28.07.2017
Allergic pharyngitis is a disease that affects the pharynx, or rather the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
The development of allergic pharyngitis occurs due to interaction with allergens and occurs together with allergic rhinitis.
Allergic pharyngitis occurs in people of all ages, but young people who live in urban areas and inhale polluted air along with harmful substances are often susceptible to the disease.
The disease is severe and difficult to correct; the performance and quality of life of the patient deteriorates. It is important to identify and begin to treat the disease in the early stages.
Allergic pharyngitis is a difficult to tolerate illness, so treatment should be started at the earliest stages
Causes of allergic pharyngitis
Allergic pharyngitis is observed in people living in regions with cold climates. The disease occurs as a reaction of the immune system to the penetration of pathogenic organisms and allergens into the body.
Irritants for the onset of illness can be varied and are individual for each person.
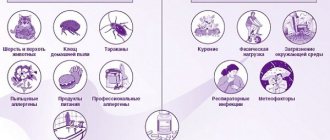
The following substances can act as a provocateur of allergic pharyngitis:
- dust in the apartment and on the street;
- pollen of various plants;
- car exhaust gases;
- animal hair;
- medications;
- tobacco smoke;
- chemicals and cosmetics;
- food products.
Allergic pharyngitis occurs in young, able-bodied people who work in hazardous industries involving chemicals.
Cold climates that harbor varieties of bacteria and infections are one of the common causes of allergic pharyngitis.

The main cause of the disease is weakened human immunity.
Causes
The causes of immune inflammation of the nasopharynx are a number of irritating substances of various origins, which can lead to a tissue response only in predisposed individuals. Allergic pharyngitis has more than one development mechanism; accordingly, the clinical manifestations will differ.
The development of allergic pharyngitis is caused mainly by two types of allergies:
- Immediate-type hypersensitivity (IHT) is a rapid clinical development. More often it is an allergy to pollen (hay fever), allergic rhinitis, food allergy. Pharyngitis is also a manifestation of these diseases.
- Delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) – slow development of symptoms and pharyngitis in this case is more often formed with allergies to pet hair, dust mites, and chemicals.
Predisposition to allergic pharyngitis is due to the following:
- insufficient production of local immunoglobulin A - antibodies representing local immunity;
- dysfunction of the epithelium of the respiratory tract, as a result of which allergens easily penetrate into the nasopharynx;
- disruption of the functioning of phagocytes of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract;
- increased vascular permeability.
These factors lead to a perverted reaction of nasopharyngeal tissue in response to the allergen, which leads to immune inflammation and pharyngitis. The clinic of allergic pharyngitis in adults develops under the influence of the following factors:
- Pollen of woody plants (birch, alder, oak, hazel, maple, elm, ash, poplar).
- Pollen of cereals (rye, corn).
- Pollen from weeds and forbs (bluegrass, dandelion, timothy, wheatgrass, fescue, foxtail, plantain, wormwood, nettle, quinoa, sunflower).
- Aerosol medications (antibiotics, herbal and combination throat sprays, etc.).
- Production factors (chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, vitamin-protein complexes, suspensions of microorganisms, aerosols of synthetic detergents, perfumes).
- Wool, animal feathers.
- Fungus.
- Waste products of insects (dust mites).
- Food (fish, shrimp, nuts, honey and other products).
Development of allergic pharyngitis
There are a number of factors that provoke the development of allergic pharyngitis:
- past viral diseases;
- impaired blood circulation;
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx and oral cavity;
- long stay in the cold;
- genetic predisposition.
An important factor influencing the development of allergic pharyngitis is a weakened immune system. It is necessary to strengthen it and lead a healthy lifestyle, which will allow the body to better cope with any ailments, including pharyngitis.
Symptoms of allergic pharyngitis
Allergic pharyngitis, symptoms similar to those of a viral infection, does not occur in isolation.
But it is difficult to confuse them with the symptoms of other diseases, because the symptoms of allergic pharyngitis are specific and occur upon contact with an irritant.
The clinical picture is the same, regardless of age category; in children the symptoms are more pronounced than in adults.
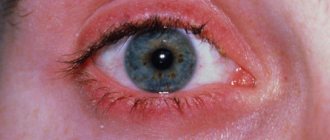
The mucous membrane of the sinuses and eyes is often affected, resulting in the manifestation of conjunctivitis.
