Skin diseases in infants are common and are considered quite dangerous. For example, eczema in infants is characterized by obvious swelling of the skin, which the baby’s parents notice in the neonatal period or during several months of the child’s life.
Clinical picture and symptoms of eczema in infants
Atopic dermatitis or eczema occurs in children with problems in the immune system, and especially often manifests itself if there are suspicions of autoimmune diseases. Inflammation of some areas of the skin may accompany chronic bronchial asthma and other respiratory diseases. It can be correctly diagnosed only in a hospital setting based on the following symptoms:
- peeling of the skin on the elbows and knees;
- swelling of tissues;
- weeping rashes on the baby’s bottom, in the folds;
- small pink spots on the skin;
- itching of a different nature (parents can notice it in the child if he is constantly nervous, spinning in a lying position).
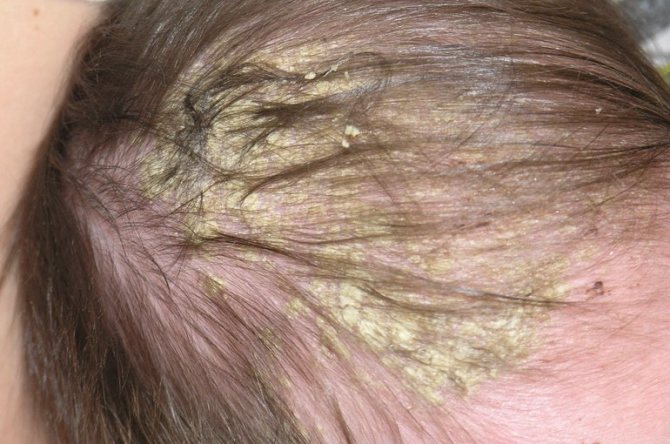
- Eczema on the baby's head brings discomfort and prevents the skin from breathing freely
If emerging atopic dermatitis is not stopped in time, it can develop into a secondary infection in an infant and develop into purulent ulcers on the skin. In such situations, doctors suspect a staphylococcal infection and refer the baby for blood and urine tests.
Note to moms! In order not to miss the development of eczema in infants into a serious pathology, it is important to know all the signs of this disease, so be sure to look at our photos with the different nature of skin rashes.
Diagnostics
Differentiation of eczema from other similar skin pathologies is carried out on the basis of:
- Anamnesis data. Recent illnesses are studied not only by the child, but also by those in contact with him.
- Physical activities. At the initial examination, the nature of the rash and enlargement of the lymph nodes are recorded.
- Ultrasound examination. Hepatomegaly is recorded, and splenomegaly is rare.
- Laboratory test results. A general blood test determines hypochromia of erythrocytes, increased levels of leukocytes, deficiency (in eczema herpetiformis) or increased number of eosinophils.
- Specific diagnostics. Tzanck tests make it possible to establish the category of pathogenic agents by scraping from the bottom of the vesicles. The polymer chain reaction (PCR) test helps determine the exact group of the virus. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects an elevated IgM titer by four or more times.
The basis for making an accurate diagnosis is the cumulative picture of clinical manifestations and research results.

Types of skin eczema in infants
In medical practice, there are four types of eczema in infants.
Seborrheic eczema (dry) rarely develops into a more serious infection and can be treated more quickly with the right medications. Accompanied by intense itching, peeling of the skin, and may resemble seborrheic dermatitis on the head of a newborn.
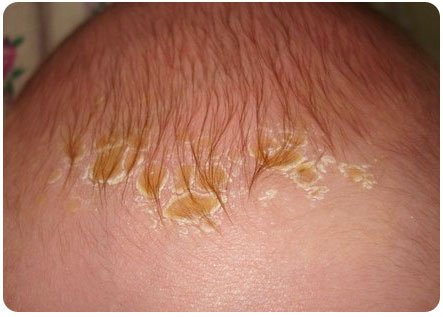
Seborrheic eczema in infants manifests itself in the form of scales in the hair and dry skin
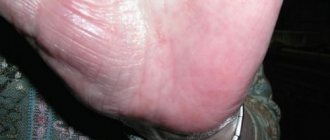
Weeping eczema in infants is a more dangerous type of skin disease, as it often turns into a purulent form due to improper treatment with medications. Its symptoms are red spots with a moist center. Due to the proliferation of bacteria, the infection spreads further throughout the body. The first foci of pathology are found on the cheeks, skin of the hands, and on the butt.

