[Allergic tonsillitis] (or rather, toxic-allergic) is one of the forms of chronic tonsillitis. It’s worth understanding everything in order.
Tonsillitis is an inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils, consisting of lymphoid tissue.
Pathogenic microflora (viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.), entering the human body through the respiratory tract, encounter defenders on its way in the form of gammaglobulin, lymphocytes, interferon. These substances are produced by the tonsils and lymph nodes.
The result of such a meeting, most often, is the death of harmful microorganisms, and nothing threatens human health.
But this doesn't always happen. If for some reason the protective substances cannot cope with pathogenic agents, then viruses, bacteria, etc. multiply intensively on the surface of the tonsils.
The tonsils eventually become inflamed and their immunoprotective ability is weakened. As a result, tonsillitis develops.
If acute inflammation of the tonsils (in other words, sore throat) occurs several times a year, i.e., has frequent frequency, then tonsillitis becomes chronic.
Causes of the disease
The main factor influencing the appearance of allergic tonsillitis is associated with an abnormal increased sensitivity reaction of the body. The palatine tonsils perform a protective function. They are a kind of barrier against harmful microorganisms that penetrate the throat along with food, liquid, and air. When immunity decreases, these bacteria lead to sore throat. Allergic tonsillitis appears with frequent sore throats.
Only in some cases is it considered a primary disease. As a rule, its appearance is preceded by a sore throat.
The allergic form appears when the body is in a state of hypersensitivity. Serious immune disorders, as a result of which a person suffered from measles or scarlet fever, can also cause tonsillitis. Violation of the formation of acquired immunity is the main cause of the disease.
You may be interested in:Medicines for allergies: list with names, ranking of the best, indications and contraindications
If a person often suffers from ARVI, it can be assumed that the cells to a particular infectious agent are poorly formed. Such patients often suffer from the same infection.
Caries or sinusitis can also be a provoking factor. Polyposis of the nasal cavity, adenoids, and deviated nasal septum can also lead to allergic tonsillitis. Even chronic rhinitis or sinusitis provokes the development of pathology.
The development of the disease is accompanied by a number of reasons
Causes of chronic tonsillitis.
- Frequent frequency of sore throats. As a rule, tonsillitis occurs again and again due to improper or inadequate treatment. Some patients prescribe therapy for themselves, relying on “grandmother’s” knowledge and not taking into account many of the nuances of the disease.
- Infections of the oral cavity: gingivitis, periodontal disease, stomatitis, etc. If these infections are not treated for a long time, then they greatly contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis, supplying the body with a new “portion” of microbes, bacteria, fungi, etc.
- Nasal infections. These include sinusitis and purulent sinusitis.
- Impaired respiratory function of the nose, which can occur due to polyps in the nasal passage, enlarged adenoids, or a broken or deformed septum.
- Dental caries. In the resulting tooth cavities, excellent conditions are created for the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria.
- Heredity. Children whose parents suffer from tonsillitis may inherit this disease.
All of the above reasons do not necessarily cause chronic tonsillitis (95% of the population has caries, but not everyone suffers from tonsillitis).
They (the reasons) begin to manifest themselves seriously if the person’s immune system is weakened. A decrease in immunity is influenced by a number of factors.
- Previous illnesses for which strong medications or complex procedures were used.
- Frequent hypothermia of the body (complete or partial).
- High fatigue - physical or mental.
- Tense nervous states of a person, depression, stress.
- Lack of sleep, lack of proper rest and, as a result, chronic fatigue.
- Alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction. These habits are called harmful because they significantly reduce immunity.
- Harmful working conditions - increased dust, gas contamination, humidity in production. People who work in cryogenic installations also often suffer from tonsillitis.
- Poor environmental conditions. High concentrations of exhaust gases in large cities and industrial emissions into the atmosphere lead to an increase in the number of patients with chronic tonsillitis.
Important to know: Is chronic tonsillitis contagious or not?
Having understood the causes of the disease, you should know what symptoms accompany it.
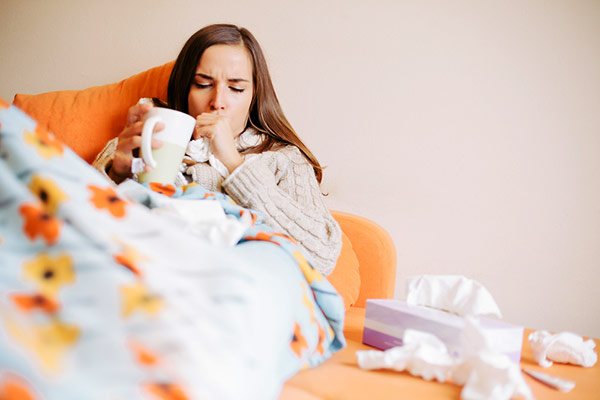

Manifestations of allergic tonsillitis
Many people know about sore throat or so-called tonsillitis. Most often people get it in autumn, winter, spring, when the wind blows and it is too damp outside.

