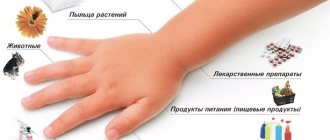
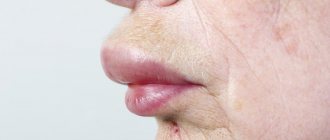
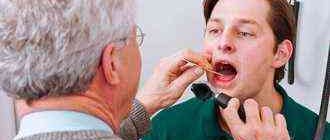
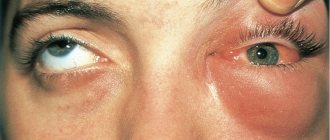
Causes of swelling
There are factors that provoke the disease.
Commonly encountered ones include:
- household dust;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- animal hair;
- chemicals;
- a certain group of drugs;
- some food products.
When allergens get on the mucous membrane of the throat, they provoke inflammatory processes.
. As the disease spreads, swelling appears.
It is difficult for a person to swallow food, as a feeling of a lump appears in the throat.
The muscles begin to actively contract, the swelling, spreading over the entire area of the pharynx, grows, blocking the access of oxygen in the upper respiratory tract.
The patient begins to choke and shortness of breath appears.
Important!
If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, due to severe swelling, suffocation occurs, which leads to death.
Signs of mucosal edema
A disease of the pharynx - pharyngitis - causes damage to the mucous membrane. Pathology accompanies inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. With swelling of the throat mucosa, the following are observed:
- discomfort, pain when swallowing;
- enlargement of the jaw and occipital lymph nodes;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- formation of a film on the surface;
- soreness;
- dryness;
- burning;
- headache;
- low-grade fever;
- bouts of dry cough;
- sensation of a foreign object;
- weakness.
Possible complications
Swelling of the larynx can cause complications such as:
- Laryngeal edema can be caused by both inflammatory processes and tissue damage,
stenosis of the respiratory tract; - asphyxia with subsequent death of the patient;
- oxygen starvation, which affects the condition of all tissues, organs and systems of the body;
- cardiac muscle hypertrophy;
- increased permeability of blood vessels.
The severity of the consequences of throat swelling depends on the root cause, the neglect of the pathological process.
What is throat swelling
With this reaction, the body responds to damage or irritation that provokes numerous causes, most of which are diseases. When the throat swells, a narrowing occurs, preventing the passage of air and the access of oxygen. Mark the location of the pathology:
- aryepiglottic, vestibular folds;
- lingual surface;
- arytenoid cartilages;
- uvula;
- subcutaneous tissue of the larynx.
Swelling of the larynx worsens a person’s condition. The development of complications cannot be ruled out:
- blood pressure increases;
- asphyxia appears - oxygen deficiency;
- hypotension is observed;
- heart rate increases;
- blood flow is activated;
- vascular permeability increases;
- bluishness of the skin is observed;
- hypoxia of the brain occurs;
- the functioning of organs and systems is disrupted;
- loss of consciousness occurs;
- death occurs.
Symptoms
Allergic laryngitis may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- burning sensation and dryness on the mucous membrane;
- cough causes pain;
- chills and fever are possible;
- pale skin tone;
- difficulty breathing;
- there is a feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- when coughing, sputum is produced;
- there is pain when swallowing, sore throat.
Allergic
Allergic swelling of the larynx is caused by a number of factors to which the human body reacts negatively.
These include food allergens, chemicals in detergents and cleaners, road and house dust, medications, poplar fluff, and even some food products without dyes and preservatives.
It is often possible to identify the factor that provokes the disease only after examination by a doctor.
Irritants entering the throat area through the nasal passages affect the laryngeal region and epiglottic cartilage.
Sometimes stenosis occurs due to the entry of an irritant through the esophagus. In this case, swelling occurs on the arytenoid cartilages.
At first, all patients with allergic swelling of the throat experience difficulty in inhaling and exhaling air, the frequency of the respiratory process increases, shortness of breath appears and the heart rate decreases.
During the examination, the doctor records swelling of the tonsils, soft palate and uvula.
