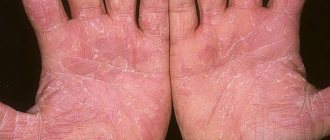
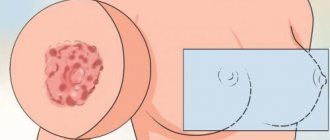
One of the varieties of chronic dermatitis of the eczematous type is dyshidrotic dermatitis. This disease is characterized by a persistent course, it often relapses and is difficult to cure. Most often, rashes with this type of disease appear on the skin of the hands; less often, the feet are affected. Let's figure out how the disease manifests itself and how it is treated.
Dyshidrotic dermatitis or eczema is commonly called an inflammatory skin disease that affects the skin of the hands and feet. The disease can develop in both children and adult patients, and women are more likely to get sick at a young age, and men - after 40 years. This disease causes redness and swelling, as well as a blistering rash.
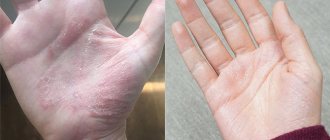
Dyshidrotic eczema of the hands - its effective treatment
Treatment depends on the type of eczema, the duration of the disease process, its severity, the age criterion of the patient and his individual qualitative characteristics.
It can be local, based on the use of ointments, anti-inflammatory creams, and complex, involving the use of drugs that suppress the immune system.
Treatment tactics depend on the diagnosis and the decisions of the attending physician.
The patient must adhere to the principles aimed at preventing the occurrence of the disease and minimizing its negative qualities.
Treatment

Dyshidrosis can cause dangerous diseases, so self-medication of the child is not recommended. As soon as parents discover symptoms of pathology in their baby, it is necessary to immediately begin therapy.
Dyshidrotic eczema should be treated with comprehensive measures aimed not only at eliminating the signs of the disease, but also at eliminating possible provoking factors.
Therapy includes:
- use of internal and external medications;
- methods of traditional medicine;
- dietary food.
If the diagnosis confirms the development of dyshidrosis in children, the patient is treated by a dermatologist-allergist, and consultation with a gastroenterologist, psychotherapist and other specialists is also necessary.
Use of medications

The attending physician prescribes internal medications that have a targeted effect:
- calcium-containing products – restoration of the functionality of the liver and thyroid gland;
- diuretics – normalization of water balance by removing excess fluid;
- corticosteroids – reducing the inflammatory process on the skin;
- enterosorbents – cleansing the body of toxins and allergens;
- antihistamines – relieve swelling, reduce pain and itching;
- atropines – decreased production of sweat gland secretions.
Causes
To this day, not a single scientist can say with 100% accuracy the cause of the disease. Some believe that it is associated with a weakened immune system and the occurrence of an allergic reaction.
Others are inclined to believe that the onset of the disease was preceded by the following factors:
- Prolonged contact with chemicals;
- Temperature effects: hypothermia or overheating;
- Stressful, depressive situations;
- Damage to the body by a number of infectious diseases that provoke pathogenic microorganisms;
- Use of personal hygiene products with high concentrations of chemicals;
- Prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet rays;
- Frequent use of antiseptics to disinfect hands;
- Radiation exposure;
- Long-term use of hormonal medications;
- Abuse of antibiotics and immunomodulators;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Presence of microtraumas, cracks on the surface of the hands.
Dyshidrosis cannot be transmitted from person to person, even through close contact with him. There is no need to be afraid of contacting such people, since the disease is not contagious. It causes discomfort to a greater extent in the patient than in the people around him.
Relapse
If the first symptoms of re-development of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Self-treatment can worsen the course of eczema, provoking a protracted inflammatory and allergic process.
There can be several reasons for relapse, ranging from food allergies to stressful situations and exacerbations of somatic diseases. It is important to understand that in people with chronic dermatosis, the “trigger lever” that initiates the inflammatory process is always ready, just a minimal influence of the irritant is enough.
There are no significant differences in symptoms during the development of relapse; the pathology is characterized by the same stages of clinical manifestations. But repeated dermatosis is always more painful and acute than the previous one.
To prevent a relapse of eczema, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid bad habits and regularly visit a doctor, following all his instructions. You should not ignore the rules and treatment regimen during an exacerbation of the pathological process.
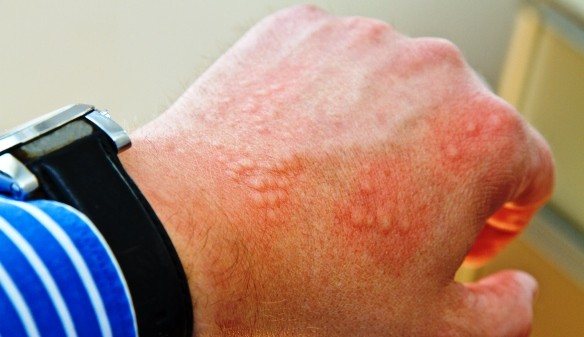
Symptoms and clinical signs
The disease comes suddenly, unnoticed by the person. Only the appearance of the first symptoms signals that measures need to be taken to prevent it.