At the beginning of the development of the disease, pain will be felt in the throat. Sometimes it seems as if something foreign has stuck to the palate, preventing normal breathing. Essentially, the foreign bodies in this case are swollen and painful tonsils.
They increase in size and block the gap in the throat. Because of this, breathing becomes difficult. It is difficult for a person to speak, swallow, and pain occurs. It even happens that opening the mouth and chewing food is accompanied by pain. A person may feel short of breath.
There is an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The surface of the tonsils becomes loose, the palatine arches swell and acquire a reddish tint. In the lacunae of the tonsils, purulent white or grayish-yellow masses with an unpleasant odor accumulate.
You may be interested in:Hypoallergenic menu: diet, permitted and prohibited foods and sample menu for the week
In addition to these symptoms of allergic tonsillitis, a noticeable enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is possible. When they are palpated, pain occurs. Against the background of the inflammatory process, the temperature rises. It's hard to knock her down. The elevated temperature will persist until the inflammatory process stops.
In young children, the temperature may be critical, requiring immediate hospitalization. The signs and symptomatic manifestations of tonsillitis are similar to infectious tonsillitis.
In severe situations, a diagnosis of “chronic toxic-allergic tonsillitis” may be made. The form of the disease requires mandatory removal of the tonsils. Moreover, against the background of the development of this pathology, dysfunction of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems may be observed.
Allergic sore throat - description, treatment, symptoms
Allergic angina has the same symptoms as other types of the disease. However, inflammatory processes in the tonsils are caused by exposure to incompatible irritants - allergens.
Infected tonsils become very swollen, which leads to impaired breathing and swallowing function. In some cases, suffocation develops and anaphylactic shock is possible.
Due to the rapid deterioration of the environment, resistance to irritants is greatly reduced . This fact contributes to more frequent treatment of patients with symptoms of this pathology.
The main difference between allergic angina and other forms of tonsillitis is the provoking factor of the inflammatory center - not bacterial, but allergic irritants.
You can protect yourself and your family from angina if you know what causes it.
Causes of allergic sore throat

The immune system of a healthy person easily copes with blood-borne allergens. A toxic-allergic reaction often occurs when the body's own defenses are weakened or when there is an innate intolerance to individual stimuli. This type of tonsillitis occurs as a complication and can lead to a number of other diseases.
However, provoking factors can be not only elements incompatible with the body, but also some concomitant diseases that cause allergic angina:
- Weather Conditions.
- Depth of Odors (tobacco smoke, chemicals, perfumes).
- Avitaminosis .
- Chronic pectoris sore throat.
- Seizures Other allergic subtypes, also seasonal.
- New medical.
- Significant change in climatic conditions .
- insect bites .
The list of possible causes is suitable for all types of atopes.
For the first symptoms of the disease, it is very important to receive qualified help in a timely manner.
Symptoms of allergic sore throat
As in other pathological processes, the symptoms of toxic allergic tonsillitis appear in several successive stages .
primary symptoms of allergic angina:
- Painful sensations in the larynx, including swallowing.
- difficulty breathing difficulty breathing function.
- The appearance of characteristic wheezing, coughing, suffocation.
- Pain and enlargement of lymphatic connections upon palpation.
- sinuses , lacrimation.
- More unpleasant taste .
Subsequent manifestations of the disease are more dangerous and require immediate medical intervention . The most common of them:
- oropharyngeal tumor.
- hyperemia and loosening of the surface of the tonsil , the appearance of plaque, burning, accumulation of mucus during examination of the pharynx.
- redness of the pharyngeal mucosa.
- Rapid increase in body temperature .
- Appearance white caps in the lacunae of glands and others.
Allergy and toxic allergy forms of the disease differ in that the second works faster , with the danger of dysfunction of the kidneys, cardiovascular system, respiratory system and requires surgical intervention to remove the tonsils.
Despite the fact that the manifestations of all types of pathology are identical, one form or another can be diagnosed.
Diagnosis of allergic sore throat

If allergic angina occurs, the intervention of a qualified doctor who can accurately determine the cause of the disease is required.
The diagnostic procedure consists of the following steps:
- Visual examination , palpation of the patient by a therapist, allergist, ENT doctor, cardiologist, immunologist.
- Exercise Laboratory Tests:
- A blood test to check the level of white blood cells to determine the degree of inflammation.
- Swab samples of the pharyngeal and tonsil mucosa to exclude viral and bacterial pathogens, i.e. acute tonsillitis.
- Immunological blood test .
- General urine test . Leather
- Skin Samples for Pathogen Detection.
The further course of treatment directly depends on the formulation of the correct diagnosis and determination of the subtype of pathology.