At the beginning of the disease, a sore throat begins to be felt, which occurs as a result of the allergen getting into the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
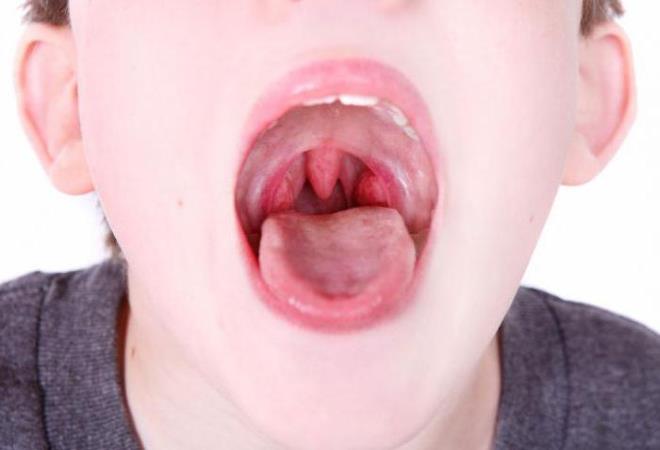
The development of pharyngitis occurs immediately after contact with an allergen
The main signs of allergic pharyngitis include:
- pain in the throat, burning sensation, heat;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- severe attacks of dry cough, which interferes with the normal swallowing process;
- acute painful sensations when swallowing and eating food;
- severe runny nose or nasal congestion;
- change in voice timbre;
- difficulty breathing, attacks of suffocation may occur;
- sneezing appears;
- itching occurs in the nose, throat or eyes;
- periodic headaches, disturbed sleep, depressed state.
Children with pharyngitis of allergic etiology may experience ear pain and itching. In some cases, allergic pharyngitis occurs with conjunctivitis, which is expressed in tearing, redness of the eyes, and itching.
Body temperature does not change, but in some cases there is a slight increase.

Allergic pharyngitis can provoke the parallel development of other diseases
Complications of allergic pharyngitis
The chronicity of acute allergic pharyngitis is often replaced first by catarrhal chronic allergic pharyngitis, and then chronic laryngitis of allergic etiology occurs.
This is fraught with the development of false croup, especially in children. Swelling of the larynx can cause suffocation. And then any resumption of contact with the allergen during chronic inflammation of the larynx can result in an exacerbation of the pathology with a fatal outcome.

Also, a chronic process can provoke the development of chronic foci of inflammation in the nasopharynx in the form of sinusitis, otitis, polyposis, tonsillitis, adenoids, etc. In any of these cases, the local immunity of the mucous membranes is reduced.
At the same time, the bacterial flora is revived, in particular streptococci, which always have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the heart, kidneys and lungs. The consequence may be rheumatism. In other words, allergic pharyngitis is a serious problem and should not be dismissed lightly; When it occurs, treatment must be carried out to completion.
The danger of allergic pharyngitis
After the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to contact an otolaryngologist so that the disease does not develop into a chronic form, which often occurs with constant contact with the source of an allergic reaction.
The symptoms of allergic pharyngitis in chronic form intensify and there is a high probability of other nasopharyngeal and ear diseases.
The danger of the chronic form of this disease is that there is a risk of swelling of the larynx, which in some cases leads to suffocation, especially in children.
The greatest threat to a patient with pharyngitis is the chronic form when the exposure of the allergen to the pharynx continues.
With a prolonged course of the disease, allergic pharyngitis turns into allergic laryngitis, which weakens the immune system and there is a high probability of the disease developing into catarrhal pharyngitis.
This form of respiratory disease leads to the development of diseases of various internal organs. From all this we can conclude that allergic pharyngitis is a serious disease that needs to be treated quickly.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of allergic pharyngitis will prevent the occurrence of terrible consequences in the form of otitis media, rheumatism and renal pathologies.
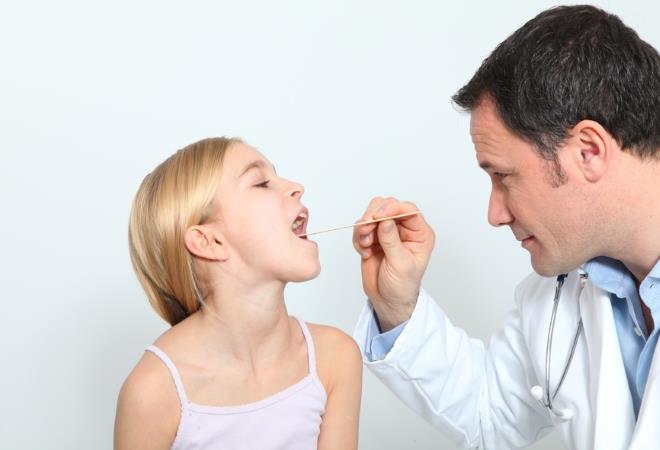
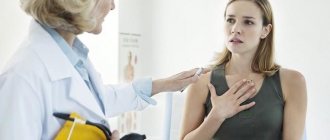
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by an ENT specialist, but only after a preliminary examination by a therapist and consultation with an allergist.
