently suffered a serious illness. This can be caused by household chemicals, cosmetics, or a reaction such as an allergy to antibiotics (skin rash).

An allergic reaction to household chemicals may occur
Treatment for such a reaction can only consist of protection from contact with the rays of the sun. If taking antibiotics cannot be stopped, then during this period you should use cotton clothing that covers the body as much as possible, an umbrella or a wide-brimmed hat.
What can be replaced
Augmentin is a synthetic inhibitor-protected penicillin. Drugs of similar chemical groups have common structural units in their composition. Consequently, it is prohibited to take all penicillins, primarily protected ones, which include Ampicillin, Ticarcillin, Piperacillin.
As an alternative, antibacterial drugs can be prescribed that have a similar effect, but from other pharmacological groups:
- Meropenem;
- Azithromycin;
- Erythromycin.
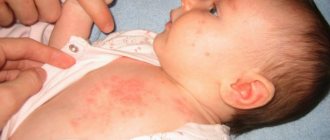
Manifestation of allergies to antibiotics in childhood
The number of children who are allergic to antibiotic treatment increases every year. This negative reaction to antibiotics in a child, the so-called hypersensitivity of the immune system, occurs during treatment. Mostly this reaction of the body manifests itself after taking drugs from the penicillin group.
The most common signs of such a pathology in a child are headache, diarrhea, stomach pain, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, itching of the skin . An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of urticaria, swelling of the eyelids and lips (Quincke's edema), itching, and rashes similar to those that appear with measles or chickenpox.

Children are sometimes more susceptible to allergies than adults
A small number of pediatric patients may experience other symptoms. The danger of an allergy to antibiotics is that, in addition to external forms of reaction to treatment, in the form of a skin rash, the child’s internal organs may suffer .
It can manifest itself in the form of reactions such as anaphylactic shock, a feeling of suffocation, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness and even loss of consciousness. Symptoms can increase quite quickly. In these cases, an urgent visit to a medical facility is necessary to take emergency measures.
Antibiotics and allergies: real and imaginary risks
On August 6, 1881, bacteriologist Alexander Fleming was born, who made a real revolution in medicine - he discovered the first antibiotic penicillin. Until the 1920s, there was no specific treatment for bacterial infections, and they often resulted in death.
During the use of antibiotics, these drugs saved many lives, but having solved one problem, they brought a number of others. This includes allergic reactions, which can sometimes themselves pose a threat to life.
MedAboutMe will tell you how hypersensitivity to antibiotics manifests itself and when you should be afraid of it.
Risk factors for developing allergies
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from antibiotic allergies. After all, a reaction can occur suddenly in any person. Yet doctors identify a number of risk factors for the development of hypersensitivity. So, people who have a history of:
Heredity (increases the risk of allergies by 15 times). Long-term use of antibiotics. Diseases such as HIV, mononucleosis, cystic fibrosis, gout, etc.
It is noteworthy that in this case the development of cross-reactions is not typical. That is, if a person has hay fever, bronchial asthma, or food allergies, this is not a risk factor.
At the same time, recent studies by American scientists from the South Carolina College of Pharmacy have revealed a connection between the use of antibiotics at an early age and the subsequent development of food allergies.
Experts analyzed the medical histories of 1,504 allergy sufferers and 5,995 healthy children and found that those who received antibiotic therapy in the first year of life suffered from food intolerance 1.21 times more often.
Moreover, the more often antibiotics were prescribed, the higher the risk of developing allergies. This picture is due to the fact that broad-spectrum antibiotics cause significant harm to the human microbiome, and this in turn affects the formation of immunity.
Skin reactions to antibiotics
Dermatological problems are the most common group of allergic reactions to antibiotics. The characteristic small, red rash is often caused by drugs that a person takes orally or that are injected. As a rule, the reaction disappears a short time after stopping the medication.
Other common manifestations of hypersensitivity to antibiotics include the following:
Hives.