Treatment of allergic sore throat

A pectogram of sore throat caused by viral pathogens precludes treatment with antibiotics . This is due to the effect of drugs on healthy microflora and can lead to the addition of fungal infections.
Bacterial angina, on the other hand, requires the prescription of penicillin and macrolide antibiotics.
In the case of allergic tonsillitis, the first steps are taken to eliminate the reaction to the stimulus. Secondary treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes .
Treatment of allergic angina has a structure and is carried out in stages:
- samples show and eliminate stimuli . The patient is prescribed antihistamines to eliminate symptoms and sensitize to the allergen.
- Introduction Vitamin complexes to maintain the general condition of the body.
- Injections Immunotherapy.
- Antipyretic drugs . Inhalation
- and Physiotherapy .
- Medicines to eliminate swelling of the processes, rinsing the throat and rinsing with antiseptics.
- For bacterial growth and secondary infections Antibiotic therapy .
- In case of complications - removal of tonsils.
- Introduction bed , drinking conditions (to avoid dehydration).
To prevent the disease, regular maintenance of the immune system , the introduction of vitamin therapy , preparation of a hypoallergenic diet and complete abstinence from contact with the irritant are required.
Complications are inevitable with premature diagnosis and improper treatment . Numerous factors can cause complications from improper treatment of the disease to the inability of the immune system to cope with the disease. Among the common diseases that can lead to this pathology are, in particular,
- Transformation of the allergic form into phlegmon angina , which leads to a severe intoxication state of the body.
- Postanginal sepsis (Lemierre's syndrome).
- Meningitis .
- Acute rheumatic fever.
- heart failure .
- Appearance of tangled Jade Buds and so on.
Complications
Allergic tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications and duration of the disease. The tonsils cease to act as a barrier to infections. On the contrary, they accumulate harmful organisms. Microbes begin to appear, the waste products of which are preserved.
The infection spreads from the tonsils throughout the body, which leads to intoxication.
With the allergic form of tonsillitis, pronounced changes in internal organs occur, and the course of existing diseases worsens.
Possible general complications:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- tonsillogenic sepsis;
- infectarthritis;
- disease of allergic or infectious etiology.
Symptoms of allergic tonsillitis have a particularly negative impact on children's bodies. For example, the disease can affect the development of the reproductive system in girls.
Possible complications, why the disease is dangerous
Possible consequences of the disease include the following:
- pharyngitis and parapharyngitis;
- heart defects;
- rheumatism;
- damage to the urinary system;
- thyroid diseases;
- infectious arthritis;
- prostate damage;
- peritonsillar abscess.
Dangerous signs of sore throat:
Degrees of toxic-allergic tonsillitis
There are two degrees of development of the disease. The main symptoms of 1st degree toxic-allergic tonsillitis are as follows:
- Headache.
- Increased body temperature.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Loss of appetite.
- General poor health.
- The cervical lymph nodes are enlarged, and when they are palpated, painful sensations occur.
- During the period of exacerbation of the disease, tachycardia and arrhythmia appear. At the same time, there are no physiological changes in the heart, and at the stage of remission, these symptoms of allergic tonsillitis in adults disappear.
- In laboratory blood tests and immunology, slight changes may be observed (leukocytosis, increased ESR, etc.). During remission, these indicators normalize.
With allergic tonsillitis of the 1st severity, a person can get a sore throat up to 3 times a year. Recovery periods after illness will be long.
Allergic tonsillitis: symptoms and causes, treatment
Tonsillitis is the name given to inflammatory processes that develop in the area of the palatine tonsils. Tonsils perform protective functions; they prevent the penetration of various pathogens.
Infectious tonsillitis is caused by microorganisms; with allergic tonsillitis, allergens of different types affect the tonsils. They are caused by seasonal natural phenomena and general immune disorders.
The peculiarity of the disease is that it is systematic.
What is allergic tonsillitis
Allergic tonsillitis occurs according to the pattern of development of acute tonsillitis, the main difference lies in the cause of the inflammatory process.
If inflammation of the tonsils, their increase in volume and change in color occurs due to the entry of an allergic type provocateur into the body, then such tonsillitis is defined as allergic. The development of inflammation leads to breathing problems, painful swallowing, and in some cases, attacks of suffocation.
Allergic tonsillitis belongs to the group of chronic tonsillitis, called toxic-allergic. This is explained by the fact that the international classification does not provide for the allocation of the allergic type into a separate class of diseases.
Form of the disease
The disease has several forms, which are united by specific symptoms.
There are simple and toxic-allergic forms. A simple sore throat is recognized by its local manifestations. Toxic-allergic is divided into 2 degrees.
Causes of health problems
The reason for the development of toxic-allergic tonsillitis is a general violation of the body's immune system. This entails complications that become the causes of the development of inflammatory processes:
- partial cure leads to regular recurrence of sore throats;
- infectious diseases of the oral cavity;
- sinus diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- systematic colds with various complications.