In the advanced stage of allergic edema of the larynx, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- it becomes painful to swallow saliva;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- there is an acute lack of oxygen even in the fresh air;
- there is choking and a sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- the cough becomes barking and rough;
- the skin turns pale and eventually acquires a bluish tint;
- chills and increased sweating do not leave the person, and an increased body temperature may be observed;
- The patient increasingly develops feelings of restlessness, anxiety and nervousness.
Stages
The disease has several stages of development.
At the initial stage
severe swelling appears that spreads down the throat, affecting the muscles. They begin to contract involuntarily.
Spasms cause shortness of breath, pain and sore throat. As the allergy develops, redness of the mucous membranes and foci of inflammation are observed.
Due to severe swelling
the upper respiratory tract is blocked, and the patient has difficulty breathing. Attacks of suffocation begin to appear.
Attention!
Even at rest, a person experiences shortness of breath.
Quincke's edema
A person has angioedema
, which affects the mucous membrane and tissue under the skin. Swelling can spread to joints, organs and the lining of the brain.
Important!
Swelling of the throat is life-threatening. It develops rapidly, within 2-5 minutes after the allergen enters the body.
A person experiences the following symptoms:
- voice change;
- whistling breathing is observed;
- speech is impaired due to enlargement of the tongue, lips, cheeks;
- hives and blisters appear that cause severe itching;
- shortness of breath suddenly begins;
- The veins in the neck become greatly enlarged;
- blue discoloration of the skin is observed;
- convulsions may occur;
- a person loses consciousness;
- the access of oxygen to the larynx is blocked, which leads to asphyxia.
Asphyxia
Attack of suffocation
I starts suddenly. It is often mistaken for an asthma attack.
It is very important to know the symptoms so you can seek medical help promptly. The most common signs of asphyxia:
- difficulty breathing;
- wheezing and whistling are heard;
- severe cough begins;
- white sputum is produced;
- the skin turns red;
- the person may lose consciousness.
Block No. 4 Emergency conditions for allergic conditions and infectious diseases
When anaphylactic shock develops, the most effective emergency treatment drug is:. Infusion therapy for anaphylactic shock should begin with intravenous administration: Which of the following diseases is NOT an allergic reaction? Specify the type of allergic reaction that causes anaphylactic shock:
Which of the following statements characterizes the course of the pathochemical stage of an allergic reaction: Which of the following characterizes the course of the pathophysiological stage of an allergic reaction: The most common route of sensitization in atopic diseases in adults is:
What antibodies are produced during an attack of atopic bronchial asthma? Regression of primary skin elements in allergic urticaria occurs within. In the pathogenesis of acute allergic urticaria and Quincke's edema play a leading role. As a rule, it begins immediately or within the first hour from the moment of the bite. Nonspecific desensitization in allergic reactions of the humoral type is possible when: In case of drug allergies, all medications are cause-significant allergens, EXCEPT:.
Having diagnosed Stevens-Johnson syndrome or Lyell's syndrome, you should prescribe:. In accordance with WHO recommendations, antipyretic therapy for an initially healthy person is carried out at a body temperature above.
Antipyretic therapy should be started immediately, regardless of the severity of hyperthermia when:. For malignant fever, emergency care includes the following pathogenetic drug therapy:
The average incubation period for anthrax is: Select the leading symptom characteristic of dehydration shock due to food toxic infections:. The selective growth medium is alkaline peptone water and meat peptone agar.
Secretion of enterotoxin and neuraminidase by cholera vibrios, which activate the cyclic adenosine monophosphate system. Acute renal failure in cholera develops as a result of all of the following reasons, EXCEPT:. Decreased diuresis, persistent insomnia, inappropriate behavior of the patient, the presence of meningeal signs. Name the means of emergency prevention of anthrax. The clinical picture of damage to the abdominal organs due to anthrax is represented by all of the following symptoms, EXCEPT:.
All of the following symptoms are common to pulmonary anthrax and pleuropneumonia, EXCEPT:. Which of the following solutions is optimal for rehydration therapy for cholera?