Weeping eczema in an infant begins with the appearance of a rash with a purulent core
Microbial eczema is caused by the development of infectious processes in the body due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus. It is characterized by obvious swelling of the skin in the affected areas.
Children say! I’m going through a difficult period, I’m sitting sad. Andreika (3 years 1 month) walks around, hugs him and says: “Mommy, why are you so upset, you have a son, don’t be upset.”
Toxic eczema in infants appears in the maternity hospital and is caused by the adaptation of the small organism to the environment. This type of disease cannot be treated systemically; only antihistamines can be used to eliminate it.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of eczema in children is quite similar to other types of dermatitis.
The disease can be recognized by the following signs:
- the upper layer of the dermis becomes covered with red spots, the process of inflammation with swelling of the affected areas is visualized;
- initial localization - face and scalp, with possible further generalization to other anatomical zones;
- neoplasms in the form of small nodules and papules;
- severe itching and burning;
- surface with intense rejection of dead cells;
- getting wet;
- after opening the papules, crusts form;
- significant weight loss due to decreased appetite;
- decreased turgor and pale skin;
- frequent crying and irritability.
Regardless of the type of eczema, focal lesions have clearly defined edges. Usually, in the evening and night periods, the itching becomes more intense, and the child begins to scratch the rash until bleeding wounds form.
When becoming chronic, the disease tends to recur under unfavorable circumstances: cold season, period of vitamin deficiency, stress, etc.
Causes of eczema in infants
Any type of atopic dermatitis is acquired in a child after birth (within several months). This may be influenced by hereditary reasons, as well as other factors that differ in internal and external. The first include:
- the entry of viruses and bacteria into the baby’s body (they often enter the baby’s body through amniotic fluid);
- affects the intestinal biocenosis and its dysbacteriosis, which arose due to problems with the endocrine system;
- vitamin deficiency or deficiency of essential vitamins and enzymes.
The second ones include:
When eczema appears in a baby, the cause may be a problem with the tummy (biocenosis, dysbiosis)
- incorrectly selected drugs for the treatment of other diseases;
- allergies to certain foods through breast milk;
- intolerance to certain baby hygiene products;
- stress in the infant due to concomitant diseases or lack of attention.
Each reason has its own explanation, so it is imperative to find it and prescribe treatment to eliminate the negative impact factor, and only then relieve the disturbing symptoms.
Causes
The cause of eczema in a child can be caused by a variety of factors. In some cases, several endogenous indicators may serve as favorable conditions for the development of the disease.
Causes of eczema in children:
- Genetic predisposition. First of all, children are susceptible in the DNA chain, which contains a mutated gene that predetermines a tendency to allergic reactions.
- Disorder of humoral-metabolic coordination. This pathology is observed with regulatory dysfunction of the nervous system. Cases of eczema occurring in children have been recorded after suffering emotional shocks or experiencing stressful situations. Such disorders are found in children who often change their place of residence, in single-parent families, after the death of a loved one, etc.
- High sensitivity of the skin - an instant allergic reaction. As a rule, such children have white skin, prone to immediate manifestations in the form of diathesis or redness when in contact with an irritant.
- Impaired immunological reactivity. Hereditary or acquired immunodeficiency provokes more severe reactions of the body to the allergen. Premature babies or those with chronic diseases are susceptible to this pathology.
- Foci of secondary infection. Some infections are combined and sometimes linked by etiology. With such configurations, the microbial flora significantly increases the pathological effect on the baby’s body, which explains the appearance of eczema symptoms.
- Artificial feeding. The mother’s refusal to breastfeed, and, accordingly, the transfer of immune antibodies, provokes a decrease in the stability of the infant’s internal environment and its ability to fight infectious agents. Also, an incorrectly selected milk formula that does not properly saturate with all the necessary microelements, which can contribute to the production of specific antibodies of the immunoglobulin G and E classes (IgG, IgE).
- Incorrectly selected care products. The skin of a newborn is most susceptible to the action of various chemicals included in cosmetic hygiene products.
In the first months after birth, the child must be bathed exclusively in a decoction of string or chamomile. Dermatologists do not recommend using any hygiene products other than herbal infusions for up to a month.
Methods for treating eczema in infants
Drug therapy may vary depending on the location of the disease, as well as the type of its development. If eczema appears on the face, legs and arms in children, medicinal ointments for topical use are prescribed: Bepanten, Boroplus, Levomekol.