The reason, which leads to one or a number of reasons, is frequent hypothermia of the body. This may be due to the peculiarities of working and living conditions.
Toxic-allergic tonsillitis often has a seasonal characteristic. Such manifestations may be caused by an insect bite, an allergen bloom, or the consumption of allergenic food products.
Clinical manifestations
Signs of the disease manifest themselves in different ways. Experts help track allergic tonsillitis after a series of laboratory tests. At the appointment, patients may complain of symptoms that are not always related to inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Diagnostic methods
The peculiarity of the disease is the frequency of its recurrence. It can be determined only after fixing the systematic appearance of tonsillitis.
Consultations with an otolaryngologist help identify the causes of tonsillitis. The doctor performs a pharyngoscopy or a deep examination of the pharynx with special lighting, and prescribes a comprehensive examination to find out concomitant diseases and exclude their influence on inflammation of the tonsils. For this purpose, clinical tests are taken.
Therapeutic measures
After making a diagnosis, the doctor determines a treatment regimen. Tonsillitis requires an integrated approach. Therapy meets several requirements:
- techniques of a local nature;
- drug effects;
- strengthening the body, increasing immunity.
Locally, the method of washing the tonsils and rinsing with antiseptic drugs is used. In some cases, surgery is performed.
Removal of tonsils is carried out when the tissue grows and is replaced by connective tissue. Tonsil abscesses require opening.
Possible consequences and complications
Allergic tonsillitis is dangerous because it is systematic in nature, which leads to the development of complications of a different nature.
Often the disease leads to a complete loss of the protective functions of the mucous membranes of the tonsils. Regular symptoms of chronic tonsillitis lead to the development of complications such as nephritis, pyelitis, rheumatoid diseases.
Experts have discovered a connection between allergic tonsillitis and thyroid dysfunction.
Prevention measures and specialist forecast
Experts recommend paying attention to increasing the immunity of the whole body. It is recommended to take vitamin complexes, immunostimulating drugs, hardening, annual proper rest, and a balanced diet.
According to experts, timely treatment and prevention yield positive results.
Yulia Kalashnik
Source: https://VipLor.ru/gorlo/tonzillit/allergicheskij-simptomy-lechenie
Second degree
With toxic-allergic tonsillitis of the 2nd severity, the symptoms will be the same. But in this case, local and general diseases will appear, which can not only harm health, but also threaten the patient’s life. The disease is also characterized by cardiac dysfunction. The following symptoms also occur:
It is in this form that removal of the tonsils is often recommended, since this organ becomes not a gateway to infections, but their active focus.
What kind of disease is this?
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils. Normally, the immune cells of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils must respond to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and fight them so that the infection does not spread throughout the body. But the immune system does not always cope with such attacks. And if for some reason the cells did not have time to react in time, then inflammation of the tonsil tissue develops.
Depending on the course of the disease, chronic and acute tonsillitis are distinguished. The latter develops rapidly and has pronounced symptoms. Chronic tonsillitis has a wave-like course, characterized by periodic exacerbations.
If we take as the basis for the classification the features of changes affecting the tissue of the tonsils, we can distinguish several forms of the disease:
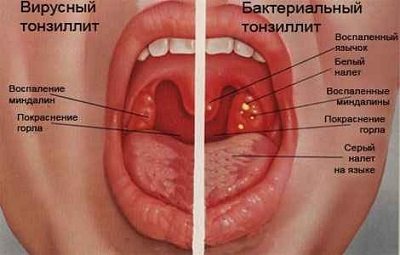
- The catarrhal form is the simplest, as it is characterized by superficial tissue damage. The photo shows that the tonsils increase in size, swelling and hyperemia occur.
- The follicular form involves the formation of follicles - small cavities filled with purulent contents. If you study the photo, you can see something like ulcers on the mucous membranes of the tonsils.
- The lacunar form is characterized by the formation of lacunae - certain depressions in the mucous membranes filled with pus. In the photo you can see holes on the surface of the tonsils. The size of the lacunae may increase, and if left untreated, they will occupy almost the entire surface of the tonsil (but cannot extend beyond its recess).
- Fibrinous form. In the photo you can see a film on the surface of the tonsils that has a yellowish tint. This plaque can extend beyond the surface of the tonsils.
- The phlegmonous form may be accompanied by melting of the tissues inside the tonsil under the influence of purulent contents and the formation of phlegmon. In the photo you can find that the affected tonsil is greatly enlarged in size, and redness may be noted.
- In the ulcerative-necrotic form of the disease, ulcers form, which lead to the death of part of the tissue. In the photo of the affected tonsils, you can find a gray or greenish coating. An unpleasant putrid odor may also appear.