The main factor in the pathogenesis of the gastrointestinal form of Salmonella infection:. Which symptom of the gastrointestinal tract is most characteristic of salmonellosis? In case of food toxic infections, the leading symptom of infectious-toxic shock is:.
Patient M. Complains of suffocation, unbearable skin itching, severe general weakness, dizziness, palpitations. From the anamnesis: he suffers from polyvalent drug allergies.
Half an hour ago I was bitten by a wasp on my upper lip. Objectively: The condition is extremely serious, consciousness is confused. Severe motor restlessness. The skin is hyperemic and covered with sticky sweat. Swelling of the eyelids, lips. On auscultation over the lungs there is vesicular breathing, a lot of dry wheezing. BH 30 per minute. Heart sounds are muffled, rhythm is correct. Heart rate per minute. The abdomen is without features. Preliminary diagnosis: Complaints of severe skin itching, headaches, feeling of lack of air, dry cough, nasal congestion.
From the anamnesis: he has been suffering from vasomotor rhinitis for many years. A sharp deterioration in health after injection of Thymalin. The condition is extremely serious. The patient is excited.
The skin is moist, pale, and there is a confluent erythematous-papular rash all over the body. Breathing is noisy. There is vesicular breathing over the lungs, and there is a mass of dry wheezing throughout all lung fields. Respiratory rate 34 per minute. Heart rate per minute. The abdomen is soft and painless. The liver is not enlarged.
Patient A. Complains of inspiratory shortness of breath, suffocation, dry cough. History: due to endometritis, the gynecologist prescribed intravenous infusions of Abaktal, after which the state of health sharply worsened, a dry paroxysmal cough appeared, shortness of breath progressing to suffocation. The condition is serious. There is an expression of fear, fright on the face, the patient is excited.
The skin is pale in color and moist. Vesicular breathing in the lungs. Preliminary diagnosis? A 36-year-old patient, 10 minutes after the second intramuscular injection of penicillin, developed urticarial rashes throughout the body, chest pain, dizziness, and shortness of breath. On examination: retardation of consciousness, pallor of the skin, heart rate per minute. Which drug should be administered first?
Patient L. Complains of shortness of breath, suffocation, dry cough, severe general weakness. She is seen by a therapist and was prescribed the drug obzidan 40 mg. After taking the obzidana tablet, she felt short of breath, suffocation, dry cough, loss of strength, and weakness. Moderate condition. Inhibited, inadequate. There is a pained expression on his face. The skin is pale and moist to the touch.
In the lungs there is vesicular breathing, dry wheezing, exhalation is prolonged. NPV 25 per minute. A 47-year-old patient with allergic rhinosinusitis felt short of air, suffocation, dry cough, and weakness after taking aspirin. Inhibited, adequate.. In the lungs there is hard breathing, dry wheezing, exhalation is prolonged.
NPV 20 per minute. After 15 minutes, the child developed itching, urticaria, numbness of the fingers, and nausea at the site where baralgin was administered. Clinical examination reveals a frequent thread-like pulse, low blood pressure, and muffled heart sounds. A 28-year-old man, after eating peanuts, experienced a sharp deterioration in his health, nausea, vomiting, and cramping abdominal pain. Suddenly the convulsions began. After taking sulfonamides, the child’s temperature increased to 39 C, and there was generalized erythema multiforme on the skin with a predominance of papular-vesicular rashes.
Patient P. From the anamnesis, he took non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinical examination reveals a frequent thread-like pulse, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, and muffled heart sounds.
From the anamnesis - he took non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinical examination revealed a frequent thready pulse, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, muffled heart sounds. After using the vaccine, the child’s temperature increased to 39 C, and there were multiple drainage bullae with purulent contents on the skin.
Nikolsky's symptom is positive. Severe hemodynamic disturbances. Complaints of shortness of breath at rest, suffocation, rashes on the face, itching. From the medical history: The deterioration occurred acutely after taking citrus fruits, rashes and swelling on the face, difficulty breathing, hoarseness, and barking cough appeared.