Red, slightly raised, flat blisters appear on the skin, which can merge into large, uneven spots. The affected areas are itchy and often hot and swollen.
Contact dermatitis.
It occurs exclusively in response to antibiotics in ointments and creams; reactions to neomycin are most often observed. Inflammation, pain, and itching appear at the site of application of the medicine. Contact dermatitis is a delayed-type reaction: if an antibiotic is prescribed for the first time, the rash appears 5-7 days after starting the drug.
Photosensitivity.
While taking antibiotics, the skin becomes more sensitive to sunlight, easily burns and becomes inflamed. It is necessary to distinguish a photoallergic reaction from a phototoxic one.
The first develops in a delayed manner, which means it manifests itself a few days after starting to use the drug. If the skin reacts to the sun immediately, we are talking about its damage - a phototoxic reaction.
Photosensitivity is most often provoked by fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides and pyrimethamine.
Severe mucocutaneous syndromes
An allergic skin reaction may be more severe and require serious treatment. In this case, lesions can occur both primary and develop after minor reactions, if the medicine has not been discontinued. Among these syndromes:
Exudative erythema multiforme.
This is a delayed-type reaction that occurs 10-14 days after starting to take the drugs. In most patients, only the oral mucosa is affected - flat papules up to 3 cm in diameter with a pronounced border appear here. However, rashes can also affect the skin, most often the palms, feet, and elbows.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
A type of exudative erythema that affects the mucous membranes, conjunctiva and skin. The patient is intoxicated, so a few days before skin manifestations the patient complains of joint pain, fever, and weakness. In this case, internal organs can be affected, and in 5-6% of cases death occurs.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome).
An acute condition accompanied by fever and damage to internal organs. Blisters appear on the skin, the epidermis is torn away, and large wounds form. Such an allergic reaction is extremely dangerous, as it leads to death in 30-40% of cases.
Other manifestations of allergies
An allergy to antibiotics can only manifest itself as an elevated temperature - this reaction occurs in 10% of patients. Moreover, since fever is often a symptom of the disease, manifestations of allergies are attributed precisely to signs of the disease, and not to hypersensitivity to the drug.
Sensitization takes 6-8 days, so the reaction will appear approximately a week after the first dose of the drug. Normalization of temperature occurs 48-72 hours after discontinuation of the antibiotic. Drug fever is most often provoked by sulfonamides, streptomycin, and vancomycin.
Long-term use of antibiotics can provoke the development of serum-like syndrome - sometimes it develops three weeks after the start of treatment. The patient experiences fever, general weakness, urticaria, often joint pain and swollen lymph nodes. In every second patient with the syndrome, internal organs are affected.
Most of the described allergic manifestations are slow-type reactions, but the most dangerous is the immediate-type reaction - anaphylactic shock. Most often it occurs after injection of penicillin; within 5-30 minutes after the injection, a person begins to experience the following symptoms:
Pale, cold extremities. Severe weakness, dizziness. Bronchospasm, laryngeal edema. Thready superficial pulse, low blood pressure.
Anaphylactic shock is dangerous, and if the patient does not receive emergency treatment (injections of adrenaline), death occurs.
Red Man Syndrome
Red man syndrome is a specific reaction to vancomycin that occurs in 5-13% of patients receiving this drug by injection. The syndrome appears within 10 minutes after the injection; the patient becomes very red and swollen in the upper body or just the neck, and there is severe itching. Other symptoms include:
Muscle and other pain. Fever, chills. Dizziness.
In severe cases, red man syndrome leads to loss of consciousness, vomiting and even cardiac arrest. Despite similar symptoms to hypersensitivity reactions, the syndrome is not a true allergy.
Initially, it was believed that it was not vancomycin itself that led to the complication, but poor purification of the drug. However, the number of patients with reactions to the drug did not decrease even after the introduction of new antibiotic preparation technologies.