Eczema in infants is treated symptomatically with Levomekol ointment
To stop the process of inflammation in the body, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, for example, Amoxiclav, Lizomycin, Erythromycin. To moisturize the affected areas, it is necessary to use Videstim or Keratolan ointments, and Fenistil ointment is used to get rid of itching. Homeopathy can be practiced as a safe treatment option.
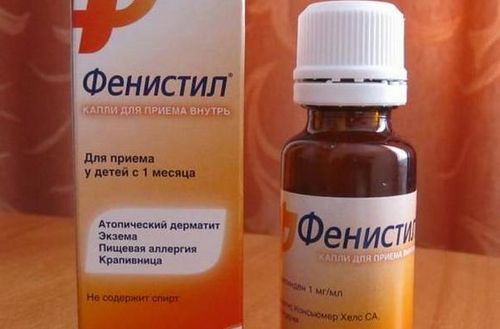
Fenistil perfectly relieves itching if eczema develops in a baby
When coin-shaped eczema is detected in an infant, the pediatrician prescribes phototherapy or the use of antibacterial drugs Oksalicin, Amiksin. Compresses with the following medications help get rid of weeping eczema in newborns and children of the first year of life: Boric acid (1%), Resorcinol (2%), Tannin (0.25%).
The microbial form of the disease must be treated by taking antibiotics Flemoxin, Amoxiclav by injection, with an age-appropriate dosage. In addition to taking medications, it is recommended to use components to restore immunity. These include vitamin complexes in MultitabsBaby and PolivitBaby suspensions.
Complications and consequences
When Kaposi's eczema is diagnosed, most children often experience loose stools and possible vomiting. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the child’s condition and take appropriate measures to replenish the water-salt balance in a timely manner. This form of the disease can cause complications in the form of: pustular rashes, meningitis, sepsis. The most dangerous manifestations are in young children - up to one year.
Dangerous complications with a fatal outcome are rarely recorded (15%): swelling of the cervical tissues, arrhythmia, pneumonia.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies are an excellent addition to the treatment of eczema in infants with medications. To alleviate the condition of the skin, be sure to make lotions from a decoction of currant and viburnum leaves (in equal quantities).
Honey tincture
Homemade honey ointment is an excellent remedy if eczema occurs in a baby
To prepare the product you will need 100 g. honey, 2 tbsp. plantain leaves, juice of three viburnum berries, 2 drops of birch tar and 1 teaspoon of petroleum jelly. All components must be thoroughly mixed, infused for one hour, and then applied to the affected areas. It is recommended to use the product for no more than five days.
Children say! It's approaching March 8, my daughter (7 years old) asks me: - Mom, what do you like to do? They had to prepare something at school about mothers for March 8th. And he immediately warns: “Others have already said about “sleeping” and “reading”...
Burdock ointment
It consists of the following ingredients: burdock oil and honey in a ratio of 1 to 2. The composition is mixed well, and the ointment is used strictly on the affected areas in the evening before bed. If you make lotions from this composition, it is recommended to add traditional chamomile infusion (2 tablespoons of inflorescences per 1 liter of boiling water).
Treatment at home
In addition to traditional methods, folk recipes demonstrate high effectiveness in treating eczema.
However, before using them, it is important to consult a doctor - each treatment method, in addition to its beneficial properties, has contraindications with side effects that are important to consider.
| Decoction for baths | Mix in equal proportions:
Pour boiling water (0.5 l) over the herbs. Infuse, cool, strain. Use for baths. The duration of the procedure is more than 15 minutes. |
| Potato juice | Grind the potatoes, squeeze out the juice, mix it with 1 tsp. honey, stir to a thick paste. Use the composition as a night compress. The next morning, remove the product and rinse your foot with warm water. If you are allergic to honey, you can use only potato juice or mix it with aloe juice. |
| Strawberry puree | Prepare berry puree. Apply to affected skin, wrap with film and wrap with a towel. Remove with warm water after an hour. |
Eczema on the legs is a fairly common dermatological disease. Without timely medical care, the disease will begin to worsen and provoke the development of serious complications. When the first signs of the disease appear, you need to take the child to a medical facility to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
What can parents do?
If the stage of eczema in infants is not serious, then it can be dealt with at home. To do this, parents must provide favorable conditions for getting rid of the disease. Follow these activities:
- wash the baby’s damaged skin daily with a decoction of oak bark in the morning and evening;
- consult a pediatric dermatologist about which healing lotions are acceptable for use, and purchase them at the pharmacy;
- Be sure to consider humidifying the indoor air. If it is not possible to purchase a special humidifier, dry your clothes on radiators after washing;

If the air is dry, a humidifier is required for eczema in infants.
