When the skin peels off, and even accompanied by painful sensations, this greatly affects the general background, mood, and quality of life of the sick person. At the same time, it is equally painful to observe the suffering of both adult patients and small children. But exfoliative dermatitis, whose characteristic feature is a layered breakdown of the skin, can even affect newborns, whose skin is already delicate. Difficulties in healing open continuous wounds may lie in correctly identifying the causes, making a diagnosis and selecting one or another treatment method.
Description of the skin disease, prerequisites for its occurrence
Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis belongs to a group of dangerous contagious diseases that most often affect children under one year of age. The disease exfoliative dermatitis is the result of the presence of spherical gram-positive bacteria from the genus Staphylococcus.
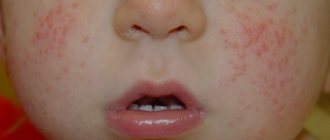
The disease initially forms on the skin of the oral cavity and then spreads throughout the body. Initially, bubbles appear on the epithelial tissue, which transform into ulcers. In this case, almost all of the infected person’s skin turns red.
The symptoms of the disease are pronounced enough to make a diagnosis without difficulty. The main thing is to eliminate other skin diseases with similar symptoms. The disease ritter exfoliative dermatitis in newborns is most often formed as a result of exposure to staphylococcus, sometimes together with streptococcus.
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults can occur for several reasons:
- as a complication of the main disease (skin reaction (dermatitis) resulting from exposure to allergens or irritants,
- as a result of inflammation of the skin by the causative agent of dermatitis, a yeast-like fungus of the Malassezia species,
- chronic allergic dermatitis, scaly lichen),
- as a result of drug use,
- when using certain pharmaceuticals that cause an allergic response.
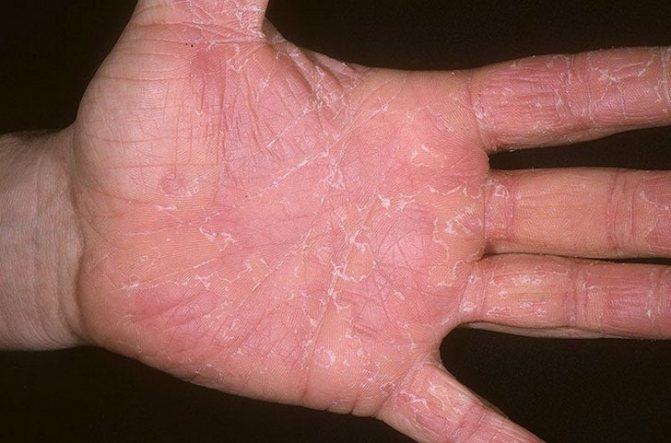
Reasons for the development of exfoliative dermatitis
The development of pathology is facilitated by the immaturity of the barrier function of the skin and the lack of its own immunity. Infection occurs in most cases in maternity wards from mother to child or from medical personnel caring for infants. The source of infection can be a focus of purulent infection located on the child’s body (inflammation of the umbilical ring), or other sick children nearby. The pathogen is transmitted through contact and household contact through hands and tools.
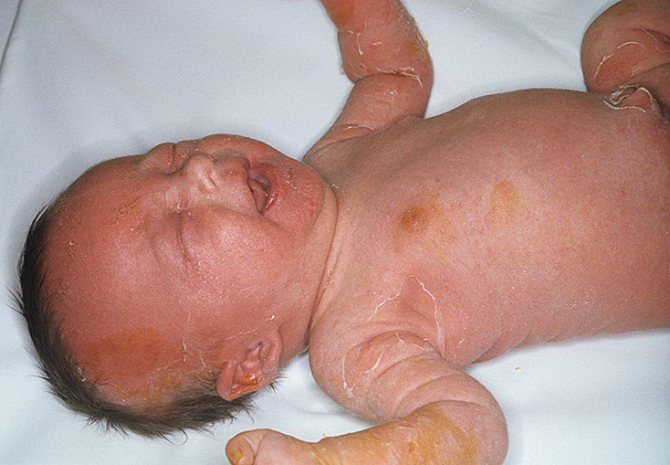
Stages of the disease in children and adults
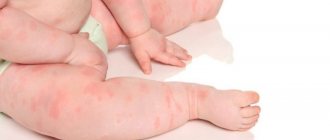
This type of dermatitis in newborns appears a couple of days after birth. The disease goes through 3 key stages.