Today it is believed that the “red man” syndrome is the result of the effect of vancomycin on the composition of the blood, in particular, on the number of platelets and leukocytes.
Features of allergy to penicillin
Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered, and today medications of the penicillin group are first-line drugs for the treatment of most staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Moreover, it is penicillins that are often associated with the development of allergies.
However, is this really so? After all, the diagnosis is often made based on complaints, and not on the basis of a detailed diagnosis.
Specialists at the Medical College of Wisconsin studied the medical histories of 597 children who had a history of reaction to penicillin and concluded that true allergies to drugs in this group are extremely rare.
Thus, 434 (almost 73%) of the subjects, based on the assessment of the described symptoms, were in the low-risk group for the development of hypersensitivity. 100 of them underwent an allergological examination, and only three had a positive skin test; none of the examined children had a hypersensitivity reaction to the administration of an antibiotic orally.
Doctors from Massachusetts General Hospital also note that an allergy to penicillin must be confirmed through detailed diagnostics. According to them, 90% of those who report hypersensitivity to penicillin can actually use drugs of this group.
The danger of replacing antibiotics threatens with serious consequences, since alternative medicines can provoke the occurrence of superinfections.
According to experts, an allergy to penicillin and refusal of this antibiotic increases the risk of infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by 69%, and by 26% - diseases provoked by Clostridium difficile.
Conclusion
An allergy to antibiotics can be quite dangerous, but it must be confirmed clinically. Unreasonable refusal of drugs threatens no less harm to health.
Take the testIs your child prone to allergic diseasesIs your child prone to allergic diseases and what is the allergen? Take the test and find out what your child should avoid and what measures to take.
Source: https://doctor.rambler.ru/news/40493623-antibiotiki-i-allergiya-riski-realnye-i-mnimye/
Treatment of allergies to antibiotics
If, after starting to take the drug, an allergy to antibiotics (skin rash) occurs, the treatment of the disease must be adjusted and measures taken to get rid of negative symptoms. Knowing how to deal with a rash and recognizing a more severe reaction can help you feel better and may even save your life.
This is interesting: Rules for choosing foundation based on skin type

Knowing how to behave, you can take the necessary measures on time
If you suspect an allergic reaction, you should immediately contact your doctor and ask for help . The antibiotic to which the reaction occurred should be stopped, and before starting the next treatment, the medical staff must be warned about the adverse reaction.
Prevention
To prevent relapses of allergies to Augmentin and products with a similar structure, you must:
- Before purchasing medications, carefully study the composition;
- when prescribing any therapeutic and diagnostic measures, notify the doctor about the presence of allergies;
- do not self-medicate;
- If an allergic reaction develops, change the medication and carry out hyposensitizing therapy.
For the primary prevention of new allergies, it is necessary to eat properly and nutritiously. A lot of vitamins, macro- and microelements, and proteins should be supplied with food. Regular walks in the fresh air and vigorous physical activity will help strengthen the immune system.
Allergen replacement
If, during treatment with an antibiotic, redness of the skin, itching or other manifestations occur, this drug should be discontinued, because with each dose of the allergen the patient’s condition worsens. After the antibiotic was discontinued, the condition gradually improved.
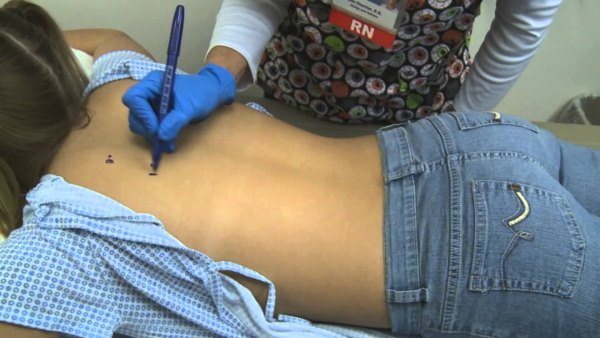
Before prescribing a new antibiotic, the doctor will refer the patient for a reaction test
But to continue treatment, you should choose another antibiotic . It is selected from the following group of drugs, having previously tested for reaction.
