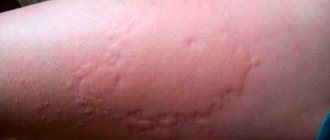
Dermatitis is a skin disease that is localized in various parts of the body and changes the integrity of the upper layers of the skin. Such reactions are typical for young children and appear for various reasons. Therefore, young mothers ask the question: “What is the difference between atopic dermatitis and allergic dermatitis?”
People underestimate unexpected redness on the skin and rash, attributing it to a temporary phenomenon and limiting themselves to wiping with alcohol tincture and creams. In some circumstances, changes in the color and structure of the skin indicate not external influencing factors, but serious pathologies of internal organs. Moreover, some drugs for external use can complicate the course of the disease. Body rashes mainly affect infants and young children.
The disease is treated by a dermatologist and an allergist.
Allergic dermatitis: symptoms and treatment of allergic dermatitis in children and adults
Allergic atopic dermatitis in children and adults is a genetic allergic reaction. The pathology is inherited from close relatives. A person is born with an individual intolerance to a particular product and upon contact with it develops atopic allergic dermatitis.
Modern medicine does not know any treatment methods that will help completely get rid of this disease. There is only therapy aimed at suppressing negative symptoms, which significantly alleviates the patient’s condition.
To answer the question of how atopic dermatitis differs from allergic dermatitis, you need to know the difference between allergies and dermatitis.
| Allergy | Dermatitis |
| Systematic disturbance in the functioning of the body. It manifests itself in symptoms that affect not only the skin, but also all organs and systems of the body. An allergic reaction develops from the following factors:
| It is a local allergic manifestation. Symptoms are accompanied by skin disorders - redness, dryness or weeping. Atopic dermatitis is genetically transmitted from parents to children. An allergic reaction is inherent in the genotype, and even a minimal amount of irritant provokes a violent immune response. Quite often, atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma occur together as a consequence of neglected dermatitis. |
The intensity of the disease is affected by age. The most severe manifestations of the disease are observed in children, especially newborns. In addition to the usual itching and redness, the child experiences:
- irritability;
- moodiness;
- loss of appetite;
- insomnia;
- Possible bowel dysfunction;
- extensive damage to the skin.
To get rid of the disease in a baby, it is necessary to adjust the mother’s diet. Parents should completely exclude the baby from contact with potential pathogens.
The difference between the terms dermatitis and allergic reaction is the basis that you need to know to cover this topic. An allergic manifestation is a systemic disorder in the functioning of the whole organism; it can manifest itself in the form of symptoms affecting the functioning of many organs and systems, including the skin.
Allergic manifestations can develop under the influence of the following factors:
- excessive exposure of the skin to a chemical or dye;
- temporary weakening of the immune system;
- concomitant blood diseases (blood-forming organs);
- low-quality cosmetics and body care products.
The difference in the occurrence of atopic dermatitis lies in the main difference between these forms - this type of pathology is inherited from parents. The pathological reaction of the immune system is inherent in the genotype; a microscopic dose of a substance is enough for it to manifest itself. In this case, the process does not depend on other factors.
Allergic dermatitis is a pathological lesion of the skin, which is always associated with exposure to an irritating factor. It is noteworthy that the disease in question occurs only in adults, because atopic dermatitis is typical for children.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face
As soon as you suspect that you have become a hostage to the disease, you should seek help from a dermatologist as soon as possible. This specialist will determine the type of skin lesion and prescribe appropriate treatment for facial dermatitis, which will include a number of comprehensive measures.
Medications
The doctor should first of all tell you how to treat dermatitis on the face using external remedies (ointments, creams) and preparations for internal use. Usually prescribed:
- Sedatives, antidepressants: infusion of valerian or motherwort, Persen, Novopassit;
- Vitamin therapy (complex or separate - pyridoxine is most often prescribed);
- Antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil);
- Immunomodulatory agents;
- Ointments for dermatitis on the face: zinc ointment, Elokom, Afloderm, Radevit, Trixera, Indomethacin, Solcoseryl;
- Hormone therapy (for advanced forms).
Among non-hormonal ointments, Losterin can be distinguished separately. This is an ointment based on naphthalan, which is used in the complex treatment of psoriasis, dermatitis, and eczema.
In addition to drug therapy, the doctor will advise how to cure dermatitis on the face by putting your lifestyle in order.
Supporting measures
Since dermatitis on the face is largely due to the lifestyle we lead (diet, mobility, bad habits), you can get rid of it only by putting it all in order. Take the following tips into account and you won’t have to worry about the condition of your skin.
- Nutrition
There is a certain diet for facial dermatitis that can speed up recovery:
- do not eat fast foods, chips, crackers;
- eat less smoked, pickled, peppered foods;
- increase the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, except persimmons, pineapples and citrus fruits;
- prohibited foods: eggs, nuts, wheat, rye, sauerkraut, seafood, honey;
- forget about alcohol;
- drink more freshly squeezed juices;
- replace fatty foods with boiled ones;
- If you have seborrheic dermatitis, you should not eat red fruits;
- It is recommended to soak vegetables and cereals in cold water for at least 10 hours;
- the meat will need to be boiled several (2-3) times;
- lean on foods that contain a lot of pyridoxine (vitamin B6): bananas, tomatoes, carrots, peas, beans, lentils, leafy vegetables, seeds, berries, cereals, cereals.
And, of course, the most important rule of a diet for facial dermatitis is to exclude allergens from food.