Based on the causes of the development of the disease, the following types of tonsillitis are distinguished: bacterial, viral, herpes, fungal.
Associated diseases
There are more than 100 of them.
Local diseases:
Common diseases:
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis can be carried out both by conservative methods and through surgical intervention.
As a rule, treatment measures almost always begin with a conservative stage. It includes:
- 1) Rinsing the palatine tonsils with antiseptic solutions that penetrate into the lacunae where pathogenic microorganisms are concentrated.
- 2) Physiotherapeutic procedures - the use of ultrasound, UHF therapy and ultraviolet irradiation.
The use of antibiotics is justified only in case of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. Modern otolaryngology gives preference to semisynthetic penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used when there is a pronounced reaction of the body, which is manifested by high temperature, symptoms of intoxication syndrome, etc. For this purpose, paracetamol, phenylephrine and others are indicated.
The main indications for surgical treatment, that is, removal of the tonsils, are:
- lack of therapeutic effect from two courses of the above therapy;
- tonsillitis, against the background of which a peritonsillar abscess developed;
- sepsis of tonsillogenic origin;
- glomerulonephritis against the background of tonsillitis;
- rheumatism;
- suspicion of malignancy (malignancy) of the pathological process.
However, before performing surgery, it is imperative to evaluate possible contraindications. These include:
- cardiovascular pathology with severe circulatory failure;
- severe renal failure;
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus;
- uncorrected arterial hypertension, in which there is a real threat of hypertensive crisis and intense bleeding from the postoperative wound;
- diseases of the blood system in which there is a high probability of bleeding.
The operation has to be delayed in the following clinical cases:
- untreated caries;
- acute periodontitis;
- menstruation;
- gestational age, close to full term;
- severe atrophy of the upper respiratory system.
It is extremely rare that complications from tonsillectomy may develop, which include:
- bleeding from a postoperative wound;
- penetration of air under the skin;
- pharyngeal hematoma;
- inflammatory complications (otitis, stomatitis, glossitis and others);
- exacerbation of general diseases.
Prevention
Diagnostics
Any sore throat requires qualified medical care. You will not be able to determine the cause of the disease and identify the pathogen on your own.
You may be interested in: Allergy to cigarettes: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention

It will be necessary to take a blood test, urine test, smear test, and undergo a medical examination. Skin testing may be necessary to determine the allergen.
For toxic-allergic tonsillitis, it is recommended to visit a cardiologist, nephrologist or pulmonologist.
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis
A diagnostic search for suspected chronic tonsillitis includes the following studies:
- 1) Pharyngoscopy - a careful examination of the tonsils and adjacent areas in order to identify the main signs of the disease.
- 2) General clinical blood test to assess the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
- 3) Bacteriological examination of discharge from the palatine tonsils with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics.
- 4) Biochemical blood test to identify markers of the immune process - seromucoid, sialic acids, fibrinogen and others.
Treatment
With allergic sore throat, the main task is to eliminate the allergen and extinguish the reaction caused by it. After this, it is necessary to remove the inflammatory process.
Prescribed rinsing of the tonsils with antiseptic drugs, taking immunostimulants, inhalations, sanitation of the nasopharynx and oral cavity. In case of exacerbations, antibiotics may also be prescribed. Antihistamines are used as mandatory therapy.
If the described treatment of allergic chronic tonsillitis does not give the desired result, then we can talk about removing the tonsils.
Local treatment is also prescribed: the use of antiseptics for rinsing the throat, treating the tonsils with sodium tetraboron during an exacerbation of the disease.
Traditional methods in this situation may not only not bring benefit, but also cause harm, aggravating the general condition of the patient.
You cannot replace the use of complex treatment prescribed by a specialist with folk remedies. Everything must be agreed with the attending physician.
Available drugs such as iodine, salt, and soda have proven themselves to be excellent. They are used for rinsing. To prepare the solution, just take 200 ml of boiled warm water, a few drops of iodine, 1 tsp. soda and 0.5 tbsp. l. salt. Mix everything, dissolve and rinse with the prepared liquid several times a day. It is important that the solution gets to the back of the throat. A fresh solution should be prepared each time.
Treatment methods
When treating this disease, it is very important to carefully select each medicine for sore throat in order to avoid possible adverse reactions and get the strongest possible effect from treatment.
Treatment instructions imply following generally accepted therapy:
- Identify the allergen and stop contacting it as much as possible.
- The use of immunotherapy - injections that can protect the body from exposure to a dangerous allergen.
- The use of antihistamines and decongestants.
- Rinsing lacunae located in the tonsils.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Do-it-yourself lubrication of tonsils with iodine-containing preparations.
- The use of therapeutic mud and ozokerite for applications, a course of 10-12 procedures, lasting no more than 15 minutes.
- UHF on the submandibular area is carried out every day, with a course of no more than 12 procedures. Thanks to this procedure, small blood vessels dilate and blood flows to the site of inflammation.