Important to remember! If an allergy to a certain group of antibiotics has already occurred, then there is a high probability of such a reaction occurring again. In this case, as a rule, a drug from the following group of antibiotics is prescribed, taking into account the patient’s age and the course of the underlying disease.
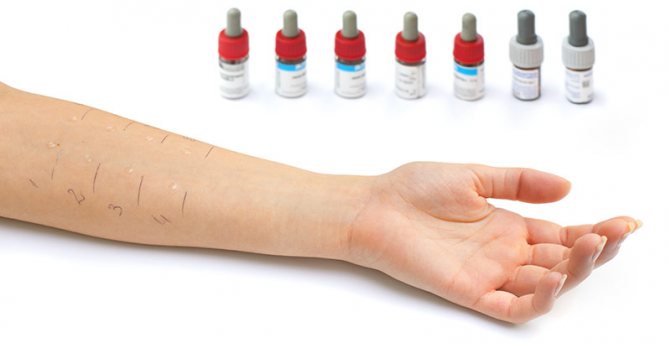
Sensitivity diagnostics
Before prescribing an antibacterial drug, the doctor interviews the patient; in the absence of cases of negative reactions to medications, diagnostics may not be carried out. If the patient has a history of similar cases, then an antibiotic is prescribed after testing to ensure the safety of the prescribed medication:
- general blood analysis;
- antibiotic test;
- blood test for immunoglobulin E.
Various studies are carried out: sublingual, skin, inhalation.
Antihistamines
Signs of an allergy to antibiotic treatment in the form of a skin rash, swelling of the mucous membranes, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, arrhythmias occur when free histamine is released into the blood vessels.
Antihistamines increase the number of white blood cells in the blood and reduce the production of histamine, which is produced by the immune system in response to an allergen. Depending on the patient’s condition, the doctor may prescribe the following antihistamines: Loratadine, Cetirizine, Diphenhydramine.

Antihistamine
Their doses will depend on a number of factors, including the patient's age and body characteristics. You should carefully study the instructions for using the medication.
Such drugs are not recommended for children under 4 years of age and elderly patients , as dizziness, irritability, and drowsiness may occur. Antihistamines, which cause drowsiness, should not be taken with antidepressants, sleeping pills, or strong pain relievers.
Attention! Antihistamines should not be used by pregnant women or women who are breastfeeding. These drugs may cause side effects in children or cause birth defects in the fetus.
Treatment

You cannot do without treatment in such a situation. Urticaria can be treated at home as recommended by your doctor, but all other anaphylactic conditions require an emergency call to the ambulance.
For outpatient treatment the following is prescribed:
- Avoiding contact with the allergen. It is necessary to stop taking the antibiotic and not take drugs from the same pharmacological group.
- Following a special diet. First of all, dairy products, citrus fruits, cocoa, coffee, vegetables and fruits painted in bright colors (red, yellow, orange) are excluded from the diet.
- Antihistamines are the main method of treatment. For children, drugs such as Zyrtec and Cystine are suitable. Adults can use Tavegil, Loratadine or Suprastin.
- If the inflammatory process is pronounced, then glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) in the form of ointments, gels or tablets for oral administration can be prescribed.
Desensitization
This method of getting rid of allergies is used for long-term treatment methods and if other methods have failed to get rid of the negative reaction.
The essence of this method is to inject a small amount of allergen subcutaneously over a long period . The dose of the administered allergen is constantly increasing, so that the body gradually gets used to it.

Desensitization - injection of an allergen under the skin
But the disadvantage of desensitization is that it is not possible to completely get rid of the manifestations of allergies; the level of sensitivity to the allergen can only decrease. The duration of treatment using this method can be up to 5-6 years. But if the result from this method is not noticed during the first 2 years, then the treatment is stopped.