- Physical activity
Physical activity improves blood circulation. If the blood delivers a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients to problem areas of the skin on the face, recovery will speed up. Therefore, play sports.
- Fresh air
Take more walks in the fresh air. Sick tissues, saturated with oxygen, will recover faster.
If you are able to change your habits and lifestyle, this will have a positive effect not only on the condition of your skin, but also on other parameters of your appearance (hair will stop falling out, fat will stop depositing on the tummy and sides, etc.). With the permission of a doctor, dermatitis on the face can be fought with the help of folk remedies.
Folk remedies
Treatment of dermatitis with folk remedies is possible only after medical consultation, otherwise complications may arise.
Milk-glycerin ointment
Mix milk (a tablespoon) with glycerin (the same amount). Add rice starch for thickness. Apply to affected areas and leave overnight.
Tar cream
Squeeze the entire tube of shaving cream into a separate container. Add 10 grams of tar to it, heat to 60°C. Lubricate problem areas 2-3 times a day.
Potato mask
Mix raw grated potatoes (100 g) with honey (10 ml).
Wine compress
Grind 4 leaves of fresh plantain, add 60 ml of dry white wine. Leave for 5 hours. Soak gauze in the infusion and apply to problem areas.
Essential applications
Mix baby cream (10 g) with myrrh and cypress esters (2 drops each).
If you begin to suspect that the spots on your face are not so harmless and may be a warning sign of dermatitis, do not hesitate: it is better to seek help from a dermatologist as soon as possible. After a course of treatment and a set of appropriate measures, you will again be able to feel the velvety and softness of your skin without peeling and unpleasant rashes. Be sure to get treatment - and then this disease will not dare to touch your face again.
Causes
Heredity
Early signs of AD can appear in the first weeks of a baby’s life, when his immunity is still very weak, and the skin is delicate and sensitive, and therefore reacts sharply to any allergens. The main reason why atopic dermatitis develops in infants is heredity. If one of the baby’s parents was susceptible to allergies at a tender age, then with a 50% probability the child will also inherit it, but if both, then the guarantee of getting the disease is 80%. Doctors identify the main causes, which, supported by a hereditary factor, give impetus to the occurrence of blood pressure.
One of the common reasons is a negative reaction to food, which occurs in 20% of infants. Dr. Komarovsky believes that the greatest danger to the immature gastrointestinal tract of a newborn is posed by food allergens, that is, poor nutrition of the mother during breastfeeding, or an incorrectly selected formula, and the first feeding of the baby.
Dysbacteriosis
A gastrointestinal disorder such as intestinal dysbiosis can also cause allergic skin reactions in newborns. To reduce the manifestation of blood pressure, when dysbiosis is diagnosed, doctors prescribe medications based on lacto- and bifidobacteria to restore intestinal microflora, and the drug Enterosgel to remove toxic substances.
Household allergens
Often, the culprits of skin rashes in children are external irritants, they can be: household dust, pollen, pets, washing powder and other detergents, synthetic clothing.
Weak immunity
A child who suffers from frequent acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections and has a weak immune system is primarily susceptible to the development of hypertension; another cause of the disease can be the gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
A difficult pregnancy for the mother, intrauterine fetal hypoxia, stress, excessive sweating and calcium deficiency in the body are all the main reasons why a newborn may be diagnosed with atopic dermatitis.
In most cases, atopic dermatitis occurs as a result of a child's genetic predisposition to allergies. If his family members often come into contact with chemicals (E-additives, GMOs), then this criterion can also cause the disease.
In addition to the main ones, there are a number of secondary causes of childhood eczema. Among them:
- intestinal upset, constipation;
- profuse sweating;
- dry skin;
- effects of synthetic underwear on the skin.
Food irritants are considered especially dangerous for sick infants. Therefore, all baby food should be hypoallergenic. The disease is also affected by the mother’s diet during breastfeeding, because the composition of milk directly depends on the food consumed.
Depending on the symptoms, there are three main forms:
- Local - lesions affect only one or two areas on the body, for example, only on the cheeks or face as a whole, or on a separate part of the neck.
- Widespread – symptoms develop in several areas of the body that are located far from each other. For example, on the cheeks and fingers.
- Diffuse – lesions take up a lot of space on the child’s body, appearing in three or more areas, for example, on the face, arms and buttocks.
Dermatitis is a group of diseases manifested as a pathological reaction of the skin (inflammation, allergy) to external (physical, chemical, biological) influence.
Dermatitis is a common disease; in particular, 10-20% of the world's population suffers from atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis is one of the causes of skin cancer.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Seborrhea of the skin: symptoms and treatment, how to treat seborrheic dermatitis on the body
The causes of dermatitis are very diverse, but they are conditionally combined into 3 groups: stress (provokes dermatitis on its own or in combination with other pathological factors), contact (burns of various origins, frostbite) and penetration - entry of a pathological agent into the blood through the gastrointestinal tract , lungs, as well as through damaged skin, intramuscularly and intravenously. Contact of a pathological agent leads to contact dermatitis, penetration - to allergic and atopic dermatitis.
Clinical manifestations are varied and depend on the type of dermatitis (itching, redness, rash, exudation and peeling of the skin), type of course, leading symptom, etc.
Treatment of dermatitis is based on a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease; always long-term and complex, including the elimination or neutralization of the pathological agent (including through diet), combating existing symptoms, preventing new ones, as well as stimulating the body’s defenses.