- The erythematous stage is characterized by damage to the oral cavity, the navel. Redness occurs, and then peeling. Similar scarlet zones, alternating with the appearance of dry crusts, appear in the folds of the skin, on the genitals and anal area, then cover the entire body.
- The exfoliative stage forms three days after the blisters open, and scarlet areas of the skin (similar to a burn) are visible. You can see what exfoliative dermatitis looks like in the photo. Characteristic signs of this stage are: fever (up to 40 C), vomiting, diarrhea.
- The regenerative stage begins 2 weeks after the onset of the disease. At this stage, it is important to monitor the child, because infection can get into hidden blisters. Despite this, the health status improves noticeably as the temperature drops, the child begins to eat and sleep well.
Exfoliative dermatitis of newborns is dangerous due to the formation of inflammation with pus when infection penetrates into the ulcers. As a result, the skin disease can occur in a more severe form, for example, otitis media, pneumonia, meningitis, or an acute inflammatory process in the peritoneum.
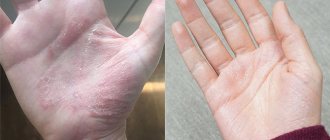
A skin disease in an adult is formed in the form of redness of the skin, as well as peeling.
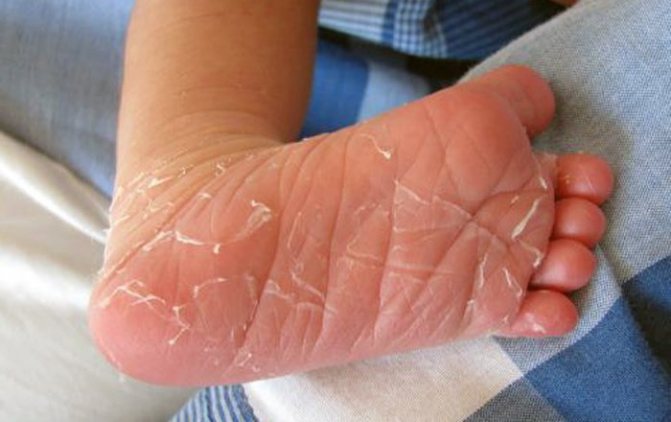
The patient feels severe irritation; blisters and ulcers appear on the surface after opening. The lymph nodes enlarge and the temperature rises. Patients may often complain of a feeling of chills.
Definition
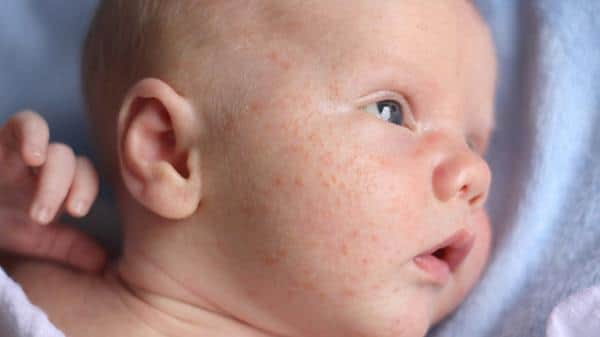
Exfoliative dermatitis is a severe infectious skin disease that affects large areas of the body and is characterized by hyperemia, bullae and peeling. The disease most often affects newborns, but people of any age and gender can get sick. Other infectious dermatitis is discussed in this article.
IMPORTANT: The pathological condition is very contagious, so when caring for the patient you should wear protective equipment (gloves, apron, mask).
Symptoms
Let's look at the symptoms of Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis in adults. The main ones look like this:
- temperature and lymph nodes increase,
- the vessels of the circulatory system are filled with blood,
- the skin thickens,
- crusts appear
- rash with the appearance of blisters and then the formation of ulcers,
- an unpleasant sensation of irritation, burning and tingling on the surface of the skin.
In older children and newborns, the symptoms differ from those in adults: redness is observed not only in the mouth, but also in the navel area. In older children, ritter's dermatitis occurs in a mild form, that is, redness and peeling of the dermis. The disease goes away within 14 days. But in children, skin disease can occur with complications.
