general information
Allergy is a pathological process in which the immune system, after the first contact with an allergen substance, produces immunoglobulins against it, and upon repeated contacts activates them.
They act on mast cells that synthesize histamine , and they release it into the blood in certain quantities (depending on the level of sensitization - sensitivity - of the immune system to the substance).
The higher the sensitization, the stronger the allergic reaction. With moderate and mild sensitization there is no threat to life, but its quality deteriorates and the likelihood of complications increases.
If the sensitization is significant, a person may experience an acute allergic reaction with anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal.
Starch is a high molecular weight carbohydrate that consists of two polysaccharides: amylopectin and amylose. It is actively used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. It is also added to wallpaper glue and used to starch clothes.
Starch is harmless and is actively used as a natural thickener. Other thickeners are also made from it, such as maltodextrin (E-459). It is easily broken down once it enters the human body and, like many other carbohydrates, provides a sufficient amount of energy.
The following types of starch are actively used:
- Potato. A quarter of potatoes consists of starch. Potato starch is used in the food and technical industries.
- Corn. Corn is one of the leaders in starch content. It, like rice, consists of two-thirds rice, so it is often used to make it.
- Rice. Most common in cosmetology and pharmacology. Has a beneficial effect on the skin.
- Wheat. A high level of plasticity and a neutral odor distinguish it favorably from other types of starch. Often used in the production of sausages, in the textile industry and a number of other industries.
Also starch has quality levels. The higher quality is used in the food industry, pharmacology and cosmetology, while the lower quality is more often used for technical purposes.
What is starch?
Starch is a chemical substance that is a long chain of carbohydrates - a polysaccharide. In addition to sugars, it contains up to 2% of other components - fats, proteins, minerals. It looks like a white powder, has no taste or smell, and in hot water it acquires viscosity and stickiness (due to this property, a paste is prepared).
In general, starch is a natural compound. It is formed in the form of granules in plants, being a by-product during the processing of glucose. Representatives of the flora world use it as a backup power source.
Photo: Potato starch is one of the most common
What plants “can” form starch? These are mainly grain crops, root vegetables, legumes and some fruits. Depending on what type of culture starch is synthesized, it is divided into several types:
- potato starch;
- wheat starch;
- rice starch;
- corn starch;
- rye starch;
- etc.
The main function that this product performs in the body is additional energy generation.
Allergenic substances
Features of starch allergy:
- Components of pure starch rarely cause an allergic reaction. Most often, protein compounds that are part of the products from which it was made (potatoes, corn, wheat, rice) act as an allergen. They remain in it in small quantities.
- The main allergens in corn starch are the proteins glutelin and zein. Other substances contained in corn can also cause an allergic reaction.
- In rice, allergens are often transport proteins that do not disappear even after careful heat treatment.
- potato allergens are patatin, tuberin, cathepsin D.
- Wheat is also found in other grains such as oats, rye, and barley. They are also used to make some types of starch.
- An allergic reaction to starch can occur in a child of any age, even infants. If a mother consumes large quantities of foods rich in starch, or foods that contain starch or starch-based thickeners, allergens enter the child’s body during feeding and affect the development of allergic reactions.
- Allergies can also occur upon contact with starch, which is contained in medicines, glue, and cosmetic products. For example, baby powder is made using large amounts of starch. If a child has a high sensitization to vegetable proteins, which are part of starch, then a pronounced allergic reaction will occur upon contact with starched clothes and sheets.
An allergy to starch can also be false: the child’s gastrointestinal tract cannot always digest it fully, which leads to the appearance of allergic symptoms.
This is due to age-related enzyme deficiency. Starch intolerance causes pseudo-allergic reactions to potatoes, corn, rice and other starch-rich vegetables and grains.
Allergy to potatoes in children and adults
Potato allergy is a very rare disease. However, even in a mild form it causes a lot of inconvenience, since potato starch is included in many popular products: infant formula and purees, boiled sausages, confectionery, ketchups and other sauces.
Potato allergy symptoms
Potato allergies can be difficult to diagnose: this vegetable is considered hypoallergenic, so it is the last one to come under suspicion.
The painful reaction is caused not by the potato itself, but by the proteins it contains (in particular, tuberin) or starch. The disease provokes cross-allergy to other nightshades: tomatoes, eggplants, physalis, peppers.