Objectively: The condition is serious. Consciousness is clear. The face is puffy, swelling of the eyelids, lips, ears, neck, rashes of a pinpoint nature in some places draining. A 9-year-old patient complains of swelling of the eyelids and lips when eating nuts.
Pathological anatomy
Acute inflammation of the larynx during the rapid course of influenza, erysipelas, scarlet fever is accompanied by pronounced swelling of the throat, which also develops quickly and spreads to the entire submucosal layer from the vestibule of the larynx to the subglottic space.
Pathological signs of edematous laryngitis are:
- Redness of the mucous membrane,
- Infiltration of the mucosa with leukocytes and lymphocytes,
- Impregnation of the submucosal layer with serous transudate,
- Activation of the mucous glands of the larynx.
Abscess of the throat and inflammation of the uvula - cone-shaped process
Throat abscess in adults is classified according to the location of the abscess:
- Anterior is the most common type, in which the upper poles of the tonsils become infected.
- Posterior - characterized by the formation of purulent foci between the posterior palatine arch and the inflamed tonsil.
- Lower - formed from below the palatine tonsils. This type of abscess is expressed in mild symptoms.
- Lateral - the rarest type, characterized by the formation of ulcers on the lateral side of the tonsils. There is a danger of complications in the form of inflammation of the neck and chest. The disease is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, and Proteus. A throat abscess develops as a result of untreated tonsillitis, sore throat, and pharyngitis. Purulent pathology can also develop when an infection enters the mucous membrane of the larynx. This is possible when a foreign object is swallowed.
Also, the cause of narrowing of the lumen can be swelling of the tongue in the throat. Inflammation of the cone-shaped process, located on the soft palate, covers the entire throat. The cause of the condition is often an allergy, injury or infectious pathology. Irritation of the tongue can be caused by a burn or injury from a fish bone.
Diagnostics
Allergic laryngitis
differentiated from viral and infectious diseases of the larynx, diphtheria, tracheitis, and pneumonia.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor performs a number of diagnostic procedures on the patient, which include:
- laryngoscopy, which examines the larynx. Using a special tube, at the end of which a miniature camera is attached, the necessary examination is carried out;
- the patient is tested for IgE;
- conduct general allergy tests;
- if necessary, a biopsy is performed to examine the inflamed tissue of the larynx.
Swelling of the mucous membrane
The tissues in the mouth and larynx are mucous membranes. It is customary to distinguish several types of swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat:
- infectious,
- symptomatic;
- toxic;
- angioedema,
- idiopathic.
Symptoms of infectious swelling of the throat are often encountered. Its main symptom is severe pain in the larynx. Symptomatic edema is a consequence of any systemic disease: liver, heart, kidneys. Toxic edema refers to the influx of fluid into the loose tissues of the larynx, which is a consequence of damage by toxic substances.
Treatment
In acute cases of the disease, the patient is sent to the hospital.
At home, treatment of allergic laryngitis is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Depending on the symptoms, the following measures are recommended:
- taking antihistamines: Suprastin, Tavegil;
- a course of antibiotics;
- taking sulfonamides;
- use mucolytics: Bromhexine, Ambroxol;
- use nasal drops or sprays: Xylene, Rinostop, Marimer;
- vitamin complexes;
- sedatives: Seduxen, Tozepam, Relanium;
- It is necessary to gargle with Furacilin solution.
Also, the patient should drink alkaline mineral water daily , inhale with soda, take warm baths before bed, and take Diazolin with Diphenhydramine to desensitize the body.
Eliminate smoking and alcohol
, avoid contact with irritants.
First aid for laryngeal swelling
First aid should be provided directly at the site of acute symptoms. Swelling of the larynx can be fatal; you must not hesitate; timely first aid can save your life.
You need to call an ambulance immediately. The person needs to be seated and ensure the flow of fresh air. Treatment with cold or hot compresses on the neck area is not permitted.
When exposed to heat, there will be a rush of fluid to the application site, which will provoke increased swelling of the larynx.