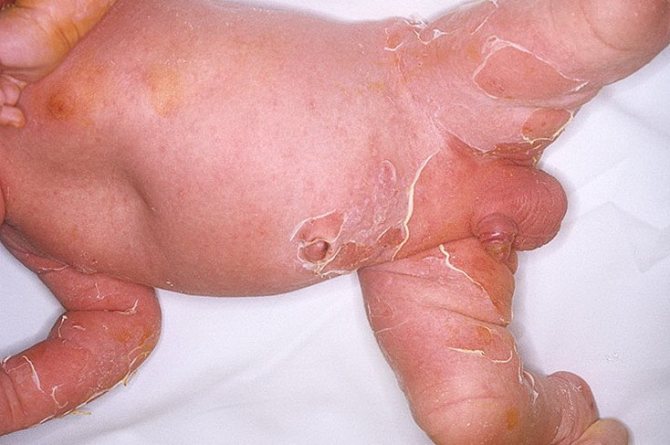
Let's look at what the disease Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis looks like at the stages of its development in a baby:
- Erythematous stage of the disease. The mucous layers of the oral cavity turn purple, and swelling can be noticed. Over time, the redness changes to watery, colorless blisters. The dermatological surfaces become loose.
- Exfoliative stage of the disease. The resulting liquid in the bubbles changes color to a more cloudy shade. The blisters crack as a result of contact with clothing and transform into wet eczema. Near such areas, the skin begins to peel off and flakes off over time. Nikolsky's signs (pemphigus sign) appear: when the wall of the bladder is pulled back with tweezers, the epidermis exfoliates outside the boundaries of the bladder. The disease resembles burns, as with the second degree of damage to the skin.
- Recovery phase. The symptoms weaken significantly, and the ulcers begin to heal.
In variants, if the disorder contains a simple form of the disease, the transition from one stage to another is almost unremarkable. With a severe course of the disease, exfoliative dermatitis increases the risk of blood poisoning, which is fraught with complications. In the rarest cases, death is likely.
Drug therapy for exfoliative dermatitis
Treatment is carried out in two directions: the patient is prescribed antibiotics for oral administration, creams and ointments with an antibacterial effect. In severe cases, corticosteroids are used. To strengthen the immune system, vitamins C and B are prescribed. Infants are advised to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Since wearing any clothing causes unbearable pain to babies, they are simply swaddled loosely in diapers previously sprinkled with zinc oxide or talc, to which antibiotic or sulfonamide powders have been added. It is advisable to immediately place sick newborn children in special cuvettes that allow maintaining optimal temperature and humidity.
In adults, the blisters are opened, the remaining skin is removed, the erosions are generously covered with antiseptic solutions, and then treated with ointments that contain glucocorticosteroids. Bathing in water with potassium permanganate is shown.

At the same time, the patient must take antibacterial drugs orally, agents that help quickly remove toxins from the body.
How is the examination carried out?
A skin disease is diagnosed and treated by a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist, so the conclusion can be determined by one of two professional doctors.

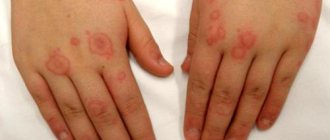
The baby is tested for syphilis, and diseases with similar symptoms are also excluded, for example:
- disease with the appearance of bullae - elements of skin rash d over 5 mm,
- inflammatory reaction to contact with an irritant,
- autoimmune disease (Dühring's dermatitis),
- a common viral disease caused by herpes,
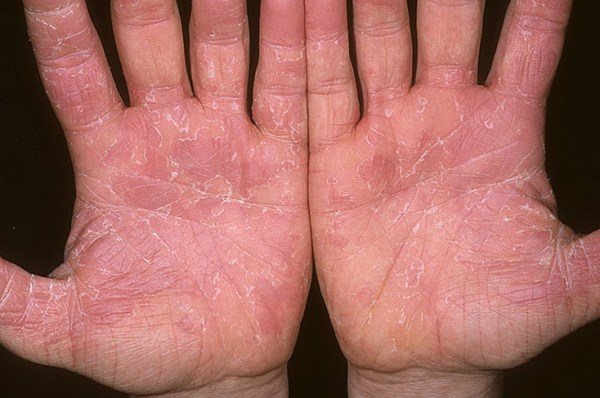
- manifestation of early congenital syphilis with the formation of blisters mainly on the palms.