Potato allergies manifest themselves in different ways. The severity of the reaction largely depends on the form in which the potatoes are consumed. Peeled, soaked in water and cooked tubers have much less starch than those prepared in other ways. Therefore, the reaction to tomato sauce with a high starch content may be more severe than to ordinary boiled potatoes.
There are 4 types of body reactions to an allergen:
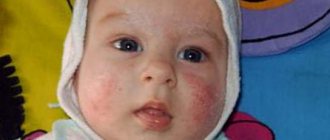
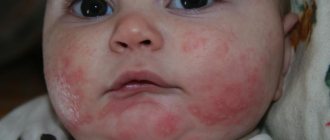
- Dermatological – itching (at the initial stage – in the oral cavity), rash (urticaria), atopic dermatitis. In mild cases, red spots or pimples filled with fluid appear around the mouth, in more severe cases they spread over the face, neck, chest, abdomen, back, and cover the entire body. Sometimes a rash on the hands occurs when peeling potatoes, especially young ones.
- Food – stabbing pain in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Respiratory – allergic cough, shortness of breath, nasal congestion, runny nose as a result of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. Usually the reaction occurs after an allergic person eats potatoes. But especially sensitive people cannot even stand the smell of freshly peeled potatoes.
- Systemic – extremely rare, but the most severe, requiring immediate hospitalization. Allergy sufferers may experience an attack of hypotension (a significant decrease in blood pressure), develop Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock.
If there is a suspicion that it is potatoes that cause an allergic reaction, it is excluded from the diet for 3–4 weeks. Then you need to eat some potatoes. If an allergy sufferer feels worse, it means that the problem is in this product.
However, the same symptoms are also caused by potato poisoning, which was grown using excessive doses of pesticides. If an adult who has not suffered from a potato allergy suddenly develops symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor and get tested.
Often it is potato starch that causes allergies.
There are several ways to determine an allergen substance:
- CAP-RAST analysis – test for the detection of class E immunoglobulin in the blood;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA, or ELISA);
- allergy screening;
- bloodless skin tests. The first option is prick tests, when the skin of the forearm is pierced in 10–15 places to a depth of 1 mm, without touching the blood vessels. One of the allergens is applied to the site of each puncture. The second option is scratch testing, when small scratches are made instead of punctures.
An allergist should determine the feasibility of conducting a particular test. Skin tests are dangerous during periods of exacerbation of the disease; they are not performed on children under 5 years of age.
Potato allergy in children
Allergy symptoms: rashes, colic, can already appear in infants up to 3–3.5 months of age. If the allergen enters the baby’s body through mother’s milk, the woman should stop eating potatoes until the end of breastfeeding.
But more often, children suffer from allergies when bottle-fed: some formulas contain starch. In such cases, you should choose expensive hypoallergenic baby food (not to be confused with medicinal formulas!), preferably based on goat's milk.
Babies from 4 months to one year are at even greater risk: potato starch is contained in children's curds and purees. But at this age, the gastrointestinal tract continues to develop, and it is difficult for it to adapt to adult food.
If an allergy to potatoes is detected in a child older than four months, it is necessary to exclude the product from complementary foods.
Next time, you can let your baby try potatoes at the age of 11–12 months, and it is advisable to prepare tubers grown using organic farming without the use of pesticides. If the allergy appears again, you should wait until 2-3 years.
It wouldn’t hurt to consult a doctor and get tested, but it’s too early to sound the alarm: in most children, potato allergy goes away after 6 years.
Preventing allergy symptoms
People allergic to potatoes must adhere to the following rules:
- carefully read the instructions for products and do not buy those that contain potato starch;
- try not to buy loose boiled sausages, baked goods and confectionery products of unfamiliar brands;
- in catering establishments, not only order dishes without potatoes, but also inform the waiter about the allergy;
- When visiting, be sure to tell your hosts about your illness (potatoes are often added to dough and curd desserts);
- do not peel potatoes, and if you still have to, wear rubber gloves;
- Always have antihistamines with you (for example, Diazolin, Suprastin or Claritin). To treat the rash, use ointments with corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, prednisolone). Be sure to take them with you on trips.
Treatment of potato allergy
For radical treatment of the disease (that is, treatment of not the symptoms, but the causes of the disease), the ASIT method has been developed - allergen-specific immunotherapy. The doctor identifies the allergen and begins to periodically introduce it little by little into the patient’s body (using injections or tablets). Adults are more often given subcutaneous injections into the shoulder; children under 5 years of age are allowed only tablets.