Symptoms:
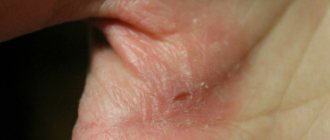
- On the upper layer of the epidermis, pinkish bubbles with transparent contents appear.
- The patient begins to be bothered by itching sensations, which indicates the possibility of expansion of the lesion of the superficial skin.
- On the back of the hands there is thickening, redness, and the skin takes on a painful appearance.
- Subsequently, the upper epidermal layer begins to peel off, crack, and fall off in plates.
Ignoring treatment of the disease leads to a deterioration in the patient’s general condition, which is reflected in the form of an increase in body temperature and disruption of metabolic processes in the body. The skin takes on an unaesthetic appearance and causes patients a lot of psychological problems, which affects their mood.
When treating dyshidrotic eczema on the fingers, any method is welcome. They will be popular and...
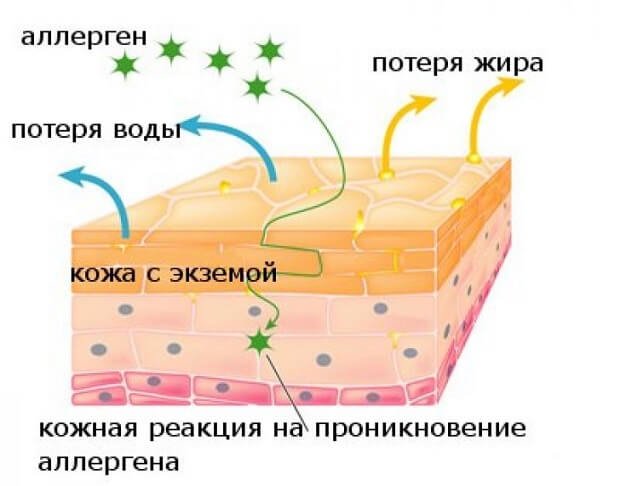
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a specialist, since it requires the use of the right medications that have anti-inflammatory, sedative, and immunomodulatory effects.
A special role is given to a healthy, balanced diet.
Timely treatment increases the likelihood of complete recovery from the disease. Only clinical signs, manifested in the appearance of large bubbles with yellow contents, make it possible to accurately recognize the disease and correctly prescribe medications.
Clinical picture
The disease develops in stages:
- First, the skin in the affected area turns red and swelling appears;
- then patients begin to feel itching and burning;
- at the next stage, vesicles appear - small bubbles filled with clear liquid;
- the bubbles are small, 1-2 mm in diameter, but they tend to grow. The bubbles are located separately or in groups;
- A characteristic feature of dyshydratosis is that the blisters can be located not only on the surface of the skin, but also in the inner layers. Therefore, they may protrude slightly above the surface of the body;
- if the vesicles are located in groups, then they tend to merge, that is, they form very large bubbles;
- after some time, the bubbles open, resulting in a weeping surface;
- when large blisters are opened, large superficial erosions are formed, these formations are very painful;
- Since the disease is accompanied by itching, scratches appear on the skin, and the presence of scratches provokes the addition of secondary infections. When affected by bacteria, suppuration and intensification of the inflammatory process are formed;
- after some time, the wet erosions dry out with the formation of dry crusts;
- After the crusts separate, the skin begins to peel off greatly.
Advice! With severe inflammation, a disturbance in general health may occur - a feeling of weakness, an increase in temperature, and an enlargement of the lymph nodes located near the site of the lesion.
Healing of erosions occurs very slowly, the surface of the skin becomes covered with a rough brown crust. With frequent relapses, the skin in the affected area thickens, becomes drier, flakes, and deep, painful cracks appear on the surface.
Diagnosis of pathology
There are no special methods for diagnosing the disease in nature. The doctor diagnoses the disease at the first visual observation of the patient’s hands. The dermatologist makes a conclusion based on the damage to the skin.
And only sometimes hand eczema requires additional research, which includes blood tests and microscopic scrapings. The reason for making a diagnosis is the presence of pathogenic microflora on the upper layer of the epidermis.
Only an experienced doctor can distinguish dyshidrosis from psoriasis or dermatitis. This suggests that at the first suspicion of the development of hand eczema, you need to contact a medical institution for help.