- In addition, if you need to learn how to treat a sore throat at home, you can use gargles with chlorophyllipt, furatsilin, miramistin, hydrogen peroxide, herbal decoctions, propolis, soda and iodine. Fortunately, there are a lot of effective remedies used in folk recipes for the successful treatment of sore throats, and their prices are striking in their cheapness.
It is worth noting that if conservative treatment is ineffective or exacerbations of the disease are too frequent, a surgical treatment method is used - tonsillectomy. During the operation, the palatine tonsils with the adjacent capsule are removed.
From the video and photos in this article, we learned about the causes and symptoms of allergic tonsillitis and toxic-allergic tonsillitis and became familiar with the treatment regimen used for these diseases.
When is the best time to remove tonsils?
To answer this question, it is necessary to consider the development of allergic tonsillitis in the context of a dysfunction of the immune system. The palatine tonsils are not the only lymphoid formations in the pharynx. They form part of the Pirogov-Waldeyer lymphadenotic pharyngeal ring.
This is the very powerful barrier that prevents the penetration of airborne infections.

With tonsillitis, the lymphoid tissue becomes inflamed and hypertrophied. It may become scarred. The disease will occur with various complications. In this case, hypertrophied tonsils will not be the main cause of frequent illnesses.
Moreover, the proliferation of lymphoid tissue acts as a compensatory mechanism. This indicates that the glands are functioning.
With the loss of tonsils, the infection can easily move lower, so a person increasingly suffers from tracheitis and bronchitis. It is worth understanding that in some situations radical surgical intervention is necessary.
The main stages of treatment of allergic tonsillitis:
Symptoms of manifestation
Patients with allergic tonsillitis experience swelling of the nasal mucosa, sneezing or a sore throat. Then the mucous membrane of the throat dries out and cracks. With seasonal allergic tonsillitis, the throat becomes reddish in color. Other signs include red eyes, increased watery eyes and dizziness.
Sometimes there is increased photosensitivity. Patients sometimes suffer from itching on the roof of the mouth and in the throat to the ears. Rarely do skin complaints appear - itching or severe locally limited redness.
If symptoms are severe, it can lead to problems concentrating and sleeping. Therefore, patients often experience severe fatigue during the day. Flu-like symptoms often occur.
Cigarette smoke, fragrances, large temperature changes or exercise also cause tonsillitis. Persistent inflammation of the mucous membrane may require surgical intervention.
Prevention
Allergic tonsillitis, the symptoms and treatment of which are described in the article, is a common disease. If you are prone to this form of the disease, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
Allergic tonsillitis is a very unpleasant disease that requires timely treatment. Preventive measures will help strengthen the immune system and avoid possible complications.
Source
Forecast
In the absence of complications, the prognosis is favorable. Provided contact with the allergen is avoided and adequate therapy is carried out, recovery occurs within 5-8 days. In this case, stable immunity to pathology is not developed. Under the influence of allergens and other factors, tonsillitis can develop again.
Allergic sore throat is a serious pathology that can cause dangerous consequences. To prevent complications from occurring, you need to start therapy on time. This will help to cope with the disease in time.
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the tonsils. The disease occurs with exacerbations, and during the period of remission it may not make itself felt. And yet, it is necessary to take measures, since inflammation can spread to other tissues and provoke the development of diseases of the joints, cardiovascular and other systems (in total, about a hundred ailments are known, the development of which can cause chronic tonsillitis).
Causes
Main causes of the disease:
- Uncured acute tonsillitis.
- Chronic diseases of the nasopharynx or upper respiratory tract, such as rhinitis, pharyngitis and others.
- Decreased immunity.
- Frequent colds.
The causes of exacerbation may be hypothermia, sudden changes in temperature, as well as colds.
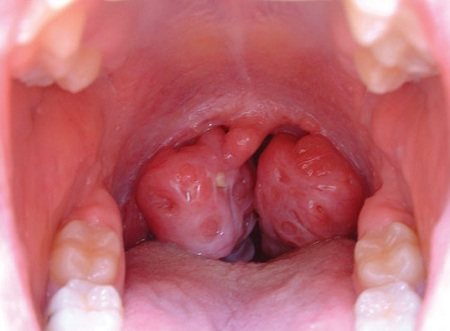
Manifestation of a chronic form of the disease
Manifestations
Symptoms that characterize chronic tonsillitis:
- Unpleasant sensations in the throat: a feeling of the presence of a foreign body or some kind of plaque, soreness, rawness.
- Periodic pain, most often appearing in the morning when swallowing.
- Frequent colds.
- Increased fatigue, chronic fatigue, weakness.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- The photo shows that the tonsils are almost always enlarged. Redness is often noted. The surface may be loose; in most cases, there are gaps that are periodically filled with pus or food debris.