During treatment, it is important to strictly adhere to the schedule of administration of the substance causing the allergic reaction. Gradually, the body gets used to the allergen, and a kind of hardening occurs.
Treatment is long-term: first, you need to visit a doctor 1-2 times a week for 3-6 months, then 1-4 times a month for 3-5 years. The method is not suitable for everyone, since 1–2 weeks before the start of treatment and in the first 3–6 months you should not take antihistamines.
According to the Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ASIT does not help about 10% of patients: mainly those who missed the treatment schedule. 5% of patients recover completely, and the rest go into remission, lasting up to 20 years.
Error in text or recipe? Select it with the mouse and press Shift + Enter
Source: https://kartofan.org/byvaet-li-allergiya-na-kartoshku.html
Reasons for appearance
Factors that influence the occurrence of an allergic and pseudo-allergic reaction to starch:
- Heredity. A child may inherit increased sensitivity to certain allergens from parents or other close relatives.
- Complications during pregnancy and childbirth. If pregnancy and childbirth were accompanied by disturbances (infectious diseases in the mother, placental abruption, hormonal imbalances, severe toxicosis, early onset of labor, birth injuries, hypoxia, etc.), the likelihood that the child will have allergic reactions increases.
- Hormonal changes associated with puberty or hormonal imbalances can also lead to hypersensitivity to certain allergens.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If a child has chronic diseases of the stomach, intestines (gastritis, ulcers), liver and pancreas, the process of digesting starch will be difficult, which can cause signs of allergies.
- Errors in the process of introducing complementary foods. If parents introduce complementary foods too early and in large quantities, the child's gastrointestinal tract may not be able to cope with the load. Allergic reactions are a common occurrence in babies who are beginning to become familiar with adult foods.
- Weakened immunity. Children with weak immune systems are more likely to have allergic reactions. Stress, frequent antibiotic therapy, chemotherapy treatment, radiation therapy, and steroids weaken the immune system.
Find out about the symptoms of yeast allergy in infants from our article.
Why are there allergies to bread and pasta?
As incredible as it may sound, people are allergic to bread, pasta, baked goods and cookies. It would seem, how can such basic products be excluded? However, people with celiac disease (this is the scientific name for this condition) have to remove these foods from their diet to stay healthy.
Celiac disease (gluten intolerance) is a hereditary disease with many nonspecific symptoms: from them it is impossible to say with complete certainty that a person has the disease - it can only be suspected.
The variety of symptoms is due to the fact that with celiac disease the absorption of nutrients from the intestines into the blood is disrupted; their deficiency can cause changes in the functioning of any organ, and hence the variety of manifestations of the disease.
Impaired absorption is explained by inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, which occurs when foods containing gluten enter the digestive system.
Gluten (gluten) is a protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats. Accordingly, it is also found in all products made from these cereals.
Since celiac disease is a genetic disease, it was long believed that it manifests itself primarily in early childhood.
It is now reliably known that symptoms of the disease may not appear for many years, and it happens that celiac disease is diagnosed for the first time in a fairly old person. Once celiac disease occurs, it will not go away.
Unrecognized and untreated, it can predetermine a person’s health for the rest of his life.
Symptoms
They vary depending on the age of the person. In children under one year of age, signs of celiac disease appear after the introduction of complementary foods (porridge) and when switching to artificial feeding.
Signs of celiac disease in children:
- prolonged, sometimes watery diarrhea (in this case it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with intestinal infections);
- vomit;
- the child’s refusal to eat and, as a result, poor weight gain, or even complete weight loss;
- irritability, tearfulness or, conversely, lethargy.
Symptoms of celiac disease in preschool children:
- attacks of nausea;
- alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- nonspecific abdominal pain;
- retardation in mental and physical development.
In adolescence and young adulthood, the processes of growth and development are especially intense, so a lack of nutrients can lead to more serious consequences and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- short height (girls 155 cm, boys 165 cm);
- delayed puberty (in girls, secondary sexual characteristics appear after 15 years);
- anemia (in adults this is often the only symptom), which does not go away even with treatment with iron supplements, which is explained by poor absorption of iron through the inflamed intestines;
— in young women, celiac disease can manifest itself as irregular menstruation, miscarriages, the birth of low-weight children, and infertility;
- rash in the form of blisters or spots on the knees, elbows and buttocks;
— depressions or grooves of a yellowish-brown color on the surface of the teeth (such changes do not occur on baby teeth);
— laboratory tests reveal an “unreasonable” increase in the levels of liver enzymes AlAt and AsAT, which normalizes after switching to a gluten-free diet;
- osteoporosis, manifested by bone pain and fractures.