Diagnosis of the disease
The disease is easily diagnosed due to its appearance. With eczema, a common occurrence is the disappearance and the same sudden appearance of characteristic symptoms - the local nature of the rash. Nevertheless, the disease is similar to similar manifestations:
- atopic dermatitis;
- dyshidrotic mycosis;
- palmoplantar psoriasis.
The listed manifestations are included in the general category of ailments, however, the medical substances used to treat them can differ significantly in their effects.
Drugs
The main treatment is aimed at relieving irritation and improving the patient’s quality of life. It is impossible to completely recover from bone dyshidrosis, which is due to the lack of evidence of the occurrence of the disease. Any factor can contribute to the appearance of bubbles.
In medicine, a regimen aimed at using antihistamine sedatives that do not induce sleep in the patient is considered effective. The use of Belloid, loop diuretics, atropine sulfate, and sedatives is highly effective in the treatment of dyshidrosis.
Compresses made from resorcinol solutions are recommended as local therapy. All of these remedies show high effectiveness in cases where the disease is primary.
When the disease covers a large area of the human body, it is recommended to use laticort or locoid, the active component of which is corticosteroids. Of the new generation drugs, doctors welcome Fluorocort and Polcortolone.
There is no specific regimen for treating this disease. The attending physician can interrupt it at any time and begin to act using a different method. An example of this is a scheme based on the use of a solution of Ethacridine Lactate, lead water, and zinc ointment. If there is no effect, synthomycin emulsion, Billatominal, and manganese baths are added to the regimen.
The result of proper treatment is to minimize itching sensations, burning of the surface of the hands, and make the patient’s life easier.
In order not to harm the developing fetus and small child, all risks and side effects of the drug are taken into account. The best method is the use of antihistamines, zinc ointment, Advantan. The use of manganese baths, herbal medicine, and calcium preparations is not prohibited.
Most modern doctors advise this subgroup of patients to focus on using grandmother’s methods
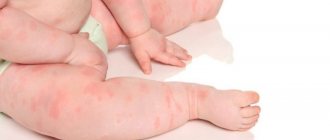
Treatment of dyshidrotic eczema in children
A detailed treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor. He focuses on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the child.
| Group of medicines | Action |
| Glucocorticosteroids for external use | Hormonal ointments relieve itching, burning, and peeling.
|
| Non-hormonal agents | They have an anti-inflammatory effect. Have a minimal number of side effects.
|
| Antihistamines | Relieves itching and produces a desensitizing effect.
|
| Antibiotics, antifungals | Preparations for external use. Prescribed for secondary infection of wounds with bacterial or fungal infection. Fight microbial pathogens.
|
When the first signs of eczema or rashes of unknown origin appear, the child should be shown to a doctor. Treating the disease on your own will only worsen the situation; the disease will quickly progress, worsening the condition. Qualified medical care will help stabilize the child’s condition and accelerate the onset of remission.
Getting rid of pathology on the legs
As noted earlier, the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema on the legs is individual in nature and is identical to the treatment of eczema on the hands.
An exception is varicose eczema, in which the following recommendations will be required:
- Wearing elastic stockings for varicose veins;
- Visiting swimming pools, fitness, aimed at strengthening the venous walls;
- The use of creams, lotions and other cosmetic preparations based on corticosteroids;
- Wearing bandages based on gelatin, Burov's solution 8%;
- The use of antihistamines;
- The use of natural-based sedatives;
- Antibiotics and antiseptics in case of complications of the disease.
Features of nutrition for eczema
Typically, the treatment regimen for eczema includes dietary adjustments. The following should be excluded from the daily menu:
- bee products;
- citrus;
- alcohol and tobacco products;
- sugar;
- canned food;
- baking;
- spicy, smoked, salty foods.
Salt cannot be completely excluded from the diet, you just need to reduce its amount. The menu is selected based on the individual characteristics of the body and disease.
A complete cure for eczema should not be expected, since this disease is chronic. However, if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the pathology will not bother a person for a long time.
Self-medication is strictly not recommended - any method of therapy has certain contraindications, and if ignored, side symptoms develop.
Treating yourself at home
Traditional methods are effective when agreed with your doctor. Otherwise, consequences may arise, aggravation of the course of dyshidrosis.
To treat dyshidrotic hand eczema at home, it is recommended to use ointments:
- Based on currants. 2 currant branches are crushed to a powder and mixed with a small amount of butter. The resulting mixture is heated in a water bath and cooled. The ointment is ready. She needs to lubricate problem areas three times a day. Currant ointment has an anti-inflammatory, regenerating effect.
- Calendula ointment. A mixture of 3 tbsp. Calendula flowers, 5g of corn oil are left to infuse for 21 days in a cool, dark place. You need to shake the container regularly. Then you need to strain it, add 1 tsp. Beeswax. All ingredients are melted in a water bath and mixed thoroughly until the mixture has a homogeneous consistency. The ointment is applied several times a day. Calendula not only helps restore the upper layer of the epidermis, but also has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect.