At home, first aid should include the following procedures:
- immerse your limbs in warm water - this will at least slightly reduce the flow of fluid to the laryngeal mucosa;
- take a hot bath for up to 10 minutes. Contraindicated for patients with body temperature over 380C;
- take desensitizing medications. Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, Fenkarol are found in most people's medicine cabinets;
- drink alkaline solutions at room temperature. This will slightly reduce the symptoms of swelling;
- take Lazolvan (Ambroxol).
Emergency assistance - what to do before the ambulance arrives
first aid to the patient during an attack before the medical team arrives
Important!
The risk of severe consequences from suffocation is too great, so in the first minutes of its onset it is important to know what measures to take to alleviate the patient’s condition.
- If possible, remove the irritant that triggered the attack.
- If the patient is conscious, give him mineral water to gargle.
- The patient can be seated comfortably. The back should rest on some support.
- Give the person any antihistamine.
- If choking occurs due to an allergy to a food product, give Smecta or Activated Charcoal.
- Open a window to bring in fresh air.
- Unbutton the collar and remove any constricting clothing.
- Sprinkle face and body with cold water.
- To reduce swelling, apply a cold heating pad or ice pack to your throat.
- In case of cardiac arrest, perform a massage. For 15 compressions, take 2 breaths. Do the massage until the ambulance arrives.
Relieving throat swelling with sore throat
Constant symptoms of sore throat and pharyngitis - swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat, pain when swallowing. A swollen throat with a sore throat causes severe discomfort and interferes with leading a normal life. A sick person should stay in bed and regularly gargle with solutions that extinguish inflammation and destroy pathogenic microflora.
- Soda and salt;
- Apple cider vinegar;
- Decoction of calendula, chamomile, sage;
- Carrot and beet juice;
- Eucalyptus leaf extract.
Preventative measures include:
- Rinsing the body with cold water;
- Daily walks in the fresh air in any weather;
- Gargling with Furacilin or chamomile decoction;
- Use of vitamin complexes;
- Periodic rinsing of tonsil lacunae.
Features of a child
The child's larynx is funnel-shaped.
It has a narrow opening and small size, the cartilage tissue is looser.
Because of these features, the health risk of edema increases several times compared to complications in adults. Swelling spreads at lightning speed. Choking can occur within 1-2 minutes.
Therefore it is important to know
symptoms of the disease in children in order to immediately provide first aid.
The most common signs:
- difficulty breathing, congestion;
- barking cough;
- when breathing, the jugular fossa will sink;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- severe tachycardia appears;
- the child begins to panic;
- the skin becomes pale;
- cold sweat appears;
- the area of the nasolabial folds acquires a bluish tint.
Important!
If at least two of these symptoms are present, call an ambulance immediately.
Relieving throat swelling due to laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx, accompanied by hoarseness, dry cough, and swelling of the throat. Swelling with laryngitis occurs mainly at night and requires immediate elimination. It is necessary to urgently call doctors, and before they arrive, provide first aid to the sick person. You especially shouldn’t hesitate if a small child is sick.
How to relieve throat swelling with laryngitis? This is done using the method below.
- A sick person sits on a chair or armchair. Buttons and zippers on outerwear are unbuttoned, and the tie is removed.
- It is advisable for the affected person to be in a room with high humidity: in the kitchen or bathroom.
- If there is no wet room nearby, then high humidity should be artificially created around the patient. It is recommended to immerse the victim’s hands or feet in a bowl of hot water. You can boil water in a saucepan and ask the sick person to breathe over the hot steam, carefully so as not to get burned. It doesn't hurt to throw a pinch of baking soda into the pan. Soda steam relieves swelling well.
- If it's warm outside, you can take the victim out into the fresh air.
- It is recommended to give a sick person alkaline drinks: hot milk with soda or heated mineral water.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of developing laryngeal edema, you must follow these recommendations:
- promptly treat upper respiratory tract diseases and infectious diseases;
- avoid contact with allergens, inhalation of fumes of alkalis and acids, hot air;
- avoid getting foreign bodies into the respiratory tract;
- avoid damage to the neck area;
- contact an otolaryngologist at the first signs of inflammatory and infectious processes.