Pharyngitis in pregnant women
As you know, any disease during pregnancy poses a danger not only to the mother, but also to the child. Allergic pharyngitis is already a serious problem, and if it occurs in the first trimester, the pregnancy can be terminated. If it appears later, premature birth is possible.
Treatment of allergic pharyngitis in adults and children is carried out differently. As for pregnant women, they need to pay special attention. A large number of drugs are prohibited from being used during this period, so doctors prescribe mild remedies in the form of inhalations, rinses, etc. To completely get rid of the pathology, you need to determine the cause and fight it.
Diagnosis of allergic pharyngitis
Diagnosis of allergic pharyngitis is carried out by an ENT specialist and an allergist, but only after examination by a therapist. The first step is to examine and interview the patient, examine the clinical picture of the disease and analyze the patient’s medical history.
The next important step is to perform a pharyngoscopy, which allows the doctor to examine the back of the throat.
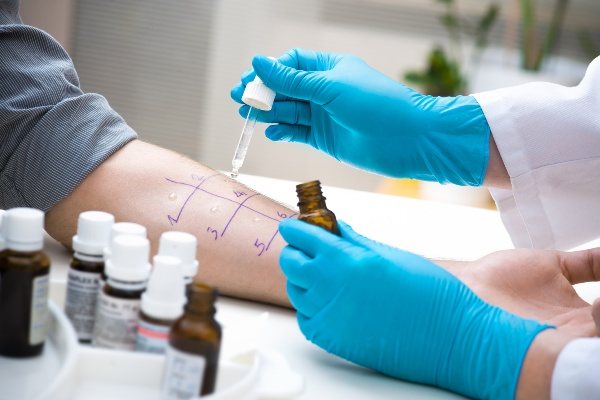
An important point in diagnosing allergic pharyngitis is identifying the type of allergen that affects the mucous membrane of the throat. For this purpose, a number of studies are carried out, skin tests are prescribed, thanks to which the cause of the disease can be established.
A characteristic sign indicating the presence of a disease such as allergic pharyngitis is an excess level of immunoglobulin E in the blood.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures for allergic pharyngitis are carried out during periods of exacerbation and remission.
On examination, there is pronounced hyperemia and swelling of the posterior wall of the pharynx, and transparent mucous discharge from the nasal cavity. During auscultation, harsh breathing may be heard. During an acute process, the patient undergoes the following studies :
- A smear of mucous discharge from the nose to check for eosinophilia.
- A general clinical blood test, which reveals an increase in the level of eosinophils.
- Blood test for total immunoglobulins G, M, E: with HNT, the E-fraction increases, with HRT – G, M.
Skin allergy tests are carried out 4 weeks after the end of treatment and in the absence of clinical manifestations.
Injection tests (prick-test), scarification tests, and provocative nasal tests are also performed. During remission, the immune status is examined (blood immunogram).
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- viral tonsillitis;
- angina;
- nasal polyps;
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- sinusitis.
Infectious diseases that occur in the same way as the main manifestations of allergic pharyngitis are characterized by an increase in temperature and an inflammatory reaction of the blood: an increase in the total level of leukocytes, band neutrophils, ESR, C-reactive protein. Sore throat is characterized by the presence of purulent plaque on the tonsils.
Methods for treating allergic pharyngitis
Immediately after diagnosing allergic pharyngitis, you need to begin comprehensive treatment of the disease. This will help quickly alleviate the patient’s condition, but also prevent the development of inflammation and serious consequences.
The main thing in effective treatment of the disease is the identification and elimination of the affecting allergen. Depending on the symptoms and the appropriate treatment, all medications are selected individually.
When the irritant is identified and eliminated, drug treatment and immunotherapy are prescribed. Medications are mandatory if it is impossible to eliminate contact with the allergen. And strengthening the immune system will speed up recovery and reduce the likelihood of relapses.