Causes of dermatitis
Here are the most important causes and predisposing factors of the disease:
- acquired predisposition due to weakened immunity;
- congenital predisposition;
- emotional and mental problems (hysteria, depression, neurosis, etc.);
- acute and chronic infections and intoxications (HIV infection, staphylococcal infection, skin candidiasis, alcoholism, drug addiction, dysbacteriosis, etc.);
- acute and chronic somatic diseases (hepatitis, pancreatitis, colitis, diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- bulimia, anorexia;
- stress;
- contact with the skin or entry into the blood of allergens (food, medications, pollen, cosmetics), detergents, acids, alkalis, etc.;
- insect bites; Lyme disease; scabies, pediculosis;
- exposure to physical factors on the skin and body (heat, cold, frost, solar and other radiation, etc.);
According to the type of course, acute and chronic dermatitis are distinguished.
According to the leading symptom, dermatitis can be dry, itchy, exudative, etc.
By location: on the face, on the scalp, on the arms, on the legs, on the torso.
Due to their occurrence, allergic, atopic, contact and seborrheic dermatitis are distinguished.
Allergic dermatitis occurs when skin comes into contact with an allergen, a substance that causes an allergic reaction. Allergens can be medications, cosmetics, perfumes, paints, polymers, etc. Clinical manifestations: redness of the skin without clear boundaries with papules and small blisters with cloudy contents. Typical allergic dermatitis is urticaria.
Atopic dermatitis - develops due to the body's increased tendency to atopy - a delayed-type allergic reaction.
Atopic dermatitis differs from allergic dermatitis in that the presence of antigens is not necessary for its occurrence.
Atopic dermatitis manifests itself as a rash on the face, on the back of the hands and feet, and on the torso; accompanied by severe skin itching.
Atopic dermatitis occurs in the form of atopic eczema (abundant areas of inflammation in the form of blisters), diathesis (typical for children of the first year of life; manifested by redness and small rashes) and neurodermatitis (clinical signs are similar to diathesis, but appear in older children).
Contact dermatitis is a pathological reaction of the skin upon contact with allergens and other irritants (light, heat, cold, acids, alkalis, dyes, etc.). It manifests itself in the form of local itching and burning, redness, swelling of the skin, sometimes with the appearance of blisters, erosions and weeping. Common symptoms include fever and chills.
Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by yeast-like fungi, which provoke an infectious-inflammatory reaction in those areas of the skin where there are sebaceous glands (scalp, hair growth boundaries, nasolabial folds, skin of the external auditory canals, behind-the-ear areas, etc.)
Seborrheic dermatitis of the trunk affects the sternum and body folds. Seborrheic dermatitis manifests itself as dry seborrhea (small white, flour-like flaking scales), as well as acute inflammatory changes: redness and plaques covered with greasy scales.
The disease is diagnosed by a dermatovenerologist, family doctor, pediatrician based on a survey and examination of the patient, as well as instrumental methods, in particular, dermatoscopy. To identify specific allergies, immunity levels, and concomitant diseases, special blood and biological fluid tests are prescribed.
Dermatitis should be distinguished from similar diseases: seborrhea, etc.
To diagnose concomitant diseases, additional instrumental studies and consultations with a therapist, pediatrician, allergist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist and other specialists may be required.
Treatment of dermatitis
First you need to determine the cause of the disease. Based on this, complex individualized long-term treatment is selected, starting with diet.
The diet involves the exclusion of foods that provoke allergic reactions (fast food, citrus fruits, chips, sweets, baked goods, artificial and alcoholic drinks, etc.
), and, on the contrary, eating foods that help restore the skin (porridge, vegetables and fruits rich in fiber and B vitamins, boiled lean meat, sardines, salmon, natural and fermented milk products, vegetable oil, tested water, etc.).
Symptomatic therapy:
- local products (ointments, creams, mash, sprays, aerosols, etc.) with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing and regenerative effects;
- enterosorbents to neutralize toxic, including allergic agents;
- antihistamines to reduce allergic manifestations;
- glucocorticoids for severe allergic reactions.
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods include narrow-band mid-wave ultraviolet irradiation, darsonvalization, galvanization and electrophoresis, sulfide and radon baths, mud therapy, etc.
Stages of development
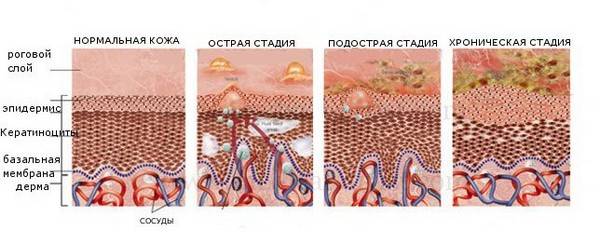
Skin diseases are divided into three stages of development. It is easier to get rid of the cause at the first stage, but, unfortunately, not many people take it seriously.
Three stages of development:
- The first signs are noticeable in early childhood. This is a mild rash with barely noticeable swelling and slight redness. Parents “heal” symptoms with ointment or folk remedies, without bothering to find out the original source of this phenomenon. With properly selected therapy, it is treated quickly and without the chance of recurrence.
- The expressed stage comes in two forms – acute and chronic. The symptoms of the first stage include itching and the development of a rash into blisters with a crust.
- Remission. Absence of the disease or its signs. It can last for months or years - it all depends on the treatment received, preventive measures and related factors.
In this case, dermatitis is no different from allergies - both processes come in acute and chronic forms, can reappear without treatment, and the first signs are similar.
At the initial stage, a person without certain knowledge and skills will not be able to identify the disease. The first stage of all skin problems is expressed by redness.
How to recognize atopic dermatitis?