In adults, celiac disease manifests itself with various symptoms of digestive disorders:
- pain and bloating;
- flatulence (gases);
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- loose or soft stools, in which feces stick to the walls of the toilet and are difficult to flush away; sometimes there is an admixture of blood in the stool;
- poor appetite or, on the contrary, increased appetite;
- nausea, occasional vomiting.
Without adequate treatment, celiac disease can lead to serious complications, including small intestinal cancer.
Diagnostics
A final and reliable diagnosis is made after examining a piece of intestine (biopsy) taken during an endoscopic examination.
In addition, the level of antibodies against tissue transglutaminase and antibodies of the IgA and IgG types is tested (for these tests, blood taken from a vein is examined).
Genetic tests can identify genes whose presence predisposes to the development of celiac disease. The presence of these genes - HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 - is not proof that a person is sick, it only indicates that he has a high likelihood of developing celiac disease.
Treatment
The only effective treatment for celiac disease is the strict exclusion of gluten-containing foods from the diet. When following a gluten-free diet, inflammation in the intestines stops and the person recovers completely. Celiac disease is often viewed not as a disease, but as a way of life.
The importance of following a gluten-free diet is evidenced by the fact that even a few crumbs of wheat bread can cause inflammation in the intestines. Therefore, the first to be included in the list of excluded products are: wheat or rye bread, muffins, cookies, pasta, cereals containing wheat, rye, oats or barley.
Products that do not contain gluten and, therefore, are safe for people with celiac disease: fresh meat, fish, fruits, vegetables. But semi-finished or finished products (for example, canned food, sausages, etc.) contain additives (for example, wheat starch, dyes, flavors) that contain gluten, so they should be excluded from the diet.
When preparing food, replace ingredients containing gluten with gluten-free ones. For example, instead of a glass of wheat flour, you can take
- 1/2 cup almond flour (this should be stored in the refrigerator)
- 1 cup buckwheat flour
- 1 cup corn flour
- 1 cup cornstarch
- 1 cup amaranth
- 7/8 cup chickpea flour
- 5/8 cup potato starch
- 1 cup sorghum flour
- 1 cup tapioca flour
- 7/8 cup rice flour
In some countries, stores sell special flour mixtures that replace wheat flour in recipes.
In addition, at the beginning of diet treatment, you should avoid eating dairy products for some time (up to several weeks) until the inflammation in the intestines subsides.
If there are people in the family who do not have celiac disease, then it is very important on their part not to “contaminate” gluten-free products with gluten. For this purpose you need:
— store gluten-free and gluten-free products separately;
- Always wipe the table surface clean after eating;
— allocate separate dishes for gluten-free products (including for cooking).
Always read the labels of the products you buy. If the label does not say that a product is gluten-free, it probably contains gluten.
You can be sure that a product contains gluten if it contains the following ingredients: wheat, wheat starch, wheat grits, wheat flour, semolina, bran, brewer's yeast, barley and any barley derivatives, rye and any rye derivatives, wheat spelled, real spelt, couscous. A particular product is more likely to contain gluten if it contains dextrin, seasonings, sauces, flavorings, flavorings, and licorice. Although pure oats do not contain gluten, they can cause inflammation of the intestinal tissue in some people with celiac disease, so it is best to exclude them from the diet.
Some medications may contain gluten in the form of additives. Be sure to tell your doctor that you have celiac disease before prescribing any treatment for you.
Among alcoholic beverages, gluten is found in beer and vodka; wine is a gluten-free drink.
Source: https://azbyka.ru/zdorovie/pochemu-byvaet-allergiya-na-xleb-i-makarony
Cross shape
A true allergy (one that is associated with hypersensitivity to components, and not with a lack of enzymes) may occur to one type of starch , but not to another.
It all depends on what exactly it is made of.
- If a child is allergic to potato starch , there is a high probability of cross-reactions to latex, birch pollen and pome crops (apples, pears, quince).
- Allergy to corn starch is accompanied by cross-reactions upon contact with sorrel and cereals.
- If you are allergic to rice starch, reactions to cereals and cane sugar may occur.