Laryngeal edema can be caused by both inflammatory processes and tissue damage. This condition, if left untreated, leads to airway stenosis and asphyxia.
It is important to be able to provide timely assistance to the patient, since with lightning-fast development of edema, a person quickly suffocates.
How does a doctor provide first aid?
Within the hospital, specific first aid measures, identical in all cases, are carried out.
- It is required to administer adrenaline intramuscularly or intravenously. If the technique does not have an effect, it is necessary to inject the drug into the root of the tongue. It is well vascularized, so the action will be fast.
- Inhalation of oxygen in various concentrations is mandatory.
- Administration of glucose and saline intravenously to normalize the patient's condition. Solutions nourish a weakened body.
- It is also necessary to administer bronchodilators based on fenoterol and ipratropium bromide.
- In the absence of the latter, the use of Prednisolone or Dexamethasone (intramuscular or intravenous) is required.
- First generation antihistamine injections.
- The use of aminophylline is required. It allows you to expand the airways and normalize breathing.
- When asphyxia develops, the soft tissues of the throat and trachea are dissected to form a stoma (tracheostomy). Required in extreme cases. The measure is temporary.
We suggest you read about Removing a nerve in a tooth - doesn’t it hurt?
Consequences of swelling
Allergic laryngitis
is a life-threatening disease that requires mandatory treatment. If the situation develops unfavorably, stenosis begins to develop.
There is a complete or partial closure of the glottis, which leads to asphyxia. Cardiac arrest occurs
, the person falls into a coma and dies.
Healthy!
If a person has ever had allergic laryngitis, there is a high probability of developing laryngeal edema, even with an infectious disease.
Adjuvant therapies
It is necessary to treat swelling of the throat in a comprehensive manner. In addition to drug treatment, experts recommend:
- follow a certain diet (exclude from the diet too dry and hard foods, spices, sugar, salt, preservatives, dyes, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, sparkling water, foods containing allergens, preservatives, additives, flavor enhancers);
- reduce fluid intake;
- eliminate bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- reduce the amount of physical activity;
- eliminate stress and swelling factors;
- use air purifiers and humidifiers;
- observe a rest regime.
Etiology
Swelling of the throat occurs in weakened individuals as a result of exposure to streptococcal toxins in the body. The risk group usually includes patients with influenza, scarlet fever, diabetes, as well as malnourished patients with symptoms of uremia and vitamin deficiency. Factors contributing to the development of throat swelling:
- Injuries,
- Ingestion of foreign bodies,
- Hot food causing soft tissue burns
- X-ray and radiological effects on the organs of the neck,
- Hypothermia from inhaling cold air or drinking cold drinks such as beer or milk,
- Acute viral infections - measles, influenza, typhoid,
- Acute bacterial infections - scarlet fever, diphtheria,
- Inflammation of the larynx, tonsils, peripharyngeal space, epiglottis - epiglottitis, phlegmons and abscesses,
- Chronic renal and cardiovascular pathology,
- Poor circulation caused by compression of the veins of the neck,
- Benign and malignant tumors of the larynx,
- Allergy to external irritants - dust, household and food allergens,
- Phlegmanous inflammation of the larynx.
Manifestations in an adult
Most often, swelling occurs in the loose tissue of the larynx. It can be limited with a slight increase in tissue and diffuse when narrowing of the larynx prevents normal breathing. With swelling of the larynx, wheezing and whistling when breathing may be present.
The inflammatory process occurs in catarrhal or edematous form. In this case, the cause of inflammation is viral or allergic in nature. Other forms of edema: fibrinous-necrotic and infiltrative. In this case, a bacterial infection is associated with inflammation.
A narrowing of the lumen of the larynx is formed due to swelling and accumulation of mucus.
Causes of laryngeal edema:
- A burn to the throat caused by eating food or liquid that is too hot.
- Flu, scarlet fever, measles.
- Throat injuries include: surgery, ingestion of a foreign object, trauma.
- Syphilis, tuberculosis in stage.
- Throat neoplasms.
- Pathologies of blood vessels and heart.
There are other reasons that lead to swelling; we need to talk about them in more detail.