The heyday of blood pressure in children mainly occurs in spring and autumn. Doctors divide the severity of the disease into several stages; pronounced symptoms of blood pressure that characterize the onset of the disease are:
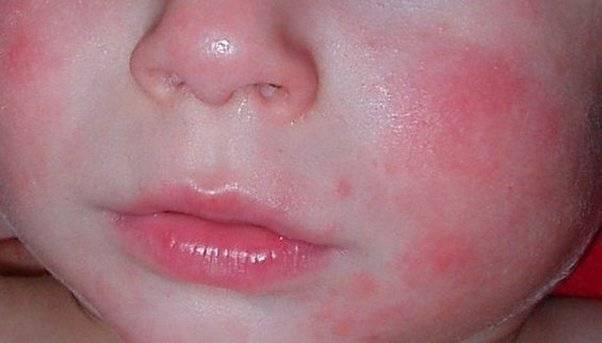
- Various rashes on the cheeks and buttocks;
- Dry, rough and flaky skin;
- Severe itching;
- The appearance of crusts on the scalp;
- Redness of the skin in the elbows and knees;
- The appearance of compactions in some parts of the body.
Second stage
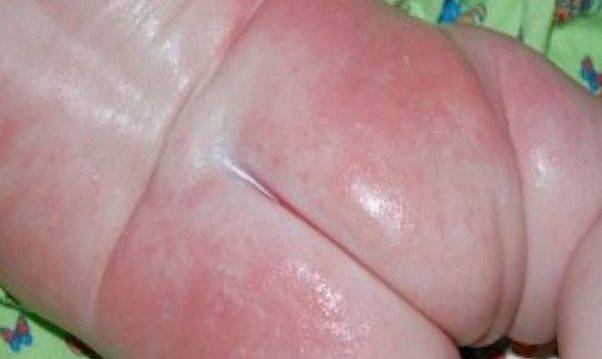
The second stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of vesicles or papules in the folds of the skin, accompanied by swelling. Over time, the blisters turn into weeping sores and greatly disturb the child; he becomes capricious, irritable and has trouble sleeping at night. To help the baby during this period, it is necessary to apply a soothing, drying cream to the skin.
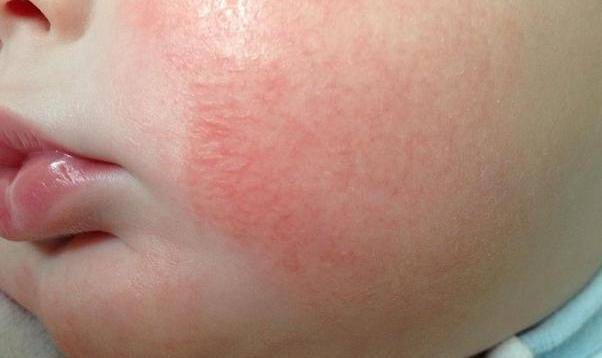
The last stage of AD is characterized by the appearance of dry crusts in place of weeping wounds, and a gradual decrease in redness, itching and swelling. The process of exacerbation passes, but improvement does not indicate complete relief from the disease. Usually, AD takes on a chronic form, so the disease does not disappear without a trace, but is in remission, which can last for several months.
How is an allergy different from dermatitis?
The concepts of atopic dermatitis and food allergy often overlap. Today, these are quite common skin diseases, which, however, have fundamental differences and it is important to learn to recognize them.
Characteristics of diathesis
In official medicine, diathesis is not considered a full-fledged diagnosis, because it is more of a borderline state of the body than a full-fledged disease. However, such a reaction should not be neglected - it may indicate a child’s predisposition to seborrhea, eczema and neurodermatitis.
By and large, diathesis can be considered a harbinger of atopic dermatitis in the future. And even despite the fact that diathesis is not considered a diagnosis for children as such, treatment for food allergies is still necessary.
Reasons for appearance
Diathesis appears in children for various reasons. A child may be born with a predisposition to such a reaction, for example, if the mother regularly overeated or ate typical allergens during pregnancy: citrus fruits, eggs, canned food, smoked meats, marinades. In addition, diathesis can be hereditary.
The course of pregnancy also influences the development of diathesis. Constant toxicosis, the environment and taking medications during pregnancy are other reasons for the development of diathesis.
Some children are even allergic to breast milk. And although this phenomenon is quite rare, it is caused by the consumption of milk of animal origin either during pregnancy or during the lactation period.
Thus, one of the main reasons for the development of diathesis is violations of the nutritional culture. The bacterial or viral nature of the diathesis cannot be ruled out.
It is observed during complementary feeding if there is a lot of sugar in the added mixtures. Please note that diathesis must end before two years.
If it continues further, it means that it is not fully treated, or has turned into a chronic food allergy.
Symptoms
Diathesis exhibits quite clear symptoms that cannot be ignored:
- Red spots appear on the cheeks;
- The skin over the spots periodically peels off and becomes gray or brown;
- In some cases, spots form on the crown of the head;
- Hygienic procedures do not eliminate skin peeling and spots;
- Diaper rash may appear;
- The face becomes somewhat swollen.
At the same time, not only the quality of the child’s skin deteriorates. With such manifestations, his motor activity also decreases, and therefore developmental deviations may be observed. The child's stool becomes watery and subcutaneous fat accumulates.
There are also manifestations on the mucous membranes. Their surface is pale, the tongue is raised with white spots. In cases of aggravated diathesis, an inflammatory process occurs in the oropharynx, tonsils, and eyes.