- Periodic slight increases in temperature (up to 37-37.5 degrees).
Treatment
How to cure chronic tonsillitis? Treatment must be comprehensive.
- During exacerbations, measures will be the same as in the acute form of the disease. It will be necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease and eliminate the symptoms.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis and others, will help restore tonsil tissue and accelerate their regeneration.
- Regular rinsing of the lacunae will be required to cleanse them of purulent contents and food debris. For such procedures, antiseptic compounds are usually used, for example, hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine and others.
- Drugs are often prescribed to strengthen and enhance local immunity (“Imudon”, “IRS-19”).
To strengthen the immune system, Imudon may be prescribed
Remember that chronic tonsillitis, like acute tonsillitis, requires treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Transition of the disease into a chronic form
Acute tonsillitis is a common disease in both adults and children. The disease can develop in isolation or against the background of other diseases of the ENT organs (rhinitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis). In the absence of proper treatment, the transition to a chronic form will not take long to occur 1,2.
Factors that provoke inflammation of the tonsils are the following 1.4:
- polyps in the nasal cavity;
- dental caries (an infectious focus in the oral cavity is one of the most common causes of many inflammatory processes in the body, including chronic tonsillitis);
- hypothermia;
- irregularly shaped nasal septum;
- sinusitis;
- adenoids (for example, the combination of enlarged adenoids and tonsillitis is very common in frequently ill preschool children and ranges from 20 to 40%)4;
- heredity (in certain families there is a predisposition to tonsillitis in several generations, especially in the female line);
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- presence of bad habits (alcohol, smoking), passive lifestyle;
- stress, physical and mental overload;
- weakened immunity;
- diseases of the respiratory and digestive systems;
- allergy.
How does a chronic disease manifest itself?
The main symptom of the chronic form of the disease is severe soreness in the throat. Its intensity is determined by the form of the current pathology. The pain syndrome can be mild or severe. But at the same time, it is permanent and fades with the use of painkillers.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis include:
- dry mouth, burning sensation;
- the presence of a white coating that affects the tongue and tonsils;
- fever or chills;
- enlargement of lymph nodes concentrated in the neck, as well as their soreness;
- enlarged tonsils, hyperemia and swelling of the back of the throat;
- general weakness, which is caused by intoxication of the body;
- poor appetite;
- difficulty breathing through the nose, cutting pain in the ears;
- feeling of nausea and vomiting, accompanied by painful sensations in the peritoneal area.
Chronic tonsillitis is determined by the frequency and persistence of its formation. It occurs after an infectious disease or when affected by coccal bacteria. In addition, a common cause of its development is untreated acute tonsillitis.
When an infection enters the human body, it damages the tonsils, on which cracks form. Subsequently, food fragments or dead cells of the body penetrate into them. All this has a positive effect on the development of the inflammatory process. At the time of remission, the disease may not make itself felt at all.
But this article will help you understand how to treat tonsillitis at home, and what medications you should use on your own.
It will also be interesting to learn about how to cure tonsillitis with folk remedies.
This article will help you understand which antibiotic for tonsillitis and pharyngitis should be used most often: https://prolor.ru/g/lechenie/lechenie-faringita-antibiotikami.html
Maybe
How does an acute illness manifest itself?
The acute form of the disease is characterized by severe symptoms. All manifestations can be detected immediately after the development of inflammation, due to which therapy can be carried out on time and the possibility of complications is excluded. In general, the disease lasts no more than 2 weeks. Viruses and fungi influence the development of the disease. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether tonsillitis is contagious or not is yes.
And although the acute form has much in common with the chronic form, it has its own symptoms:
- at night the patient has severe snoring, which is not typical for him in everyday life;
- poor sleep;
- a lot of mucus forms in the nasopharynx;
- temperature rise to high levels.
These are the primary signs of acute tonsillitis. But there are secondary symptoms that manifest themselves in the form of otitis media or rash. The initial stage of the pathology makes itself felt in the form of cutting pain. Sometimes it is so strong that the patient is not even able to talk.
Inflammation gives impetus to the formation of purulent plaque on the tonsils. It may be concentrated in the form of small islands or completely affect the pharynx. If we compare sore throat of viral and bacterial etiology, the first differs in the general condition of the patient. At first they are similar, but later the viral infection progresses a little easier and can be quickly treated.
On the video there are signs of tonsillitis:
Treating the acute form of the disease is much simpler and easier than the chronic form. At the same time, it is important not only to eliminate painful and unpleasant symptoms, but also to stop the underlying factor. In this case, treatment of the acute form takes an integrated approach.
Causes
The palatine tonsils, together with other lymphoid formations of the pharyngeal ring, protect the body from pathogenic microbes that penetrate along with air, water and food. Under certain conditions, bacteria cause acute inflammation in the tonsils - sore throat. As a result of repeated tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis can develop. In some cases (about 3% of the total number of patients), chronic tonsillitis is a primarily chronic disease, that is, it occurs without previous tonsillitis.