- An allergy to wheat starch is accompanied by reactions to cereals, especially those containing gluten (rye, spelled, barley, oats).
Also, various types of starch are contained in many tablets as auxiliary substances to slow down the rate of absorption (for example, Aspirin, Analgin, white coal, Panangin and many others).
But it is contained there in small quantities, so it will cause a pronounced allergic reaction in the presence of very high sensitization to the allergen.
Starch and its derivatives are used as thickeners (dextrin, maltodextrin), so parents should read the ingredients of products before giving them to a child with allergies.
Allergic reaction to starch
Among all food allergic reactions, starch allergy is not very common, but its occurrence in a child can become a real problem, because this polysaccharide is found in many vegetables and prepared foods.
Signs of an allergic reaction
The symptoms of an allergy to starch are no different from the manifestations of any other food allergic reaction, which is why parents are not immediately able to understand which product caused the baby’s poor health. Most often, a child exhibits the following symptoms:
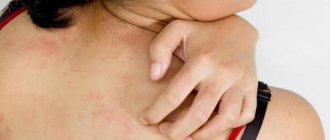
rashes on the skin, represented by small bubbles with transparent contents or blisters;
- itching and burning of the skin, which makes the child worry and scratch;
- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- frequent and excessively loose stools;
- nasal congestion and copious mucous discharge from the nasal passages.
In more severe cases, there is swelling of the soft tissues, especially in the face and extremities. In addition, swelling of the upper respiratory tract may develop.
This condition is life-threatening and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
It is noteworthy that the symptoms decrease and gradually disappear a few days after foods containing starch are completely excluded from the menu.
It is also worth noting that allergies do not occur immediately, since sensitization of the body is a long process.
In most cases, the first use of starch does not cause any pathological symptoms, but subsequent feeding of the baby with products containing it is already accompanied by signs of an allergic reaction.
Due to the fact that the digestion of this complex carbohydrate takes time, an allergy develops several hours after its repeated consumption.
If parents give their child foods containing starch in small quantities, allergy symptoms may appear within a few days. In this case, it can be even more difficult to associate them with starch consumption.
Causes
An allergy is an overreaction of the immune system that develops in response to a substance entering the body. In children, such conditions occur much more often than in adults.
This is due to the fact that the child’s immunity is going through stages of development, and some “mistakes” are possible in its functioning.
As the body develops, the function of the immune system is completely normalized, and allergic reactions in most cases cease.
Another factor that contributes to the development of allergies is the unpreparedness of the child’s digestive system to break down and absorb complex carbohydrates. In childhood, digestive enzymes are produced in relatively small quantities, so often all starch is not digested, some of it accumulates in the body, causing an allergic reaction over a long time.
What to do if you have an allergy?
First of all, it is necessary to stop the allergen entering the body. This is not so easy to do, because starch is found in many vegetables, fruits and cereals. However, the record holders for the content of this complex carbohydrate are:
- bananas (especially green ones);
- potato;
- corn;
- rice;
- legumes
It should also be remembered that a large amount of starch is present in pasta, jelly, various cereals (especially semolina) and wheat flour.
The accelerated removal of the allergen from the body is facilitated by the consumption of liquid, so during the period of a rapid allergic reaction, let the child drink water (if swelling occurs, a temporary restriction of the drinking regime may be necessary).
Ready-made purees intended for baby food often suffer from the presence of starch, so be sure to study the composition before purchasing. Unfortunately, some unscrupulous manufacturers, in order to save money, add starch to vegetable, fruit and meat purees without indicating this on the label.
Finally, do not forget that starch is a component of most powdered milk formulas, so their composition must also be carefully analyzed. Particular attention should also be paid to the fact that starch is used as a base in the production of some tablets, pills and syrups.
In most cases, to eliminate allergy symptoms, the pediatrician prescribes the following medications:
- antiallergic (“Ketotifen”, “Cromohexal”);
- antihistamines (“Loratadine”, “Cetirizine”);
- anti-inflammatory.
To reduce skin itching, special creams and ointments are used. Severe allergic reactions may require the use of corticosteroid medications. The choice of medications and determination of dosages is solely the responsibility of the doctor, based on the age of the child and how severe the allergy symptoms are.
Until your baby's allergies go away, try to fill his diet with dishes and foods that contain a minimal amount of starch or no starch at all. Feel free to add it to the menu
- broccoli and other types of cabbage;
- zucchini and regular zucchini;
- Bell pepper;
- pumpkin;
- tomatoes;
- cucumbers;
- carrot;
- apples;
- pears.