Description of atopic dermatitis
To delineate the difference between atopic and allergic dermatitis, the etiology and manifestations of the second disease should be studied.
Atopic dermatitis is a disease of an allergic nature, one of the most common not only among children, but also among adults. This disease is chronic and most often has a hereditary nature.
It is based on reactions associated with disorders of the immune system, so it can occur regardless of food intake. Therefore, in this case, treatment is not aimed at correcting nutrition, but, first of all, at taking immunomodulator drugs.
Connection with diathesis
By and large, diathesis is considered one of the stages of atopic dermatitis. The latter is divided into three stages.
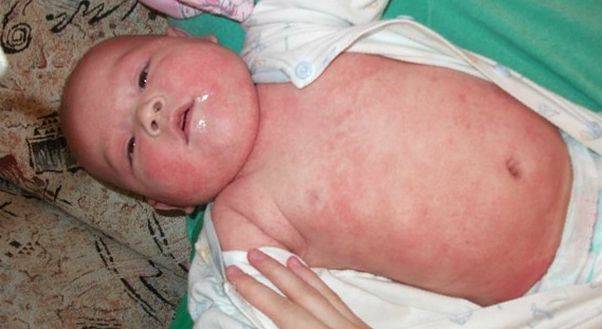
Infantile dermatitis or diathesis - manifests itself before two years of age in the form of red spots, most often found on the forehead and cheeks. It occurs quickly and can spread to the arms and legs. In the acute stage, bright red spots and bumps appear on the skin.
Lumps form on skin folds, elbows and knees, and the entire skin becomes dry and flaky. There is increased skin pigmentation around the eyes.
Outside of exacerbation, atopic dermatitis manifests itself in dry skin, small cracks appearing on the hands and between the fingers. Thus, childhood diathesis may be one of the stages of atopic dermatitis.
How to distinguish
The definition of diathesis or dermatitis is quite complex, since it is quite difficult to distinguish them at first and in the first months of a child’s life. Their symptoms are quite similar, but there are certain differences:
- With proper treatment, diathesis will go away by the age of two, unlike atopic dermatitis, which can remain with the child for life.
- Dermatitis after a few years leads to exacerbations of respiratory allergies, and in the long term – to bronchial asthma.
- When suffering from dermatitis, frequent diseases of the respiratory system, susceptibility to infectious lesions, conjunctivitis, and loose stools often occur.
- By normalizing the diet and selecting the right diet, diathesis goes away, but atopic dermatitis does not.
Otherwise, the differences are discovered only by the doctor after diagnosis. As a diagnosis, a laboratory test of blood and urine is prescribed, as well as an analysis of the immune system, and a skin allergy test is performed.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is somewhat more difficult to treat than diathesis. First of all, children's skin constantly needs hydration to prevent cracks and wounds. For this, lotions and baby creams must be of high quality, since the skin of such a child may react with a new wave of allergic reactions if the products are of poor quality.
All foods that are allergenic to one degree or another are eliminated from the diet: citrus fruits, strawberries, eggs, canned food, smoked meats. You should also limit the use of dishwashing detergents and clothing powders - dishes are washed with soda and salt, and the powders are selected to be hypoallergenic.
Swimming is required only in warm water. If this is possible, the baby continues to be fed breast milk to improve immunity. The drugs are prescribed only by the attending physician. Usually they are hormonal and non-hormonal, but during the treatment of young children, preference is primarily given to drugs of a non-hormonal nature.
Bacterial nature of atopic dermatitis
The gram-positive bacterium staphylococcus inhabits the human body from a very early age. Staphylococcus lives in the intestines, on the surface of the skin, in the mouth, in the sinuses, and with good immunity does not cause any special problems to its carrier, but on the contrary stimulates the body’s defense systems to produce antibodies.
Newborns, as a rule, do not have strong immunity, so the staphylococcus bacteria that inhabit the child’s body begin to actively multiply, leaving toxic products of their vital activity in the small body, which, when accumulated, provoke pathological changes in the skin. When staphylococcus gets on inflamed areas of the skin, it aggravates the inflammatory process and leads to the development of atopic dermatitis.
Dermatitis, the cause of which is Staphylococcus aureus, is typical for babies whose intrauterine development occurred with various deviations, delays and gestosis, and during the birth process there was a long anhydrous period.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Children's thrush in the mouth: what it looks like, causes and treatment of candidiasis in children
Symptoms of dermatitis caused by staphylococcus:
- Spots of rich brick color appear on the body;
- The rash is localized primarily on the face, front of the neck, behind the ears, groin, back and armpits;
- Characteristic blisters form on the body, and then detachment of the upper layers of skin occurs;
- The disease develops rapidly, within 1-2 days;
- The temperature rises and symptoms of general malaise are observed.
Symptoms
Causes of dermatitis
The main signs of the disease include:
- increased body temperature;
- formation of redness, swelling;
- the affected lesions peel off;
- intense itching develops;
- bronchospasm;
- conjunctivitis;
- tear production increases;
- sneezing and nasal congestion.
The atopic form will appear upon contact with a minimal amount of the allergen. A common allergy tends to occur in waves - a reaction does not occur with every contact with an irritant, it all depends on the general condition of the body and surrounding factors.
The main symptoms of pathology in children according to the type of atopic reaction will be:
- increased body temperature;
- redness, peeling, swelling and itching of the skin;
- tearfulness, sneezing, nasal congestion;
- bronchospasm;
- conjunctivitis
The difference between the atopic form and the simple form will be the minimum dose of the substance that interacts with the human body and the pattern in the manifestation of the reaction. A simple form of allergy can occur in waves; a pathological response does not occur to every contact of the patient with an allergen (depending on his general condition and surrounding factors).