Complications
Exfoliative dermatitis can lead to the following complications:
- otitis;
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- peritonitis;
- phlegmon;
- acute enterocolitis.
The disease can acquire an even more severe form if other infectious lesions in the form of pneumonia, otitis media, meningitis, etc. are added to the course of the disease. In this case, the disease is extremely severe, and the consequences are extremely dangerous, including death.
There is also a milder form of dermatitis. The course of the disease in this case is difficult to divide into stages; it is more erased and blurred. With proper diagnosis and treatment, after 10-14 days the baby’s skin inflammatory processes begin to subside; a sign of recovery is lamellar peeling of the skin. After peeling, new epithelium appears and the affected areas recover.
Adult therapy
You can see what exfoliative dermatitis looks like in adults in the photo. When the disease is mild without complications, adults can be treated at home, naturally only after diagnosis. To achieve a result, the main thing is to find out the root cause and eliminate it: stop the medication that causes inflammation of the skin, restore glucose levels.

While searching for the cause of the disease, after culture, treatment begins, which includes taking pharmaceuticals (local and systemic therapy).
Local treatment – treatment of blisters and ulcers with solutions, organic compounds formed during the oxidation of aniline, application of antibacterial ointments (Levomekol). When the disease appears due to a chronic non-infectious skin disease (psoriasis) or fungal infection, the doctor prescribes PUVA therapy.
Systemic therapy depends on the background and severity of exfoliative dermatitis. When the disease is caused by microorganisms, medications are needed; when it is a fungal process, anti-fungal substances are needed; in case of impaired glucose metabolism, it is necessary to restore the concentration of sugar in the blood. The treatment of lichen planus is attributed to the substance isotretinoin. When the factor is not determined, systemic substances are administered exclusively as needed (one drug at a time).
Stages of development in newborns
Scalded skin syndrome has 3 stages of development. Each of them has its own clinic. Let's take a closer look at them.
Erythematous
This stage is characterized by the appearance of hyperemic areas of the skin in the mouth and navel. Over time, the skin peels off. Later, the same signs of the disease appear in large skin folds, in the genital area and around the anus.
The process then covers the entire body. Redness may also appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose or genitals. Flaky areas have swelling and large blisters with a diameter of 5 mm. It is for this reason that this dermatitis is also called bullous.
Exfoliative
This stage occurs 3 days after the onset of the disease. It is characterized by the opening of blisters and the appearance of red areas of the skin, reminiscent of a burn. The baby develops a fever, diarrhea and vomiting. The newborn does not latch on to the breast, appetite is reduced, and body weight is lost. If help is not provided, the child may die.
Regenerative
Corresponds to 10-14 days of illness, if medical care is provided to the infant. Swelling, redness and body temperature decrease, appetite appears, and sleep is restored.
Ritter's disease has 3 degrees of severity:
- mild - a small number of blisters, there is no clear stage of disease development. The child recovers within 10-14 days;
- medium - clear stages of disease development are characteristic. Recovery without complications;
- severe - infection of opened blisters, passage of bacteria into the blood, spread of the pathogen throughout the body.
Treatment for babies
Treatment of Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis in newborns is carried out only in a hospital. The baby is in the room with his mother. The child is in a separate ditch. Children are prescribed medications that are administered intravenously. These are cephalosporin antibiotics (cephaloridine), which are effective against various diseases and are not toxic.

A group of antibiotics with a bactericidal type of action eliminates bacteria by inhibiting cell wall synthesis, so the drug acts effectively and quickly, accelerating the healing process.
To prevent dehydration, treatment with Polyglucin solution is used or Hartmann's saline solution (Ringer's solution with lactate) is used. Newborns and infants may require additional glucose administration. A 10% or 20% solution is injected. To prevent the formation of dysbiosis due to the introduction of antibiotics into the body, the doctor may prescribe probiotics.