The risk of developing chronic tonsillitis increases with immune disorders. General and local resistance of the body decreases after suffering from infectious diseases (scarlet fever, measles, etc.) and during hypothermia. In addition, the overall immune status of the body can be affected by improper treatment with antibiotics or unjustified use of antipyretics for sore throat and other infectious diseases.
The development of chronic inflammation of the palatine tonsils is facilitated by impaired nasal breathing due to polyposis of the nasal cavity, enlargement of the inferior turbinates, curvature of the nasal septum and adenoids. Local risk factors for the development of chronic tonsillitis are foci of infection in neighboring organs (adenoiditis, sinusitis, carious teeth). About 30 different pathogenic microorganisms can be detected in the tonsils of a patient with chronic tonsillitis, however, in the depths of the lacunae, pathogenic monoflora (staphylococcus or streptococcus) is usually found.
Classification
There are simple (compensated) and toxic-allergic (decompensated) forms of chronic tonsillitis. The toxic-allergic form (TAF), in turn, is divided into two subforms: TAF 1
and
TAF 2
.
– A simple form of chronic tonsillitis
.
In the simple form of chronic tonsillitis, local signs of inflammation predominate (swelling and thickening of the edges of the arches, liquid pus or purulent plugs in the lacunae). Enlargement of regional lymph nodes may be observed. – Toxic-allergic form 1
.
Local signs of inflammation are accompanied by general toxic-allergic manifestations: fatigue, periodic ailments and slight increases in temperature. From time to time, pain in the joints appears, and with exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, pain in the heart area without disturbing the normal ECG pattern. Recovery periods for respiratory diseases become long and protracted. – Toxic-allergic form 2
. The above-mentioned manifestations of chronic tonsillitis are accompanied by functional disorders of the heart with changes in the ECG pattern. Possible heart rhythm disturbances and prolonged low-grade fever. Functional disorders in the joints, vascular system, kidneys and liver are detected. General (acquired heart defects, infectious arthritis, rheumatism, tonsillogenic sepsis, a number of diseases of the urinary system, thyroid and prostate glands) and local (pharyngitis, parapharyngitis, peritonsillar abscesses) associated diseases are added.
Symptoms
The simple form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by scant symptoms. Patients are concerned about the sensation of a foreign body or awkwardness when swallowing, tingling, dryness, and bad breath. The tonsils are inflamed and enlarged. Outside of exacerbation, there are no general symptoms. Characterized by frequent sore throats (up to 3 times a year) with a protracted period of recovery, which is accompanied by fatigue, malaise, general weakness and a slight increase in temperature.
In the toxic-allergic form of chronic tonsillitis, tonsillitis develops more often than 3 times a year, often complicated by inflammation of neighboring organs and tissues (peritonsillar abscess, pharyngitis, etc.). The patient constantly feels weak, tired and unwell. The body temperature remains low-grade for a long time. Symptoms from other organs depend on the presence of certain associated diseases.
Complications
With chronic tonsillitis, the tonsils turn from a barrier to the spread of infection into a reservoir containing a large number of microbes and their metabolic products. Infection from affected tonsils can spread throughout the body, causing damage to the heart, kidneys, liver, and joints (associated diseases).
The disease changes the state of the body's immune system. Chronic tonsillitis directly or indirectly affects the development of certain collagen diseases (dermatomyositis, scleroderma, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus), skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis) and peripheral nerve lesions (sciatica, plexitis). Long-term intoxication in chronic tonsillitis is a risk factor for the development of hemorrhagic vasculitis and thrombocytopenic purpura.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is made on the basis of a characteristic history (recurrent tonsillitis), data from an objective examination by an otolaryngologist and additional studies. Pharyngoscopy reveals hyperemia, thickening of the edges and swelling of the palatine arches. Possible fusion of the palatine arches with the triangular fold and tonsils. Loosening of the tonsils is often observed (especially in children). The lacunae of the tonsils contain pus, sometimes with an unpleasant odor. Enlargement of regional lymph nodes is often detected.
In the toxic-allergic form of chronic tonsillitis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, aimed at identifying associated diseases and assessing the severity of the pathology.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for chronic tonsillitis are selected depending on the form and stage (exacerbation, latent course) of the disease. Conservative therapy includes local effects on the affected tonsils and general measures aimed at strengthening the body and increasing immune status.
Local treatment includes washing the tonsils and rinsing with antiseptic solutions. Antiseptic and antibacterial drugs are injected into the tonsils. They use sucking tablets - oroseptics, and use local immunomodulators. Aromatherapy with essential oils of tea tree, cedar, lavender and eucalyptus (inhalation and rinsing) is recommended. It is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.