There are some features of the manifestation of pathology in different age categories of patients. The symptoms in newborns and infants are especially clearly different:
- excitability, insomnia;
- lack of appetite;
- bowel dysfunction - diarrhea (does not occur in every specific case);
- extensive skin rash (all over the body) - small red dots.
Diagnosis of the allergen is complicated by the fact that symptoms can remain even with a complete refusal of complementary foods (only breast milk or formula). In this case, it is necessary to analyze in detail the mother’s diet and the components included in the mixture.
The symptoms of the disease are varied and depend on the age of the child, the characteristics of his health, diet and composition, living conditions, environment and climate.
The main symptoms accompanying the course of this disease are:
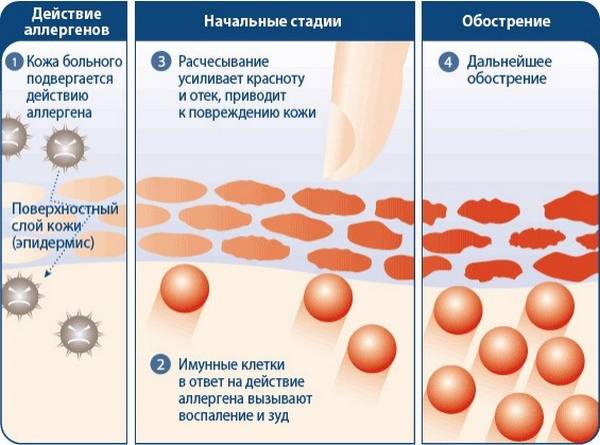
- Itching. It has varying degrees of intensity, sometimes it is unbearable, usually intensifies in the evening and at night. This symptom can deprive the child of appetite, leads to insomnia and worsens not only the physical but also the mental health of the child. The course of the disease becomes more complicated if the child begins to tear the affected areas with his own hands in an attempt to relieve the itching. In this case, cracks and wounds may appear at the site of the rash, through which infections and bacteria enter.
- Redness. A sign of inflammation. The process occurs due to the flow of blood to the affected areas as a result of dilation of blood vessels. Most often, redness is accompanied by itching and peeling.
- Peeling. This is the death of the upper layer of the skin and the detachment of dead cells from the epidermis. Problem areas are characterized by severe dehydration. The epithelium becomes very thin, so even the slightest impact with minor objects leads to the formation of wounds and cracks.
- Wetting (diaper rash). The process of separating serous fluid through the smallest affected areas of the upper layer of skin. It looks like a reddened spot with a collection of small bubbles. It causes severe itching, but such areas should not be touched, as it is very easy to damage such formations.
- Papular rash. Red bumps that resemble pimples. Causes swelling and redness. The only positive thing is that the papular rash leaves no traces behind.
In addition to the main symptoms, there are also other forms of damage that are accompanied by changes in the pigmentation of the skin, the appearance of a crust on it, inflammation of the hair follicle, and damage to the skin on the lips.
Effective methods to solve the problem
For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to determine the irritant that provoked the disease.
Therefore, an important part of the treatment of allergic dermatitis is correct diagnosis. After this, treatment is carried out in several stages
The first stage involves eliminating the allergen.
To do this, it is necessary to carry out the following procedures:
eliminating contact with substances that cause abnormal reactions in the body (heavy metals, plastics, synthetic materials, household chemicals, cosmetics); drug treatment of infections, viruses, parasites that affect the body from the inside; timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland.
Sometimes this is enough for the disease and its symptoms to disappear. At this stage, antibiotics and antihistamines (for example, Claritin, Citrine, Zodak) are used.
The second stage is the fight against external manifestations of allergic dermatitis (rashes, itching, peeling of the skin). For the treatment of local skin lesions, ointments, gels, sprays, as well as compresses for external use are effective.
Such products contain components that have antimicrobial and antifungal effects (Oxycort, Triderm and their analogues). Laser therapy is also used to treat external manifestations of dermatitis.
At the third stage, relief from accompanying symptoms occurs (headaches, intoxication of the body, swelling of the face, sleep disturbances). Patients are prescribed topical medications to improve the general condition of the body. This is necessary so that he has the opportunity to resist the disease.
An important point in the treatment of allergic dermatitis is strengthening the immune system, following a special diet, and maintaining a correct lifestyle.
Diagnostics
Causes of dermatitis
Atopy is characterized by the stability of symptoms and a natural reaction to the same substance, be it dust, animal hair or food. Diagnosis is based on skin tests, analysis of diet and lifestyle, medical history and genetic tests.
The first allergic symptoms that appear on the baby’s body should prompt his parents to immediately seek medical help. A dermatologist will conduct a visual examination of the baby and refer him for further examinations.
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Tests and samples to identify allergens;
- Bacteriological culture in case of suspected staphylococcus;
- Blood serum examination;
- Feces for dysbacteriosis.
Thanks to these studies, the doctor will determine the culprit of the allergy, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
To diagnose the disease, a special sequence of procedures has been developed that is used all over the world:
- To begin with, the basic picture of the disease is identified. These criteria include redness, itching, swelling, rash, peeling, etc.
- Next, they look for a connection between the disease and food or other allergens. Most often, mothers of babies can track changes in the child’s skin reaction to other foods and a change in diet. In addition, not only food products are tested, but also household irritants: chemicals, pets or common cosmetics for children.