Healthy areas of the skin are treated with Fukortsin solution, and the blisters are opened.
Therapeutic measures
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults is not nearly as dangerous as in children. Hence the difference in the degree of urgency of treatment.
Although even adults often have to undergo infusion therapy due to the large loss of protein, iron and electrolytes.
Treatment methods are determined by three points:
- the severity of the pathology;
- the age of the patient (directly related to the first point);
- and the possible cause of the disease, if one can be determined.
Based on local treatment.
Skin areas are treated with salicylic alcohol to disinfect and prevent secondary infection.
Emollients are used:
- Emolium;
- Lipikar;
- Atopic et al.
- Emollients restore pH and water-electrolyte balance of the skin.
- They form an additional lipid layer that prevents moisture loss.
- Promote the synthesis of elastin and collagen in the thickness of the dermis.
For severe inflammation, hormonal ointments can be used:
- Akriderm;
- Advantan;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone;
- Sinaflan.
Zinc oil or zinc paste is often used.
If exfoliative dermatitis is observed in newborns, urgent intensive use of antibiotics is required, which are prescribed parenterally.
Since this implies a severe staphylococcal infection, the following is used:
- cephalosporins of the latest generations (Cefotaxime, Cefepime, Ceftaroline);
- or macrolides (Roxithromycin, Josamycin).
Antistaphylococcal plasma and antistaphylococcal gamma globulin are administered. Infusion therapy with Dextran (analogue - complex saline solution) is used against dehydration.
In adults, drug treatment is highly dependent on the underlying causes.
In severe forms, systemic glucocorticosteroids are used:
- Prednisolone;
- Dexamethasone;
- Diprospan.
For cascading allergies, antihistamines can be used:
- Suprastin;
- Ebastine;
- Loratadine;
- Erius (Desloratadine).
For autoimmune pathologies, the use of special immunosuppressants (Azathioprine).
For infection - antibiotics.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies can serve as a good additional therapy, and also act as a preventative measure.
Examples of folk recipes:
- add one teaspoon of birch tar to any hypoallergenic cream, heat it in a water bath to 70 degrees, lubricate skin lesions 2 times a day;
- add 50 g of sour cream to freshly prepared mashed potatoes, wrap in a bandage or gauze and apply this compress to the affected areas for one hour;
- Gauze compresses soaked in yarrow decoction help a lot.
Before using traditional recipes, notify your dermatologist.
Various complications often arise.
Loss of protein, iron, electrolytes and water can lead to damage to internal organs.
Inflammation can trigger a secondary infection. The same Staphylococcus aureus, which is normally found in small quantities on the skin of many people.
Less commonly, chronic skin inflammation threatens the generation of atypical cells (oncological neoplasms).
Treatment with folk remedies
When treatment is prescribed to an adult, the doctor may additionally recommend therapy with folk remedies. It is not recommended to treat the disease on your own, because even seemingly harmless herbs can worsen your health. The following treatment methods are prescribed from folk remedies:
- compresses and lotions,
- bathing in herbal infusions,
- taking the decoction internally.
For treatment, baths with decoctions of string, celandine or chamomile are used. To make it, you need to take 300 grams of a mixture of plants, which are filled with two liters of water. Boil the liquid for fifteen minutes.

Decoctions for drinking are made from calendula. To prepare the drink, you need to pour 2 tbsp. l. plants 0.5 liters of boiling water. The broth sits for half an hour, then it needs to be strained. Use 125 ml of the product up to four times a day.
Prevention measures
For adults:
- eliminate the allergen,
- lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right,
- skin diseases are treated at the initial stage.
Prevention to exclude skin diseases in babies:
- periodic inspection of maternity hospital staff for the presence of a carrier,
- mothers should be tested for the presence of staphylococcus,
- the process of treating (disinfecting) chambers with quartz,
- the use of gauze bandages by doctors when examining babies.

To summarize, it is worth noting that if you have any suspicions and identify similar signs of the disease, you need to seek advice from the clinic. It is not difficult to recognize the disease, since the symptoms are pronounced. To confirm or refute the diagnosis of the disease, it is necessary to do a tank culture - a technique for studying the bacteriological component in a liquid taken from formed bubbles.