Drugs that cause allergies

There are several main groups of antibiotics. These include:
- penicillin;
- tetracycline;
- sulfonamides;
- aminoglycosides;
- chloramphenicol;
- cephalosporin;
- syntomycin;
- macrolides.
It is on their basis that most antibacterial agents are made. Most often, allergic reactions are provoked by drugs from the penicillin group. This is because penicillin was invented first.
Traditional recipes for eliminating skin rashes
An alternative to treating allergies to antibiotics with medications is traditional medicine. There are several ways to get rid of skin rashes. The simplest and most accessible method is treatment with medicinal herbs: nettle, celery, yarrow, hawthorn, valerian or lemon balm.
Decoction of medicinal plants
The prepared decoction of the medicinal plant is applied to the affected areas 2-3 times a day. The decoction is prepared by infusing 1 tbsp in a water bath for 10 minutes. l. herbs per 200 ml of boiling water.
Celery
Celery juice is consumed half an hour before meals, 1 tsp. Juice is prepared from a fresh plant using a juicer, or by squeezing the plant, grated on a fine grater.

A plant that helps get rid of skin rashes
Allergen c1 – penicillin G, IgE
[21-062] Allergen c1 – penicillin G, IgE 600 rub.
Quantitative determination in the blood of specific immunoglobulins of class E to the antibacterial drug of the penicillin series - benzylpenicillin.
Synonyms Russian
Specific immunoglobulins class E to penicillin G (benzylpenicillin).
English synonyms
Allergen, Drug, Penicilloyl G, IgE; Penicillin G (benzylpenicillin) , IgE Ab in Serum.
Research method
Chemiluminescent immunoassay.
Units
kU/l (kilounit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Penicillin G (benzylpenicillin) is a natural broad-spectrum antibiotic obtained through industrial fermentation of the mold Penicillium chrysogenum. Benzylpenicillin inhibits the synthesis of bacterial cell wall components, which causes the destruction of microorganisms.
It is active against gram-positive bacteria (many strains of staphylococci and streptococci), actinomycetes, as well as corynebacteria diphtheria, anthrax bacilli, gonococci, Treponema pallidum and some other spirochetes.
Bacteria that produce the enzyme penicillinase, most gram-negative bacteria, rickettsia, protozoa, viruses and fungi are resistant to the action of penicillin and other β-lactam antibiotics.
Benzylpenicillin is prescribed strictly for bacterial infections caused by sensitive pathogens, for example, pneumonia, pleural empyema, bronchitis, septic endocarditis, wound infections, purulent infections of the skin, soft tissues and mucous membranes (including
erysipelas, impetigo, secondary infected dermatoses), peritonitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis, ENT infections (angina), meningitis, diphtheria, gas gangrene, scarlet fever, gonorrhea, leptospirosis, syphilis, anthrax, pulmonary actinomycosis, urinary and biliary tract infections , treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases in obstetric and gynecological practice, eye diseases.
In medical practice, benzylpenicillin sodium, potassium or novocaine salt is used. Benzylpenicillin is administered intramuscularly, intravenously, and also into the cavities, under the conjunctiva, into the spinal canal, and into the trachea.
Penicillin antibiotics began to be used in the 1940s, and their ability to cause allergic reactions became known almost immediately.
Penicillin molecules are too small to produce an immune response on their own.
However, the β-lactam ring of penicillins is capable of covalently binding to serum and cell wall proteins, forming a hapten-carrier conjugate, which may already have allergenic properties.
According to statistics, allergies to penicillins are observed in 10% of patients. Anaphylactic reactions to penicillins occur in 1-4 per 10,000 patients treated with these drugs.
From a clinical and pathogenetic point of view, allergic reactions to penicillins are divided into reactions of immediate (within one hour from taking the drug) and delayed (from 1 to 48 hours) types. The immediate type of reaction is usually associated with the presence of IgE antibodies, while the delayed type is due to T-cell mechanisms.