- A blood test is taken. If the results reveal the presence of eosinophils, this will be evidence of allergization of the body. If an allergy is detected, then the development of the disease has begun.
- Serum immunoglobulin E in the blood is examined. In atopic dermatitis, its level will be increased.
- Conduct provocative tests. In case of illness in a baby, such procedures are rarely carried out and only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Carrying out these diagnostic methods helps determine the presence of disease in the child’s body.
conclusions
What is the difference between atopy and allergy?
Atopy is the body’s reaction to an allergen, like a classic allergy. However, in the first case, the disease occurs mainly in children and through genetic transmission from parents or older generations of relatives (if the parents remained carriers and did not suffer from pathology). The allergic type manifests itself at different ages.
Symptoms also differ: allergies primarily occur at the site of close contact with an irritant, and atopy occurs in various parts of the body.
Atopic dermatitis or allergy? These two varieties belong to the same group - allergic manifestations. They have a lot in common - the same symptoms, similar symptoms and reaction patterns. But there are some differences in causes and treatment. A person without special skills and experience will not determine the cause of the disease, so a visit to a dermatologist (allergist) is extremely important.
It has been proven that children tend to “outgrow” food allergies to many foods. Only a few of them remain allergenic for the patient’s body throughout his life. However, they are a threat only to those who are predisposed to allergies. But in atopic dermatitis, food plays a provoking role only when its participation in the mechanism of disease development is proven.
Treatment methods
Of all types of dermatitis, the atopic form is the most difficult to treat. When starting treatment for AD with medications or folk remedies, first of all it is necessary to exclude the child’s contact with possible allergens (including food), improve the functioning of his digestive system, cure dysbiosis and strengthen the immune system.
All medications used are divided into several groups according to their purpose:
- Antihistamines (Fenistil, Zodak, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Prednisolone);
- Antiseptic (Fukortsin, Zelenka, Salicylic ointment, Levomekol);
- Antibacterial (Amoxiclav, Zinnat, Neomycin);
- Immunomodulatory (Immunal);
- Vitamin complexes and calcium gluconate;
- Cream for external use (Gistan, Bepanten, Emolium);
- Sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb).
Antihistamines are intended to reduce allergic manifestations in the body and have a mild sedative effect, these include: Fenistil, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Zodak. They are available in free pharmacies and are available in the form of gels, drops and tablets. Unfortunately, the treatment process with antihistamines is quite long and their effectiveness is currently in doubt, but pediatricians persistently prescribe Fenistil and Zyrtec to their patients.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for atopic dermatitis are indicated in cases where staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria were found on the baby's skin. Due to the resistance of microbes to a wide group of antibacterial agents, treatment of blood pressure must be carried out with the latest generation of drugs, carefully selecting and changing drugs in case of ineffectiveness. Taking antibiotics can provoke dysbiosis in the child’s intestines, so bifidumbacterin is prescribed in parallel with them.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators come to the aid of other medications in cases where the disease is caused by a child’s reduced immunity, but they should not be abused in infancy, in order to avoid autoimmune disorders of the body in the future.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How allergies occur in infants
Vitamins
Vitamin complexes and herbal medicines can not only significantly enhance the effect of basic medications, but also cause allergies in infants, so their use should be agreed with a specialist.
Creams and ointments
The cream for softening the skin and eliminating dryness plays an important role in the treatment of blood pressure. Recently, Emolium cream, which restores and nourishes the skin, has become widespread. Emolium cream consists of natural ingredients and is very effective for irritation and inflammation of the skin, softens, moisturizes and protects the epidermis, does not contain dyes or fragrances.
Sorbents
Any allergic reaction is associated with poisoning of the body with toxins, so when starting treatment, doctors often resort to the help of sorbents. The drugs Enterosgel and Polysorb are approved for use in infancy. Once in the body, Enterosgel attracts all harmful toxic substances and removes them from the body.
Pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky believes that antihistamines such as Fenistil and Suprastin reduce sweating, which means they lead to dry skin, and therefore does not recommend abusing them in the treatment of blood pressure. For external use, Komarovsky advises using panthenol-based cream or Emolium cream, and in severe cases, corticosteroid hormones. Enterosgel and Polysorb consider intestinal sorbents to be a safe and effective remedy, especially for allergic reactions to food.
It is unlikely that it will be possible to cure atopic dermatitis with folk remedies, but with their help you can slightly alleviate the child’s condition. The main thing to remember is that the use of any means must be agreed with the attending physician.
Remedies, called folk remedies, are divided into 2 groups according to the method of application: external and internal. External ones, in turn, are divided into lotions, ointments and compresses, and internal ones into decoctions or tinctures. Naturally, sensible parents would not think of treating an infant with tinctures prepared with alcohol, and the baby’s reaction to herbal decoctions may not be predictable. But an ointment or cream prepared with your own hands is quite suitable for babies and will have a beneficial effect on damaged skin.
To soothe irritated skin and relieve itching, you can make a compress of raw potatoes, grated on a fine grater, or a lotion of black tea. Good folk remedies include various soothing baths with flaxseed or herbs. The water temperature for such procedures should be in the range from 34 to 36 degrees.
Rubbing damaged skin with folk remedies based on bay leaves, oak bark, birch buds, pear leaves, chamomile and nettle gives a quick positive result; such lotions perfectly relieve the inflammatory process, prevent the proliferation of pathological microorganisms and soothe itching.