When to see a doctor
The patient should be alerted to the slightest symptoms of allergy development
. If breathing problems begin, swelling and shortness of breath appear.
It is necessary to take antihistamines as quickly as possible and use cold compresses to relieve swelling. Next, immediately call an ambulance to provide qualified treatment.
A person predisposed to allergies must carefully monitor their health.
Antihistamines should always be in your home medicine cabinet.
to provide first aid to yourself. It is important to visit an allergist twice a year and take all prescribed medications for prevention. This will avoid allergic laryngitis.
Methodological development for residents studying in the specialty “allergology and immunology”
Media files on Wikimedia Commons. Angioedema, or Quincke's edema, is a reaction to various biological and chemical factors, often of an allergic nature. Manifestations of angioedema are enlargement of the face or part or limb. The disease is named after the German doctor Heinrich Quincke, who first described it in the year. The disease is manifested by the occurrence of edema in places with developed subcutaneous tissue - on the lips, eyelids, cheeks, and oral mucosa. The color of the skin does not change.
Prevention
As a preventive measure you need:
- avoid hypothermia;
- do hardening (to strengthen the immune system);
- do not eat hot foods (to avoid burns of the tongue and throat);
- stop smoking;
- systematically undergo a medical examination to identify chronic diseases.
Such an attentive attitude towards oneself will give a positive result: a person will have a greater chance of being healthy. If, despite preventive measures, laryngeal stenosis still develops, then timely seeking emergency help will save the patient’s life.
How to treat a swollen throat
Often inflammatory processes are accompanied by swelling of the larynx.
How to relieve swelling of the throat, what are the causes of the symptom, methods of its diagnosis and treatment. articles
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Treatment with folk remedies
It is known that swelling of the throat is rarely an independent disease. Most often, it indicates the development of various pathological processes in the human body.
Moreover, this condition is extremely dangerous, as it can lead to suffocation with a rapid increase in swelling and narrowing of the lumen in the larynx. In this case, you need to know how to relieve throat swelling in order to quickly restore breathing.
In the treatment of throat edema, both medicinal methods and traditional medicine methods are used. In order to find the most effective treatment, it is necessary to determine the causes of the pathological condition.
Causes
Swelling can be caused by various factors, both inflammatory and non-inflammatory. To understand how to relieve throat swelling, you should analyze the possible causes of the unpleasant symptom. So, soreness and swelling in the throat can be caused by:
- laryngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- purulent inflammation of the base of the tongue;
- allergic reactions to medications, food;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, and organs of the cardiovascular system;
- problems with blood circulation in the pharynx as a result of excessive compression of the lymph nodes;
- mechanical damage during surgery, burns of the mucous membrane.
To prescribe correct and effective treatment for swelling in the throat, you should know not only the causes, but also the main symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms
Among the main signs of edema are:
- pain when swallowing saliva and food;
- dryness, sore throat;
- noisy breathing;
- difficulty breathing as a result of increased swelling and narrowing of the throat;
- hoarseness leading to complete loss of voice.
As the pathological process worsens, swelling increases, shortness of breath appears, pale skin, rapid pulse, and a feeling of panic may occur.
Upon visual examination, thickening of the epiglottis is noticeable in the area of swelling, and swelling can also spread to the arytenoid cartilages.
Swelling caused by inflammatory processes is characterized by pronounced redness of the mucous membrane and dilation of blood vessels. Whereas non-inflammatory edema is not accompanied by hyperemia.
Treatment
If the patient experiences a feeling of constriction and pain in the throat, he should receive immediate assistance to quickly relieve swelling of the throat and restore breathing.
Important! If first aid for laryngeal edema is not provided on time, there is a risk of complications, the development of asphyxia and suffocation.
How to treat swelling of the throat? Before qualified medical assistance is provided, you can reduce swelling on your own.
- The first thing to do when the throat is swollen is to facilitate the access of oxygen: unbutton the collar, take the person out into the fresh air.
- If the swelling is caused by an allergy, you should stop exposing the body to the allergen and take antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin). In severe situations, to relieve laryngeal edema, treatment is based on the use of corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone).