Among cereals, buckwheat contains the least amount of starch, so sometimes it can replace other cereals.
Symptoms and signs
The main signs of an allergic reaction:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- weakness;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- pain and heaviness in the abdomen;
- skin rash;
- swelling of the skin and mucous membranes;
- peeling of lips;
- runny nose;
- redness of the eyes;
- cough (mostly paroxysmal);
- suffocation;
- labored breathing;
- lacrimation.
In children of any age, allergic symptoms manifest themselves almost equally. But infants under six months of age and newborns experience respiratory symptoms less frequently than older children.
The younger the child, the more severe allergic reactions occur.
Danger
If sensitivity to the allergen is high, there is a risk of developing these conditions:
- angioedema;
- anaphylactic shock.
An ambulance should be called if the child experiences one or more of the following symptoms:
- breathing is significantly difficult, the child is choking, gulping for air;
- his skin and mucous membranes are significantly swollen;
- the rash has spread throughout the body and is accompanied by very severe itching;
- the child lost consciousness;
- heart rhythm is abnormal;
- severe, repeated vomiting is observed.
If a child has previously had severe allergic reactions, it is important for parents to keep epinephrine .
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures allow you to identify the allergen and exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
The following analyzes and tests are carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- prick test;
- skin patch tests;
- examination of feces (dysbacteriosis and parasitic diseases);
- provocative test.
Also, if necessary, studies are carried out to identify diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which may cause a false allergy when eating food with starch.
Treatment
Medicines used for allergic reactions:
- Anti-allergenic agents : Grandim (injection and in the form of suppositories - after one month), Supramin (for children over a month old), Avil (syrup for infants and newborns, tablets after 12 years).
- Epinephrine. Used in emergency situations to relieve an acute allergic reaction. To simplify the process of administering the drug, you can purchase a syringe pen: with its help you can quickly and easily administer the medicine.
- Adsorbents: Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel. These remedies can be given to newborns and infants.
folk remedies for the treatment of allergies with caution and only after consultation with a doctor: their components can also cause an allergic reaction.
Examples of traditional methods:
- infusion with chamomile;
- lotions from a series;
- nettle decoction.
Before using any product, apply a small amount to your child's skin. If his condition worsens and a rash appears on the skin, the product should not be used .
To protect your child from allergic reactions and related complications, it is important to exclude from his diet all foods with the type of starch to which the child is allergic.
If the baby is still breastfed, the mother should follow a diet. You should also avoid using baby powder.
Authorized Products:
- different varieties of cabbage;
- cucumbers;
- turnip;
- radish;
- pumpkin;
- oat groats;
- garlic;
- various salads;
- onion.
Products that are important to exclude:
- industrial desserts, jams, sweets with cream, curds (thickeners based on starch are often used there);
- pasta;
- wheat groats, barley, rye, oats;
- bakery products;
- potatoes, corn;
- corn sticks;
- bananas;
- rice;
- peas;
- semolina.
If parents have difficulty choosing a menu, they should consult an allergist.
How is the disease treated?
People of any age can be allergic to starch. Treatment of the disease is the same as for any other hypersensitivity. Since allergies cannot be treated, all therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
To improve your well-being, use:
- Antihistamines like Zyrtec and Tavegil. They reduce the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Skin manifestations are eliminated with antipruritic ointments. Usually they use Bepanten, Panthenol, Gistan. If anti-inflammatory drugs do not bring relief, they can resort to ointments made on the basis of glucocorticosteroid hormones. These medications cannot be used for a long time, so the doctor must determine the dosage and duration of the course.
- Enterosorbents that accelerate the removal of allergens from the body. These are Activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel.
An allergy to starch in a child requires closer attention from doctors.
Prevention
Basic methods that will reduce the risk of an allergic reaction:
- potatoes should be introduced into a child’s diet no earlier than 8 months: they contain a lot of starch;
- if the child is weakened, you should not rush into complementary feeding;
- Since undercooked starch is less digestible in the body, foods containing it should be thoroughly boiled.
If a child develops a rash after eating a product with starch, it is important not to self-medicate so as not to worsen the condition. An allergist in the hospital will determine the cause of symptoms, prescribe medications and give recommendations.
In many children, the allergy disappears on its own after a few years.
You can learn about the harm of starch