Dr. Komarovsky reminds that therapy for any disease should be carried out by a qualified doctor, and treating dermatitis with folk remedies, without consulting a medical professional, can be dangerous. Therefore, timely consultation with a doctor is the key to a speedy recovery.
In order to get rid of childhood eczema as soon as possible, it is better to use effective medications, which are divided into the following categories:
- Moisturizing and softening creams – “Bioderma”, “ISIS Pharma”. The action of both products is aimed at restoring damaged areas, enriching the skin with nutrients and moisturizing it. The selected cream should be applied to the child's skin twice a day.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments – “Advantan”, “Sinoderm” and others. They protect the skin from inflammation, prevent further development of inflammation, etc. process.
- Wet lotions based on antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. They activate and prolong the effect of the medicine on the affected areas of the skin, increasing their effectiveness. You need to apply the drug to a gauze cloth, place it on the child’s body, cover it with film and a warm cloth. Remove after a quarter of an hour. Such drugs can be: “Bepanten”, “Panthenol”.
- Antimicrobial drugs - Hexicon, Levomycetin, Dioxidin. Due to the content of antiseptics and antibiotics in their composition, they help destroy bacteria on the surface of the skin.
Antibiotics are used for the systemic treatment of childhood eczema. These drugs destroy viral bacteria and remove them from the body.
Also, for the full course of treatment, antihistamines are used - Exoderil or Pantoderm. They are responsible for blocking active allergens in the body and reducing allergic skin reactions to the pathogen.
Sedatives (for example, “Losterin”) are used for a sedative and hypnotic effect, and the glucocorticoid group of drugs (such as “Levamisole”) is used to maintain and increase the body’s immune forces.
There are drugs for both internal and external use. The first category includes tinctures and decoctions of medicinal herbs, and the second category includes ointments, lotions and compresses.
It is clear that infants cannot be treated with tinctures prepared with alcohol. But it is also possible that herbal infusions can have a negative impact on young children. Therefore, it is better to use external mixtures that have a soothing effect on irritated areas of the skin.
Recipe No. 1 “Grated raw potato gruel”
Ingredients: raw peeled potatoes.
How to prepare: Wash one or two medium-sized potatoes. Peel the skin. Take a grater and grate from the smallest side.
How to use: Apply to your child's redness.
Result: the gruel will help relieve itching and other unpleasant sensations.
Recipe No. 2 Compress made from black tea infusion.
Ingredients: black tea leaves and flax seeds.

How to prepare: boil 1 liter of water, pour in 4 tablespoons of black tea leaves and a dessert spoon of flax seeds. Leave for up to 30 minutes.
How to use: draw a bath for your child, pour the prepared broth into it. The temperature of the water in the bath can fluctuate in the range of 34-36°C.
Result: a bath of broth will perfectly soothe the baby’s skin.
Lotions based on nettle, chamomile, oak bark, bay leaves, birch buds and pear leaves do an excellent job of treating skin redness, eliminating itching and providing protection against infections and bacteria. You need to wipe the damaged skin with herbal tinctures several times a day.
Most likely, it will not be possible to completely cure a child of an illness using traditional medicine. However, natural remedies made from natural ingredients will definitely reduce the symptoms and help the child cope with the course of the disease more easily.
Treatment is exclusively symptomatic, the following medications are used:
- hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments (“Sinaflan”, “Triderm”, “Beloderm”);
- antiallergic drugs (“Claritin”, “Diazolin”, “Suprastin”);
- children's antiallergic suspensions (Fenistil, Zirtek);
- adsorbents – remove toxins and allergens from the body (“Activated carbon”, “Polysorb”, “Lactofiltrum”).
Causes of dermatitis
Treatment of atopic allergic dermatitis is complex. The treatment regimen is selected individually and only by the attending physician.
Therapy must include:
- antiallergic drugs;
- corticosteroid anti-inflammatory;
- external agents based on emollients;
- antiseptic solutions;
- vitamin complexes with immunomodulators;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- desensitization of the body;
- physiotherapy;
- sedatives;
- drugs to improve the functions of the digestive system;
- folk recipes.
Treatment is aimed not only at eliminating the cause, but also at reducing the manifestations of the disease. Traditional therapy methods are not able to eliminate the disease on their own; they are necessary to combat negative symptoms.
Therapy
The effectiveness of treatment of atopic allergies is possible with complete isolation of the patient from the aggressive irritant.
Only if there is no contact with the allergen can we talk about recovery.
To speed up the therapeutic process, medications are prescribed:
- Antihistamines: block the action of free histamine, the excessive release of which leads to severe allergic reactions. Antihistamines have different forms of release: tablets, ointments, emulsions, serums, injection solutions. Drugs in this group: Zirtec, Rupafin, Claritin, Tavegil.
- Corticosteroid medications: a category of powerful medications with pronounced anti-inflammatory effects. Effectively eliminate skin manifestations of atopic epidermal sensitization. Thanks to the effects of drugs, stable remission can be achieved. Corticosteroids: Prednisolone, Sinaflan, Lokoid, Hydrocortisone.
As a complement to drug therapy to relieve painful symptoms of the disease, traditional medicine recipes using natural extracts of plants and herbs used as compresses and lotions do not lose their relevance. Particularly effective are:
- coltsfoot;
- chamomile;
- sagebrush;
- plantain;
- currant leaves.
To mobilize the body's defenses during the treatment of insidious atopic pathology, physiotherapy is prescribed:
- Exposure to electromagnetic pulses.
- Phonophoresis using medicinal ointments, usually corticosteroids.
- Laser therapy aimed directly at the inflammatory focus.