- Eliminate all allergy-causing foods from your diet if you are breastfeeding.
Note to moms! It is necessary to treat eczema at home and using folk remedies only after consulting a doctor, since self-therapy can cause complications and secondary infection of the skin.
Photo of childhood eczema: what it looks like
The childhood stages of the disease have a similar set of symptoms as in adults. At the acute stage, the rash forms quickly, with large affected areas and is accompanied by severe itching. The entire development cycle of papules occurs in an accelerated manner; as a result of their opening, crusts form, after which all symptoms begin to subside.
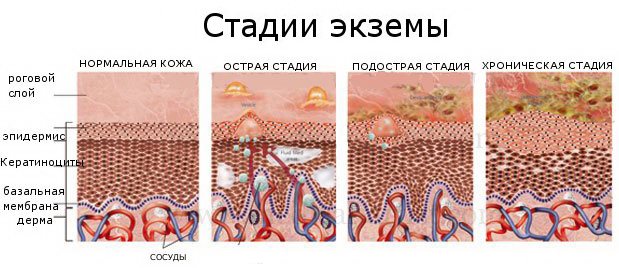
The subacute stage is characterized by a rash with a bluish tint and moderate itching.
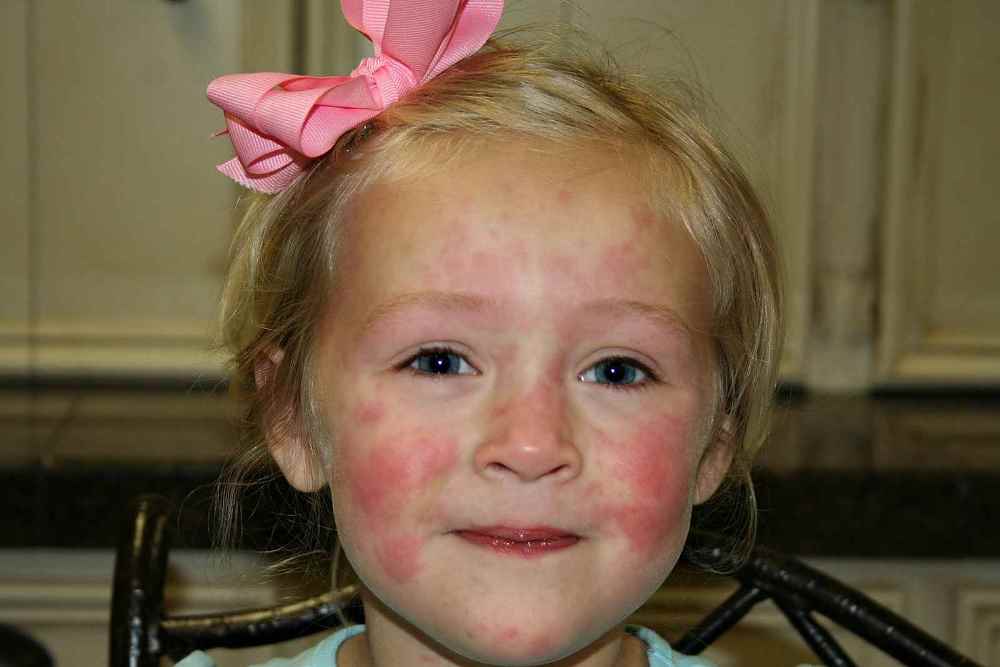
Main article: What eczema looks like
A few words about preventive measures

Any risk of eczema in the neonatal period arises during uterine development due to the incorrect attitude of the expectant mother to her current status. Therefore, it is important to follow several recommendations.
- Explore and practice nutritional options for pregnant women.
- Be sure to give up bad habits (they can cause other pathologies).
- Do not eat a lot of sweets and carbohydrates (only in the required quantity).
- After birth, it is not recommended to wrap the baby in order to avoid overheating and, as a result, the occurrence of prickly heat with complications.
- Do not introduce early complementary foods, since the baby’s gastrointestinal tract must be prepared for this during the first six months of its life.
By putting these simple tips into practice, you will be able to protect your child from the manifestations of atopic dermatitis and many other skin pathologies.
Dr. Komarovsky examines in detail the problem of eczema in infants and older children - watch the video.