- To reduce swelling, you can drip vasoconstrictor drugs into the nose (Nazol, Nazivin).
- If swelling develops as a result of an insect bite, it is necessary to apply a tourniquet or bandage above the lesion site and take an antihistamine.
- Swelling caused by a viral or bacterial infection is treated with antiviral drugs or antibiotics, depending on the type of infection.
- To relieve the symptom, hot foot baths are used, and mustard plasters are placed on the calves.
Treatment in a hospital is primarily aimed at carrying out procedures that will relieve swelling and restore breathing. In this case, treatment can be carried out both conservatively and using surgical intervention.
Conservative therapy includes a set of measures aimed at quickly normalizing the patient’s condition and restoring full breathing. The following drugs are used for this:
- antiallergic drugs;
- antibiotics (Augmentin);
- corticosteroids;
- diuretics (Furosemide);
- intravenous administration of vitamin C, calcium gluconate and glucose to support the body;
- sedatives and tranquilizers (Apaurin, Diapam).
Also used as treatment are inhalations of adrenaline and hydrocortisone, and oxygen masks are used.
If conservative treatment methods do not give a positive result and the swelling not only does not decrease, but also continues to progress, you should know what to do with swelling of the throat in this case. Most often, doctors resort to emergency surgical measures - tracheotomy. This is an incision in the throat where a tube is inserted to allow air to enter the airways unhindered.
During the entire treatment period, certain precautions should be taken, adhering to the following recommendations:
- follow a diet - eat exclusively warm food in liquid or puree form, completely eliminating any seasonings and spices;
- exclude intense physical activity, fast walking;
- reduce the load on the ligaments and speech apparatus.
Treatment with folk remedies
If swelling of the throat does not cause severe discomfort and difficulty breathing, you can try to reduce the discomfort at home using alternative medicine methods.
- Gargling with solutions of baking soda (1 teaspoon per glass of warm water) and decoctions of medicinal herbs, for example, chamomile, calendula. If you are not allergic, you can add a few drops of essential oil, such as eucalyptus, to the soda solution. The rinsing procedure must be repeated several times a day until the swelling, soreness and pain in the throat disappear completely.
- A cold compress applied to the throat area will help reduce swelling caused by non-infectious diseases. This could be a heating pad with cold water or pieces of ice wrapped in a towel.
- Inflammation and swelling in the throat area can be reduced with carrot juice and honey. It is necessary to consume the freshly prepared solution three times a day, at least 100 ml at a time.
- You can remove excess fluid from the body and reduce swelling with the help of rosehip decoction, which has a pronounced diuretic effect. To do this, brew a tablespoon of rose hips in a liter of boiling water, leave for several hours and drink half a glass throughout the day.
Nadezhda Chernobay
Sources: medscape.com, health.harvard.edu, medicalnewstoday.com.
Source: https://globalmedclub.ru/bolezni-gorla/novoobrazovaniya/chem-snyat-otek-gortani.html
First aid
The danger of swelling of the throat is high and there is a high risk of death in the absence of qualified assistance. You should not only thoroughly understand the symptoms of the pathology, but also clearly know the sequence of actions for providing first aid.
- An ambulance must be called immediately.
- Unbutton your shirt collar and remove other clothes so as not to impede breathing.
- Perform gastric lavage with a solution of potassium permanganate and clean water. This is relevant for an allergic reaction provoked by a food product.
- Give the required amount of activated carbon.
- If an insect bites you, remove the sting immediately. A tourniquet should be applied slightly above the affected area. This will prevent the allergen from spreading through the blood.
- If possible, lower the upper and then the lower limbs into a hot bath. This will significantly ease the condition.
- Place the person on their back. If possible, place a cushion or pillow under your feet.
- Provide air access, make sure that the tongue does not roll back.
- Apply cold to the throat to relieve swelling and alleviate the general condition.
- Apply vasoconstrictor drops to your nose.
- Inject an antihistamine intramuscularly or give a tablet.
- Give as much water as possible to drink until doctors arrive.