- Starch-based ointment. To prepare the ointment you will need 1 tbsp. Starch, 30 ml Vaseline. The prepared ointment is used to treat damaged areas. Covering the cracked surface of the hands with starch ointment helps relieve itching sensations and minimize redness of the upper layer of the epidermis.
The use of baths based on medicinal plants is highly effective in treatment. The main ones are medicinal chamomile, oak bark, and celandine.
All herbs are freely available in pharmacy kiosks. When purchasing them, instructions are included that allow you to study the purpose of the drug.
All of these herbs have effective medicinal properties.
Any treatment, even drugs that are harmless from the patient’s point of view, must be agreed at least with a dermatologist.
Local therapy
Together with systemic substances, experts advise the mandatory use of medications whose action is directed locally. For such purposes, ointments, creams, and other products that are applied directly to the area where there is irritation are suitable:
- talkers with a drying effect;
- ointments containing drying, antiseptic and restorative elements;
- lotions prepared on the basis of furatsilin, boric acid solution, Burov's liquid;
- antiseptic substances such as "Fukortsina".
Features of the therapeutic diet
Dyshidrotic lesions of the skin of the hands require proper healthy nutrition, which can speed up the healing process. To do this, exclude from your main diet foods that contain gluten (gluten).
Such products are grains. Scientists are inclined to believe that they play an important role in the occurrence of an allergic reaction and weakening of the immune system.
To reduce dyshidrosis, give preference to the following foods:
- Fish, meat, steamed or baked;
- Buckwheat, corn;
- Vegetables, except those of exotic origin;
- Black and white rice;
- Oils: vegetable, butter;
- Lactic acid products;
- Eggs;
- Bobov.
The patient can consume these food products with complete confidence, since they do not contain gluten.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- Honey;
- Chocolate;
- Alcohol;
- Citrus.
The amount of salt consumed should not go off scale. This is necessary for uniform removal of fluid and to prevent swelling of the patient.
To minimize the occurrence of relapses, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, avoid hypothermia and overheating of the skin.
Water procedures should not be long. When it comes to skin care products, preference should be given to hypoallergenic ones.
Classification and forms
Skin disease is divided into several forms, depending on the cause and symptoms. Classification of the disease:
- True
The disease begins to appear on the face and later spreads to the limbs. The vesicles quickly burst, which distinguishes the true (idiopathic) form from other types of the disease. The peak development of the pathology occurs between the ages of 30 and 40 years, but can also be observed in young people. The clinical picture of the disease is manifested by specific symptoms (typical localization, rashes appear for no apparent reason on unchanged skin), simplifying diagnosis.
- Microbial
Microbial eczema is a type of dermatitis, characterized by the development of the disease against the background of disease or as a result of microbial and fungal infections of the skin. Unlike other forms, microbial eczema is manifested by the appearance of ulcers. A similar phenomenon for the true and contact forms is a complication. Often the appearance of microbial eczema is associated with the presence of damage to the skin in the form of wounds, cuts, burns, and trophic ulcers. This form accounts for about 1/3 of all cases of eczema.
- Contact
The cause is a pathological allergic reaction to a certain irritant (food, cosmetics, fabric, household chemicals, medicines, jewelry, plants). People with a genetic predisposition to allergies are often affected. The acute form of contact eczema is characterized as contact dermatitis.
It is classified according to the nature of its flow. There are 3 stages of the disease:
- Spicy.
It is characterized by a sudden appearance of vesicles, a pronounced change in phases, and intense symptoms (swelling, redness, itching). Wetting of the lesion with copious discharge of fluid is observed. Vesicles are replaced by erosions, then crusts of yellow, brown or gray color. The duration of the course is 3-6 weeks.
- Subacute.
The development of the disease is not as rapid as in the acute form. Symptoms and exudate are moderate. The affected area is distinguished by the acquisition of a bluish tint. The duration of the disease can last up to 24 weeks.
- Chronic.
There is coarsening, thickening of the stratum corneum, increased infiltration, itching and hyperemia. Exacerbation of the chronic form is characterized by the appearance of exudate.

Possible consequences on the fingers
Ignoring treatment of the disease and taking preventive measures leads to consequences that will bring discomfort and ruin life.
Lack of treatment helps to keratinize the upper layer of the epidermis, and peeling of the skin does not stop. Over time, the patient feels constant weakness, fatigue, and migraines. The immune system weakens, the patient’s emotional state leaves much to be desired.
In parallel with the indicated symptoms, the patient begins to become apathetic and loses his appetite. The temperature is unstable and subfebrile.
The consequences of the disease most strongly affect small children and women bearing a child.