Treatment of pharyngitis is carried out both with medication and with the help of physiotherapy
Diagnosis and treatment of allergic inflammation of the pharynx
An ENT doctor can identify pharyngitis after a thorough interview and examination of the patient. Sometimes, especially in the chronic course of the disease, pharyngoscopy is necessary. Treatment should be prescribed by an allergist or, for adults, a general practitioner, and for children, a pediatrician. When receiving treatment from several specialists at once, you can increase the effectiveness of therapy and the speed of recovery. Before treating allergic pharyngitis, the causes that caused the reaction should be eliminated (get rid of bad habits, change jobs). It is necessary to remove the plaque that has formed on the mucous membrane of the throat and “feed” the immune system. Pharyngitis in adults and children can be treated with:
- folk and traditional medicine;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- warming up the throat;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- antibiotic therapy.
According to the data obtained, treatment of chronic and acute pharyngitis with antibacterial drugs reduces the likelihood of developing rheumatism by 80% and other complications (abscess, otitis media). As a rule, penicillin antibiotics are prescribed; sometimes preference is given to macrolides, cephalosporins and lincosamides. If, 3 days after using antibacterial agents, manifestations of the disease remain, then the treatment is considered ineffective. The specialist must decide on another treatment. You cannot reduce the course of these medications. Antihistamines (Claritin, Cetrin, Zyrtec, Fenistil) are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. It is not recommended to use first-generation drugs because they increase the viscosity of sputum. It is imperative to get rid of foci of chronic infection in the orgasm, for example, caries. Inhalation and rinsing with decoctions of calendula, sage, mint, eucalyptus, chamomile and hop or pine cones are considered effective symptomatic treatment that is safe for children. Procedures should be carried out regularly 3 to 6 times a day. For cooking you need to take 2 tbsp. herbs and boil it in 200 ml of water. Bee products are not used because they are very allergenic. Iodine-containing drugs are also excluded. If you have allergic pharyngitis, you should definitely adhere to a certain diet. It is recommended to exclude seafood, mushrooms, honey, smoked meats, whole milk, canned foods, eggs, and citrus fruits from the diet. You should also remove alcohol and carbonated drinks, red and sour fruits, vegetables, chocolate, and grains from your diet. After normalization of the condition, you can switch to your usual diet. To reduce irritation of the pharynx, it is necessary to avoid irritating, salty, spicy, rough foods, hot and cold foods. The diet should be dominated by greens, cereals, cucumbers, zucchini, green fruits, lean meat and dairy products. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiseptic and antibacterial agents are used for local treatment. Gargling with hexoral solution, isotonic solution, chlorhexidine, furatsilin, miramistin, rotokan and potassium permanganate, iodine, hydrogen peroxide or salt diluted in a glass of water can help eliminate soreness and dryness in the throat. It is recommended to lubricate the throat with collargol, protargol or a solution of silver nitrate. In complex therapy, all patients are prescribed sprays (Cameton, Camphomen, Decathylene, Ingalipt, Stopangin) and lozenges (Faryngosept, Ajisept, Septolete, Strepsils, Salvia). Cytovir-3, Kagocel, Arbidol, Gripferon and Aflubin help speed up recovery and increase the immune response. The formation of local specific immunity is promoted by interferon, imudon, lysobact and IRS-19. In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser coagulation;
- galvanotherapy;
- cryotherapy;
- cauterization with silver nitrate and vagotil.
We recommend reading: Leukocyte intoxication index: decreased or increased, what does it mean
In complex advanced forms of the disease, novocaine blockades are performed using vitreous, aloe and traumeel. Sometimes physiotherapy is recommended: electrophoresis, magnetic and laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, inductometry, mud or paraffin applications. Climatic treatment plays an important role; the sea coast and mountainous areas are ideal for this.
Treatment of allergic pharyngitis with medications
Medications and physical therapy are an integral part of the treatment of allergic pharyngitis. Antiviral and antihistamine drugs are prescribed, which quickly and effectively eliminate allergy symptoms.
In more advanced cases, when the patient develops allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma, the patient is prescribed vasoconstrictor drugs and glucocorticosteroids, the use of which must be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
Prevention of allergic pharyngitis
By following preventive measures, the likelihood of allergic pharyngitis will significantly decrease. To do this, you need to change your usual lifestyle. In general, it will be enough to avoid interaction with irritants that provoke an allergic reaction.
But, there are some other recommendations that will reduce the risk of allergic pharyngitis:
- strengthening the immune system with immunostimulating drugs. It is also recommended to consume vitamins and minerals;
- prevent the development of chronic forms of respiratory diseases;
- you need to breathe not through your mouth, but through your nose;
- carry out wet cleaning of the premises at least 2 times and ventilate the apartment every day;
- get rid of bad habits such as cigarettes and alcohol;
- harden the body.