Immediate reactions to antibiotics may include urticaria, angioedema, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, or anaphylactic shock.
Delayed reactions are characterized by a maculopapular rash, delayed urticaria/angioedema, in rare cases exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exenthematous pustulosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis. Risk factors for the development of severe allergic reactions are concomitant pathologies, such as cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, neoplasms, and use of beta blockers.
There is significant cross-reactivity between various penicillins, as well as primarily first-generation cephalosporins.
Diagnosis of an allergy to antibiotics is not easy and includes skin prick tests, intradermal administration of the drug, provocative administration of the drug, and determination of IgE-specific antibodies.
In case of immediate allergic reactions, skin and provocative tests, despite their high sensitivity, can cause severe allergic manifestations, including life-threatening reactions. When examining patients with positive skin tests for penicillin G and amoxicillin, specific IgE antibodies to benzylpenicillin were detected in 68%.
Determination of IgE-specific antibodies to penicillin G, compared to skin prick tests, is slightly less sensitive, but more specific and safe for the patient.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to benzylpenicillin and other penicillin antibiotics;
- for differential diagnosis of the causes of allergic reactions in children and adults while taking antibiotics.
When is the study scheduled?
- When planning to prescribe benzylpenicillin or other penicillins in patients with suspected antibiotic allergies;
- when examining children and adults with urticaria, angioedema, rhinoconjunctivitis, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock after the use of antibacterial drugs.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0 – 10 IU/ml.
Reasons for the positive result:
- immediate hypersensitivity to penicillin G.
Reasons for negative results:
- lack of IgE sensitization to this allergen;
- long-term restriction or exclusion of contact with the allergen.
Important Notes
- The absence of IgE antibodies does not exclude the possibility of developing delayed-type allergic reactions to this drug. It is recommended to determine the delayed type of hypersensitivity using patch tests.
- Performing this study is safe for the patient compared to skin tests (in vivo), since it eliminates the patient’s contact with the allergen. Taking antihistamines and age characteristics do not affect the quality and accuracy of the study.
Also recommended
[02-029] Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukocyte formula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear to detect pathological changes) [08-017] Total immunoglobulins E (IgE) in serum [21-673] ImmunoCAP ISAC allergy chip (112 allergenic components ) [21-018] Allergen c203 – ampicillin, IgE [21-017] Allergen c204 – amoxicillin, IgE
+ determination of specific immunoglobulins class E for other allergens
Who orders the study?
Allergist, pediatrician, therapist, surgeon, general practitioner.
Literature
- LevineBB, PriceVH. Studies on the immunological mechanisms of penicillin allergy: II. Antigenic specificities of allergic wheal-and-flare skin responses in patients with histories of penicillin allergy. Immunology 1964; 36: 542-56.
- Blanca M, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Warrington R, Romano A, Demoly P et al. Side chain specific reactions to betalactams: Twelve years later. Clin Exp Allergy 2002; 32: 192-7.
- Bousquet PJ, Kvedariene V, Co-Minh HB, Martins P, Rongier M, Arnoux B et al. Clinical presentation and time course in hypersensitivity reactions to β-lactams. Allergy 2007; 62: 872-6.
- Blanca M, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Reche M, Moya MC, Rodriguez JL et al. Clinical evaluation of Pharmacia CAP System RAST FEIA amoxicilloyl and benzylpenicilloyl in patients with penicillin allergy. Allergy 2001; 56: 862-70.
- Goldberg A, Confino-Cohen R. Skin testing and oral penicillin challenge in patients with a history of remote penicillin allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma immunol 2008; 100: 37-43.
- Vervloet D., Pradal M., Birnbaum J., Koeppel MC Drud allergy. Phadia AB. 2012; 77-82.
Source: https://helix.ru/kb/item/21-062